Valsacor®
When using Valsacor® in patients with hypertension, regular monitoring of laboratory parameters is not required.
Double blockade of the RAAS
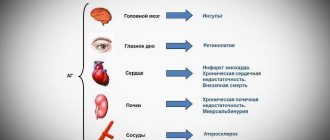
In some patients, double blockade of the RAAS was accompanied by the development of severe arterial hypotension, syncope, stroke, hyperkalemia and renal dysfunction (including acute renal failure).
The simultaneous use of ARB II, including valsartan, with drugs that affect the RAAS, such as ACE inhibitors or aliskiren, is not recommended; if such therapy is necessary, blood pressure, renal function, and blood plasma electrolyte levels should be carefully monitored. Concomitant use of ARB II, including valsartan, with drugs containing aliskiren is contraindicated in patients with diabetes mellitus and/or with moderate or severe renal impairment (GFR less than 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 body surface area) and is not recommended in other patients.
The simultaneous use of ARB II with ACE inhibitors is contraindicated in patients with diabetic nephropathy and is not recommended in other patients.
Hyponatremia and/or dehydration
In patients with severe hyponatremia and/or dehydration, for example, due to taking large doses of diuretics, in rare cases, arterial hypotension with clinical manifestations may develop at the beginning of therapy with Valsacor®. Before starting treatment, it is recommended to restore sodium levels and/or replenish blood volume, in particular by reducing the doses of diuretics.
If arterial hypotension with clinical manifestations develops, the patient must be placed in a horizontal position and, if necessary, a 0.9% sodium chloride solution should be administered intravenously. Therapy with Valsacor® can be continued only after stabilization of hemodynamic parameters.
Hyperkalemia
Concomitant use of potassium-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, eplerenone, triamterene, amiloride), potassium supplements, potassium-containing nutritional supplements or other drugs that can increase serum potassium levels (for example, heparin) is not recommended. It is necessary to monitor the potassium content in the blood plasma.
Renal artery stenosis
Short-term use of valsartan in patients with renovascular hypertension, which developed secondary to unilateral stenosis of the artery of a single kidney, was not accompanied by significant changes in renal hemodynamics, creatinine concentrations or serum urea nitrogen. Because other drugs that affect the RAAS can increase serum urea and creatinine concentrations in patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or solitary renal artery stenosis, continuous monitoring of these values is recommended as a precaution.
Condition after kidney transplantation
The safety of Valsacor® in patients who have recently undergone kidney transplantation has not been established.
Primary hyperaldosteronism
Patients with primary hyperaldosteronism are resistant to antihypertensive drugs that affect the RAAS, therefore the use of Valsacor® is not recommended for such patients.
Stenosis of the aortic and/or mitral valves, HOCM
The drug Valsacor® should be used with caution in patients with hemodynamically significant stenosis of the aortic and/or mitral valves or with HOCM.
Renal dysfunction
In patients with impaired renal function, no change in drug doses is required, since there is no data on the use of the drug Valsacor® in severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min or 0.167 ml/s) and in patients on hemodialysis, in such cases In cases, the drug is recommended to be used with caution. Concomitant use of ARB II, including valsartan, or ACE inhibitors with aliskiren is contraindicated in patients with impaired renal function (GFR less than 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 body surface area).
Liver dysfunction
For patients with impaired liver function, biliary cirrhosis and cholestasis, Valsacor® at a dosage of 320 mg is contraindicated, since the maximum daily dose should not exceed 80 mg.
History of angioedema
Among patients with angioedema (swelling of the larynx and vocal cords, causing obstruction of the airways and/or swelling of the face, lips, pharynx and/or tongue) during treatment with Valsacor®, cases of development of angioedema in the anamnesis were observed, including when taking ACE inhibitors. If angioedema develops, the drug should be immediately discontinued and the possibility of its re-use should be excluded.
Arterial hypertension
For hypertension, the drug Valsacor® can be used in monotherapy or simultaneously with other antihypertensive drugs, in particular with diuretics.
CHF/increasing survival of patients with acute myocardial infarction
It is possible to use the drug Valsacor® in combination with other drugs used for acute myocardial infarction (thrombolytics, acetylsalicylic acid as an antiplatelet agent, beta-blockers and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins)).
The simultaneous use of Valsacor® and ACE inhibitors in this category of patients is not recommended, since this combination therapy does not lead to additional clinical effect and is accompanied by an increased risk of developing AEs compared to therapy with the two drugs separately.
In patients with CSP, triple combination therapy (with Valsacor®, an ACE inhibitor and a beta-blocker) is not recommended, since it does not lead to additional clinical effect and is accompanied by an increased risk of developing AEs.
The use of Valsacor® in patients with CHF or acute myocardial infarction often leads to a slight decrease in blood pressure. As a rule, discontinuation of the drug is not required if dosing instructions are followed.
In patients whose renal function may depend on the activity of the RAAS (for example, in patients with CHF II-IV FC according to the NYHA classification), therapy with ACE inhibitors and ARB II is accompanied by oliguria and/or an increase in azotemia, and in rare cases, AKI and/or death outcome. Since valsartan is a II ARA, the possibility of deterioration of renal function with its use cannot be excluded.
Initiation of therapy in patients with XCII or acute myocardial infarction should be done with caution. Renal function should always be assessed when assessing patients.
Special information on excipients
The drug Valsacor® contains lactose, therefore the drug is contraindicated in patients with lactase deficiency, lactose intolerance, and glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
Pharmacological properties
What are Valsacor tablets for? The drug normalizes fluid pressure in the circulatory system, maintains normal A/D levels, and improves heart function.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The active substance valsartan reduces vascular resistance, normalizes systolic pressure, and has a positive effect on cardiac output.
Hydrochlorothiazide belongs to the category of thiosides and has a diuretic effect. Removes potassium and sodium ions, as well as excess water from the body. Enhances the therapeutic effect of valsartan and reduces side effects.
The effect after taking the medicine lasts for 24 hours.
The medicine is quickly absorbed and absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and does not accumulate in the liver. It is excreted from the body by the kidneys within 6-8 hours.
Analogs
In cases of ineffectiveness of this drug or its individual intolerance, the doctor selects an analogue or substitute for further treatment. An alternative remedy differs in composition, but is identical in effect.
Identical in composition:
According to the mechanism of action:
The drug does not have hormonal substitutes.
The material was prepared specifically for the website venaprof.ru, edited by pharmacist M.N. Aleksandrova.
Valsacor: patient reviews, price, analogues of the drug for blood pressure
To treat the chronic course of heart failure, arterial hypertension and increase the survival of patients after an acute heart attack, the drug Valsacor, an angiotensin-2 receptor antagonist, is used.
You can purchase the medicine at a pharmacy; a doctor's prescription is required for purchase. The cost is determined by the dosage and type of drug. Thus, Valsacor tablets 80 mg (30 pcs.) cost 350 rubles, 160 mg (No. 30) - 420 rubles, 320 mg (No. 30) - 650 rubles. Valsacor N (160 + 25 mg) 500 rubles, 80+12.5 mg – 390 rubles, and Valsacor ND 160 +25 mg – 700 rubles.
Description of the drug Valsacor, instructions for use with dosages, drug compatibility and special instructions, possible substitutes and their cost - we will consider further.
Contraindications
The drug is not approved for use in patients:
- patients with diabetes mellitus;
- with cirrhosis of the liver;
- with impaired renal function;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- during pregnancy and pregnancy;
- children under 16 years of age.
Use with caution in patients after a kidney transplant.
Side effects
The drug is well tolerated by patients, but in case of individual intolerance, side effects of Valsacor are detected against the background of violations of the doctor’s recommendations. Undesirable reactions occur in the form of:
- abdominal pain;
- skin rash;
- dry cough;
- angioedema;
- headache;
- increased fatigue.
If some of these symptoms are detected, you must stop treatment and notify your doctor.
In childhood, during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The safety of the drug in young children has not been established. The medication is not recommended for treatment in pediatrics.
When planning pregnancy, the patient needs to switch to alternative treatment with a substitute drug. During gestation, taking the drug is contraindicated. The medication may cause fetotoxic and neonatal toxic effects.
The active substance is absorbed into breast milk, so during lactation the patient is recommended to switch to artificial feeding.
Overdose
If you independently increase the dose and frequency of use of the drug, an overdose occurs with subsequent negative manifestations:
In rare cases, collapse and shock with death.
The victim needs to undergo symptomatic therapy - rinse the stomach, induce vomiting, and administer saline intravenously to normalize the water-salt balance.
Directions for use and dosage
At what pressure is Valsacor suitable for use? Tablets are prescribed for all phases of arterial hypertension, as well as its chronic form.
What is the dosage of Valsacor? The medication is taken orally once a day, one tablet in the morning, with water. For the best therapeutic effect, the drug should be used at the same time.
For patients in whom Valsacor 80 did not provide visible improvements in the complex treatment of hypertension, the doctor replaces the drug with Valsacor N 160 to further reduce blood pressure. The dose is increased over the course of a week to 160 mg twice a day according to the patient’s condition.
A pronounced hypotonic effect occurs after four weeks of regular use. The duration of therapy depends on the clinical picture and complexity of the disease.