Compound
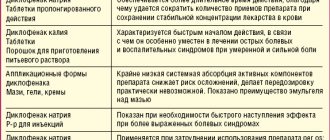
In Diclofenac 5% gel, the active substance - diclofenac sodium - is included in a concentration of 50 mg/g, in 1% - in a concentration of 10 mg/g.
Excipients: isopropyl alcohol, benzyl alcohol, carbomer 940, sodium metabisulfite, polysorbate 80, triethanolamine, purified water. Composition of Diclofenac ointment: Diclofenac sodium (10 or 20 mg/g), propylene glycol, dimethyl sulfoxide, macrogol 400 and 1500.
Composition of Diclofenac injections: Diclofenac sodium (25 mg/ml), sodium metabisulfite, mannitol (E421), benzyl alcohol, sodium hydroxide, propylene glycol, water for injection.
Diclofenac rectal suppositories contain 50 or 100 mg of Diclofenac sodium and solid fat.
Composition of enteric-coated tablets: 25 or 50 mg Diclofenac sodium, disubstituted calcium phosphate, starch, magnesium stearate, polyvinylpyrolidone K30, purified talc, cellulose acetate, indoresin, diethyl phthalate, carmoisin varnish, titanium dioxide, Ponceau 4R varnish, red and yellow iron oxide .
Composition of tablets in p/o: 25 mg Diclofenac sodium, milk sugar, sucrose, povidone, stearic acid, potato starch. Shell: castor oil, cellacephate, titanium dioxide, tropeo-lin O dyes and azorubin.
Composition of retard tablets: 100 mg Diclofenac sodium, hypromellose, hyaetellose, Kollidon SR, sodium alginate, MCC, magnesium stearate. Shell: collicut MAE 100 R, povidone, talc, propylene glycol, titanium dioxide, iron oxide yellow and red.
Composition of eye drops: Diclofenac sodium (1 mg/ml), sodium chloride and dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate, propylene glycol, sodium hydroxide, hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate and disodium edetate, water for injection.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The NSAID Diclofenac is a derivative of phenylacetic acid . Its mechanism of action is based on the ability to suppress the biosynthesis of Pg (prostaglandins) - biologically active lipids that are mediators of fever, pain and inflammation.
Like other NSAIDs, it prevents platelet .
The drug is quickly and completely absorbed; food slows down absorption for 1-4 hours (reducing Cmax by 40%). Cmax when taken orally is observed after 2-3 hours. Changes in this indicator are dose-dependent.
The pharmacokinetic profile does not change with repeated administration. If the recommendations for use are followed, it does not accumulate in the body.
Bioavailability – 50%. It is more than 99% bound to plasma proteins (mainly bound to albumin ). Penetrates into the synovium and breast milk.
Half of the dose taken is metabolized during the “first passage” through the liver. The process is based on single or multiple hydroxylation and conjugation with glucuronic acid. Plasma T1/2 - 1-2 hours.
60% of the dose is excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolic products, less than 1% in its pure form, the rest of the administered drug is excreted in bile.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Diclofenac
NSAID, a derivative of phenylacetic acid with pronounced anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activity. The pharmacological properties of diclofenac are due to its ability to inhibit the biosynthesis of certain prostaglandins as a result of inhibition of the enzyme prostaglandin synthetase. By blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins, diclofenac eliminates or significantly reduces the severity of symptoms of inflammation. Diclofenac reduces the increased sensitivity of nerve endings to mechanical stimuli and biologically active substances produced at the site of inflammation, induced by prostaglandins; leads to a decrease in body temperature, preventing the effect of prostaglandins on the hypothalamic link of the thermoregulation process; reduces the concentration of prostaglandins in menstrual blood and the intensity of pain during primary dysmenorrhea. The use of diclofenac helps to increase the range of motion in the affected joints, reduce pain at rest and during movement. In vitro , diclofenac at a concentration equivalent to that achieved in human tissue during treatment does not inhibit the biosynthesis of cartilage tissue proteoglycans. Inhibits platelet aggregation. Diclofenac is quickly and completely absorbed from the digestive tract. The maximum concentration in the blood after taking diclofenac orally in tablet form is achieved within 20–60 minutes. Eating at the same time slightly slows down the rate, but not the volume, of absorption. Considering that about 50% of diclofenac is metabolized during the first passage through the liver, the AUC when diclofenac is taken orally or used in the form of rectal suppositories is almost 2 times less than in the case of parenteral administration of an equivalent dose. After repeated administration of diclofenac, the pharmacokinetic parameters do not change. Almost 99.7% of diclofenac binds to serum proteins (mainly albumin). The apparent volume of distribution is 0.12–0.17 l/kg body weight. Diclofenac penetrates into the synovial fluid, where its maximum concentration is reached 2–4 hours later than in the blood plasma. The apparent half-life from synovial fluid is 3–6 hours. 2 hours after reaching the maximum concentration in the blood plasma, the concentration of diclofenac in the synovial fluid remains higher; this pattern persists for approximately 12 hours. Biotransformation of diclofenac occurs partly by glucuronidation of the unchanged molecule, but mainly through single and multiple methoxylation, which leads to the formation of several phenolic metabolites (3′-hydroxy-, 4′-hydroxy-, 5′- hydroxy-, 4′,5-dihydroxy- and 3′-hydroxy-4′-methoxydiclofenac), most of which are conjugated with glucuronic acid. Two of them are pharmacologically active, but to a much lesser extent than diclofenac. The total systemic clearance of diclofenac from blood plasma is 263 ± 56 ml/min, the final half-life from blood plasma is 1–2 hours. The half-life of 4 metabolites, including two pharmacologically active ones, is also short and amounts to 1–3 hours. One of the metabolites is 3-hydroxy-4-methoxydiclofenac - has a longer half-life, but this metabolite is pharmacologically inactive. About 60% of administered diclofenac is excreted in the urine in the form of glucuronic conjugates of the intact molecule of the active substance and in the form of metabolites, most of which are also converted into glucuronic conjugates. Less than 1% of diclofenac is excreted unchanged. The rest of the administered dose is excreted as metabolites in bile and feces. There are no significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac in elderly people, patients with kidney disease, chronic hepatitis or compensated cirrhosis.
Contraindications for use
The description of the drug Diclofenac indicates that the drug is contraindicated in:
- hypersensitivity to its components;
- active ulcer, perforation of the walls of the digestive canal, gastric and intestinal bleeding;
- inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract;
- “aspirin asthma”;
- severe functional failure of the heart, kidneys, and liver.
General contraindications for Diclofenac are also recent coronary artery bypass , pregnancy (contraindication for suppositories - the last 3 months of pregnancy), lactation and age under 6 years.
Rectal use of the drug is also contraindicated for proctitis .
Ointment and gel should not be used on areas of the body with damaged skin integrity.
In pediatric practice, 50 mg suppositories and O-coated tablets are prescribed from the age of 14. Retard tablets and 100 mg suppositories are intended exclusively for the treatment of patients over 18 years of age.
An absolute contraindication to the use of eye drops is hypersensitivity to their components.
Drops are prescribed with caution for “ aspirin asthma ”, superficial herpetic keratitis , diseases that are accompanied by disorders of plasma hemostasis; children, elderly people, pregnant and lactating women.
Indications for use of the drug Diclofenac
Rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, gout, lumbago, neuralgia, myalgia, pain due to traumatic injuries of the musculoskeletal system and soft tissues, primary dysmenorrhea, as a symptomatic remedy for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs. In ophthalmology: inhibition of miosis during cataract surgery; prevention of the inflammatory process in the postoperative period for cataracts and surgical interventions in the anterior parts of the eye; prevention of cystoid macular edema before and after operations for lens removal and implantation; non-infectious inflammatory processes involving the anterior parts of the eye (chronic non-infectious conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis); post-traumatic inflammatory process with penetrating and non-penetrating wounds of the eyeball (as an addition to local antibacterial therapy); to reduce the severity of eye pain in photophobia.
Side effects of Diclofenac
When taken orally, the following side effects are possible: dyspepsia, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the digestive canal, perforation of its walls, gastric and intestinal bleeding, increased drowsiness, dizziness, hypersensitivity reactions, irritability.
After using the drops the following are noted:
- burning sensation;
- corneal clouding;
- impaired clarity of perception (immediately after instillation);
- iritis;
- hypersensitivity reactions.
Side effects of injections
Intramuscular injections of Diclofenac may be accompanied by a burning sensation at the injection site, abscess, and necrosis of adipose tissue.
Side effects of the drug Diclofenac
pain in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, ulcerogenic effect, gastrointestinal bleeding, intestinal perforation, exacerbation of ulcerative colitis, headache, loss of consciousness, dizziness, sensory or visual impairment (diplopia), tinnitus, insomnia, irritability, seizures, acute renal failure, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome. Nephropathy occurs in most cases as a result of very long-term use of diclofenac. It is possible to develop allergic reactions, including cross reactions, to other NSAIDs. Long-term use of diclofenac can cause the development of a hypertensive crisis due to inhibition of prostaglandin biosynthesis in the kidneys. Very rarely, hemolytic anemia and hematopoietic disorders (thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia) are observed; sometimes - liver damage. When using eye drops, a transient mild or moderate burning sensation may occur; rarely - blurred vision immediately after instillation of eye drops, hypersensitivity reactions accompanied by itching and hyperemia, photophobia, punctate keratitis.
Instructions for use of Diclofenac
Diclofenac injections: instructions for use
To alleviate acute conditions or relieve an aggravated chronic disease, Diclofenac in ampoules is administered 1 time intramuscularly (deeply). Subsequently, the patient is transferred to the tablet form of the drug.
The dosage of injections is 25-50 mg 2 or 3 times a day.
Diclofenac is administered intravenously by drip. The highest dose is 150 mg/day. Before administration, the contents of the ampoule should be diluted in 0.1-0.5 liters of 0.9% NaCl solution or 5% dextrose solution. Sodium bicarbonate solution is first added to the infusion solutions (0.5 ml if the solution concentration is 8.4%, and 1 ml if the concentration is 4.2%).
The duration of the infusion, depending on the intensity of the pain, is from half an hour to an hour and a half.
To prevent postoperative pain, the infusion is recommended to be carried out with a “shock” dose - 25-50 mg of Diclofenac over 15-60 minutes. Subsequently, the drug is administered at a rate of 5 mg/hour (until the highest daily dose is reached - 150 mg).
How many days can you inject Diclofenac?
IM injections of Diclofenac are allowed for no more than 2 days in a row. In some cases, the course of treatment with injections can last up to 5 days.
How often can you inject the drug?
NSAIDs cause quite serious side effects, so it is optimal to use Diclofenac no more than once every three months, 3-5 injections per course.
Diclofenac gel: instructions for use
A single dose of the gel depends on the size of the painful area. As a rule, from 2 to 4 grams of the product are used. The cream should be applied to the skin at the site of pain projection and rubbed gently. During the day, the procedure is repeated 3-4 times.
To enhance the effect, the gel can be used with tablets, suppositories or injections of medication.
Diclofenac ointment: instructions for use
The ointment is taken in the same quantity as the gel and rubbed into the skin over the inflammation in the same way. The maximum dose is 8 g/day. Frequency of use: 2-3 times/day.
Diclofenac tablets: instructions for use
Diclofenac tablets (Acri, UBF, Stada, Sandoz, etc.) are taken orally with food or after meals (without chewing or crushing). Adults should take 50 to 150 mg/day. in 2-3 doses.
Diclofenac: how to take retard tablets?
Diclofenac retard is taken 100 mg once a day.
If after taking 100 mg of Diclofenac the desired effect is not achieved, you can additionally take 1 tablet of 50 mg (usual duration of action).
Diclofenac suppositories: instructions for use
The starting dose for an adult is 50-150 mg/day, depending on the indications. In this case, the patient should receive no more than 150 mg of diclofenac sodium in total during the day. The daily dose should be divided into 2-3 doses.
For children 6-15 years old, the dose is selected at the rate of 0.5-2 mg/kg/day. For rheumatoid arthritis, the highest daily dose may be 3 mg/kg.
Instructions for eye drops
Before surgery, the patient is administered 1 drop of solution 5 times every 30-35 minutes. After surgery - 3 times, 1 drop. In the future, treatment is continued, instilling 3-5 rubles/day. 1 drop each. The duration of treatment depends on the characteristics of the clinical situation.
Additionally
The regimen for using drugs from different manufacturers is the same: that is, there is no difference in how to use Diclofenac-Acri and, for example, Diclofenac Stada .
Special instructions for the use of Diclofenac
Prescribed with caution to persons with dyspeptic symptoms, diseases of the digestive tract, hypertension (arterial hypertension) or circulatory failure, renal failure, as well as patients who have recently undergone surgery. Throughout the course of treatment, it is recommended to monitor renal and liver function. When taking diclofenac for a long time, you should refrain from driving vehicles and performing potentially dangerous activities that require increased attention and speed of reactions. Taking diclofenac during pregnancy is contraindicated. During breastfeeding, it can be prescribed only according to strict indications and under close medical supervision.
Overdose
An overdose can cause central nervous system disorders and digestive disorders. The first ones most often manifest themselves:
- dizziness and headaches;
- increased excitability;
- clouding of consciousness;
- phenomena of hyperventilation with increased convulsive readiness.
Disorders of the digestive system are manifested by: nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding.
In severe poisoning, liver damage, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and hypotension are possible.
The drug does not have an antidote. Special measures, such as hemoperfusion , dialysis or forced diuresis , do not guarantee the removal of the drug due to its almost complete binding to plasma proteins and intensive metabolism.
Due to the low systemic absorption of the gel/ointment, overdose is considered unlikely. Accidental ingestion of the gel or ointment may cause systemic adverse reactions.
The patient is prescribed gastric lavage, vomiting is stimulated, and an enterosorbent . Therapy is symptomatic.
Interaction
Simultaneous use with:
- lithium preparations , phenytoin or digoxin - helps to increase the plasma concentration of these drugs;
- antihypertensive drugs and diuretics - reduces the effectiveness of these drugs;
- potassium-sparing diuretics - leads to hyperkalemia ;
- GCS or other NSAIDs - causes adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract;
- acetylsalicylic acid - helps reduce the serum concentration of diclofenac;
- cyclosporine - increases the nephrotoxic effect of the latter;
- antidiabetic drugs - can provoke hyper- or hypoglycemia ;
- methotrexate - can lead to increased concentrations and increased toxicity of the latter;
- anticoagulants - requires regular monitoring of hemocoagulation .
If indicated, eye drops can be combined with other ophthalmic agents that contain corticosteroids (at least a 5-minute break must be maintained between instillations).
Drug interactions Diclofenac
It should not be used simultaneously with other NSAIDs (including salicylates and pyrazolone drugs), since with such a combination there is a risk of mutual potentiation of toxic effects and a decrease in the effectiveness of one of the drugs. When used simultaneously with anticoagulants, the risk of developing hemorrhagic complications increases significantly. When combined with lithium salts, diclofenac may increase the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma. Co-administration of digoxin with diclofenac after 48–72 hours can lead to a significant increase in the concentration of the glycoside in the blood plasma; after stopping taking diclofenac, digoxin levels return to normal after 48 hours. Diclofenac causes sodium and fluid retention in the body, reducing the effectiveness of antihypertensive and diuretic drugs. When combined with diuretics, potassium levels should be monitored. It is not advisable to prescribe simultaneously with cyclosporines. GCS may potentiate the toxic effects of diclofenac. For patients taking methotrexate, diclofenac is prescribed 24 hours before or after taking methotrexate, since the plasma concentration and toxicity of the latter may increase.
Diclofenac analogues: what can replace injections and tablets?
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Voltaren Emulgel
Ultrafastin
Indomethacin
Dicloran
Dicloran Plus
Dolgit
Nise
Ketonal
Ketorol
Febrofeed
Fastum gel
Finalgel
Bystrumgel
Deep Relief
Butadion
Diklovit
Artrosilene
Olfen
Fanigan Fast
Diclofenac tablets can be replaced with tablets Bioran , Voltaren , Diclak , Diclogen , Adolor . These similar drugs are also available in ampoules.
Diclofenac-Acri ointment and Diclofenac-Acri retard ; capsules, solution, tablets and ointment Diclofenac Sodium; Voltaren transdermal patch , Diclobene , Diclofenac-Ratiopharm , Dorosan , Ortofen , Diclofenac-AKOS , Ortofer , SwissJet , Diclak Lipogel .
Analogues of Diclofenac (drugs similar in their mechanism of action, which belong to the same pharmaceutical group with it): Artrosilene , Aceclofenac , Deep Relief , Ibuprofen , Ibalgin , Indomethacin , Nise , Nimulid , Nurofen , Finalgel , Ketonal , Piroxicam- , Ketorol , Fastum gel , Revmonn , Keplat , Ketanov , Meloxicam , Movalis .
Diclofenac (eye drops) has the following analogues: synonyms - Voltaren Ofta , Diklo-F , Diclofenaclong , Uniclofen ; drugs similar in their mechanism of action are Indocollir , Acular LS, Nevanac , Ketadrop , Broxinac .
What is better - ointment or gel? Why is the gel prescribed and what is the ointment for?
The basic basis of the ointment is fat, the gel is water, so the ointment is a more viscous substance compared to the gel. It absorbs more slowly and in some cases can cause clogged pores.
The gel quickly spreads and dries on the skin, forming a thin protective film and leaving no stains on clothes. It simultaneously supplies moisture and dries.
Due to the presence of fat in its composition, the ointment has a predominantly softening and moisturizing effect. Because of this, ointments are used mainly to treat irritated and flaky skin. The gel is more effective for the deeper layers of the skin and joints.
Voltaren or Diclofenac - which is better?
Voltaren is an imported (and therefore more expensive) generic version of the drug. That is, there is no significant difference in the action of these funds.
Voltaren is distinguished only by the fact that when applied externally, it is more quickly absorbed into tissues and penetrates into the site of inflammation, and when taken orally, it retains the concentration necessary to relieve pain and inflammation longer.
Which is better: Movalis or Diclofenac?
The active ingredient of Movalis , meloxicam (a derivative of ethanol acid), like diclofenac sodium, belongs to the group of NSAIDs. Diclofenac non-selectively inhibits the activity of the COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, while meloxicam exhibits selectivity for COX-2.
Suppression of COX-2 ensures the therapeutic effectiveness of NSAIDs, suppression of COX-1 can provoke adverse reactions from the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract.
Thus, if we talk about the effectiveness of the drugs, they have proven themselves to be approximately the same. Comparing which is better - diclofenac or meloxicam - in terms of the frequency of side effects, we can conclude that Movalis ( meloxicam ) is better tolerated by patients.
In addition, unlike its analogue, meloxicam has a stimulating effect on the metabolism of cartilage tissue.
Which is better: Diclofenac or Ibuprofen?
Ibuprofen- based drugs indiscriminately suppress COX. That is, having the same indications for use and contraindications, they also provoke the same side effects.
However, unlike its analogue, Ibuprofen is somewhat better tolerated by children and pregnant women, which makes it possible to use it (albeit with caution) in pediatrics and obstetrics and gynecology practice.
Ketonal or Diclofenac - which is better?
Ketonal belongs to the group of drugs called ketoprofen , a substance that has a strong analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. Ketonal is ten times more effective than ibuprofen , which makes its use advisable for the treatment of spinal injuries and osteochondrosis .
Non-selectively suppressing COX, it quickly causes adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract, even when used externally.
What is better - Diclofenac or Ketorol?
Ketorol is a non-selective COX inhibitor. According to doctors, the effectiveness of Ketorol is higher than the effectiveness of Diclofenac tablets, and the effectiveness of the injection solution is comparable. Moreover, with comparable analgesic effectiveness, the duration of action of Ketorol is twice as long as that of its analogue.
Diclofenac (more often in injections than in tablets) more often than Ketorol caused adverse reactions - mainly from the gastrointestinal tract. They were regarded by the physician as minor and doubtfully related to therapy, and did not require discontinuation of treatment.
Which is better: Diclofenac or Ortofen?
The drugs Diclofenac and Ortofen have no fundamental differences, since they are based on the same active substance.
Which is better: Diclofenac or Diclofenac Retard?
Retard tablets are used to treat chronic rheumatic pain . Regular tablets are used to relieve acute pain. Thus, the choice of dosage form is completely determined by the indications for use.
Aceclofenac and Diclofenac - the difference
Aceclofenac is a derivative of phenylacetylic acid.
It is distinguished by its high bioavailability and high rate of reaching peak concentration in the blood (1-3 hours), the ability to be completely metabolized into pharmacologically active products (one of which, by the way, is diclofenac).
In addition to the main effect, Aceclofenac suppresses the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor, which are the most important pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Today this drug is considered one of the best. Its advantages:
- availability;
- high quality;
- a balanced combination of anti-inflammatory and analgesic effectiveness with
- well tolerated.
The place of diclofenac in the treatment of acute pain
Pharmacodynamic properties The anti-pain effect of diclofenac is primarily due to the suppression of cyclooxygenase (COX), an enzyme that regulates the conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins, which are mediators of inflammation, pain and fever [1]. Diclofenac inhibits both COX isoenzymes, mostly COX-2 (Fig. 1). Compared to ibuprofen and naproxen, it has less effect on COX-1, and therefore is less likely to cause damage to the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). At the same time, inhibition of COX-1 (although less pronounced than that of non-selective NSAIDs) may explain the greater effectiveness of diclofenac compared to selective COX-2 inhibitors (meloxicam, celecoxib) in a situation where COX-1 is also involved in the pathogenesis of the disease. The effect on COX-2 of diclofenac is less than that of etoricoxib and rofecoxib, which reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications [2]. Thus, diclofenac has a balanced effect on COX-1 and COX-2. Apparently, in addition to the effect on COX synthesis, the analgesic effect of diclofenac is due to other mechanisms - activation of several types of potassium channels, occurring with the participation of NO and cyclo-GMP at the peripheral level [3,4] and effects on opioid receptors through the influence on tryptophan metabolism at the central level [5,6]. Pharmacokinetic properties and dosage forms Injectable forms of diclofenac are of great interest for the treatment of acute pain. When administered intramuscularly, the analgesic effect of diclofenac occurs within 15–30 minutes. For this reason, injectable forms of diclofenac are well suited for the treatment of acute pain. As a rule, 1 injection per day is prescribed, however, in severe cases, 75 mg of diclofencac can be administered twice at intervals of several hours, changing sides of administration. The duration of parenteral use should not exceed 2 days; if necessary, continue treatment, use tablets or rectal suppositories. In practice, a significant problem limiting the intramuscular use of diclofenac is the pain of the injection itself. A recent study showed a simple way to make intramuscular injection of diclofenac less painful - as it turns out, it is enough to change the needle to a new one immediately before the injection. Pain during injection appears to be largely due to the fact that while the nurse is drawing diclofenac from the ampoule, the needle becomes dull and becomes coated with drug particles [7]. Of the oral forms of diclofenac, capsules with accelerated absorption from the gastrointestinal tract are of interest for the treatment of acute pain. However, along with the rapid onset of the effect, they are distinguished by its short duration. Double action capsules - fast and prolonged - do not have this drawback. These include the generic drug Naklofen® Duo (KRKA). One capsule of Naklofen® Duo contains two types of pellets (Fig. 2): • enteric pellets (25 mg diclofenac); • • modified release pellets (50 mg diclofenac). The maximum concentration of diclofenac in plasma is achieved after 30–60 minutes. after taking the Naklofen Duo capsule. The therapeutic concentration is maintained twice as long as when using enteric-coated tablets. In cases where oral administration of the drug is possible, Naklofen Duo can be a good alternative to parenteral analgesics. If enteral administration of drugs is contraindicated (after operations on the gastrointestinal tract, with vomiting), rectal administration of diclofenac is possible. The maximum concentration when administering diclofenac by the rectal route is achieved after 1 hour. It is important that the pharmacokinetic parameters change little in the presence of renal or hepatic failure. In mild renal impairment, the half-life remains unchanged. When creatinine clearance decreases to less than 10 ml/min. the time of elimination of metabolites increases, but no significant increase in their level in the blood is observed. In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated liver cirrhosis, pharmacokinetic parameters do not change. There are no changes in the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac following repeated administration. Thus, diclofenac is characterized by stable pharmacokinetic parameters, which makes the effect of the drug predictable. Safety The balanced effect of diclofenac on COX-1 and COX-2 results in a favorable safety profile: a relatively low risk of both ulcerogenic effects and cardiovascular events. Pharmacokinetic features make it possible to use diclofenac for mild renal and liver failure. It has been shown that diclofenac does not have side effects atypical for NSAIDs (such as erythema multiforme with piroxicam) [8]. As a result, the use of diclofenac is possible in most clinical situations. There are the following contraindications to the use of the drug: • hypersensitivity to diclofenac; • complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs (including a history); • the period after aorto-coronary bypass surgery; • erosive and ulcerative changes in the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum, active gastrointestinal bleeding; • inflammatory bowel diseases in the acute phase; • cerebrovascular bleeding or other bleeding and hemostasis disorders; • severe liver failure or active liver disease; • severe renal failure (creatinine Cl less than 30 ml/min.), incl. confirmed hyperkalemia, progressive kidney disease; • decompensated heart failure; • inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis; • III trimester of pregnancy, breastfeeding period [9]. Pharmacoeconomic aspects Thanks to the availability of generics, diclofenac is an affordable drug for the treatment of pain. For example, in pharmacies in Moscow, 5 ampoules of Naklofen (75 mg) cost about 50 rubles, 20 capsules of Naklofen® Duo (75 mg) - 130 rubles, Naklofen rectal suppositories (50 mg) - 60 rubles. [10]. As a result, treatment with diclofenac is available to patients regardless of their income. Research results Use of diclofenac for postoperative pain Diclofenac has been successfully used for the treatment of postoperative pain in various areas of surgery: after laparoscopic operations [11], cesarean section [12,14], plastic surgeries [15], orthopedic interventions [16], maxillofacial surgery and dentistry [17,18], in urology [19]. The results of these studies [11–19] indicate that diclofenac can reduce the intensity of postoperative pain and reduce the need for narcotic analgesics. Of particular interest is the use of a combination of analgesic and pronounced anti-inflammatory effects of diclofenac. Thus, MC Buyukkurt [17] compared the effect of a single injection of prednisolone in combination with or without diclofenac on the severity of pain, swelling and trismus after extraction of third molars. The researchers randomized 45 patients into 3 groups: in the 1st group, 25 mg of prednisolone was administered intramuscularly immediately after the intervention, in the 2nd group - 25 mg prednisolone and 75 diclofenac, in the 3rd group - placebo (0.9% sodium chloride solution). In the prednisolone and prednisolone-diclofenac combination group, the intensity of pain and swelling 6 hours after the intervention decreased compared to placebo. Moreover, in the group in which diclofenac was used, on the 2nd and 7th days after surgery, the restriction of movements of the lower jaw was less pronounced than in the placebo group and in the prednisolone alone group. Diclofenac has been successfully used in the treatment of postoperative pain in children. A recent meta-analysis summarized data on the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac in this age group [20]. The authors recommend using single doses of 0.3 mg/kg parenteral, 0.5 mg/kg rectal, and 1 mg/kg oral administration in children aged 1–12 years. This dosage has a pharmacokinetic profile (area under the drug concentration curve in the blood) that is similar to 50 mg of diclofenac in an adult. Use of diclofenac for renal and hepatic colic Diclofenac is the most widely used NSAID for renal colic. This drug has become the standard against which the effectiveness of other drugs is compared. The intramuscular form of the drug is used, a single dose is 50 mg or 75 mg [21]. Data from experimental studies indicate that in renal colic, diclofenac not only relieves pain, but also promotes relaxation of the ureters: diclofenac has been shown to promote relaxation of the smooth muscles of the ureters. Compared with papaverine, diclofenac was 2 times more effective in terms of muscle relaxation [22]. For hepatic colic, diclofenac at a dose of 75 mg intramuscularly reduces the intensity of pain and the risk of developing acute cholecystitis [23]. The use of diclofenac for acute gynecological pain The use of diclofenac for acute pain associated with gynecological causes is justified due to the combined analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect of the drug. SJ Downing et al. showed that diclofenac reduces the sensitivity of fallopian tube cells to the effects of the inflammatory mediator histamine: the severity of the electrophysiological response and the intensity of muscle contraction decreases. It is noteworthy that other NSAIDs studied in this study (acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen, indomethacin and naproxen) did not have such a significant effect on fallopian tube reactivity [24]. Diclofenac is widely used for aldodysmenorrhea. Research results show that this drug can not only reduce pain intensity, but also improve exercise tolerance [25] and restore subjective and objective sleep quality [26] during the menstrual period. Conclusion Diclofenac is well-deservedly popular in the treatment of acute pain. The positive qualities of the drug include a balanced pharmacodynamic profile, which includes anti-inflammatory activity along with analgesic activity, the ability to achieve optimal pharmacokinetic characteristics due to the presence of various dosage forms, high safety and an affordable price. In addition, the great advantage of this drug is the long experience of its use - since 1974. Both therapeutic and possible side effects of diclofenac have been studied. Today we can say with confidence that, unlike newer drugs, it does not conceal unpleasant “surprises”. Over 37 years of clinical practice, diclofenac has been time-tested, and not only has not become obsolete, but has become a classic. This fact is worth a lot.
Literature 1. Kharkevich D.A. Pharmacology - M.: GEOTAR MEDICINE, 1999. - 664 pp. 2. Grosser T, Fries S, FitzGerald GA. Biological basis for the cardiovascular consequences of COX–2 inhibition: therapeutic challenges and opportunities. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:4–15. 3. Tonussi CR, Ferreira SH. Mechanism of diclofenac analgesia: direct blockade of inflammatory sensitization. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan 14;251(2–3):173–9. 4. Liu LY, Fei XW, Li ZM, Zhang ZH, Mei YA. Diclofenac, a nonsteroidal anti–inflammatory drug, activates the transient outward K+ current in rat cerebellar granule cells. Neuropharmacology. 2005 May;48(6):918–26. 5. Bjorkman RL, Hedner T, Hallman KM, Henning M, Hedner J. Localization of the central antinociceptive effects of diclofenac in the rat. Brain Res. 1992 Sep 11;590(1–2):66–73 6. Mahdy AM, Galley HF, Abdel–Wahed MA, el–Korny KF, Sheta SA, Webster NR. Differential modulation of interleukin–6 and interleukin–10 by diclofenac in patients undergoing major surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2002 Jun;88(6):797–802. 7. Aac E, Gune UY. Effect on pain of changing the needle prior to administering medicine intramuscularly: a randomized controlled trial. J AdvNurs. 2011 Mar;67(3):563–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365–2648.2010.05513.x. Epub 2010 Dec 28. 8. O'brien WM. Adverse reactions to nonsteroidal anti–inflammatory drugs. Diclofenac compared with other nonsteroidal anti–inflammatory drugs. Am J Med. 1986 Apr 28;80(4B):70–80. 9. Radar Directory. https://www.rlsnet.ru 10. https://aptekamos.ru 11. O'Hanlon JJ, Beers H, Huss BK, Milligan KR. A comparison of the effect of intramuscular diclofenac, ketorolac or piroxicam on postoperative pain following laparoscopy. Ulster Med J 1996 May;65(1):51–4. 12. Al-Waili NS. Efficacy and safety of repeated postoperative administration of intramuscular diclofenac sodium in the treatment of post-cesarean section pain: a double-blind study. Arch Med Res. 2001 Mar–Apr;32(2):148–54. 13. Bourlert A. Diclofenac intramuscular single dose to decrease pain in post operative Caesarean section: a double blind randomized controlled trial. J Med Assoc Thai. 2005 Jan;88(1):15–9. 14. Surakarn J, Tannirandorn Y. Intramuscular diclofenac for analgesia after cesarean delivery: a randomized controlled trial. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009 Jun;92(6):733–7. 15. Saray A, Buyukkocak U, Cinel I, Tellioglu AT, Oral U. Diclofenac and metamizol in postoperative analgesia in plastic surgery. ActaChirPlast. 2001;43(3):71–6. 16. Hynes D, McCarroll M, Hiesse–Provost O. Analgesic efficacy of parenteral paracetamol (propacetamol) and diclofenac in post-operative orthopedic pain. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006 Mar;50(3):374–81. 17. Buyukkurt MC, Gungormus M, Kaya O. The effect of a single dose prednisolone with and without diclofenac on pain, trismus, and swelling after removal of mandibular third molars. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006 Dec;64(12):1761–6. 18. Oncul AM, Cimen E, Kucukyavuz Z, Cambazolu M. Postoperative analgesia in orthognathic surgery patientsdiclofenac sodium or paracetamol? Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011 Mar;49(2):138–41. Epub 2010 Jul 10. 19. Kara C, Resorlu B, Cicekbilek I, Unsal A. Analgesic efficacy and safety of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs after transurethral resection of prostate. IntBraz J Urol. 2010 Jan–Feb;36(1):49–54. 20. Standing JF, Tibboel D, Korpela R, Olkkola KT. Diclofenac pharmacokinetic meta–analysis and dose recommendations for surgical pain in children aged 1–12 years. PaediatrAnaesth. 2011 Mar;21(3):316–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1460–9592.2010.03509.x. Epub 2011 Jan 30. 21. Renal colic in adults: NSAIDs and morphine are effective for pain relief. Prescrire Int. 2009 Oct;18(103):217–21. 22. Sivrikaya A, Celik OF, Sivrikaya N, Ozgur GK. The effect of diclofenac sodium and papaverine on isolated human ureteric smooth muscle. IntUrolNephrol. 2003;35(4):479–83. 23. Akriviadis EA, Hatzigavriel M, Kapnias D, Kirimlidis J, Markantas A, Garyfallos A. Treatment of biliary colic with diclofenac: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Gastroenterology. 1997 Jul;113(1):225–31 24. Downing SJ, Tay JI, Maguiness SD, Watson A, Leese HJ. Effect of inflammatory mediators on the physiology of the human Fallopian tube. Hum Fertil (Camb). 2002 May;5(2):54–60. 25. Chantler I, Mitchell D, Fuller A. Diclofenac potassium attenuates dysmenorrhea and restores exercise performance in women with primary dysmenorrhea. J Pain. 2009 Feb;10(2):191–200. Epub 2008 Nov 28. 26. Iacovides S, Avidon I, Bentley A, Baker FC. Diclofenac potassium restores objective and subjective measures of sleep quality in women with primary dysmenorrhea. Sleep. 2009 Aug 1;32(8):1019–26. 27. Warner et al. FASEB J. 2004,18: 790-804
Diclofenac with alcohol - compatible or not?
Diclofenac and alcohol are incompatible.
Consequences of alcohol with NSAIDs
Drinking alcohol during treatment with NSAIDs can cause:
- deterioration of liver function;
- reducing the effectiveness of the drug;
- development of unpredictable complications and adverse reactions;
- hypertension and, as a consequence, increased congestion in the circulatory system and intoxication of the body.
Injections and alcohol are not compatible, since the injection form of the drug stimulates the activity of the central nervous system, and alcohol, on the contrary, inhibits it. As a result, quite serious neurological disorders are possible.
Diclofenac during pregnancy and breastfeeding
All dosage forms during pregnancy are used in exceptional cases, taking into account the benefit/risk ratio.
Like other NSAIDs, in the 3rd trimester the drug can cause a lack of uterine contraction in a woman in labor and/or premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in a newborn.
The medicine can penetrate not only into milk, but also through the placental barrier, even when using dosage forms for external therapy. Thus, even the use of gel and ointment during pregnancy can disrupt the development of the fetus.
The drug affects fertility, so it is not recommended for women who are planning a pregnancy, as well as for women who have problems with fertilization.
Reviews of Diclofenac
Diclofenac is an effective and affordable remedy that can quickly cope with pain and inflammation.
Reviews about the gel, as well as reviews about Diclofenac ointment, are in most cases positive. The drug provides good pain relief for back pain, joint pain, sprains, and bruises. A big advantage of dosage forms for external use is their good tolerability.
If we analyze reviews of tablets and reviews of Diclofenac injections, we can conclude that at least 20% of patients develop quite serious complications during treatment. And this is the main disadvantage of the drug, despite its high anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity .
Reviews of Diclofenac suppositories (in particular, the use of suppositories in gynecology) also indicate that treatment may be accompanied by side effects. However, when used correctly and following the doctor’s recommendations regarding the dosage regimen, they can quickly achieve the desired result. Eye drops with diclofenac sodium have proven themselves no less well.
For a long time, the drug was considered the “gold standard” among other NSAIDs, but this fame was earned by the original drug, which was created by Ciba-Gaigi and is currently produced by the pharmaceutical corporation Novartis International AG.
Negatively on the reputation of a medicine that was considered not only effective. but also quite safe, due to the emergence of numerous generics, the main advantage of which is often their low cost.
Diclofenac price
The price of Diclofenac injections is 35-55 rubles. The price of Diclofenac ointment in Moscow is from 40 to 65 rubles. The price of Diclofenac in tablets is from 14 rubles. The price of suppositories with Diclofenac 100 mg No. 10 is 75-80 rubles. The price of Diclofenac gel is 39-120 rubles. Eye drops will cost approximately 37-40 rubles. A transdermal patch with diclofenac (Voltaren) costs from 140 rubles.
You can buy injections in Ukraine for 15-17 UAH (price for 5 ampoules). The cost of injections for package No. 10 is 28-30 UAH. How much the ointment and gel cost depends on the volume of the tube and the manufacturer. The price varies from 12 to 37 UAH. Candles cost 16-25 UAH. Drops with diclofenac (for example, the drug Diphtal) will cost approximately 45 UAH.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
LuxPharma* special offer
- Fanigan fast gel (Diclofenac Sodium) 100g
1590 RUR order
ZdravCity
- Diclofenac Retard Obolenskoye tablets p.p.o. intestinal 100 mg 20 pcs. JSC Obolenskoe farm. company
50 rub. order
- Diclofenac Renewal tab. with prolong. vysv. p/o captivity. 0.1g 20pcs JSC PFK Update
90 rub. order
- Diclofenac rectal suppositories 50 mg 10 pcs Tula Pharmaceutical Factory LLC
79 RUR order
- Diclofenac-Altpharm supp. rectal 100 mg No. 10Altfarm LLC
104 rub. order
- Diclofenac rectal suppositories 100 mg 10 pcs Tula Pharmaceutical Factory LLC
87 RUR order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Diclofenac retard tablets 100 mg No. 20 Hemofarm LLC
71 RUR order
- Diclofenac (supp. rect. 100 mg No. 10) DHF OJSC
54 RUR order
- Diclofenac-Akrikhin gel (tube 1% 40g) Akrikhin OJSC
148 RUR order
- Diclofenac ampoules 25mg/ml 3ml No. 5Hemofarm
49 RUR order
- Diclofenac gel (tube 5% 50g) Sintez (Kurgan) OJSC
RUB 176 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Diclofenac-Darnitsa 2.5% 3 ml No. 5 solution PrAT" Pharmaceutical company "Darnitsa", Ukraine
22 UAH. order - Diclofenac sodium 50 mg No. 10 tablets PAT "Khimpharmzavod" Chervona Zirka", Kharkov, Ukraine
4 UAH order
- Diclofenac sodium 0.05 g No. 30 tablets PAT "Khimpharmzavod" Chervona Zirka", Kharkov, Ukraine
10 UAH.order
- Diclofenac sodium 2.5% 3 ml N10 PAT "Lubnipharm", Ukraine
26 UAH order
- Diclofenac sodium KV 0.025g N30 capsules PAT "Kiev Vitamin Plant", Kiev, Ukraine
12 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Diclofenac gel Diclofenac gel 1% tube 40g Ukraine, Red Star JSC
15 UAH order
- Diclofenac tablets Diclofenac tablets. p/o 25 mg No. 30 Ukraine, Darnitsa ChAO
11 UAH order
- Diclofenac gel Diclofenac forte gel 3% 50g Ukraine, Zdorovye LLC
51 UAH order
- Diclofenac ampoule Diclofenac sodium solution d/in. 25mg/ml 3ml No.5 Ukraine, Lekhim-Kharkov JSC
17 UAH order
- Diclofenac gel Diclofenac gel 1% 40g Ukraine, Farmak OJSC
20 UAH order
show more