Macular degeneration, or age-related macular degeneration (AMD), is a common name for several diseases of different nature that have the same damaging effect on the central part of the fundus of the eye, called the macula (macula).
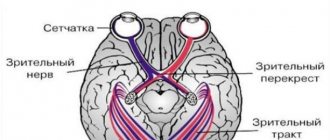
The inner shell of the eyeball consists of several layers of light-sensitive cells, which ensure the perception and transmission of light impulses from the eyeball along the conductive tract (optic nerve) to specialized parts of the brain for further decoding and transformation into the images we see.
The visual field is the totality of all visible objects that the eye perceives in a stationary position. There are central and peripheral vision, which differ in their tasks and characteristics. Both types of vision are extremely important and provide complete perception of information about the world around us.
Central, or object vision, is responsible for visual acuity and allows us to distinguish the size, color and shape of objects, and also provides the ability to distinguish small details of an image. It is thanks to central vision that a person is able to read and write, perform small tasks such as threading a needle or stringing beads, and can also recognize faces. The photoreceptors that provide central vision are located in an area of the retina called the fovea. This is a tiny depression located in the center of the macula, in its location it corresponds to the posterior pole of the eyeball. It is the macula that provides the greatest visual acuity.
Why does macular degeneration develop?
The trigger point for the development of macular degeneration is changes in the retinal vessels, which are responsible for the normal supply of nutrients to the retinal cells. If the delivery of nutrients to the retinal tissues is disrupted, its cells begin to experience oxygen starvation, which triggers a cascade of pathological reactions here.
Among the main causes of AMD is age. Despite the fact that degenerative changes in the macula are also found in middle-aged patients, the main group of patients with AMD consists of people over the age of 60 years. Other factors contributing to the development of AMD are hereditary predisposition, overweight and obesity, and bad habits (smoking). The disease is statistically more often detected in women with white skin color.
Table of contents:
Symptoms of age-related macular degeneration Eye macular degeneration: treatment methods Contraindications Advantages of treatment at the Santa Clinic Age-related macular degeneration is one of the common diseases in patients over 50 years of age. The pathology is based on a malnutrition of the retina, in particular its central zone. One of the reasons for such changes is aging, but heredity also plays a significant role. To treat age-related macular degeneration, both traditional and surgical methods are used.
Classification of macular degeneration
There are several morphological types of the disease, each of which is characterized by its own course and prognosis.
"Dry" type of macular degeneration
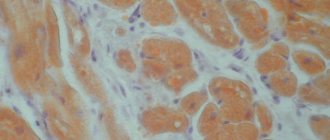
The “dry” form of AMD (also called the non-exudative form) is a prognostically favorable variant of the disease course, which is detected in approximately 90% of patients with age-related macular degeneration. It is characterized by progressive thinning and atrophy of the macular tissue, accompanied by the appearance of drusen - yellowish pigment deposits located under the retina. Drusen themselves are not dangerous and do not cause vision impairment, but they are a marker that age-related atrophic changes are occurring in the macula and the patient has a “dry” form of macular degeneration.
Eye damage in the “dry” form of AMD is often asymmetrical, but as the disease progresses, both eyes are gradually involved in the pathological process. Visual acuity may remain unchanged for a long time. During the non-exudative form of AMD, three stages are distinguished: early, intermediate and late.
At an early stage of the disease, a small number of small drusen are detected in the fundus. There are no signs of visual impairment. As the disease progresses, it enters an intermediate stage, which is characterized by the identification of multiple drusen, as well as atrophic changes in the retina. Some patients experience a central vision defect that appears as a blurry spot, as well as poor vision in low-light conditions. At a late stage, in patients with a non-exudative form of AMD, destruction of macular tissue can be detected, and therefore the spot in the field of vision becomes darker and acquires significant dimensions. The leading complaint at this stage of the disease is distinct difficulties with recognizing faces, reading, writing, that is, with everything that requires good central vision.
"Wet" type of macular degeneration
The “wet” form of AMD (synonyms exudative or neovascular macular degeneration) is diagnosed in approximately 10% of patients with age-related macular degeneration and has a serious prognosis. Exudative macular degeneration progresses rapidly and is accompanied by pronounced changes in the fundus and progressive deterioration of vision. Vision rapidly declines, never reaching complete blindness, since peripheral vision does not suffer and provides the patient with light perception and the ability to navigate in space.
The “wet” form is based on the process of pathological neovascularization. This variant of the course of the disease is characterized by the growth of fragile pathologically altered vessels under the retina. The growth of blood vessels is the body's attempt to provide better delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the macula. However, due to the fact that the newly formed vessels are functionally inferior, the expected improvement does not occur. On the contrary, these abnormal vessels are easily damaged, leading to hemorrhages and accumulation of fluid and blood in the space between the retina and the choroid. The outcome of such processes is the appearance of gross cicatricial changes in the area of the macula and a significant loss of central vision: the so-called absolute central scotoma is formed - a large opaque spot in the center of the visual field.
In some cases, the exudative form of AMD may have a hidden course, when the growth of new vessels under the retina is slow, and the processes of fluid leakage under the retina are weakly expressed. The prognosis in this case is more favorable compared to the classic course of the disease, which always leads to gross changes in retinal tissue and significant loss of vision.
Symptoms of AMD
As a rule, the patient simply does not notice the onset of the disease due to the absence of any “acute” vision problems. But, given that retinal dystrophy affects central and color vision, the standard sequence of disease development can be described as follows.
- First, the brightness and contrast of color perception are lost and visible lines are distorted, and the patient also lacks the illumination that was sufficient before.
- At the next stage, when reading and writing texts with the usual glasses, the Patient notices the loss of individual letters or entire words.
- Then there is a loss of visual acuity at near and far distances.
- Later, as the disease progresses, a spot appears in front of the eye, at first translucent, then completely opaque, sharply worsening vision, depriving the Patient of the ability to distinguish objects and people’s faces.
Age-related macular degeneration is a disease of a paired organ, the damage extends to both eyes. Most often, retinal dystrophy manifests itself and progresses more actively in one eye. The manifestation of the disease in the fellow eye may not occur immediately, even 5-8 years after the diagnosis of AMD. If the Patient does not undergo regular check-ups with an ophthalmologist, he himself may not immediately notice any vision problems that have arisen, since the better-seeing eye takes on the additional load.
How does age-related macular degeneration manifest?
None of the variants of the course of AMD are accompanied by any pain.
Without timely and complete treatment, progressive age-related macular degeneration leads to irreversible changes in the retina, manifested in the form of decreased visual acuity or blindness. To prevent vision deterioration, at the slightest suspicion of retinal damage, you should consult a doctor.
The “dry” form is characterized by complaints of blurred and blurred vision, which become more pronounced as an increasing percentage of the cells in the macula are destroyed. In an advanced stage, a dark spot appears in the center of the visual field, significantly impairing central vision.
An early manifestation of the “wet” form of AMD is distortion of the outlines of visible objects and curvature of straight lines. This symptom is easily determined by performing the Amsler test. The distortions are caused by fluid leaking under the retina, which accumulates in the area of the macula and lifts it. Such an uneven light-receiving zone creates curved outlines of visible objects.
Diagnosis of age-related macular degeneration
The examination begins with standard diagnostic procedures (determining visual acuity, examining the fundus, measuring the visual field). If characteristic changes are detected in the retina, an extensive vision examination is prescribed, including the diagnostic methods listed below.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT, OCT) allows non-invasively, that is, without penetrating into the eye cavity with the help of any instruments, to obtain intravital sections through the entire thickness of the retina and thus evaluate its structure. The method allows you to identify drusen, abnormal vessels, macular edema and other changes.
Fluorescein angiography (FA) helps to visualize altered retinal vessels and determine which treatment method will be most effective (laser coagulation, intravitreal injections, photodynamic therapy).
Perimetry is a technique that allows you to assess the state of the visual field. Since macular degeneration is characterized by damage to central vision, perimetry can identify areas of loss of visual fields (scotomas).
The Amsler test (grid) is a simple and informative method that allows you to identify a characteristic symptom of the “wet” form of macular degeneration - curvature of lines. The Amsler grid looks like thin intersecting horizontal and vertical lines. A patient with exudative AMD sees the lines in the drawing as uneven, broken, or pale. The larger the area of the macula involved in the pathological process, the more distorted the lines will appear when tested.
Indocyanine green angiography (ICGA) , like FA, requires intravenous administration of a contrast agent. After some time, a series of sequential photographs of the retina are taken in infrared light. This diagnostic procedure allows you to determine changes in the retina that are not detected by FA.
Review of retinal treatment at the Excimer Clinic
Sh. Svetlana, Moscow
Thank you for the prompt and high-quality work. Today we did a comprehensive examination and strengthened the retinas of both eyes. Many thanks to the doctor, a man of his profession (unfortunately I forgot to ask his last name) received me in room 307a. I was left with a pleasant impression;) After a while I will undergo vision correction. Thanks to all!
A. Alexander Isakovich, Moscow
I, Alexander Isakovich Alterman, am simply shocked by the attention and sensitivity of Dr. Kalashi Zurab Yusupovich and Irina Srgeevna Yusupova. I am a disabled person of the 2nd group, a labor veteran born in 1938.
Pilipchak Snezhana, Moscow
On Saturday (May 16, 2015) I had laser coagulation (strengthening the retina), done by Olga Aleksandrovna Plyukhova!! I express my deep gratitude to her for her HUMANITY, for her understanding and patience... it was a bit painful for me, but if you compare the coagulation 9 years ago , Olga Alexandrovna has golden hands!!!! Next Saturday, May 23, there will be laser correction, I'm terribly afraid)) And about the clinic. Before the consultation in Excimer, I had a consultation at the Moscow Eye Clinic (Moscow, m. Semenovskaya), earth and sky!!! At the MGK they did not find a retinal dehiscence during the examination and immediately recommended me to do a correction (and what would have happened to me???!!!!) I wonder!! Yes, Excimer is several times more expensive, but I’m not buying sausage, I’m buying good eyesight!! You can't regret it!!! Thanks everyone! I don’t understand where the bad reviews come from, everyone is so nice, the equipment is at the highest level, as is the qualifications of the nurses and doctors!
All reviews on the topic
Treatment of age-related macular degeneration
The “dry” form of AMD has no specific treatment. In the initial and intermediate stages, efforts should be directed mainly at preventing or slowing the progression of retinal changes to an advanced stage, which is accompanied by significant deterioration of vision. For this purpose, vitamin preparations and supplements with a high content of antioxidants (lutein, zeaxanthin), folic acid, vitamins C, B6, B12, A and E, and zinc are prescribed.
It is recommended to use available means of physiotherapy and conduct courses at home (AMBO-01 vacuum glasses), this improves the blood supply to the eyes and enhances the effect of the drugs.
In addition, it is necessary to stop smoking, review your diet and make it as balanced as possible, consuming fresh sea fish, green leafy greens, brightly colored fruits and vegetables. You should protect your eyes from exposure to direct ultraviolet rays (limit exposure to bright sun, wear sunglasses).
Disease prevention
In order to prevent the occurrence of AMD, it is recommended to systematically undergo an ophthalmological examination, especially after 45 years. Experts also advise protecting your eyes from excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation (using sunglasses). It has been proven that people who spend a lot of time in the sun are 4 times more likely to be diagnosed with macular degeneration. Ophthalmologists strongly advise giving up cigarettes. It has been proven that smoking significantly increases the risk of developing and progressing AMD (about 5 times). In addition, doctors recommend limiting the consumption of fatty foods and monitoring cholesterol levels (high cholesterol levels impair blood circulation in the eyes). You should include foods that are good for your eyesight in your diet: blueberries, lettuce, cabbage, spinach, fish, eggs, grapefruit and others. In autumn and winter, it is advisable to take vitamin complexes. In general, experts advise leading an active lifestyle, spending more time outdoors and, as far as possible, reducing visual stress.
Our website offers a wide selection of contact lenses, multifunctional solutions and moisturizing eye drops. You can purchase world bestsellers at a competitive price. Fast delivery of products and high level of service Ochkov.Net will pleasantly surprise you!
Video: can dry macular degeneration be cured?
The treatment tactics for the “wet” form of AMD will be completely different: laser coagulation of the retina, photodynamic therapy, and intravitreal injections are used. All of these methods usually slow the progression of pathological symptoms of the disease. Unfortunately, methods that would completely cure the “wet” form of macular degeneration have not yet been found; in some cases the disease progresses despite treatment.
As a means of rehabilitation, an operation to install an additional Shariot macular lens may be recommended, which allows the patient to see well at close range and read without additional means (magnifying glasses, etc.).
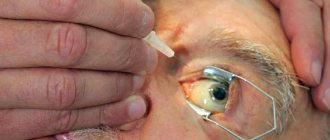
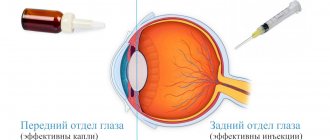
For intravitreal administration in the exudative form of AMD, drugs from the group of pathological vessel growth blockers (anti-VEGF drugs) are used: Lucentis (bevacizumab), Eylea (aflibercept), Avastin (ranibizumab) or Macugen (pegaptanib). Despite its proven effectiveness, such treatment remains expensive due to the high cost of drugs and the need for regular intraocular injections. A break in treatment is accompanied by a decrease in the achieved effect and loss of visual functions.
Laser coagulation of the retina is a method of targeted thermal influence on newly formed, altered vessels using the finest laser beams. Unfortunately, this method can only be used in a small proportion of patients due to the fairly high risk of visual impairment as a result of exposure to the central region of the retina.
Photodynamic therapy is a method of introducing photosensitizing substances (visudine, verteporfin, photolon) into the bloodstream. These substances accumulate in functionally incompetent vessels, after which they are activated by exposing the retina to laser radiation with a certain wavelength. The free radicals and oxygen molecules released in this process cause the destruction of defective retinal vessels, which, in turn, slows down the process of vision deterioration.
In a number of scientific studies, combination treatment methods with the simultaneous use of anti-VEGF drugs and photodynamic therapy have shown their effectiveness compared to monotherapy. At the moment, the combined use of several techniques remains a controversial issue among most ophthalmologists.
Ophthalmologists at our medical center specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of retinal diseases. Our specialists guarantee accurate diagnosis using modern equipment and use the most effective methods for treating eye diseases.
Contraindications
For each of the listed methods of treating macular degeneration, there are contraindications. But there are also diseases in which any of the listed methods is dangerous:
- oncology;
- bleeding disorders;
- severe somatic conditions;
- lack of light perception.
The choice of which method to treat age-related macular degeneration is made by an ophthalmologist after conducting a comprehensive examination of the patient, taking into account the identified contraindications.