What's happened
A stroke is a sudden disruption of the normal blood supply to the brain.
Based on the nature of the disorders, there are two main types of stroke: ischemic (often called cerebral infarction) and hemorrhagic (including subarachnoid hemorrhage). This article will talk about ischemic stroke, which is 4 times more common than hemorrhagic stroke. The word “ischemic” literally means that there is not enough blood flowing to one or another organ - with such a stroke, blood does not flow to the brain due to blockage or severe narrowing of the main arteries. As a result, brain tissue cells die.
Treatment and rehabilitation
The patient receives treatment in a hospital. All patients with suspected stroke are hospitalized on an emergency basis. The optimal period for providing medical care is the first 3 hours after a brain accident has occurred. The person is placed in the intensive care unit of a neurological hospital. After the acute period has been overcome, he is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit.
Until the diagnosis is established, basic therapy is carried out. The patient’s blood pressure is adjusted, the heart rate is normalized, and the required blood pH level is maintained. To reduce cerebral edema, diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed. Craniotomy is possible to reduce the degree of compression. If necessary, the patient is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Be sure to direct efforts to eliminate the symptoms of stroke and alleviate the patient’s condition. He is prescribed medications to lower body temperature, anticonvulsants, and antiemetics. Medicines that have a neuroprotective effect are used.
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the type of stroke. In case of ischemic brain damage, it is necessary to restore nutrition to the affected area as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that resolve blood clots. It is possible to remove them mechanically. When thrombolysis fails, the patient is prescribed Acetylsalicylic acid and vasoactive drugs.
If a patient develops a hemorrhagic stroke, it is important to stop the bleeding. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that thicken the blood, for example, Vikasol. It is possible to perform an operation to remove the resulting hematoma. It is aspirated using special equipment, or through open access by performing craniotomy.
Relatives and friends should provide support to the patient and not leave him alone with the problem. Psychologists are involved in the work. Sessions with a speech therapist are often required.
Causes and prevention of ischemic strokes
Most often, the cause of a cerebral infarction is the movement of a blood clot through an artery and clogging it in a narrow place. A thrombus is a blood clot that is primarily made up of platelets. With normal vascular patency, platelets are responsible for blood clotting, but with atherosclerosis, cholesterol plaques form, narrowing the lumen of the artery, because of this, the usual blood flow is disrupted, side turbulence is formed, and platelets stick together into clots. Also, the cause of the formation of a blood clot can be an increased level of sugar in the blood: when it occurs, microtraumas form in the walls of the artery due to an increase in blood density, which also disrupts normal blood flow.
The cause of a cerebral infarction can also be a narrowing of the lumen of a large artery by more than half. You can read more about this using the example of carotid artery stenosis (note: link to article). When an artery narrows, the blood supply to the brain does not completely stop, so a person often experiences a so-called minor stroke. A minor stroke is similar in symptoms to a regular stroke. Although the degree of damage is much less, this condition requires immediate medical attention: further deterioration of the condition of the arteries can lead to a stroke with all its consequences.
A person cannot influence the movement of a blood clot through the vessels, but everyone can pay attention to a number of risk factors, eliminate them if possible, in order to prevent the formation of a blood clot and minimize the risk of ischemic stroke.
- It is important to undergo a course of treatment and periodically check your condition with a doctor if you have a chronic disease, such as diabetes mellitus, confirmed atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, or various disorders of the heart and blood vessels.
- Experts strongly recommend giving up tobacco and alcohol.
- It is advisable to maintain an active, mobile lifestyle.
- You need to monitor your diet and avoid a strong imbalance towards fats and fast carbohydrates.
The above points are effective measures to prevent not only stroke, but also many other diseases, proven through numerous studies.
But there are also risk factors that we cannot influence. Among them are old age (over 60 years old) and heredity (if immediate relatives suffered a stroke, or they were found to have serious vascular disorders).
Who is at risk
There are people who need to be especially wary of developing a stroke, as they are at risk.
Among them:
- Persons with hypertension.
- Patients with diabetes.
- Men and women over 65 years of age.
- People with abdominal obesity.
- Persons with a hereditary predisposition to vascular pathologies.
- Patients who have previously had a stroke or heart attack.
- Patients with diagnosed atherosclerosis.
- Women over 35 years of age taking oral contraceptives.
- Smokers.
- People suffering from heart rhythm disturbances.
- People with high cholesterol levels.
Most often, patients with the listed diagnoses are registered at the dispensary. Special mention should be made of people living in a state of chronic stress. Emotional stress negatively affects all systems of the body and can cause a stroke.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke
Almost never a cerebral infarction is asymptomatic. You may have already come across actively distributed reminders on the timely recognition of a stroke: after all, it is very important to call an ambulance and provide medical assistance to the patient as early as possible - the earlier assistance is provided, the less brain damage.
The main symptoms of ischemic stroke are:
- dizziness,
- loss of orientation in space,
- vomit,
- convulsions,
- impaired coordination, speech, vision, writing, reading, swallowing,
- inability to move individual limbs and/or perform simple manipulations such as raising two arms at the same time, brushing teeth, or turning pages of a book.
The symptoms are extremely varied. They depend primarily on which particular part of the brain was deprived of blood supply - then exactly the function for which this part is responsible will be disrupted.
At the same time, all the symptoms do not appear; you may notice one or more - and this is a good reason to immediately call an ambulance.
Treatment and rehabilitation
The patient receives treatment in a hospital. All patients with suspected stroke are hospitalized on an emergency basis. The optimal period for providing medical care is the first 3 hours after a brain accident has occurred. The person is placed in the intensive care unit of a neurological hospital. After the acute period has been overcome, he is transferred to the early rehabilitation unit.
Until the diagnosis is established, basic therapy is carried out. The patient’s blood pressure is adjusted, the heart rate is normalized, and the required blood pH level is maintained. To reduce cerebral edema, diuretics and corticosteroids are prescribed. Craniotomy is possible to reduce the degree of compression. If necessary, the patient is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus.
Be sure to direct efforts to eliminate the symptoms of stroke and alleviate the patient’s condition. He is prescribed medications to lower body temperature, anticonvulsants, and antiemetics. Medicines that have a neuroprotective effect are used.
Pathogenetic therapy is based on the type of stroke. In case of ischemic brain damage, it is necessary to restore nutrition to the affected area as quickly as possible. To do this, the patient is prescribed drugs that resolve blood clots. It is possible to remove them mechanically. When thrombolysis fails, the patient is prescribed Acetylsalicylic acid and vasoactive drugs.
In case of a stroke, it is extremely important to provide timely treatment to the damaged areas of the brain. A course of use of the drug accelerates the process of recovery of brain cells after a stroke, even in cases of impaired blood circulation or hypoxia. This allows for rapid restoration of memory, thinking, speech, swallowing reflex and restoration of other functions of daily activities. Gliatilin has a positive effect on the transmission of nerve impulses, protects brain cells from repeated damage, which prevents the risk of recurrent stroke.
The drug is well tolerated by patients; it is contraindicated for use by pregnant, lactating women and people with hypersensitivity to choline alfoscerate.
Courses will need to be taken regularly. You definitely need to do physical therapy, undergo physical therapy, and visit a massage therapist. After a stroke, many patients have to restore motor skills over a long period of time and learn to care for themselves independently.
Relatives and friends should provide support to the patient and not leave him alone with the problem. Psychologists are involved in the work. Sessions with a speech therapist are often required.
Diagnosis of stroke
Diagnosis of a stroke is quite complex, because to identify the cause and assess brain damage, and therefore the consequences of a stroke, the doctor will need a large amount of data.
To visualize the condition of the brain vessels, CT or MRI can be used, depending on the situation. A fairly informative study on the state of blood flow will be angiography - an X-ray examination using a contrast agent injected into the vessels.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe blood and urine tests; test for glucose and cholesterol levels; conduct an ultrasound examination.
Who is at risk
There are people who need to be especially wary of developing a stroke, as they are at risk.
Among them:
- Persons with hypertension.
- Patients with diabetes.
- Men and women over 65 years of age.
- People with abdominal obesity.
- Persons with a hereditary predisposition to vascular pathologies.
- Patients who have previously had a stroke or heart attack.
- Patients with diagnosed atherosclerosis.
- Women over 35 years of age taking oral contraceptives.
- Smokers.
- People suffering from heart rhythm disturbances.
- People with high cholesterol levels.
Most often, patients with the listed diagnoses are registered at the dispensary. Special mention should be made of people living in a state of chronic stress. Emotional stress negatively affects all systems of the body and can cause a stroke.
Pathogenesis
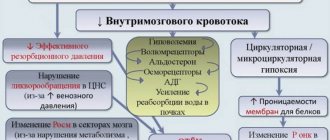
A certain sequence of molecular biochemical changes in the brain substance, caused by acute focal cerebral ischemia, can lead to tissue damage, resulting in cell death (cerebral infarction). The nature of the changes depends on the level of decrease in cerebral blood flow, the duration of this decrease and the sensitivity of the brain substance to ischemia. The degree of reversibility of tissue changes at each stage of the pathological process is determined by the level of decrease in cerebral blood flow and its duration in combination with factors that determine the sensitivity of the brain to hypoxic damage.
The term “infarction core” refers to a zone of irreversible damage, and the term “ischemic penumbra” (penumbra) refers to a zone of reversible ischemic damage. The duration of the penumbra's existence is the most important point, since over time, reversible changes become irreversible. The oligemic zone is a zone in which a balance is maintained between tissue needs and the processes that provide these needs, despite the decrease in cerebral blood flow. It is capable of existing for an indefinitely long time without passing into the core of the infarction, therefore it is not classified as a penumbra.
Classification
Ischemic stroke can be a consequence of one or another disease of the cardiovascular system. There are several pathogenetic variants of ischemic stroke. The TOAST (Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment) classification, which is most widely used, distinguishes the following types of ischemic stroke:
- cardioembolic - ischemic stroke caused by arrhythmia, valvular heart disease, myocardial infarction;
- atherothrombotic - ischemic stroke that occurred due to atherosclerosis of the large arteries, which resulted in arterio-arterial embolism;
- lacunar - ischemic stroke caused by occlusion of small arteries;
- ischemic stroke associated with other, more rare causes: blood hypercoagulation, arterial wall dissection, non-atherosclerotic vasculopathies;
- ischemic stroke of unknown origin - a stroke with an unknown cause or with the presence of two or more possible causes, when it is not possible to establish an accurate diagnosis.
In addition, a minor stroke is distinguished when the existing symptoms regress during the first three weeks of the disease.
There are also several periods of ischemic stroke:
- The most acute period is the first 3 days. Of these, the first three hours were defined as a “therapeutic window”, when it is possible to use thrombolytic drugs for systemic administration. In case of regression of symptoms during the first day, a transient ischemic attack is diagnosed;
- acute period - up to 4 weeks;
- early recovery period - up to six months;
- late recovery period - up to 2 years;
- period of residual effects - after 2 years.