Home | About us | Delivery | Advertisers | Login | Registration
The pharmacy is closed on Sundays and holidays.
- Medicines
- dietary supplementsVitamins
- Categories from A to Z
- Brands from A to Z
- Products from A to Z
- Medical equipment
- beauty
- Child
- Care
- Honey products appointments
- Herbs and herbal teas
- Medical nutrition
- Journey
- Making medicinesStock
Pharmacy online is the best pharmacy in Almaty, delivering medicines to Almaty. An online pharmacy or online pharmacy provides the following types of services: delivery of medicines, medicines to your home. Online pharmacy Almaty or online pharmacy Almaty delivers medicines to your home, as well as home delivery of medicines in Almaty.
my basket
Apteka84.kz is an online pharmacy that offers its customers medicines, medicinal and decorative cosmetics, dietary supplements, vitamins, baby food, intimate products for adults, medical equipment and thousands of other medical and cosmetic products at low prices. All data presented on the Apteka84.kz website is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical care. Apteka84.kz strongly recommends that you carefully read the instructions for use contained in each package of medicines and other products. If you currently have any symptoms of the disease, you should seek help from a doctor. You should always tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you take. If you feel you need further help, please consult your local pharmacist or contact our GP online or by telephone.
© 2021 Pharmacy 84.
Valvir, 10 pcs., 500 mg, film-coated tablets
Inside
Regardless of food intake, tablets should be taken with water.
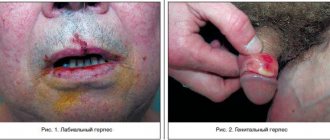
Treatment of skin and mucous membrane infections caused by HSV, including newly diagnosed and recurrent genital herpes (Herpes genitalis), as well as labial herpes (Herpes labialis)
Immunocompetent adults and adolescents aged 12 to 18 years.
The recommended dose is 500 mg 2 times a day. In case of relapse, treatment should continue for 3 or 5 days. In the case of primary herpes, which can occur in a more severe form, treatment should begin as early as possible, and its duration should be increased from 5 to 10 days. In case of relapses of HSV, it is considered most correct to prescribe the drug Valvir in the prodromal period or immediately after the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease. The use of valacyclovir may prevent the development of lesions if it is given at the first signs and symptoms of relapse due to HSV.
As an alternative treatment for labial herpes, the use of the drug Valvir at a dose of 2000 mg 2 times a day for 1 day is effective. The second dose should be taken approximately 12 hours (but not earlier than 6 hours) after taking the first dose. When using this dosage regimen, the duration of treatment should not exceed 1 day, because Exceeding the duration of this course of treatment does not result in additional clinical benefit.
Therapy should be started when the earliest symptoms of herpes labialis (ie, tingling, itching, burning) appear.
Prevention (suppression) of recurrent infections of the skin and mucous membranes caused by HSV, including genital herpes, incl. in adults with immunodeficiency
Immunocompetent adults and adolescents aged 12 to 18 years.
In immunocompetent patients, the recommended dose is 500 mg once daily. After 6–12 months of treatment, it is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy.
Adults with immunodeficiency.
In adult patients with immunodeficiency, the recommended dose is 500 mg 2 times a day. After 6–12 months of treatment, it is necessary to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy.
Prevention of infections caused by CMV and diseases after solid organ transplantation
Adults and teenagers aged 12 to 18 years.
The recommended dose is 2000 mg 4 times a day, prescribed as early as possible after transplantation. The dose should be reduced depending on creatinine Cl. The duration of treatment is usually 90 days, but in high-risk patients the course of treatment may be extended.
Treatment of herpes zoster (Herpes zoster) and ophthalmic herpes zoster
Adults.
The recommended dose is 1000 mg 3 times a day for 7 days.
Special patient groups
Children.
The effectiveness of treatment with Valvir in children has not been studied.
Elderly patients.
It is necessary to take into account the possible impairment of renal function in elderly patients, and the dose of Valvir should be adjusted accordingly. It is necessary to maintain adequate water and electrolyte balance.
Renal dysfunction.
It is recommended to reduce the dose of Valvir in patients with severe renal impairment (see dosage regimen in Table 2). In such patients, it is necessary to maintain adequate water and electrolyte balance.
table 2
Dose adjustment of Valvir for use in adults and adolescents aged 12 to 18 years with impaired renal function
| Indications | Creatinine Cl, ml/min | Dose of the drug Valvir |
| Herpes zoster and herpes zoster ophthalmicus in immunocompetent adults (treatment) | at least 50 | 1000 mg 3 times a day |
| from 30 to 49 | 1000 mg 2 times a day | |
| from 10 to 29 | 1000 mg 1 time per day | |
| less than 10 | 500 mg 1 time per day | |
| HSV (treatment) | ||
| Immunocompetent adults and adolescents aged 12 to 18 years | at least 30 | 500 mg 2 times a day |
| less than 30 | 500 mg 1 time per day | |
| Labial herpes in immunocompetent adults and adolescents aged 12 to 18 years (treatment) | at least 50 | 2000 mg 2 times a day |
| from 30 to 49 | 1000 mg 2 times a day | |
| from 10 to 29 | 500 mg 2 times a day | |
| less than 10 | 500 mg 1 time per day | |
| HSV (prevention (suppression) | ||
| Immunocompetent adults and adolescents aged 12 to 18 years | at least 30 | 500 mg 1 time per day |
| less than 30 | 500 mg 1 time every 2 days | |
| Adults with immunodeficiency | at least 30 | 500 mg 2 times a day |
| less than 30 | 500 mg 1 time per day | |
| Prevention of infections caused by CMV in adults and adolescents aged 12 to 18 years | not less than 75 | 2000 mg 4 times a day |
| from 50 to 75 | 1500 mg 4 times a day | |
| from 25 to 50 | 1500 mg 3 times a day | |
| from 10 to 25 | 1500 mg 2 times a day | |
| less than 10 or in patients on hemodialysis | 1500 mg 1 time per day | |
Additional information for indication: treatment of skin and mucous membrane infections caused by HSV, including newly diagnosed and recurrent genital herpes (Herpes genitalis), as well as labial herpes (Herpes labialis).
There is no experience with the use of Valvir in children with creatinine Cl values less than 50 ml/min/1.73 m2.
Additional information for the indications for the prevention of infections caused by CMV and diseases after solid organ transplantation.
It is necessary to frequently determine creatinine Cl, especially during periods when renal function changes rapidly, for example, immediately after transplantation or engraftment, and the dose of Valvir is adjusted in accordance with creatinine Cl values.
Additional information for the indications for the treatment of herpes zoster (Herpes zoster) and herpes zoster ophthalmicus.
Valvir should be used after hemodialysis in patients undergoing intermittent hemodialysis.
Patients with impaired liver function.
Based on a study using a single dose of valaciclovir 1000 mg in adult patients with mild to moderate liver cirrhosis (with preserved synthetic liver function), no dose adjustment of Valvir is required.
Pharmacokinetic data in adult patients with severe liver dysfunction (decompensated cirrhosis), impaired synthetic liver function and the presence of portacaval anastomoses also do not indicate the need for dose adjustment of the drug Valvir, however, clinical experience with these pathologies is limited.
Information on doses greater than 4000 mg/day for patients with infections caused by HSV and CMV is listed in the "Special Instructions" section.
Valvir
Suction
After oral administration, valacyclovir is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, quickly and almost completely converted to acyclovir and valine. This conversion is probably carried out by the liver enzyme valacyclovirhydralase.
When taking valacyclovir in a dose of 1000 mg, the bioavailability of acyclovir is 54% and is not reduced by food intake. The pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir is not dose-dependent.
The rate and extent of absorption decrease with increasing dose, resulting in a less proportionate increase in maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) compared to the therapeutic dose range and a decrease in bioavailability at doses above 500 mg.
Table 1. Results of assessing the pharmacokinetics of acyclovir when taking single doses of valacyclovir from 250 mg to 2000 mg in healthy volunteers with normal liver function
| Pharmacokinetic parameters of acyclovir | 250 mg (N=15) | 500 mg (N=15) | 1000 mg (N=15) | 2000 mg (N=8) | |
| Cmax | µmol/l | 9,7±1,71 | 15,0±4,23 | 23,1±8,53 | 36,9±6,36 |
| µg/ml | 2,20±0,38 | 3,37±0,95 | 5,20±1,92 | 8,30±1,43 | |
| Tmax | hours (h) | 0,75 (0,75-1,5) | 1,0 (0,75-2,5) | 2,0 (0,75-3,0) | 2,0 (1,5-3,0) |
| AUC | hxmmol/l | 24,4±3,65 | 49,3±7,77 | 83,9±20,1 | 131±28,3 |
| hxmkg/ml | 5,50±0,82 | 11,1±1,75 | 18,9±4,51 | 29,5±6,36 | |
Cmax - maximum concentration in blood plasma;
Tmax is the time until the maximum concentration in the blood plasma is reached;
AUC is the area under the concentration-time pharmacokinetic curve.
Cmax and AUC values reflect the average standard deviation.
Values for Tmax reflect the median value and range of values.
The maximum concentration of valacyclovir in blood plasma is only 4% of the concentration of acyclovir, the median time to reach it ranges from 30 to 100 minutes after taking the drug. 3 hours after dosing, the concentration of valacyclovir reaches the level of quantitative determination or below.
Valacyclovir and acyclovir have similar pharmacokinetic parameters after single and multiple doses. VZV and HSV do not significantly alter the pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir and acyclovir after oral administration of valacyclovir.
Distribution
The degree of binding of valacyclovir to plasma proteins is very low (15%). The extent of penetration into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is defined as the ratio of AUC in CSF to AUC in plasma and is about 25% for acyclovir and the metabolite 8-hydroxyacyclovir (8-OH-ACV); about 2.5% for the metabolite 8-(carboxymethoxy)methyl-guanine (CMMG).
Metabolism
After oral administration, valacyclovir is converted to acyclovir and L-valine through first-pass metabolism in the intestine and/or hepatic metabolism. Acyclovir is converted into small metabolites: CMMG under the influence of ethyl alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase: 8-OH-ACV under the influence of aldehyde oxidase. Approximately 88% of the total cumulative plasma exposure is due to acyclovir. 11% - CMMG and 1% - 8-OH-ACV.
Valacyclovir and acyclovir are not metabolized by isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system.
Removal
In patients with normal renal function, the half-life of acyclovir from blood plasma after a single or multiple doses of valacyclovir is about 3 hours. Less than 1% of the administered dose of valacyclovir is excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Valaniclovir is excreted from the body by the kidneys mainly in the form of acyclovir (more than 80% of the dose taken) and the metabolite of acyclovir - CMMG
Special patient groups
Patients with impaired renal function
The elimination of acyclovir correlates with renal function, and acyclovir exposure increases with the severity of renal failure.
In patients with end-stage renal disease, the mean half-life of acyclovir after valacyclovir is approximately 14 hours, compared to approximately 3 hours with normal renal function.
Plasma and CSF exposures to acyclovir and its metabolites CMMG and 8-OH-ACV were assessed at steady state after multiple doses of valacyclovir in 6 patients with normal renal function (mean creatinine clearance 111 mL/min, range 91-144 mL/min). receiving 2000 mg every 6 hours, and 3 patients with severe renal impairment (mean creatinine clearance 26 ml/min, range 17-31 ml/min) receiving 1500 mg every 12 hours. In severe versus normal renal impairment renal function in the blood plasma, as well as in the CSF, the concentrations of acyclovir, CMMG and 8-OH-ACV were 2, 4 and 5-6 times higher, respectively. There was no difference in the extent of acyclovir CSF penetration (defined as the ratio of CSF AUC to plasma AUC), CMMG, or 8-GH-ACV between the two populations with severe renal impairment and normal renal function.
Patients with liver dysfunction
Pharmacokinetic data show that in patients with hepatic impairment, the rate of conversion of valacyclovir to acyclovir is reduced, but not the extent of this conversion. The half-life of acyclovir is independent of liver function.
Pregnancy
A study of the pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir and acyclovir in late pregnancy found an increase in the daily AUC value at steady state when taking valacyclovir daily at a dose of 1000 mg per day, which was approximately 2 times higher than the AUC when taking oral acyclovir at a dose of 1200 mg per day.
HIV infection
In patients with HIV infection, the distribution and pharmacokinetic characteristics of acyclovir after oral administration of one or more doses of 1000 mg or 2000 mg of valacyclovir remain unchanged compared to healthy volunteers.
Organ transplantation
The maximum concentration of acyclovir in organ transplant patients receiving 2000 mg valacyclovir 4 times a day was comparable to or higher than the maximum concentration observed in healthy volunteers receiving the same dose.
The established daily AUC values can be characterized as noticeably higher.