Characteristics of the drug
Heparin is a drug that interferes with the formation of the high molecular weight protein fibrin in order to prevent the formation of blood clots in the coronary arteries. In addition, the action of the medication is aimed at stopping the growth of already formed fibrin clots and reducing the activity of blood clotting factors.
The drug for injection is available in bottles with a dosage of 5 ml
The administration of the drug in small quantities can slightly increase the properties of blood aimed at dissolving formed blood clots, and in large doses heparin causes a slowdown in the process of dissolving blood clots.
To reduce the risk of coronary heart disease and restore the normal balance of the liquid part and formed elements of the blood, doctors prescribe Heparin injections. The treatment regimen and dose of the administered drug are selected individually, since the drug can accumulate on the inner surface of blood vessels, which leads to an increase in the negative charge of blood cells. Due to this, surface adhesion decreases and platelet gluing process is inhibited.
Patient reviews
Antonina, Saransk “After suffering a myocardial infarction, my father was prescribed a course of treatment with Heparin injections. As the doctor said, this was necessary to prevent a second attack. Fortunately, the therapy went without complications, now dad is home and feeling well.”
Valery, Tambov “I have been using heparin-based ointment for a very long time. This drug helps me get rid of the discomfort of hemorrhoids, relieves pain and inflammation. Of course, I know that the medicine should be taken as prescribed by the doctor, but I don’t always have time to visit the hospital. There were no side effects associated with the use of the ointment.”
Elena, Khimki “I am a doctor and I know that anticoagulant drugs, which include Heparin, often provoke undesirable consequences. I use the product myself only when necessary. I suffer from varicose veins, so antithrombotic therapy is necessary for me. Once a year I undergo treatment with injections, and during exacerbations of the disease I use ointment. The medicine helps well.”
Pharmacological properties
Most patients have a question: why is it necessary to prescribe Heparin injections? The drug is used in the form of a solution for injection, as this promotes rapid penetration of the active substance into the bloodstream and instantly slows down the process of coagulation of biological fluid.
The drug causes a moderate vasodilator effect
The drug exhibits the following effects in the body:
- increases renal blood supply;
- increases the tone of cerebral vessels;
- slows down enzymatic activity of the brain;
- reduces the rate of excess aldosterone synthesis in the adrenal glands;
- promotes the activation of parathyroid hormone;
- controls the level of adrenaline in the blood.
In complex therapy for patients diagnosed with coronary insufficiency, administration of the solution helps prevent the development of the following pathologies:
- acute thrombosis of coronary vessels;
- reducing the number of relapses of myocardial infarction;
- reduction in the number of deaths after coronary heart disease.
A low dosage of the drug is used to prevent the formation of blood clots inside blood vessels and in patients after surgery. Large doses of the drug are intended for the treatment of pulmonary arterial thromboembolism or venous blockage.
Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacological effect of the described drug lies primarily in the process of inhibiting the formation of fibrin. When Heparin is administered intravenously, the following effect is achieved:
- increased renal blood flow;
- increasing the resistance of cerebral vessels;
- decreased surfactant activity in lung tissues;
- decreased production of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex;
- preventing the formation of blood clots in the arteries;
- prevention of primary and recurrent myocardial infarctions;
- prevention of cases of sudden death of the patient.
The effect of the drug when used as an injection occurs quite quickly
The use of Heparin in the form of an ointment or gel makes it possible to relieve the inflammatory process in the affected areas and achieve resorption of blood clots and skin hematomas. As a result, existing blood clots dissolve, and new ones do not form. The mechanism of action of Heparin when used topically is to inhibit thrombin synthesis, reduce platelet aggregation, and suppress hyaluronidase activity.
Important! Both forms of release of the drug have their own indications for use and contraindications. The decision to prescribe this or that drug is made solely by the doctor.
Indications for use
Patients with impaired blood clotting function are recommended to undergo a course of Heparin injections. The drug has a broad pharmacological effect, so in medicine it is used not only as an anticoagulant.
To prevent blood clotting, the drug is used during the hemodialysis procedure.
Administration of the solution is indicated in the presence of the following conditions:
- progressive form of angina;
- IHD in the acute phase;
- prevention and treatment of thrombosis of various origins;
- after operations related to pathology of the heart and blood vessels;
- pathology of the valve apparatus;
- inflammation of the heart valves;
- blockage of the renal vein by a thrombus;
- inflammatory kidney diseases;
- bronchial asthma;
- systemic inflammatory conditions;
- cleaning of venous catheters.
Good results are obtained by using the solution for prophylactic purposes, in case of clot formation in the lumen of peripheral arteries and after surgery in the heart area.
Use in pediatrics
Heparin for children in various release forms is prescribed by the attending physician if there are indications for use. Injections are often used to prevent blood clots after surgery. There are no age restrictions, but before reaching 3 years of age, injections are prescribed only if necessary.
The drug in the form of an ointment is prescribed to children from one year of age, despite the fact that the instructions prohibit the use of the drug under 3 years of age. If you are prone to bleeding or are at risk of developing it, Heparin is contraindicated in children.
Duration of pharmacological effect
If the solution is administered by intradermal injection into the abdominal area, the patient should know that they must be done frequently, since the pharmacological effect occurs quickly and its duration is short-lived. When the drug is administered intravenously, an almost instantaneous inhibition of blood clotting is observed, while its effect lasts up to 5 hours.
To prevent the formation of fibrin clots, the duration of action of the drug increases slightly
After an injection into the muscle, the therapeutic effect occurs after 30 minutes and lasts for 6 hours. The effect of intradermal administration occurs within 40 minutes and lasts up to 8 hours.
Methods of administration
Complex therapy of acute venous and arterial thrombosis involves continuous intravenous drip administration of Heparin solution for several days. If there are possible contraindications to intravenous infusion, the drug must be administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
The optimal route for administering Heparin is considered to be the abdominal wall.
After surgery or directly during the operation, the solution is injected into the artery or intravenously. Then, during the first days after surgery, the administration of Heparin is continued intravenously.
In ophthalmology, in case of acute blockage of the vessels of the retina or dystrophic changes inside its membrane, the drug is administered intravenously, and then intramuscular injections are used.
Heparin solution for intravenous and subcutaneous administration 5000 IU/ml 5 ml bottles 5 pcs. in Moscow
For medicinal purposes
Heparin is prescribed as a continuous intravenous infusion or as regular intravenous injections, as well as subcutaneously (in the abdomen).
For preventive purposes
— subcutaneously, 5000 IU/day, at intervals of 8–12 hours. The usual place for subcutaneous injections is the anterolateral abdominal wall (in exceptional cases, it is injected into the upper region of the shoulder or thigh), using a thin needle, which should be inserted deeply, perpendicularly , into a fold of skin, held between the thumb and index finger until the solution is injected. The injection sites should be alternated each time (to avoid the formation of a hematoma). The first injection must be performed 1–2 hours before the start of surgery; in the postoperative period - administered for 7-10 days, and if necessary - for a longer time.
The initial dose of heparin administered for therapeutic purposes is usually 5000 IU and is administered intravenously, after which treatment is continued using subcutaneous injections or intravenous infusions.
Maintenance doses are determined depending on the route of administration:
- for continuous intravenous infusion, 1000–2000 IU/hour (24000–48000 IU/day) is prescribed, diluting heparin with 0.9% sodium chloride solution;
- with regular intravenous injections, 5000–10000 IU of heparin is prescribed every 4–6 hours;
- for subcutaneous administration, 15,000–20,000 IU is administered every 12 hours or 8,000–10,000 IU every 8 hours.
Intravenous injections are recommended only for initial doses or if for some reason intravenous infusion or subcutaneous administration cannot be used. Repeated intravenous injections cause significant fluctuations in hemostasis and more often cause dangerous bleeding, so they are prescribed only when absolutely necessary.
For adults with thrombosis of mild to moderate severity, it is administered intravenously, 40,000–50,000 IU/day for 3–4 administrations; for severe thrombosis and embolism - 20,000 IU intravenously 4 times a day with an interval of 6 hours.
For health reasons, 25,000 IU is administered intravenously once, then 20,000 IU every 4 hours until a daily dose of 80,000–120,000 IU is reached. When administered intravenously, at least 40,000 IU is added to the daily volume of infusion solution.
The duration of heparin therapy depends on the indications and route of administration. For intravenous use, the optimal duration of treatment is 7–10 days, after which therapy is continued with oral anticoagulants (it is recommended to prescribe oral anticoagulants starting from the 1st day of heparin treatment or from 5 to 7 days, and stop the use of heparin on the 4–5 day of combination therapy) . In case of extensive thrombosis of the iliofemoral veins, it is advisable to carry out longer courses of treatment with heparin.
Laboratory monitoring of the effectiveness and safety of sodium heparin therapy
The dose of heparin sodium should be adjusted based on laboratory blood clotting parameters. When using heparin sodium, it is necessary to monitor the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) or blood clotting time (BCT). The dose of heparin sodium administered is considered adequate if the aPTT is 1.5 to 2.0 times the normal value or if the patient's ICR is 2.5 to 3.0 times the control value.
With continuous intravenous infusion of heparin sodium, it is recommended to determine the initial aPTT, then determine the aPTT every 4 hours, followed by increasing or decreasing the rate of infusion of heparin sodium until the target aPTT level is achieved (1.5-2 times normal), then determine the aPTT every 6 hours .
When bolus intravenous administration of heparin sodium is recommended, it is recommended to determine the initial aPTT, then determine the aPTT before each bolus, followed by an increase or decrease in the administered dose of heparin sodium.
When administering sodium heparin subcutaneously, it is recommended to monitor the aPTT 4–6 hours after injection, followed by an increase or decrease in the administered dose of sodium heparin.
When using sodium heparin in low doses to prevent thromboembolic complications, it is not necessary to monitor the aPTT.
Continuous intravenous infusion is the most effective way of using sodium heparin, better than regular (periodic) injections, because provides more stable hypocoagulation and is less likely to cause bleeding.
Use of heparin sodium in special clinical situations
Primary percutaneous coronary angioplasty for acute coronary syndrome without ST segment elevation and myocardial infarction with ST segment elevation: sodium heparin is administered intravenously as a bolus at a dose of 70–100 IU/kg (if the use of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitors is not planned) or at a dose of 50 –60 IU/kg (when used together with inhibitors of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors).
Thrombolytic therapy for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: sodium heparin is administered as an intravenous bolus at a dose of 60 IU/kg (maximum dose 4000 IU), followed by intravenous infusion at a dose of 12 IU/kg (not more than 1000 IU/hour) for 24– 48 hours. The target APTT level is 50–70 sec or 1.5–2.0 times higher than normal; APTT monitoring 3, 6, 12 and 24 hours after the start of therapy.
Prevention of thromboembolic complications after surgery using low doses of sodium heparin:
subcutaneously, deep into the fold of the skin of the abdomen. The initial dose is 5000 IU 2 hours before surgery. In the postoperative period: 5000 IU every 8–12 hours for 7 days or until the patient’s mobility is completely restored (whichever comes first). When using sodium heparin in low doses to prevent thromboembolic complications, it is not necessary to monitor the aPTT.
When preventing thrombus formation in the postoperative period, the first injection should be performed 1–2 hours before the start of surgery; in the postoperative period, administer for 7–10 days, and, if necessary, for a longer period.
Application in cardiovascular surgery during operations using extracorporeal circulatory systems:
the initial dose of sodium heparin is not less than 150 IU/kg body weight. Next, sodium heparin is administered by continuous intravenous infusion at a rate of 15–25 drops/min, 30,000 IU per 1 liter of infusion solution. The total dose of heparin sodium is usually 300 IU/kg body weight (if the expected duration of the operation is less than 60 minutes) or 400 IU/kg body weight (if the expected duration of the operation is 60 minutes or more).
Use in hemodialysis:
Initial dose of heparin sodium: 25–30 IU/kg (or 10,000 IU) intravenous bolus, then continuous infusion of heparin sodium 20,000 IU/100 mg sodium chloride solution at a rate of 1500–2000 IU/hour (unless otherwise indicated in the instructions for use of the systems for hemodialysis).
Application in pediatrics:
Adequate controlled studies of the use of heparin sodium in children have not been conducted. The recommendations presented are based on clinical experience.
Initial dose: 75–100 IU/kg IV bolus over 10 minutes.
Maintenance dose: children aged 1-3 months - 25-30 IU/kg/hour (800 IU/kg/day), children aged 4-12 months - 25-30 IU/kg/hour (700 IU/kg/day day), children over 1 year - 18–20 IU/kg/hour (500 IU/kg/day) intravenously.
The dose of heparin sodium should be adjusted based on coagulation parameters (target aPTT 60–85 seconds).
Switching to warfarin therapy: To ensure a sustained anticoagulant effect, therapy with heparin sodium at full dose should be continued until a stable target INR level is achieved. After this, the administration of sodium heparin must be stopped.
Switching to dabigatran therapy: Continuous intravenous heparin sodium should be discontinued immediately after the first dose of dabigatran. With divided intravenous administration, the patient should take the first dose of dabigatran orally 1–2 hours before the scheduled administration of the next dose of sodium heparin.
Features of dosage selection
The dose of the administered solution depends on the degree of thrombosis, the severity of symptoms and the individual sensitivity of the patient to the drug. In patients, it is necessary to constantly monitor coagulogram parameters, since if the dose is incorrectly selected, the blood clotting period can significantly exceed the norm, which can lead to bleeding.
Before discontinuing the drug, the daily dosage must be reduced so that there is no increase in the intervals between injections
According to the instructions for use, the dosage of the drug is prescribed depending on the route of administration:
- Intravenous drip infusions. The daily dosage is selected at the rate of 400 U/kg.
- Intramuscular and subcutaneous injections. The dose of the solution should not exceed 600 units/kg per day.
- Intravenous administration. Single dose – 100 units/kg.
After completing the course of Heparin therapy, anticoagulant treatment with indirect-acting drugs is prescribed, the administration of which begins one day before the first reduction in the dose of the active substance.
Release form and composition of the drug
The medicine Heparin is produced in several dosage forms. These include:
- Heparin solution;
- ointment;
- gel.
Heparin injection solution has a clear or light yellowish tint, odorless, and is available in ampoules of 5 and 10 pieces in a cardboard box.
The ointment is packaged in aluminum tubes of 10 or 25 g. Each of which is placed in a cardboard package, including an insert with instructions for use.
The gel is produced in tubes with different dosages, packaged in 15, 20, 30, 50 and 100 g. Each package contains an annotation on the use of the drug.
The drug Heparin includes the main active ingredient - heparin and auxiliary components.
Use of the product during pregnancy
During pregnancy, women's blood viscosity may change. An increase in the number of platelets leads to increased coagulability of biological fluid. According to statistics, 10% of pregnant women are susceptible to homeostatic disorders. Therefore, some doctors prescribe Heparin during pregnancy, when the therapeutic effect of the drug is higher than the possible side effects.
Long-term use of heparin may increase a pregnant mother's risk of bleeding
According to clinical studies, the drug does not penetrate the transplacental barrier, which means it does not pose a threat to the fetus. The treatment regimen for a pregnant woman is somewhat different, for example, the calculation of the dose of the injected solution depends on the woman’s weight category, and the frequency of injections is limited to two.
The use of Heparin should be carried out under the strict supervision of specialists, since spontaneous labor may develop. In case of long-term treatment, it is recommended to take a blood test for coagulation once every two days, and with heparin therapy for more than 7 days, the test is taken once every 3 days.
The use of the medication may interfere with the distribution of calcium in the body. Thus, a pregnant woman may experience acute calcium deficiency, so along with the use of Heparin, supplements containing all the necessary microelements should be taken.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the use of Heparin are determined depending on the form of production of the drug.
Medicine in injections is prohibited for patients with the following conditions:
- the body's sensitivity to the active components of the drug;
- diseases characterized by a tendency to bleeding;
- pathological aortic dissection;
- intracranial aneurysm;
- suffering from traumatic brain injury;
- hemorrhagic strokes;
- arterial hypertension not amenable to drug control;
- acute liver and kidney diseases;
- menstruation period;
- threat of premature birth or miscarriage;
- recent birth, lactation;
- ulcerative lesions of the stomach and intestines.
If you are prone to bleeding, the drug is contraindicated
Contraindications for Heparin in the form of ointment and gel are individual intolerance to the active component, conditions accompanied by disruption of the process of normal blood clotting, postoperative sutures and open wounds on the body, ulcerative lesions.
Important! During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the use of Heparin gel or ointment is allowed only as prescribed by a doctor under his close supervision.
Special Recommendations
Heparin therapy is carried out under strict control of hemocoagulation parameters. A coagulogram is carried out in the first week of treatment with the drug and immediately after surgery, the optimal number of studies is 1 time every 2-3 days. With fractional administration of the solution, a blood test is done immediately before the injection.
It is not recommended to abruptly interrupt the course of treatment with Heparin, as this may lead to the initiation of thrombus formation. Therefore, it is necessary to gradually reduce the dosage of the drug with the parallel use of indirect anticoagulants. The only exceptions are cases of individual intolerance to some components of the solution.
Despite the possibility of intramuscular injection of the solution, experts do not recommend it due to the fact that bruises form at the injection site.
Solution dosage
For various conditions, the drug is used in the form of intramuscular injections or intravenous administration. In this case, a clear technique algorithm is used, adherence to which helps to achieve the maximum therapeutic effect and prevent negative consequences. Usually the interval between injections is at least 8 hours, but no more than 12.
The medical worker must strictly observe the dosage of the administered drug. Violation of instructions provokes a lack of effect or an overdose.
When treating thrombosis, it is recommended to administer 5 thousand units to the patient. In particularly severe conditions, the doctor may increase the dosage to 10 thousand units. As an alternative therapy, the patient is prescribed 15 thousand units every 12 hours.
In medical practice, Heparin is diluted in 1000 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution. It is not recommended to inject into the same place, which is associated with the development of local reactions on the skin after the injection. Compliance with the administration technique ensures a minimum amount of dermal irritation and side effects.
Important! Heparin is diluted exclusively with saline solution. Self-administration of injections is dangerous for the health and life of the patient.
Algorithm for the correct administration of Heparin
Injections of the drug are carried out strictly as prescribed by a specialist. Injections of the drug are made at a strictly defined time of day, so patients often practice self-injections of the solution into the abdominal area. This route of administration is considered the most convenient at home.
Insulin syringes are used for injections, since a thin needle causes minimal pain.
Algorithm for how to give injections in the abdominal area:
- Perform hand hygiene using soap and antiseptic.
- Before manipulation, prepare a bottle of solution, a syringe, sterile cotton wool, and alcohol.
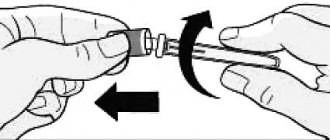
- Using a special nail file, open the bottle and collect the required amount of solution.
- Disinfect the injection site. Use your thumb and forefinger to form a fold of skin on your abdomen.
- Insert a needle into the fold formed, press the plunger and slowly inject the medicine.
- Remove the needle and apply cotton wool to the injection site.
Features of treatment
It is advisable to use heparin intravenously for a long time during hospital treatment.
The doctor must take into account the specifics of administering Heparin. Simultaneous intramuscular administration of other medications with Heparin solution is used extremely rarely, only if necessary.
If the effect of Heparin is absent when prescribing injections, it is important to monitor the level of antithrombin III in the patient’s blood.
Among people suffering from arterial hypertension, it is necessary to regularly monitor blood pressure.
The drug is prescribed with extreme caution among women who have intrauterine devices, with active tuberculosis, and during treatment with radiation therapy.
Among elderly patients, the dosage of the drug should be reduced, since standard doses of the drug increase the risk of bleeding.
The ointment or gel should not be applied to open wounds. Avoid contact of the product with the mucous membrane of the mouth, eyes, and genitals.
Side effects
If you follow the Heparin treatment regimen, the symptoms of the disease gradually decrease, but situations arise when taking the medicine causes side effects:
- allergic reaction;
- migraine headaches;
- osteoporosis;
- dysfunctions of the digestive tract;
- diarrhea;
- hyperthermia;
- skin rashes;
- bleeding;
- impaired renal function.
The most common complications of taking the medication are nausea and vomiting.
As a rule, side effects occur due to uncontrolled or prolonged use of the medication. To reduce the risk of negative effects, it is necessary to observe the dosage of the solution and adhere to the treatment regimen.
Side effects
Side effects of Heparin with proper use of the drug are quite rare, as evidenced by positive reviews from doctors and patients. Failure to follow the instructions for use may cause complications such as bleeding. More often, this consequence is diagnosed in people with impaired renal and liver function, among patients over 65 years of age.
Side effects from the use of the drug can be in the form of thrombocytopenia with vascular thromboembolism and hemorrhage. In most cases, this condition develops during drug therapy for 7 or more days.
The doctor is obliged to warn the patient about possible side effects
At the injection site, the patient may experience swelling, pain, and redness of the dermis. As a rule, after discontinuation of the drug, the negative consequences go away on their own and do not require special treatment.
What can be replaced
An analogue of Heparin is also a solution of a drug, but from a different production.
The following solution analogues exist:
- Sodium Brown.
- Richter.
- Frayn.
The use of these funds should be carried out after consultation with a specialist.
Thus, Heparin is a good drug for thinning the blood and preventing the development of blood clots inside blood vessels. However, during its use it is necessary to carefully monitor blood clotting parameters and follow the chosen therapeutic course.
Drug interactions
The therapeutic effect of the described medication is enhanced when combined with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antiplatelet agents. When used simultaneously with Tetracycline, antiallergic drugs, nicotine, the effect of Heparin is reduced.
When using the drug, its drug interactions must be taken into account.
Reviews
Ivan, 50 years old I had a myocardial infarction several years ago. This was followed by a long recovery period, during which I was prescribed daily Heparin injections. After the course of treatment, hemostasis indicators were restored, however, to prevent further thrombus formation, I periodically take injections of the drug.
Svetlana, 42 years old I have problems with blood clotting, it has become too thick. Against this background, I developed a thrombosis in my leg, which is why I have a severe limp when walking. The doctor ordered me to take Heparin injections in the stomach for 1 month. Thanks to this medication, everything went away, although bruises formed on my stomach during the course, but this is not so important.
Igor, 28 years old My mother was diagnosed with varicose veins in her lower extremities; a vessel was blocked in one of her legs, so she was prescribed surgical treatment. In the postoperative period, she was prescribed to undergo heparin treatment. The result is obvious, the condition of the veins has improved significantly. At the moment, the disease is not progressing; my mother periodically undergoes medication treatment, as this also serves as a good prevention of myocardial infarction.
Application of ointment and gel
Instructions for using Heparin in the form of an ointment imply local use of the product. The ointment is used to treat affected areas 2 to 4 times a day. The product should not be applied to open wounds and postoperative sutures.
When treating varicose veins, it is forbidden to rub the product in, as this can cause the inflammatory process to spread throughout the vein and cause a blood clot to break off.
Heparin ointment is applied in strict accordance with the instructions
To treat hematomas and abrasions, the ointment is applied throughout the day; usually longer treatment is not required.
For varicose veins in the anal area, the product is used for compresses.