The organs of the genitourinary system are very sensitive to changes in the body and the external environment. There are a large number of causes of pathological changes: from infectious and inflammatory processes to cancer.
It is important to take a responsible approach to the diagnosis and treatment of organs of this system. Neglect of medical recommendations, minor deviations from treatment tactics can lead to the development of complications or chronicity of the process.
One of the features of diseases of the genitourinary system is the frequent involvement of several organs in the process. Infections of the urethra and bladder can “rise” to the kidneys and vice versa. Therefore, to maintain health, it is extremely important to be observed by a specialist and carry out comprehensive treatment of the pathology.
Organs of the genitourinary system
In order to better understand diseases of the genitourinary system, it is first necessary to understand anatomy and physiology. The genitourinary system is a combination of organs of the urinary and reproductive systems. In some cases, anatomical structures may relate to both systems at once (for example, the urethra in men).
The main organs of the urinary system are:
- Kidneys This paired organ is located in the lumbar region. The kidneys are bean-shaped and are supported in a fixed position by the ligamentous apparatus and the fat capsule. They filter the blood and remove harmful and toxic substances from the body. During the day, tens of liters of primary urine pass through this organ, are concentrated, and the final excretion product is formed. Another important function of the kidneys is to maintain normal blood pressure. High blood pressure is not always a sign of cardiac pathologies; it is also important to pay attention to the functioning of the kidneys.
- Ureters This organ starts from the kidneys and ends at the junction with the bladder. The ureters carry urine into this reservoir.
- The bladder's main function is to store urine.
- Urethra (urethra) The last link that serves to remove urine from the body.
The structure of the organs of the urinary system is almost identical. Significant differences are observed only in the urethra: in women it is shorter and wider, in men it is long and narrow. These features cause differences in the course of some diseases.
But the organs of the reproductive system in men and women have significant differences. The male genital organs include:
- testicles, as well as their appendages;
- vas deferens, ejaculatory ducts;
- seminal vesicles;
- urethra;
- prostate (prostate gland).
The external organs of the reproductive system in men are the scrotum and penis.
The female reproductive system consists of the following anatomical structures:
- ovaries, as well as their appendages;
- uterus;
- the fallopian tubes;
- vagina.
In women, the external organs of the reproductive system are the labia majora and minora, as well as the clitoris.
Prevention
Doctors have several recommendations that will help avoid the development of diseases of the urinary system:
- Do not overcool the urinary organs - dress according to the weather and do not wear short jackets and thin pants in cold weather, do not sit in the cold and do not spend a lot of time in cold water.
- Drink enough fluids throughout the day.
- Avoid unprotected sex with an untrusted partner.
- Maintain good hygiene - take a shower every day, wear clean underwear made from natural materials, change feminine hygiene products on time during menstruation.
- Do not abuse alcohol, tea and coffee, fatty, smoked and pickled foods.
- Stop smoking. Smoking increases the risk of developing cancer of the urinary system by 4 times.
- Treat diseases on time. Even mild cystitis can become chronic and, once in the kidneys, cause the development of pyelonephritis, a more severe and dangerous disease.
- Monitor the course of your chronic diseases and undergo regular medical examinations.
The most common pathologies
The most common pathologies of the bladder are:
- Diverticula A sac-like depression forms in the wall of the bladder, which is connected to the cavity by a small channel. The size of the pouch can vary significantly. As a rule, bladder diverticula are rare. However, multiple diverticulosis is sometimes diagnosed. Typical localization of the pathological process: on the side or behind the bladder. The main cause of the disease is developmental anomalies in the wall of the organ during the prenatal period. Acquired diverticula are quite rare and develop against the background of prostate adenoma.
- Cystitis The female body is more susceptible to the development of inflammatory diseases due to the anatomical features of the urethra: it is wide and short, so pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate the bladder. Cystitis is diagnosed much less frequently in men. The main reason for the development of pathology is the penetration of infection into the bladder and the development of inflammation. People who lead a sedentary lifestyle are also at risk. Since stagnation of urine creates a favorable environment for the growth and reproduction of pathogens.
- Cystalgia (bladder neurosis) Accompanied by severe pain. Cystalgia is often diagnosed in individuals with a labile nervous system. As a rule, these are girls and women with increased emotionality, mood swings and increased sensitivity. Cystalgia is quite often diagnosed in women who, for some psychological reason, avoid sexual intercourse. There are no objective data indicating pathology of the genitourinary system. Therefore, treatment is carried out simultaneously with the study of the emotional state by a psychologist or psychiatrist.
- Urolithiasis Disorders of nutrition and metabolism lead to the formation of stones or sand in the organs of the genitourinary system. Formations can appear in both the kidneys and the bladder. They have different configurations and structures. The course of urolithiasis is accompanied by a period of exacerbations and remissions. For a long time, the resulting stone does not disturb its bearer in any way. However, when it gets into a narrow space (for example, the ureter), unbearable pain appears, blood in the urine, etc. The sad trend is that urolithiasis is becoming “younger”. Now not only young people, but even teenagers are faced with pathology.
- Tumors of the genitourinary system Tumors can be benign or malignant. Under an unfavorable combination of factors, benign neoplasms can become malignant (acquire a malignant character), and their course becomes more aggressive. The main danger of tumors is their long asymptomatic course. Quite often, pain and discomfort appear only when the neoplasm has grown deep into the tissue of an organ or even neighboring anatomical structures.
- Bladder atony (urinary incontinence) A delicate problem that is usually not talked about. However, not only older people suffer from urinary incontinence, but also young girls (for example, after childbirth). This condition significantly worsens the quality of life of patients, causes a feeling of inferiority and the development of complexes. Therefore, it is extremely important to carry out timely diagnosis of this condition and select adequate therapy.
- Other diseases Cysts, sclerosis, tuberculosis, ulcers are only a small part of the diseases of the genitourinary system in women and men. The list of urological diseases is quite wide, so it is important to be closely monitored by a specialist to exclude the development of even one of them.
Risk factors
No person is immune from diseases of the urinary system, but there are a number of risk factors that increase the likelihood of an infectious or oncological disease. These include:
- Urogenital infections;
- Unprotected sexual intercourse;
- Insufficient genital hygiene;
- Pregnancy;
- Smoking;
- Excessive consumption of salt and red meat;
- Uncontrolled use of medications and dietary supplements;
- Diabetes;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Obesity.
The above does not mean a 100% probability of developing diseases, but if you find yourself at risk, you should pay attention to your health and not ignore the symptoms. Talk to your doctor about ways to improve your quality of life and reduce your risks.
Pregnant women should definitely see a gynecologist in a timely manner and report any suspicious symptoms. In 7% of cases during pregnancy, pyelonephritis develops when infected with a bladder infection.
Symptoms of diseases of the genitourinary system
Diseases of the genitourinary system are characterized by a variety of symptoms. The severity of discomfort is not always directly proportional to the degree of organ damage. Many diseases are asymptomatic for a long time and are accidentally discovered during preventive examinations by a specialist. The main symptom of diseases of the genitourinary system is pain. Quite often it is of a pronounced nature. During attacks, patients behave restlessly and try to find a comfortable position that will reduce discomfort.
In addition, phenomena such as:
- Frequent night urination Normally, the frequency of night urination should not exceed 1-2 times. If you do not drink large amounts of fluids or diuretics, then a frequent urge to urinate at night should become an alarming symptom.
- Painful urination Pain can appear both before and during the process. Pain during urine output is a common symptom of cystitis and sexually transmitted infections. Therefore, it is important to identify the causative agent of the disease. This will help you choose adequate treatment tactics.
- Urinary incontinence is a symptom of many diseases of the genitourinary system. It may appear due to trauma to the bladder, weakening of the pelvic floor muscles, etc.
- Frequent urination An increase in the frequency of urination can be associated with both kidney and urethral diseases. Based on the medical history and symptoms of the disease, the doctor selects the optimal treatment algorithm.
- Changes in the color of urine Urine may change color due to the appearance of blood in it. This phenomenon is called macrohematuria. However, the color of urine may not always be a reliable indicator of blood impurities, since there is a phenomenon of microhematuria: red blood cells are visible only under a microscope. However, even a small amount of them is not the norm.
These are the main symptoms that accompany almost any disease of the genitourinary system. However, they may additionally be accompanied by specific characteristics. So, with endometriosis, pain may appear in the abdomen and anus. Many diseases are accompanied by a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, and renal colic appears. To establish the correct diagnosis, it is necessary not only to consult a doctor, but also to undergo tests, as well as use instrumental diagnostic methods.
General information about cystitis
Among bladder diseases, the most common is inflammation, called cystitis.
Cystitis is an infectious disease. In the first place among pathogens is E. coli, in second place is staphylococcus, and sexually transmitted infections are also important [2]. More often it occurs in women. More than a third of women aged 20 to 40 experience at least 1 episode of urinary infection during the year. In 50% of women, cystitis recurs within a year, which in 90% of cases is due to re-infection. Frequent relapses lead to chronic cystitis. Chronic inflammation in the organ can result in other diseases and cause partial obstruction of the bladder neck and urethra. Against the background of chronic inflammation, polyps, diverticula, leukoplakia may appear, and infected stones—struvite—can form [2].
There are different types of cystitis [3]:
- eosinophilic;
- ray;
- drug;
- thermal;
- traumatic, etc.
Cystitis is most often an infectious disease, therefore, treatment is aimed at getting rid of the causative agent of the infection. Antibacterial therapy is considered the main treatment for cystitis.
Herbal diuretics are used as part of the complex treatment of urinary tract infections [2]. These include Fitolysin® paste for preparing a suspension for oral administration. The drug contains 9 plant components, as well as 4 essential oils, helps relieve inflammation, spasm and pain [9]. Suspension from Phytolysin® paste is prepared quickly. There is no need to infuse or strain anything, as is the case with herbal infusions; you just need to dissolve the product in water and drink [4].
Which doctor should I contact if symptoms appear?
Several specialists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of the genitourinary system. Among them, special attention deserves:
- urologist;
- nephrologist;
- andrologist;
- gynecologist.
Consultation with these specialists helps to accurately differentiate diseases, prescribe adequate treatment and a diagnostic plan. If you are in doubt about which specialist to visit first, you can always consult a therapist. Based on your complaints, this doctor will coordinate your further actions and prescribe the first necessary tests.
Symptoms of bladder diseases
Signs of bladder damage include [6]:
- hematuria - the appearance of blood in the urine. Blood in the urine is a serious symptom of a disease of the genitourinary system, often cancer, and therefore it is always necessary to determine the source of bleeding and its cause;
- cloudy urine, sediment, unpleasant putrid odor;
- dysuric manifestations: frequent daytime or nighttime urination, sudden uncontrollable urges, urinary incontinence, painful, difficult urination, urinary retention (sluggish stream, need to strain, urine leakage drop by drop);
- lower abdominal pain.
These signs occur in different diseases of the organ, but the degree of their severity may vary. If such symptoms appear, you should see a doctor.
Diagnosis of diseases of the genitourinary system
To identify the localization of the pathological process, as well as its nature, a comprehensive examination is required. The most common diagnostic measures for diseases of the genitourinary system are:
- Ultrasound examination This method has long proven itself for diagnosing diseases of the pelvic organs. Its main advantages are safety, high accuracy and affordable price. Ultrasound examination helps to monitor the patient’s condition over time, which is extremely important in the treatment of many pathologies of the kidneys and bladder.
- Computed tomography is a highly accurate modern method of examining patients with diseases of the genitourinary system. Thanks to computed tomography, it is possible to obtain a detailed image of the pathology and examine it in several sections. The disadvantage of computed tomography is the low availability of the study, especially in small towns.
- Laboratory tests An obligatory minimum when diagnosing diseases of the genitourinary system is the appointment of a clinical blood test with a leukocyte formula, a biochemical analysis of blood plasma, as well as a general urine test. Depending on the clinical picture, this list may be supplemented.
- X-ray examination Excretory urography is also one of the most common methods for diagnosing kidney and bladder diseases. The study is carried out using a contrast agent, so it is important to inform your doctor about allergic reactions, if any.
This is just a small list of studies that are carried out to diagnose diseases of the genitourinary system. The list can be supplemented as prescribed by a specialist.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
Ultrasound examination is the main way to effectively recognize pyelonephritis, cystitis or urethritis, the diagnosis of which is complicated by the similarity of symptoms and the presence of concomitant diseases. This is both the cheapest and safest method (compared to computed tomography and especially MRI. An example is an ultrasound of the prostate, the price of which does not exceed 500 rubles in most paid clinics and departments. Often an ultrasound of the prostate gland is performed together with an examination of other pelvic organs.
General information about the treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system in men and women
Treatment of almost any disease begins with conservative therapy. The patient is prescribed medications and is informed of the need to follow a gentle diet. Depending on the severity of the symptoms of the disease, individual dosages of medications are selected.
In inflammatory diseases, the first priority is to eliminate the source of infection. Antibacterial drugs are used for treatment. To relieve pain and accompanying symptoms, antispasmodics, diuretics, and herbal medicine can be used.
When tumors are detected, a histological examination of the biopsy specimen is performed, and then a decision is made on the procedure for the operation. Depending on the severity of organ damage, surgical techniques may vary significantly.
Treatment
Bladder treatment is carried out by a general practitioner and a urologist. Sometimes consultation with related specialists is required: gynecologist, venereologist, oncologist, surgeon, neurologist, etc. Conservative and surgical treatment methods are used. A specialist can also recommend a therapeutic diet, special exercises (for example, for incontinence), and lifestyle changes [2].
Bibliography:
- Paukov V.S. Pathology: manual / Ed. V.S. Paukova, M.A. Paltseva, E.G. Ulumbekova - 2nd ed., revised. and additional - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2015. - 2500 pp., p. 17, chapter 14, pp. 92-103.
- Lopatkin N. A. Urology / Ed. ON THE. Lopatkina - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2011. - 1024 pp., p. 48, ch. 26.02, pp.1-16.
- Khalilova U.A., Skvortsov V.V. et al. Cystitis. Nurse. 2018; 6:6-11.
- Instructions for use of the drug PHYTOLYSIN® Paste for the preparation of a suspension for oral administration.
- Chibisov S.M., Illarionova T.S. et al. Urolithiasis: range of medicines. Basic research. – 2006. – No. 11 – P. 21-30.
- Glybochko P.V. Urology. From symptoms to diagnosis and treatment. Illustrated guide: textbook. manual / ed. P.V. Glybochko, Yu.G. Alyaeva, N.A. Grigorieva - Moscow: GEOTAR-Media, 2014. - 148 p., p. 33, p. 2., p. 5-8.
- Lyubarskaya Yu.O., Atduev V.A. Overactive bladder. Remedium. Volga region. June 2014; 5 (125): 36-41.
- Yarin G.Yu., Wilhelmi I.A. Interdisciplinary approach to the treatment of bladder endometriosis. Urology. 2018; 4: 118-121.
- As part of complex therapy, Fitolysin® Paste for the preparation of a suspension for oral administration relieves pain in cystitis caused by inflammation and spasm, due to its anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic effect, relieves frequent urges due to its antispasmodic effect.
General information about oncological diseases of the genitourinary system
Tumors of the genitourinary organs in men account for about 9.2% of all malignant neoplasms. Over the past 10 years, the number of pathologies in this group has increased by approximately a third. This makes us think about the importance of timely diagnosis of these diseases and adequate treatment.
Malignant neoplasms are dangerous due to their insidiousness. They grow for a long time and damage surrounding tissues completely asymptomatically. An oncological disease can be detected even in a person who does not present any complaints. And only when the tumor reaches a large size does it begin to disrupt the functioning of organs and systems. For example, compression of the bladder by a tumor leads to problems with urination. The outflow of urine is disrupted, discomfort and pain appear. And by the time you see a doctor, the tumor can already metastasize to vital organs. This makes the prognosis less favorable and significantly complicates treatment.
This course of diseases determines the trends of modern medicine. Prevention is the key to the health of every person. Even in the absence of complaints, it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations and tests at least once a year. There is no need to wait for the manifestations of the disease, because by this time it may already be too late to carry out treatment.
Ultrasound diagnostics is the main method for identifying urological diseases. Regular examinations make it possible to diagnose tumors of the kidneys, bladder, prostate and testicles in the early stages. The earlier pathological changes in the organ were detected, the more favorable the prognosis for treatment.
Modern ultrasound machines make it possible to detect tumors of the smallest size: penile cancer, kidney cancer, testicular tumors, etc. This is evidenced by the many years of experience of diagnosticians and positive experience in treating patients with early-stage urological cancer.
It is very painful to watch a person quickly “burn out.” Until recently active and cheerful, he is losing weight, losing the perky sparkle in his eyes, and coming to terms with the proximity of death. Relatives and friends of this person are ready to give any money for treatment, to go to the best clinics in the world, just to save him. But all this often does not lead to results. Money, fortunately or unfortunately, cannot solve everything in this life. But all you had to do was carve out a couple of hours for yourself in the hustle and bustle of life and visit medical specialists once a year and undergo an examination. And then the outcome could be completely different.
There is a list of warning symptoms that should be a reason for immediate contact with an ultrasound specialist, and then with a urologist. Among them:
- Hematuria. The appearance of obvious bloody discharge in the urine usually indicates the development of a serious disease: cancer or inflammatory.
- Dysuria. This phenomenon is accompanied by painful or difficult urination.
- Lower back pain.
- Stomach ache.
- Swelling or hardening of the testicles.
Based on the ultrasound report and laboratory data, the urologist will be able to correctly diagnose and prescribe timely, adequate therapy.
Don't neglect your health. If an ultrasound detects a suspicion of a tumor, undergo further examination. Don’t put off your health “for later.” After 2 or 3 months, the changes may become irreversible and it will be impossible to help.
Detection of a tumor in the early stages is the key to successful treatment.
Bladder cancer: diagnosis and treatment
Oncological diseases of the bladder are widespread. Every year the disease affects more than 430 thousand people in the world. And this figure continues to grow steadily.
In Russia, bladder cancer is one of the leaders of sad statistics. In terms of frequency, it is second only to prostate cancer in men and kidney cancer in women.
The development of the disease is promoted by:
- Tobacco smoking In recent years, the role of this factor has increased significantly due to the popularity of electronic cigarettes. In smokers, malignant neoplasms of the bladder occur 4-7 times more often compared to people without bad habits.
- Age Men and women over 55 are most at risk of developing bladder cancer. However, disappointing current trends indicate that oncology is “getting younger” and affecting people of working age.
- Gender The incidence of bladder cancer is much higher in men than in women. However, representatives of the fair sex have a more unfavorable prognosis for the outcome of the disease.
- Chemicals and medications The bladder is a reservoir for the accumulation of urine containing substances toxic to the body. Therefore, working in hazardous chemical plants and taking certain groups of medications may increase the risk of developing urinary tract cancer.
- Chronic bladder diseases Stones and infectious lesions lead to constant low-grade inflammation and impaired cell differentiation. The larger and stronger the damage, the higher the risk of the appearance of atypical, malignant cells.
The main symptoms of bladder cancer are:
- macrohematuria, microhematuria (appearance of blood in the urine);
- frequent and painful urination;
- frequent urination at night (nocturia);
- lower back pain localized on one side;
- loss of appetite and weight loss against a background of general well-being.
The appearance of blood in the urine is one of the most alarming symptoms. It occurs in more than 92% of patients diagnosed with bladder cancer. Blood in the urine is not always visible to the naked eye: sometimes it is only single red blood cells that are detected during a microscopic examination.
Due to regular blood loss, anemia is observed in a clinical blood test. As a rule, the more pronounced the symptoms, the more advanced the stage of the oncological process will be during diagnostic measures.
A malignant tumor is classified according to the TMN system, which allows us to describe the key features of the tumor process:
- Tumor Size of the primary tumor, location
- Nodus (node) Metastases in regional lymph nodes, their location and number
- Metastasis (metastases) Metastases in distant lymph nodes and other organs, their number and location
Bladder cancer can be complicated by the following conditions:
- Compression of the ureteric orifice by a tumor. Leads to disruption of urine outflow and functional changes in the kidneys.
- Pyelonephritis. Inflammatory disease of the renal parenchyma of bacterial origin.
- Kidney failure. Develops due to the progression of functional changes in kidney tissue.
- Anemia.
- Ureterohydronephrosis.
- Chronic urinary retention.
To ensure adequate urine flow, doctors are forced to perform surgery to remove the nephrostomy.
Typical localization of distant metastases in bladder cancer:
- brain;
- lungs;
- bones.
The main diagnostic measures for identifying bladder cancer are:
- Urethrocystoscopy This is an endoscopic examination that allows you to evaluate the condition of the bladder, as well as the urethra.
- Biopsy and histological examination are carried out to detect atypical bladder cells.
- Computed tomography makes it possible to diagnose even the most minor changes in tissues, allowing one to suspect the development of a tumor process.
- Ultrasound examination Detects pathological formations of the bladder. Modern equipment and extensive experience of ultrasound diagnostic doctors also make it possible to detect changes in the structure of the organ in the early stages. The method is accessible and suitable for carrying out preventive examinations in all groups of the population.
Bladder cancer treatment
The main method of treating cancer is surgery. Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may also be used. The choice of treatment tactics largely depends on the type of bladder cancer, as well as the extent of the pathological process.
Early consultation with a doctor is the key to a favorable outcome. The larger the bladder tumor and the number of metastases, the more unfavorable the prognosis of the disease. Regular preventive examinations allow you to identify pathological changes much earlier, as well as make treatment more effective.
To reduce your risk of developing bladder cancer, you should:
- Quit active and passive smoking.
- Maintain a drinking regime (the amount of water is calculated individually depending on body weight).
- Reduce exposure to occupational hazards (do not neglect the use of personal protective equipment if you work in hazardous industries).
- Treat acute diseases of the genitourinary system in a timely manner.
Following these simple rules will help to significantly reduce the risk of developing bladder cancer.
Kidney cancer: symptoms and treatment
Kidney cancer belongs to the group of oncological diseases. This pathological process can be either unilateral or bilateral. Kidney cancer quickly begins to grow deep into the kidney tissue and metastasizes to neighboring organs and systems. Tumor cells contribute to the destruction of healthy tissues and replace them. As a result, the organ cannot fully participate in blood filtration, and intoxication of the body increases.
There is a worldwide trend towards an increase in the incidence of kidney cancer. This is due to a significant increase in life expectancy in developed countries. Every year in Russia, kidney cancer is diagnosed in more than 20 thousand people. Men suffer from kidney cancer more often, but in women this pathology more often causes death.
Kidney cancer also occurs in children. Oncology in childhood is represented by embryonic nephroblastoma. It accounts for 90% of kidney tumors in children. Its main features are:
- rapid growth and metastasis;
- hereditary predisposition is detected in only 2% of cases;
- most often detected between the ages of 2 and 5 years;
- about 10% of cases are accompanied by other developmental defects;
- up to 10% of cases – bilateral kidney damage.
Until now, it has not been possible to reliably establish risk factors for the development of kidney pathologies. However, it is believed that the appearance of renal oncology is facilitated by:
- tobacco smoking (including passive);
- long-term use of diuretic drugs;
- occupational hazards (agricultural chemicals, dyes, etc.);
- overweight, metabolic syndrome;
- arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
- long-term hemodialysis;
- viral hepatitis;
- genetic predisposition;
- polycystic kidney disease.
Quite often, kidney cancer occurs against the background of nephrosclerosis, which is formed due to damage to kidney tissue by harmful factors of various etiologies. Early identification of risk factors allows you to minimize their impact on the body and, in the future, avoid the development of kidney cancer.
Symptoms of kidney damage by cancer
The most characteristic of internal kidney damage are:
- arterial hypertension (renal origin);
- cachexia or significant weight loss;
- increased body temperature, fever;
- amyloidosis (deposition of pathological amyloid protein in the kidneys);
- increased ESR;
- anemia;
- increased calcium levels in the blood;
- polycythemia;
- impaired renal function;
- hematuria;
- general weakness, dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting.
In children, the first symptoms of kidney cancer may be the appearance of blood in the urine, as well as a dense, “bulging” abdomen.
Complications of kidney cancer are:
- Metastases in the lungs Accompanied by a cough not associated with ARVI and pulmonary pathology. Hemoptysis may occur.
- Metastases in the brain are accompanied by severe pain in the skull and neuralgia.
- Metastases in the liver Accompanied by a bitter taste in the mouth. Pain appears in the right hypochondrium, the skin and mucous membranes become jaundiced.
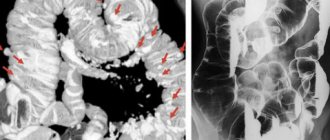
- Metastases in the bones Aches and pains appear in the bones. During X-ray examination, characteristic metastatic formations are detected. The incidence of fractures increases due to increased fragility of bone tissue.
The danger of cancer lies in its long asymptomatic course. In order to diagnose pathology in a timely manner, a responsible approach to your health is necessary: it is important to regularly attend preventive examinations and take tests. The main diagnostic measures are:
- CT with intravenous contrast;
- Ultrasound diagnostics;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- renal angiography;
- biopsy with histological examination;
For the treatment of kidney cancer, the following are used:
- surgical interventions;
- immune therapy;
- targeted therapy;
- chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy;
- hormonal therapy.
The prognosis of the disease is more favorable when cancer is detected at an early stage.
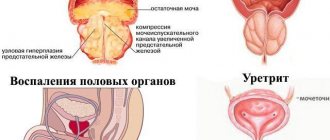
Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system
Infections of the reproductive and urinary systems are quite common. More than 50% of women have experienced the symptoms of these diseases at least once in their lives. Among men under 35 years of age, about 15% experience diseases of the genitourinary system. And over the age of 50, this percentage increases rapidly. In particular, this is associated with the onset of prostate adenoma.
In childhood, infectious and inflammatory processes are much less common; they are observed in 8% of girls and 2% of boys.
The insidiousness of pelvic inflammatory diseases lies in the high probability of transition from an acute inflammatory process to a chronic one, as well as in the involvement of neighboring organs and systems in the pathology. Thus, cystitis leads to pathological changes in the kidneys. Therefore, it is important to diagnose the pathology in a timely manner and consult a specialist.
How do infections develop in men and women?
Differences in the anatomical structure of organs lead to specific manifestations of the disease.
In women, infections develop more often and faster. This is due to the fact that their urethra is shorter and wider. This makes the infection penetrate faster. Therefore, women have urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) and cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Additional prerequisites for the development of these pathologies are the proximity of the anus and vagina. In case of violations of hygiene rules, microtraumas during sexual intercourse, a favorable environment appears for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
In men, the urethra is an organ not only of the urinary system, but also of the reproductive system. During ejaculation, seminal fluid passes through it. Infections in men most often develop after sexual intercourse, as well as when the urethra is compressed by an enlarged prostate gland. The latter factor contributes to stagnation of urine and the proliferation of bacteria and viruses in it.
The main symptoms of the development of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system are:
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- pain during urination;
- pain in the abdomen and lower back of varying degrees of severity and character;
- burning during urination;
- change in urine color, cloudiness;
- change in urine odor;
- frequent and painful urge to urinate.
In addition to local symptoms of infection, general symptoms appear: weakness, nausea, vomiting, increased body temperature.
Classification of genitourinary infections of various types
Infectious lesions of the urinary system can be classified according to location and nature of the course.
The most common localizations are infections of the lower sections: bladder, urethra. The upper urinary tract (kidneys and ureters) is less commonly affected.
Depending on the nature of the disease, it can be complicated or uncomplicated.
With the development of complications, disturbances in the outflow of urine, structural changes appear and are supplemented by concomitant diseases. Most often, the development of complicated infections is caused by atypical pathogens.
Nonspecific infections are caused by representatives of opportunistic microflora. Normally, these microorganisms live in the human body and do not cause disease. But when the immune system is weakened, staphylococci, streptococci, and E. coli become the cause of pathology.
Specific infections are those that are sexually transmitted:
- gonococci;
- Trichomonas;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma, etc.
Common pathogens of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system
The most common diseases of the genitourinary system are bacteria, viruses, protozoa and fungi.
The causative agents of uncomplicated infections are:
- Escherichia coli (E.Coli) in about 90% of cases;
- saprophytic staphylococcus (Staphylococcus saprophiticus) about 5% of cases;
- proteus mirabilis (Proteus mirabilis);
- Klebsiella spp.
An uncomplicated type of infection is usually provoked by one type of bacteria. Complicated infections can be caused by a combination of several pathogens.
The causative agents of specific infections are:
Gonorrhea
The causative agents of the disease are Neisser's gonococci. The inflammatory process is localized on the mucous membranes of the genitourinary system. Under unfavorable circumstances, the infection can spread to the rectum, eyes, oral mucosa, etc.
The incubation period for gonorrhea is 3–5 days. The main symptoms are:
- pain during urination;
- purulent discharge from the urethra;
- frequent urination.
In men, gonorrhea often occurs subacutely, the clinical picture is erased, and the symptoms are less pronounced.
Chlamydia
The disease most often has a hidden course. Caused by chlamydia. The main symptoms are:
- itching in the perineal area;
- pathological discharge from the genitals;
- lower back pain;
- discomfort when urinating.
Chlamydia accounts for about 20% of sexually transmitted infections.
Who is at risk for genitourinary infections?
Diseases of the genitourinary system can develop at any age. However, the most susceptible to developing infections are:
- Women A special risk group is women during menopause, as well as girls who do not use barrier methods of contraception.
- Persons with developmental anomalies of the genitourinary organs.
- Patients with chronic diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Patients with immunodeficiency conditions.
- Patients with pathologies of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus).
Diagnosis of genitourinary infections
First of all, you should contact a urologist. You may also need to consult a dermatovenerologist if you suspect a genitourinary tract infection.
Next, laboratory and instrumental studies are prescribed:
- Urinalysis (general urinalysis, Nechiporenko urine analysis).
- Clinical blood test with leukocyte formula.
- Urine culture for microflora (necessary to determine the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics).
- Biochemical blood test (to determine the level of creatinine and urea in the blood serum).
- ESR.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis (to determine the condition of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, etc.).
- Urographic examination.
- Computed tomography of the pelvic organs (if necessary).
Treatment of genitourinary infections
The main group of drugs used to treat genitourinary infections are antibiotics. Depending on the severity of symptoms, the method of administration is selected individually. They can be prescribed in the form of tablets, intramuscular or intravenous injections. Nowadays you can buy antibacterial drugs without a prescription in almost any pharmacy. However, you should not self-medicate. If you do not determine the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms to an antibiotic or choose the wrong treatment tactics, the course of the disease will only worsen.
To ensure quality treatment, you should definitely seek qualified medical help.
Benefits of treatment at the Healer medical center
An integrated approach is important in diagnosing diseases of the genitourinary system. Pathologies can be extremely diverse in their manifestations, so a large number of laboratory and instrumental research techniques are required, as well as consultations with related specialists.
At the Healer medical center, all professionals are gathered in one place. Our highly qualified specialists will understand even the most complex clinical cases. Our policy is to order only those studies that are necessary to confirm and differentiate the diagnosis. No overpayments for unnecessary tests!
You can complete all examinations quickly and comfortably in one place. Our clinic strives to help every patient return to an active and healthy lifestyle as soon as possible!