Valcycon®
Inside, regardless of food intake, with water.
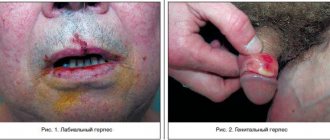
Treatment of herpes zoster (Herpes zoster)
Adults:
The recommended dose is 1000 mg 3 times a day for 7 days.
Treatment of infections caused by HSV (Herpes simplex)
Adults:
The recommended dose for treatment of an episode is 500 mg 2 times a day for 5 days.
In more severe cases of the onset of the disease, treatment should begin as early as possible, and its duration can be increased from 5 to 10 days. In case of relapse, treatment should continue for 3 or 5 days. For recurrent HSV, it is ideal to prescribe valacyclovir in the prodromal period or immediately after the first symptoms of the disease appear.
As an alternative for the treatment of labial herpes, the administration of valacyclovir at a dose of 2 g 2 times a day is effective. The second dose should be taken approximately 12 hours (but not earlier than 6 hours) after the first dose. When using this dosage regimen, the duration of treatment is 1 day. Therapy should be started when the earliest symptoms of herpes labialis appear: tingling, itching and/or burning.
Prevention (suppression) of recurrent infections caused by HSV
Adults:
In patients with preserved immunity, the recommended dose is 500 mg 1 time per day.
In patients with immunodeficiency, the recommended dose is 500 mg 2 times a day.
Prevention of transmission of genital herpes to a healthy partner
For infected immunocompetent individuals with relapses no more than 9 times a year, the recommended dose of valacyclovir is 500 mg once a day for a year or more, daily.
There are no data on infection prevention in other patient populations.
Prevention of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection after transplantation
Adults and teenagers aged 12 years and older:
The recommended dose is 2 g 4 times a day, prescribed as early as possible after transplantation. The dose should be reduced depending on creatinine clearance (CC). The duration of treatment is 90 days, but in high-risk patients the course of treatment can be extended.
Special patient groups
Patients with impaired renal function:
- treatment of herpes zoster and infections caused by HSV, prevention (suppression) of relapses of infection caused by HSV, prevention of transmission of genital herpes to a healthy partner
It is recommended to reduce the dose of valacyclovir in patients with a significant decrease in renal function (see dosage regimen in Table 1). Adequate hydration should be maintained in such patients.
There is no experience with the use of valacyclovir in children with CC values less than 50 ml/min/1.73 m2.
Table 1
| Indications | CC, ml/min | Valacyclovir dose |
| Herpes zoster | 15-30 | 1 g 2 times a day |
| less than 15 | 1 g 1 time per day | |
| Treatment of infection caused by HSV (according to the regimen of 500 mg 2 times a day) | less than 15 | 500 mg 1 time per day |
| Treatment of labial herpes (according to the regimen of 2 g 2 times a day for one day) | 31-49 | 1 g twice a day |
| 15-30 | 500 mg twice a day | |
| less than 15 | 500 mg once | |
| Prevention (suppression) of recurrent infections caused by HSV: - patients with normal immunity - patients with reduced immunity – reducing the risk of transmission of genital herpes | ||
| less than 15 | 250 mg 1 time per day | |
| less than 15 | 500 mg 1 time per day | |
| less than 15 | 250 mg 1 time per day |
For patients on hemodialysis, it is recommended to use valacyclovir immediately after the end of the hemodialysis session at the same dose as in patients with CC less than 15 ml/min.
— prevention of cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection after transplantation
The regimen for valaciclovir in patients with impaired renal function should be established in accordance with Table 2.
table 2
| CC, ml/min | Valacyclovir dose |
| 75 or more | 2 g 4 times a day |
| from 50 to less than 75 | 1.5 g 4 times a day |
| from 25 to less than 50 | 1.5 g 3 times a day |
| from 10 to less than 25 | 1.5 g 2 times a day |
| less than 10 or hemodialysis* | 1.5 g 1 time per day |
* In patients undergoing hemodialysis, valacyclovir should be prescribed after the end of the hemodialysis session.
It is necessary to determine QC frequently, especially during periods when renal function changes rapidly, for example, immediately after transplantation or engraftment, and the dose of valacyclovir is adjusted in accordance with QC values.
Patients with liver dysfunction
In adult patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment with preserved synthetic function, no dose adjustment of valacyclovir is required.
Pharmacokinetic data in adult patients with severely impaired liver function (decompensated cirrhosis), impaired synthetic liver function and the presence of portacaval anastomoses also do not indicate the need to adjust the dose of valacyclovir, however, clinical experience with this pathology is limited.
Children under 12 years of age
There is no data on the use of Valcicon® in children.
Elderly patients
No dose adjustment is required, except in patients with significant renal impairment. It is necessary to maintain adequate water and electrolyte balance.
Valcicon, 10 pcs., 500 mg, film-coated tablets
Inside,
regardless of food intake, washed down with water.
Adults
Treatment of herpes zoster (Herpes zoster):
The recommended dose is 1000 mg 3 times a day for 7 days.
Treatment of infections caused by HSV:
The recommended dose for treatment of an episode is 500 mg 2 times a day for 5 days. In more severe cases of the onset of the disease, treatment should begin as early as possible, and its duration can be increased from 5 to 10 days. In case of relapse, treatment should continue for 3 or 5 days. For recurrent HSV, it is ideal to prescribe valacyclovir in the prodromal period or immediately after the first symptoms of the disease appear.
As an alternative for the treatment of labial herpes, the administration of valacyclovir at a dose of 2 g 2 times a day is effective. The second dose should be taken approximately 12 hours (but not earlier than 6 hours) after taking the first dose. When using this dosage regimen, the duration of treatment is 1 day. Therapy should be started when the earliest symptoms of herpes labialis (ie, tingling, itching, burning) appear.
Prevention (suppression) of recurrent infections caused by HSV:
in patients with preserved immunity, the recommended dose is 500 mg 1 time per day. In patients with immunodeficiency, the recommended dose is 500 mg 2 times a day.
Prevention of transmission of genital herpes to a healthy partner:
For infected immunocompetent individuals with relapses no more than 9 times a year, the recommended dose of valacyclovir is 500 mg once a day for a year or more every day.
There are no data on infection prevention in other patient populations.
Adults and children 12 years and older
Prevention of CMV infection after transplantation:
The recommended dose is 2 g 4 times a day, prescribed as soon as possible after transplantation. The dose should be reduced depending on creatinine clearance. The duration of the course is 90 days, but in patients at high risk, the course of treatment can be extended.
Special patient groups
Renal dysfunction:
- treatment of herpes zoster and infections caused by HSV, prevention (suppression) of relapses of infection caused by HSV, prevention of transmission of genital herpes to a healthy partner.
It is recommended to reduce the dose of valacyclovir in patients with a significant decrease in renal function (see dosage regimen in Table 1). Adequate hydration should be maintained in such patients.
There is no experience with the use of valacyclovir in children with creatinine Cl values less than 50 ml/min/1.73 m2.
Table 1
| Indications | Creatinine Cl, ml/min | Valacyclovir dose |
| Shingles ( Herpes Zoster ) | 15–30 | 1 g 2 times a day |
| less than 15 | 1 g 1 time per day | |
| Treatment of infection caused by HSV (according to the regimen of 500 mg 2 times a day) | less than 15 | 500 mg 1 time per day |
| Treatment of labial herpes (according to the regimen of 2 g 2 times a day for 1 day) | 31–49 | 1 g 2 times a day |
| 15–30 | 500 mg 2 times a day | |
| less than 15 | 500 mg 1 time per day | |
| Prevention (suppression) of recurrent infections caused by HSV: | ||
| - patients with normal immunity | less than 15 | 250 mg 1 time per day |
| - patients with reduced immunity | less than 15 | 500 mg 1 time per day |
| – reducing the risk of transmission of genital herpes | less than 15 | 250 mg 1 time per day |
For patients on hemodialysis, it is recommended to use valacyclovir immediately after the end of the hemodialysis session at the same dose as in patients with creatinine Cl less than 15 ml/min.
— prevention of CMV infection after transplantation.
The regimen for valaciclovir in patients with impaired renal function should be established in accordance with Table 2.
table 2
| Creatinine Cl, ml/min | Valacyclovir dose |
| ≥75 | 2 g 4 times a day |
| from ≥50 to <75 | 1.5 g 4 times a day |
| from ≥25 to <50 | 1.5 g 3 times a day |
| from ≥10 to <25 | 1.5 g 2 times a day |
| <10 or hemodialysis* | 1.5 g 1 time per day |
* In patients undergoing hemodialysis, valacyclovir should be prescribed after a hemodialysis session.
Creatinine clearance should be determined frequently, especially during periods when renal function is rapidly changing, such as immediately after transplantation or engraftment, and the dose of valacyclovir should be adjusted according to creatinine clearance.
Liver dysfunction.
In adult patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment with preserved synthetic function, no dosage adjustment of valacyclovir is required. Pharmacokinetic data in adult patients with severely impaired liver function (uncompensated cirrhosis), impaired synthetic liver function and the presence of portacaval anastomoses also do not indicate the need to adjust the dose of valacyclovir, however, clinical experience with this pathology is limited.
Children.
There is no data on the use of Valcicon® in children under 12 years of age.
Elderly patients.
No dose adjustment is required unless there is significant impairment of renal function. It is necessary to maintain adequate water and electrolyte balance.
Valcicon 500mg n42 tab.
Side effects From the central nervous system: headache, dizziness, psychotic symptoms, agitation, decreased mental capacity, ataxia, coma, confusion or depression of consciousness, dysarthria, encephalopathy, mania, hallucinations, convulsions, tremor. These reactions are reversible and are usually observed in patients with impaired renal function or against the background of other predisposing conditions. In patients with a transplanted organ receiving valacyclovir in high doses (8 g/day) for the prevention of cytomegalovirus infection, neurological reactions develop more often than when taken in lower doses. From the respiratory system: dyspnea. From the digestive system: nausea, abdominal discomfort, vomiting, diarrhea, reversible disturbances in liver function tests (increased activity of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase), which are sometimes regarded as manifestations of hepatitis. From the hematopoietic system: leukopenia (mainly observed in patients with reduced immunity), thrombocytopenia, anemia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. From the skin: erythema multiforme, rashes, photosensitivity, alopecia. Allergic reactions: itching, urticaria, angioedema, anaphylaxis. From the urinary system: pain in the projection of the kidneys, renal dysfunction, incl. acute renal failure, renal colic. Renal colic may be associated with impaired renal function. From the senses: visual impairment. Laboratory indicators: decreased hemoglobin content, hypercreatininemia. Other: dysmenorrhea, nasopharyngitis, respiratory tract infections, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, fatigue; In patients with severe immunocompromise, especially in adult patients with advanced HIV infection, receiving valacyclovir in high doses (8 g / day daily) for a long time, cases of renal failure, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia (sometimes in combination) have been observed. ). Similar adverse reactions have been observed in patients with the same diseases, but not receiving valacyclovir.
Special instructions In patients at risk of dehydration, especially in elderly patients, adequate fluid replacement must be ensured during the treatment period. Since acyclovir is excreted by the kidneys, the dose of Valcicon should be adjusted depending on the degree of renal impairment. Patients with renal failure are at increased risk of developing neurological complications and should be closely monitored. As a rule, these reactions are reversible and disappear after discontinuation of the drug. In patients with chronic renal failure (CRF), it is recommended that creatinine clearance be determined frequently, especially during periods when renal function is rapidly changing (particularly immediately after transplantation or engraftment), and the dose of valacyclovir is adjusted according to creatinine clearance. There are no data on the use of valacyclovir in high doses (4 g or more per day) in patients with liver disease, so high doses of Valcicon should be administered to them with caution. Suppressive therapy with valacyclovir reduces the risk of transmission of genital herpes, but does not eliminate the risk of infection and does not lead to a complete cure. Therapy with Valcicon is recommended in combination with safe sex. Taking the drug in high doses for a long time in conditions accompanied by severe immunodeficiency (bone marrow transplantation, clinical forms of HIV infection, kidney transplantation) led to the development of thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic-uremic syndrome, including death. If side effects from the central nervous system occur (including agitation, hallucinations, confusion, delirium, convulsions and encephalopathy), the drug is discontinued. Effect on driving vehicles and machinery There is no data on the effect of valacyclovir, used in therapeutic doses, on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery. However, when assessing the patient's ability to drive a car or move machinery, it must be taken into account that side effects from the central nervous system may occur, so caution should be exercised.
Overdose Symptoms: with an overdose of valacyclovir, acute renal failure and the development of neurological symptoms may occur, including confusion, hallucinations, agitation, depression of consciousness and coma, nausea and vomiting are also noted. To prevent overdose, caution should be exercised when using the drug. Many cases of overdose have been associated with the use of the drug to treat patients with impaired renal function and elderly patients due to non-compliance with the dosage regimen (repeatedly receiving doses of valacyclovir that exceed the recommended ones). Treatment. Patients should be closely monitored for timely diagnosis of toxic manifestations. Hemodialysis significantly accelerates the elimination of acyclovir from blood plasma and can be considered the optimal treatment method in case of symptomatic overdose.
Interaction with other drugs Cimetidine and tubular secretion blockers reduce the effect (they reduce the rate, but not the completeness of conversion to acyclovir). No dosage adjustment is required in individuals with normal creatinine clearance. Nephrotoxic drugs increase the risk of developing renal dysfunction. Caution should be exercised (monitor changes in renal function) when combining Valcicon in higher doses (4 g per day or more) with drugs that affect other renal functions (for example: cyclosporine, tacrolimus). Acyclovir is excreted by the kidneys, mainly unchanged, through active renal secretion. Concomitant use of drugs with this elimination mechanism may lead to increased plasma concentrations of acyclovir. After prescribing Valcicon at a dose of 1000 mg, cimetidine and probenecid, which are eliminated in the same way as valacyclovir, increase the AUC value of acyclovir and thus reduce its renal clearance. Due to the wide therapeutic index of acyclovir, dose adjustment of Valcicon is not required in this case. Caution must be exercised in the case of simultaneous use of valacyclovir in higher doses (4 g per day or higher) and drugs that compete with acyclovir for the elimination pathway, since there is a potential threat of increased plasma levels of one or both drugs or their metabolites. An increase in the AUC value of acyclovir and the inactive metabolite mycophenolate mofetil was noted when these drugs were used simultaneously. The pharmacokinetics of valacyclovir does not change when taken concomitantly with digoxin, aluminum/magnesium-containing antacids, and thiazide diuretics.
Storage conditions and shelf life : Protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Shelf life : 2 years.