General information
New methods for diagnosing and determining the causes of diseases appear in modern medicine regularly. However, determining ESR in human blood is still an effective diagnostic method.
It is used for diagnostic purposes in both children and adults. Such a study is prescribed both when a patient who is concerned about a certain disease contacts a doctor, and during preventive examinations. Any doctor can interpret this test. ESR is included in the group of general blood tests (CBC). If this indicator is elevated, you need to determine the cause of this phenomenon.
Important Notes
Material for research Capillary blood.
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications). Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood. Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age (for special indications)! According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible: in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
What is ESR in the blood?
Those who are prescribed such a study are interested in why an ESR analysis is performed and what it is. So, the abbreviation ESR is the capital letters of the term “ erythrocyte sedimentation rate ”. Thus, using this test, the erythrocyte in the blood can be accurately determined.
Erythrocytes are, as you know, red blood cells. anticoagulants act on them over a certain period, they settle at the bottom of the capillary or test tube. The time during which a blood sample taken from a patient is divided into upper and lower layers is defined as ESR. It is assessed by the height plasma layer , which was obtained during the research process, in millimeters per 1 hour. The ESR indicator is nonspecific, however, it has high sensitivity.
If the ESR level in the blood is elevated, this may indicate the development of various disorders in the body. So, sometimes this is an indicator of the development of infectious, oncological, rheumatological and other pathologies even before the manifestation of obvious symptoms of diseases. Accordingly, if the ESR level is normal, the doctor, if necessary, prescribes other tests.
The ESR norm for women is 3 to 15 mm/h. But you need to take into account that this indicator also depends on age - normally it can be different for women under 30 and after 30 years. If necessary, the norm of red blood cells in the blood of women is also determined. In pregnant women, ESR increases starting from the fourth month. It should be taken into account that the ESR rate in pregnant women may vary depending on the period of gestation.
The norm for ESR in men is from 2 to 10 mm/h. A general blood test also determines red blood cells in the blood of men.
The normal ESR level in the blood of children depends on the age of the patient.
This value in the diagnostic process is important for:
- differentiation of diagnosis ( appendicitis and ectopic pregnancy , angina pectoris and myocardial infarction , rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis , etc.);
- determining the body's response during the treatment of patients with tuberculosis , lymphogranulomatosis , rheumatoid arthritis , etc.;
- determining a disease that occurs latently (but it should be borne in mind that even normal ESR values do not exclude the development of a disease or neoplasm in the body).
Sometimes this concept is referred to as ROE . ROE in the blood and ESR are identical concepts. Speaking about ROE in the blood, we understand that this is an erythrocyte sedimentation reaction . Once upon a time, this very concept was used in medicine, that is, the norm of ROE in the blood for women, the norm of ROE in the blood of children, etc. were determined. Currently, this concept is considered outdated, but any doctor understands what ROE is in a blood test, what ROE is in oncology, etc.
Correction
Conservative therapy
A transient increase in ESR after exercise, food intake or medications does not require correction. Elderly people with high ESR without other clinical and laboratory signs of any pathology also do not need any intervention. To normalize the pathological increase in ESR, it is necessary to treat the nosology that caused its development.
- Fighting infection
. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed according to sensitivity. If the patient's condition is serious and requires immediate treatment, broad-spectrum antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones) are used. For influenza, oseltamivir is used; for other acute viral infections, symptomatic therapy is used. For the treatment of chronic viral hepatitis, combinations of peligated interferon with ribavirin and entecavir are effective. - Anti-inflammatory therapy
. For diseases accompanied by immune inflammation, anti-inflammatory drugs are needed - glucocorticoids (prednisolone), cytostatics (azathioprine, methotrexate), 5-aminosalicylic acid derivatives (sulfasalazine). If they are ineffective, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors - monoclonal antibodies (infliximab) are used. - Blood thinning
. If the cause of the heart attack is thrombosis or embolism, antiplatelet agents (clopidogrel, acetylsalicylic acid) and anticoagulants (heparin, warfarin, dabigatran) are prescribed. Thrombolytics (streptokinase) are used to dissolve a blood clot. - Chemotherapy.
Antitumor drugs (alkylating agents, antimetabolites) are used to treat cancer. Malignant blood diseases require a combination of several chemotherapy drugs.
Surgery
In case of acute abdominal pathology (cholecystitis, pancreatitis), it is necessary to perform a surgical (sometimes emergency) operation - pancreatic resection, laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Endovascular thrombectomy is performed to remove the thrombus. In case of myocardial infarction, percutaneous coronary intervention (stent placement) is performed. Unsuccessful conservative therapy for oncohematological diseases is considered an indication for bone marrow transplantation.
Diseases in which there is an increased ESR in the blood
If a patient has an elevated ESR in the blood, what this means is determined by the doctor during the diagnostic process. After all, this indicator is very important for diagnosis if the development of a certain disease is suspected. In the diagnostic process, a qualified doctor takes into account not only the fact that the patient has an increased value, but also determines what the presence of other symptoms indicates. But still this indicator is very important in many cases.
ESR: increased in diseases
An increased ESR in the blood of a child and an adult is observed if a bacterial infection - during the acute phase of a bacterial infection.
In this case, it does not matter where exactly the infections are localized: the picture of the peripheral blood will still reflect the inflammatory reaction.
viral infectious diseases occur . What specifically causes this indicator to increase is determined by the doctor during a comprehensive examination.
Thus, we are talking about the development of a certain pathological process if the ESR is higher than normal. What this means depends on the value of the indicator. Very high values – more than 100 mm/h – occur with the development of infectious diseases:
- for sinusitis , bronchitis , pneumonia , ARVI , colds , tuberculosis , influenza , etc.;
- for cystitis , pyelonephritis and other urinary tract infections ;
- for fungal infections , viral hepatitis ;
- in oncology (high rates can be observed for a long time).
During the development of an infectious disease, this value does not increase quickly; an increase is observed after 1-2 days. If the patient has recovered, the ESR will be slightly elevated for several more weeks or months. The reasons for a high ESR with normal leukocytes may indicate that the person has recently suffered a viral disease: that is, the leukocyte count has already returned to normal, but the red cell sedimentation rate has not yet.
The reasons for increased ESR in the blood in women may be associated with pregnancy, therefore, in the diagnostic process, the doctor must take into account these reasons for the increase in ESR in the blood in women.
An increase in ESR is a typical symptom in the following diseases:
- diseases of the biliary tract and liver;
- inflammatory diseases of a purulent and septic nature ( reactive arthritis , etc.);
- blood diseases ( sickle anemia , hemoglobinopathies , anisocytosis );
- ailments in which tissue destruction and necrosis ( stroke , heart attack , tuberculosis , malignant neoplasms);
- pathologies of the endocrine glands and metabolic disorders ( obesity , diabetes , cystic fibrosis , etc.);
- malignant degeneration of the bone marrow, in which red blood cells enter the blood that are not ready to perform direct functions ( myeloma , leukemia , lymphoma );
- autoimmune diseases ( scleroderma , lupus erythematosus , rheumatism , etc.);
- acute conditions in which the blood becomes more viscous ( diarrhea , bleeding , vomiting , postoperative conditions , etc.).
Diagnostics
Any, even asymptomatic, increase in ESR requires contacting a doctor to find out the cause. The doctor asks the patient in detail whether there was an increase in body temperature, whether the patient experienced pain in the joints, muscles, fatigue, etc. This can help in the diagnostic search. An additional examination is prescribed, depending on what nosology is suspected:
- Blood tests
. The concentration of hemoglobin and blood cells (erythrocytes, platelets, leukocytes) is measured. Very often an increase in the level of fibrinogen and C-reactive protein is detected. The blood is checked for the presence of autoaggressive antibodies (aCCP, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, antibodies to double-stranded DNA). In severe bacterial infections, high levels of presepsin and procalcitonin are observed in the blood. - Identification of the infectious agent
. Antibodies to antigens of viruses, bacteria, parasites are determined using ELISA methods and serological tests. PCR detects DNA and RNA of microorganisms. Microscopy, bacteriological culture of urine, sputum, and blood are performed. A stool test is performed for worm eggs. - Radiography
. With tuberculosis, an X-ray of the lungs shows an increase in mediastinal lymph nodes and infiltration in the upper lobes of the lungs. In paraproteinemic hemoblastoses, x-rays of the bones reveal numerous foci of bone tissue destruction. Multiple myeloma is characterized by a “puncture sign” on a skull x-ray. - Ultrasound
. An ultrasound scan of the abdominal cavity reveals thickening of the walls of the gallbladder in cholecystitis, enlargement and diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma in pancreatitis, and enlargement of the liver and spleen in hemoblastosis. - Angiography.
In case of infarctions of various organs caused by thrombosis, radiography or computed tomography with contrast reveals a filling defect at the site of vessel occlusion. With systemic vasculitis (Horton's, Takayasu's arteritis), areas of vascular stenosis are visible. - Histological studies
. If the cause of increased ESR is oncological pathology, a biopsy is necessarily performed. A common symptom is the detection of a large number of atypical cells. In patients with malignant blood diseases, a predominance of blast cells is noted in the bone marrow aspirate, and atypical lymphoid proliferation is noted in the lymph node biopsy.
Normal and pathological ESR values
In medicine, the physiological limits of this indicator are determined, which are the norm for certain groups of people. Normal and maximum values are shown in the table:
| In children (value depends on the age of the child) | Among women | In men |
|
|
|
ESR during pregnancy
If this value is increased during pregnancy , this is considered a normal condition. The normal ESR rate during pregnancy is up to 45 mm/h. With such values, the expectant mother does not need to be further examined and the development of pathology is not suspected.
Methods used to test ESR blood
Before deciphering what ESR means in a blood test, the doctor uses a certain method to determine this indicator. It should be noted that the results of different methods differ and are not comparable.
Before performing an ESR blood test, it must be taken into account that the obtained value depends on several factors. The general analysis must be carried out by a specialist - a laboratory employee, and only high-quality reagents are used. The analysis in children, women and men is carried out provided that the patient has not eaten food for at least 4 hours before the procedure.
What does the ESR value show in the analysis? First of all, the presence and intensity of inflammation in the body. Therefore, if there are abnormalities, patients are often prescribed a biochemical analysis. Indeed, for high-quality diagnostics it is often necessary to find out in what quantity a certain protein is present in the body.
ESR according to Westergren: what is it?
The described method for determining ESR - the Westergren method - currently meets the requirements of the International Committee for Standardization of Blood Studies. This technique is widely used in modern diagnostics. For such an analysis, venous blood is needed, which is mixed with sodium citrate . To measure ESR, the distance of the stand is measured, the measurement is taken from the upper limit of the plasma to the upper limit of the red blood cells that have settled. The measurement is carried out 1 hour after the components have been mixed.
It should be noted that if Westergren's ESR is elevated, this means that this result is more indicative for diagnosis, especially if the reaction is accelerated.
ESR according to Wintrob
The essence of the Wintrobe method is the study of undiluted blood that was mixed with an anticoagulant. The desired indicator can be interpreted using the scale of the tube in which the blood is located. However, this method has a significant drawback: if the reading is above 60 mm/h, the results may be unreliable due to the fact that the tube is clogged with settled red blood cells.
ESR according to Panchenkov
This method involves the study of capillary blood, which is diluted with sodium citrate - 4:1. Next, the blood is placed in a special capillary with 100 divisions for 1 hour. It should be noted that when using the Westergren and Panchenkov methods, the same results are obtained, but if the speed is increased, then the Westergren method shows higher values. Comparison of indicators is in the table below.
| According to Panchenkov (mm/h) | Westergren (mm/h) |
| 15 | 14 |
| 16 | 15 |
| 20 | 18 |
| 22 | 20 |
| 30 | 26 |
| 36 | 30 |
| 40 | 33 |
| 49 | 40 |
Currently, special automatic counters are also actively used to determine this indicator. To do this, the laboratory assistant no longer needs to dilute the blood manually and track the numbers.
How to prepare
The duration of the analysis does not exceed 5-10 minutes. As a rule, the procedure is accompanied by slight pain and discomfort in the puncture area, but the discomfort passes very quickly. If capillary blood is needed, then before piercing the third or fourth finger of the left hand, the skin in this place is treated with an alcohol cotton ball. After this, using a special medical blade, a small incision is made on the fingertip (its depth does not exceed 3 millimeters). The resulting drop of blood is disposed of with a sterile napkin, after which the laboratory assistant proceeds to collect the biomaterial. Having collected the required amount, the wound surface is lubricated with an antiseptic, and a cotton swab with alcohol is applied to the puncture site.
If the analysis involves taking biomaterial from a vein, then the patient’s forearm is tightened with a medical tourniquet or strap, after which he must work a little with his fist (clench and unclench) for better vascular filling. The site of the intended puncture is treated with an alcohol wipe, after which a needle is inserted into the selected vessel, to which a test tube is connected to collect the released blood. Having collected a sufficient amount of biomaterial, the needle is removed, and a cotton swab with alcohol is applied to the wound.
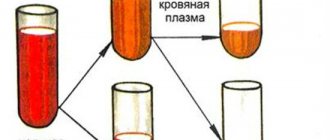
To calculate ESR, an anticoagulant is placed in the biological material to prevent clotting. Then it is sent to a vertical container for 60 minutes. Since the specific gravity of red blood cells exceeds the weight of plasma, gravity forces them down to the bottom of the container. Because of this, 2 visible layers are formed in the test tube: the upper (colorless plasma) and the lower (erythrocyte accumulations). Then the laboratory assistant takes measurements of the top layer. The indicator corresponding to the mark between the red blood cells and the plasma zone on the test tube scale is ESR (indicated in mm/h).
Today there are 2 main ways to detect ESR:
- Panchenkov's method. The capillary is divided into exactly one hundred compartments, and later 5% sodium citrate is added to it to the “P” level. Then the capillary is filled with biomaterial up to the letter “K”. The resulting mixture is mixed and installed vertically. The assessment takes place after 60 minutes.
- Westergren method. Here, venous blood is used, mixed with sodium citrate 3.8% in a ratio of 4:1. It can be mixed with Trilot B followed by the addition of sodium citrate or saline solution in an amount of 4:1. The study is carried out in test tubes equipped with a 200 mm scale. The result is assessed after 60 minutes. This technique is used everywhere, and its main distinguishing feature is the type of test tubes and measuring scale used.
Despite the coincidence of the results of these methods, the Westergren method is famous for its greater sensitivity to exceeding the ESR indicator, and therefore it is considered highly accurate and informative.
ESR in the blood: what do certain values mean?
As mentioned above, normal ESR values for a healthy man are considered to be 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 mm per hour; for women, the normal value is from 2 to 15 mm/hour. Therefore, for women, a value of 12, 13, 14, 15 is considered normal. However, indicators for women in adulthood can normally be 16, 17, 18, 19, 20.
If the value exceeds the norm by several units, then the blood condition can be considered relatively normal. That is, an indicator of 21, 22 in a woman can be considered acceptable, as well as values of 23, 24 mm/h. When a woman is pregnant, this meaning is even greater. Therefore, expectant mothers have no reason to believe that a reading of 25 means something unpleasant. During pregnancy, the analysis may show 28, 29. ESR 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 38 is also not evidence of the development of pathological processes in pregnant women.
This indicator increases with age. Therefore, if an ESR value of 40 is noted in elderly patients, the doctor determines what disease this is a symptom of and what it means by the accompanying signs. Normal values for older people are 43, 50, 52, 55 mm/h, etc. However, for young people, values of 40-60 mm/h are possibly evidence of serious disorders. Therefore, after receiving the analysis data, it is necessary to consult in detail about why the ESR is 60, what it could be, and undergo further research.
Low value
As a rule, the reasons for a low value of this indicator are associated with exhaustion of the body, weight loss, taking corticosteroids, hyperhydration, and muscle atrophy. Sometimes ESR is lowered in diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Increasing ESR
A similar result may be caused by the following pathologies:
- Infection or inflammation.
- Connective tissue diseases (RA, SLE, vasculitis, etc.).
- Burn disease.
- Neoplasms of different etiology and localization.
- Myocardial infarction. In the post-infarction period, the maximum occurs after about 7 days (in this case, you need to contact a vascular surgeon).
- Anemia. These diseases are characterized by a decrease in red blood cells and an increase in their sedimentation rate.
- Injury.
- Amyloidosis (a pathology characterized by the formation of a pathological protein - amyloid).
Despite the discrepancy between normal limits, if a complete blood count of ESR showed an increase in this indicator, this does not necessarily indicate the presence of a problem. This result also occurs in healthy individuals: in women during the menstrual cycle, during pregnancy, or in overweight individuals. This also occurs when taking a number of medications, so you should consult your doctor in advance.
What affects the ESR indicator?
In both women and men, the level of ESR is influenced by a number of different factors, both physiological and pathological. The key factors that most influence this analysis are identified:
- When determined by different methods - according to Westergren et al. - the norm of ESR in the blood of women is higher than that of men. So, an ESR of 25 in a woman may be normal. This is due to the physiological characteristics of blood in women.
- What is the normal ESR level in a woman’s blood depends on whether she is pregnant. For expectant mothers, the norm is from 20 to 45 mm/h.
- A higher ESR is observed in women who take contraceptives . Under this condition, a woman may have a normal ESR of 30. What this means, whether there is a pathology, or whether we are talking about a normal physiological indicator, must be determined by the doctor.
- In the morning, the rate at which red cells settle is higher than in the afternoon and evening, and differences in age do not matter here.
- Signs of accelerated sedimentation are observed when exposed to acute phase proteins.
- If inflammation and an infectious process develops, the values change a day later. how leukocytosis and hyperthermia . That is, on the first day of the disease the indicator can be 10, 14, 15 mm/h, and a day later it can increase to 17, 18, 20, 27, etc.
- ESR is elevated if there is a chronic source of inflammation in the body.
- A reduced value is observed with increased blood viscosity .
- A decrease in sedimentation rate occurs under the influence of anisocytes and spherocytes; the rate becomes greater under the influence of macrocytes.
How is ESR determined?
To determine ESR, blood is placed for an hour in a narrow long test tube with divisions
A coagulant is added to the blood obtained from the patient to prevent it from clotting and it is placed in a narrow, high tube in a horizontal position for one hour. Red blood cells have a higher specific gravity than plasma, so they begin to sink to the bottom under the influence of gravity. Thus, the blood is divided into two layers: the lower one is red blood cells, the upper one is plasma. The height of the plasma layer is used to estimate ESR in millimeters per hour. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate will be the number on the division of the test tube, which is located at the border of plasma and erythrocytes.
If a person is healthy, the rate at which red cells drop is very low. In inflammatory diseases, its level increases. This is explained by the fact that in the acute phase of inflammation the fibrinogen content in the blood increases. In addition, globulins are released into the blood - protective antibodies against pathogenic agents (fungi, viruses, bacteria, etc.). As a result, red blood cells stick together and settle to the bottom faster. The faster they fall, the more severe the disease.
ESR usually begins to increase a day or two after the onset of the disease. It reaches its peak at the time of recovery, normalizes gradually and can remain elevated for some time when the person is already practically healthy. Blood is taken repeatedly for ESR, since changes in the indicator over time are more informative.
Elevated ESR in children
When the ESR norm in children is exceeded, most likely an infectious inflammatory process develops in the body. But it should be taken into account, when determining ESR according to Panchenkov, that other indicators of the CBC ( hemoglobin , etc.) are also increased (or changed) in children. Also, in children with infectious diseases, their general condition worsens significantly. In case of infectious diseases, the ESR is high in the child already on the second or third day. The indicator can be 15, 25, 30 mm/h.
If red blood cells are elevated in a child’s blood, the reasons for this condition may be the following:
- metabolic disorders ( diabetes , hypothyroidism , hyperthyroidism );
- systemic or autoimmune diseases ( bronchial asthma , rheumatoid arthritis , lupus );
- blood diseases , hemoblastosis , anemia ;
- diseases in which tissue decay occurs ( tuberculosis , myocardial infarction , cancer ).
It is necessary to take into account: if even after recovery the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased, this means that the process is proceeding normally. It’s just that normalization is slow, but after about one month after the disease, normal levels should be restored. But if there are doubts about recovery, then you need to do a re-examination.
Parents must understand that if a child’s red blood cells are higher than normal, this means that a pathological process is taking place in the body.
But sometimes, if a baby’s red blood cells are slightly elevated, this means that some relatively “harmless” factors are influencing:
- in infants, a slight increase in ESR may be associated with a violation of the mother's diet during natural feeding ;
- period of teething;
- after taking medications ( Paracetamol );
- with a lack of vitamins ;
- with helminthiasis .
Thus, if red blood cells are elevated in the blood, this means that the child is developing a certain disease. There are also statistics on the frequency of increase in this value in various diseases:
- in 40% of cases, a high value indicates infectious diseases ( respiratory tract diseases , tuberculosis , urinary tract diseases , viral hepatitis , fungal diseases );
- in 23% - oncological processes of various organs;
- in 17% - rheumatism , systemic lupus ;
- in 8% - cholelithiasis , inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract , pelvic organs , anemia, ENT diseases , injuries , diabetes , pregnancy ;
- 3% — kidney disease.
Classification
There are no clear digital gradations for dividing the increase in ESR by degree. Conventionally, moderate and high degrees are distinguished. According to the mechanism of occurrence they distinguish:
- True increase in ESR
. The cause is various inflammations, infectious, and oncological pathologies. Develops as a result of dysproteinemia, which increases erythrocyte aggregation. - False increase in ESR
. False acceleration of ESR is observed in anemia, azotemia, alkalosis, and high blood cholesterol levels. The cause of this phenomenon is various pathological processes in which the ESR increases due to changes in the number or shape of red blood cells, the protein-lipid composition of plasma, a shift in blood pH, and the presence of other chemical compounds.
When can increasing ESR be considered safe?
As you know, an increase in red blood cells in the blood, as a rule, indicates that a certain inflammatory reaction is developing in the body. But sometimes the reasons for the increase in red blood cells in the blood of women and men are not so categorical.
We are talking, first of all, about allergies , when analysis in men and women helps to judge whether anti-allergy treatment is being carried out correctly (fluctuations in the initially elevated ESR should be taken into account). That is, if the clinical effect of the drug occurs, then gradually the normal ESR level in the blood of men, as well as in women, will be restored.
A hearty breakfast before the test can also increase this indicator; a strict diet and fasting can also change it.
ROE can change during menstruation, during pregnancy and after the birth of a child.
Reasons for acceleration and deceleration of ESR
Analysis for ESR is an auxiliary test that gives a preliminary result. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is not enough and additional research is needed. An erythrocyte sedimentation rate that is different from normal most often means that various pathological processes are developing in the body.
ESR increases in any inflammatory diseases accompanied by a rise in temperature
The causes of elevated ESR are various diseases, including:
- Acute and chronic infections and inflammations.
- Pneumonia.
- Liver diseases.
- Tuberculosis, syphilis.
- Myocardial infarction.
- Kidney diseases.
- State of shock.
- Anemia.
- Skin infectious diseases.
- Lymphoma.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland.
- Autoimmune diseases: lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatic fever.
- Fractures and bone injuries.
- Tissue necrosis.
- Surgical interventions.
- Infectious heart diseases.
- Consequences of taking certain drugs.
A very high erythrocyte sedimentation rate is observed in autoimmune diseases:
- Allergic vasculitis.
- Hyperfibrenogenemia.
- Giant cell arteritis.
A low level indicates conditions such as:
- hypofibrenogenemia;
- circulatory failure;
- polycythemia;
- hyperbilirubinemia;
- taking corticosteroids;
- reactive erythrocytosis;
- vegetarianism;
- loss of muscle mass, starvation.
False-positive ESR tests
In medicine there is also the concept of a false positive analysis. An analysis of ESR is considered such if there are factors on which this value depends:
- anemia (no morphological changes in red blood cells occur);
- increase in the concentration of plasma proteins , with the exception of fibrinogen ;
- hypercholesterolemia;
- renal failure;
- obesity ;
- pregnancy;
- old age of a person;
- administration of dextran ;
- a technically incorrect study;
- taking vitamin A ;
- recent vaccination against hepatitis B.
What to do if the reasons for the increase are not determined?
If the analysis is normal, but the causes of the increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate cannot be determined, it is important to conduct a detailed diagnosis. It is necessary to exclude oncological diseases , so lymphocytes , GRA, and the norm of leukocytes in women and men are determined. During the analysis process, other indicators are also taken into account - whether the average volume of erythrocytes is increased (what this means - the doctor will explain) or whether the average volume of erythrocytes is decreased (what this means is also determined by the specialist). Urine tests and many other studies are also carried out.
But there are cases when high ESR levels are a feature of the body, and they cannot be reduced. In this case, experts advise regular medical examinations, and if a certain symptom or syndrome appears, consult a doctor.
How to reduce ESR in the blood?
The doctor will tell you in detail about ways to reduce this indicator with the help of medications after the study. He will prescribe a treatment regimen once the diagnosis has been made. It is strictly not recommended to take medications on your own. You can try to reduce it with folk remedies, which are mainly aimed at restoring normal function of the immune system , as well as cleansing the blood. Effective folk remedies can be considered herbal decoctions, teas with raspberries and lemon, beet juice, etc. How many times a day to take these remedies, how much you need to drink, you should find out from a specialist.