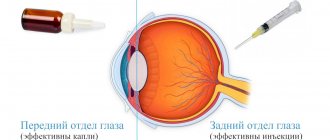
Different retinal diseases require different treatment methods. Some of them are treated exclusively surgically. But a number of diseases can usually be treated in the initial stages with conservative methods - using medications (eye drops, injections).
The main goal of conservative treatment of retinal pathologies is to relieve inflammation, proliferation of newly formed vessels, as well as eliminate degenerative changes and swelling of the retina. In some cases, prescriptions are made for prophylactic purposes (“to strengthen the retina”). At the same time, the use of drugs in the form of drops is not always effective, because they do not penetrate very well into the back of the eye (in this case it is recommended to use injections or tablet forms).
Anterior and posterior parts of the eye
Retinal angiopathy - treatment with drops
Angiopathy is a pathology of retinal vessels caused by various negative factors (hypertension, diabetes mellitus). In order to eliminate its manifestations, an ophthalmologist in the early stages of the disease or as part of complex therapy prescribes certain eye drops to patients.
The goal of such therapy is to activate the metabolic processes of the organ of vision, stimulate the speed of local blood flow, and improve the process of tissue nutrition. Eye drops are becoming one of the components of therapy for symptomatic treatment. Eye drops are becoming one of the components of therapy for symptomatic treatment. Read below what medications are prescribed.
Eye drops are convenient, but not very effective.
Taufon
The main component of the solution is taurine. Apply the solution 1-2 drops in each eye three times a day for a long time. The drug is produced in bottles of 5 and 10 ml.
Indications for use of Taufon:
- Moderate retinal angiopathy.
- Corneal injuries.
- Early stage cataract.
- Dystrophic changes in the retina and cornea.
- Open angle glaucoma.
Expected effect:
- Stabilization of cell membranes.
- Acceleration of the regeneration process of traumatic corneal injuries.
- Activation of metabolic and energy processes.
- Normalization of IOP.
Emoxipin
This is a synthetically produced antioxidant, a solution of which is instilled daily, three times a day, 1-2 drops in each eye. Treatment lasts several days or for a long time - as prescribed by a doctor. The drug is not prescribed to pregnant women, as well as to persons with allergies to the components of the solution.
Indications for use:
- Diabetic retinal angiopathy.
- Cerebral circulation disorders.
- Various origins of hemorrhage in the eye.
- Corneal burns.
- Complicated myopathy and glaucoma.
Expected effect:
- Resorption of small hemorrhages on the retina.
- Protects the mesh shell from bright light.
- Strengthening the walls of blood vessels, reducing their permeability.
- Stimulation of local blood flow.
Emoxipine and Taufon (taurine) are the most popular eye drops for retinal diseases
Quinax*
Expected effect:
- Stimulation of metabolic processes in tissues.
- Activation of antioxidants.
- Increased lens transparency.
*At the moment, the drug is no longer available.
Aisotin
Able to increase and restore visual acuity in case of eye diseases. Available in 10 ml bottles. It is instilled three times a day, 1-2 drops, for 2-3 months.
Indications for use:
- Diabetic angiopathy.
- Restoring visual function after eye surgery.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Eye burns.
- Redness of the eyes.
- Glaucoma.
It is better to discuss the use of any medications with your attending ophthalmologist.
Emoxy optic
Substitute for Emoxipine at a lower cost.
- Indications for use:
- Eye burn.
- Bleeding in the eye.
- Progressive myopia.
- Inflammatory processes of the organ of vision.
Expected effect:
- Normalization of the permeability of vascular walls.
- Stimulation of local blood circulation.
- Resorption of hemorrhages in the eye.
- Elimination of the effects of oxidative stress.
- Increasing tissue resistance to hypoxia.
Irifrin®
When performing ophthalmoscopy, single instillations of a 2.5% Irifrin® solution are used. As a rule, to create mydriasis, it is enough to introduce 1 drop of 2.5% Irifrin® into the conjunctival sac.
Maximum mydriasis is achieved after 15-30 minutes and persists for 1-3 hours.
If it is necessary to maintain mydriasis for a long time, Irifrin® can be re-instilled after 1 hour.
In adults and children over 12 years of age with insufficient pupil dilation, as well as in patients with a rigid iris (pronounced pigmentation), 10% Irifrin in the same dose can be used for diagnostic pupil dilation.
To relieve spasm of accommodation, a 2.5% solution of Irifrin® in children over 6 years of age and adults is prescribed 1 drop in each eye at night every day for 4 weeks.
In case of persistent spasm of accommodation, it is possible to use a 10% solution of Irifrin® in children over 12 years of age and adults, 1 drop in each eye daily at night for 2 weeks.
For diagnostic procedures, a single instillation of a 2.5% Irifrin® solution is used:
- as a provocative test in patients with a narrow anterior chamber angle profile and suspected angle-closure glaucoma. If the difference between the values of intraocular pressure before instillation of Irifrin® and after dilation of the pupil is from 3 to 5 mm Hg, then the provocative test is considered positive;
- for differential diagnosis of the type of injection of the eyeball: if 5 minutes after instillation there is a narrowing of the vessels of the eyeball, then the injection is classified as superficial; if redness of the eye persists, it is necessary to carefully examine the patient for the presence of iridocyclitis or scleritis, as this indicates an expansion of deeper vessels .
For iridocyclitis, a 2.5% or 10.0% solution of Irifrin® is used to prevent the development and rupture of already formed posterior synechiae; to reduce exudation into the anterior chamber of the eye. For this purpose, 1 drop of the drug is instilled into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye(s) 2-3 times a day.
In glaucomo-cyclic crises, the vasoconstrictor effect of phenylephrine helps to reduce intraocular pressure, which is most pronounced when using a 10% solution of the drug.
To relieve glaucomatous-cyclic crises, 10% Irifrin® is instilled 2-3 times a day.
When preparing patients for surgical interventions, a single instillation of a 10% Irifrin® solution is performed 30-60 minutes before surgery to achieve mydriasis. After opening the membranes of the eyeball, repeated instillation of the drug is not allowed. The 10% solution is not used for irrigation, soaking tampons during surgery and for subconjunctival administration.
Intraocular injections
Intravitreal injections are the injection of a drug directly into the eye cavity (into the vitreous body). Such injections are performed for hemorrhages (partial hemophthalmia), wet form of macular degeneration, retinal edema, the appearance of newly formed vessels and other serious eye diseases.
In our clinic, intravitreal injections are performed by ophthalmologists with extensive experience in complex intraocular injections in sterile procedure rooms, in compliance with appropriate medical protocols. Such therapy for retinal pathologies, using effective medications, allows one to preserve visual function and also achieve a significant improvement in visual acuity.
Lucentis
The active component of the drug is ranibizumab, a substance that suppresses excessive angiogenesis (the formation of pathological blood vessels), which is characteristic of age-related macular degeneration. In addition, it helps relieve macular edema, normalizing the thickness of the retina. The drug quickly penetrates completely into the layers of the retina, reducing the size of the lesion, preventing possible hemorrhages and further progression of the growth of newly formed vessels with a pathological wall. More about Lucentis >>>
Eilea
The active substance of Eylea is aflibercept. Its action is aimed at inhibiting the progression of age-related macular degeneration (wet form). In addition, it has the ability to act effectively and safely in reducing visual acuity in the case of diabetic macular edema and edema caused by retinal vein occlusion.
The innovative drug Eylea has a long-lasting effect, so injections can be performed less frequently than with Lucentis, which is much more convenient for patients. More about Eylea >>>
Ozurdex
It is used in cases of macular edema caused by occlusion of the retinal veins. The drug is produced in the form of a thin implant in the form of a rod, which is inserted into the vitreous body. The implant contains the potent steroid dexamethasone, which begins to be released inside the vitreous in small portions. This innovative method of dosed delivery of a medication to the affected area significantly increases the duration of action of the hormone, which can last up to six months. Read more about Ozurdex >>>
Parabulbar and intravitreal injections are performed under sterile conditions
Irifrin
Irifrine (phenylephrine) is an ophthalmic drug from the sympathomimetic group. Dilates the pupil, facilitates the evacuation of aqueous humor - the internal environment of the eye, reduces the lumen of the vessels of the conjunctival membrane. Used:
• with inflammation of the iris and ciliary body;
• to dilate the pupil during a number of diagnostic procedures (for example, ophthalmoscopy), ophthalmic surgical (including laser) interventions;
• to eliminate redness of the eyes;
• for the treatment of Kraup-Posner-Schlossmann syndrome;
• with false myopia caused by dysfunction of the ciliary muscle.
Irifrin is a vasoconstrictor whose mechanism of action is similar to that of norepinephrine. Its angiotonic effect is somewhat less pronounced than that of norepinephrine, but is more persistent. The vasoconstrictor effect of the drug begins to develop 30-90 seconds after instillation. The duration of the vasoconstrictor effect is 2-6 hours. Pupil dilation is observed 10-60 minutes after instillation of a single dose. This state is maintained for two hours (with instillation of a 2.5% solution), up to 3-7 hours (with instillation of a 10% solution). Paralysis of the ciliary muscle of the eye does not occur, because phenylephrine (the active component of the drug) has only a minor effect on the ciliary muscle. To dilate the pupil, as a rule, a 2.5% solution is used with the possibility of repeated instillation if it is necessary to maintain the pupil in a state of mydriasis for a longer period of time.
In patients with a hard (rigid) and pigmented iris, a 10% solution can be used. For false myopia, use a 2.5% solution before bedtime in each eye for one month. In case of persistent dysfunction of the ciliary muscle in patients over 12 years of age, a 10% solution can be used for 14 days. For inflammation of the iris and ciliary body, both 2.5% and 10% solutions are used. Frequency of use: 2-3 times a day. In patients with diabetes mellitus, special caution should be exercised when using the drug due to the increased risk of developing hypertension due to autonomic disorders. The same applies to older people: with age, the risk of reactive constriction of the pupils increases. Combining Irifrin with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) should be under regular medical supervision, which should also be present for three weeks after discontinuation of MAO inhibitors. The use of a 12.5% solution in excess of the recommended dosage in patients with traumatic eye injuries, after surgical interventions on the organs of vision, as well as in persons with pathologies of tear production may lead to an increase in the absorption of the active component, which, in turn, increases the risk of systemic adverse reactions . The use of Irifrin during pregnancy and breastfeeding is possible only after a comprehensive assessment of the benefit/risk ratio.
Treatment regimens for retinal angiopathy
Drug therapy in the case of angiopathy and its vascular complications should be comprehensive. If necessary, treatment can be continued in courses. Before prescribing it, an ophthalmologist develops a specific, most effective regimen for using drugs. As a rule, these are the following appointments:
- Drug therapy aimed at activating blood circulation in the vessels of the eyes is necessary. This is a course treatment with Emoxipin, Vazonit, Mildronate, Arbiflex, Solcoseryl, Trenatal. They help activate local microcirculation processes. Another property of these drugs is improving the plasticity of red blood cells. This allows them to move faster through the small vessels of the eyes.
- Pentoxifylline and Curantil help prevent possible thrombus formation. Xanthiol nicotinate and nicotinic acid improve blood rheology.
- To reduce vascular permeability, ginkgo biloba and calcium dobesilate are prescribed.
- Actovegin injections are designed to provide better nutrition to the eye tissues. To improve metabolic processes in eye tissues, ATP and cocarboxylase are used.
- It is mandatory to take vitamin complexes to maintain eye health - Lutein-intensive, Anthocyan Forte. It is important to take ascorbic acid, which accelerates microcirculation processes in blood vessels and maintains visual acuity.
- For diabetic retinopathy, it is necessary to adhere to a special diet that can neutralize diabetes mellitus and improve blood flow in the retinal vessels. It is worth remembering that prohibited foods include any food rich in fast carbohydrates (baked sweets, sweet soda, etc.). The same applies to excessively high-calorie foods. Limiting salt is also important, because it helps normalize metabolism and improve recovery processes.
- Vigorous physical exercise, included in the daily routine to give energy to the muscular system, also improves the condition of the eye vessels.
- When treating angiopathy caused by hypertension, it is mandatory to lower blood pressure levels through medications and specially designed dietary adjustments. To do this, you should contact a cardiologist and nutritionist.
- It would not be superfluous to prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures. In the case of angiopathy, magnetic therapy courses and acupuncture can show good results.
- Another physiotherapeutic method is “Sidorenko Glasses”. This device combines the effects of pneumomassage, infrasound, phonophoresis, and color therapy. The powerful effect on the retina of such a complex makes it possible to achieve good results in a short time.
- Treatment also helps with massage courses on the cervical spine.