Published: 06/17/2021 12:50:00 Updated: 06/17/2021
Gout is a systemic disease characterized by impaired purine metabolism in the body and the deposition of urate crystals in the joints. The main manifestation of the disorder is considered to be repeated attacks of arthritis with intense pain in the joints and the appearance of tophi - gouty nodules. Also, with this disease, accumulation of salts in the kidneys is possible with the development of urolithiasis and renal failure.
The prevalence of the disease among adults in Europe ranges from 0.9 to 2.5%, and in the United States reaches 3.9%. Gout is most often diagnosed in men over 40 years of age. Among women, the pathology occurs 6-7 times less often.
Causes of gout
The main cause of gout is considered to be a violation of uric acid metabolism, leading to its excess in the blood - hyperuricemia.
This condition occurs when the intake of purines from food increases, when their metabolites simply do not have time to be excreted in the urine, or when the excretory function of the kidneys is impaired, as well as in the case of accelerated destruction of cells containing the nucleosides adenine and guanine in RNA and DNA, from which urinary tract is formed. acid in the human body. In this case, uric acid salts (urates) accumulate in the soft tissues of various organs, mainly in the joints, provoking their inflammation. Gout is also known as the “disease of feasting kings.” It received this name because the main source of its occurrence was considered to be excess in food and alcoholic beverages.
Now the disease has been studied in more detail and the following factors predisposing to the development of the pathology have been identified:
- consumption of foods rich in purines - meat, fatty fish, legumes, caffeine-containing products, offal (kidneys, liver, brain), seafood, as well as alcohol in large quantities;
- consumption of carbonated, sweet drinks and fruit juices;
- obesity;
- hemolytic anemia, leukemia, lymphoma;
- genetic defects (usually in men) and reduction of enzymes involved in the metabolism of uric acid;
- the use of medications such as diuretics, cytostatics, salicylates.
In women, gout usually develops in postmenopause, so the disease is also associated with hormonal changes in the body.
Gout symptoms
From Greek, gout is translated as “foot in a trap,” since the patient is primarily bothered by intense pain in the first metatarsophalangeal joint of the foot, knee or ankle.
It is also possible to involve the hand in the form of oligo or polyarthritis (inflammation of two or many joints). In this case, the joint becomes swollen, the skin above it acquires a red tint and begins to shine. This form of the disease is called acute gouty arthritis. The first clinical manifestations of the pathology may be preceded by a long asymptomatic period of hyperuricemia, when disorders are detected only by laboratory blood tests.
The first attacks of pain occur suddenly, mainly in the early morning or at night, tend to increase on the first day and completely disappear within a few hours or within a day. During an exacerbation of gout, signs of intoxication may also be present - increased body temperature, chills, weakness. After inflammation subsides, gouty arthritis occurs again, usually within six months to two years. As the disease progresses, the duration of periods of its asymptomatic course decreases, joint pain occurs more often and is more difficult to tolerate.
When going into a chronic form, gouty arthritis is accompanied by deformation and limitation of movements in the joints, pain of varying intensity becomes constant. Subsequently, deposits of uric acid crystals become visible. Under the skin, most often in the joint area, tophi appear - white or yellow nodules with crumbly, curdled contents. The formation of ulcers and purulent wounds is possible over them.
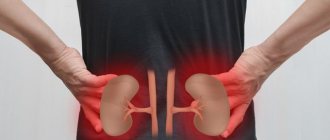
Hyperuricemia is accompanied by frequent exacerbations of concomitant diseases - coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis. If gout complications develop, their characteristic symptoms are added. For urolithiasis, this is nagging pain in the lower back, periodic appearance of blood in the urine, and frequent urination at night. With a prolonged course of chronic tophi gout, the articular cartilage is destroyed, limitation of joint mobility persists outside periods of exacerbation, and complete fusion of the joint space with the formation of ankylosis (complete immobility of the joint) is possible. Depression can also be a consequence of constant pain.
Diagnostics
CT, MRI studies
The Department of Computed and Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Center conducts a wide range of highly informative studies, both to diagnose all pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, and to determine concomitant diseases of other organ systems.
The department has extensive experience, the accuracy of the diagnoses is confirmed by data obtained during operations, which confirms the high qualifications of our radiology doctors, who have degrees of candidates and doctors of science, and 20 years of experience in CT and MR diagnostics of congenital and acquired defects, vascular anomalies , coronary disease, etc. The presence of the latest generation CT and MR tomographs and the latest computer data processing programs in the Center allows, without invasive procedures and hospitalization, to obtain a comprehensive, accurate diagnosis of the pathology of the coronary arteries, cerebral vessels, kidneys, lower extremities, aorta and pulmonary artery , diagnose heart and vascular defects. And also using MRI to evaluate the condition of the myocardium, heart function, blood flow in the heart and blood vessels, diagnose any cardiopathy, identify inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) and scar in the myocardium after a heart attack. Cardiac surgery patients often require dynamic monitoring with CT and MRI to evaluate the results of the operation and determine further treatment tactics. The presence of stents, coronary artery and vascular shunts, conduits, artificial valves and prostheses is not a contraindication to performing MRI of any organ, including the heart. The department also performs CT and MR diagnostics of concomitant pathologies of the brain, chest organs (lungs, mediastinum), abdominal cavity, kidneys, and spine. CT and MR studies of the heart and blood vessels are carried out in adults and older children on an outpatient basis, in comfortable conditions, using modern expert-class equipment. If it is necessary to administer a contrast agent, it is injected into the cubital vein, painlessly and safely, using an injector syringe; before contrast studies, you must refrain from eating and drinking for at least 4 hours; After a contrast study, the patient is advised to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day.
For children under 5 years of age, including children in the first year of life, CT and MRI studies of the heart and blood vessels are performed while the child is in medicated sleep, under the supervision of an anesthesiologist; therefore, in such cases, hospitalization in a hospital for 2 days is necessary.
Contraindications to CT and MRI studies with contrast agents are allergic reactions to contrast agents and renal failure.
The studies are carried out by prior appointment of the patient (via a call center, website or by telephone at the CT and MRI Center department) and a referral from the attending doctor of the clinic, with a clear indication of the purpose and objectives of the study, in the absence of contraindications to the administration of contrast agents.
The research results are provided to the patient or his authorized representative in the form of a conclusion with a description, calculated data and images, in accordance with standardized protocols; If necessary and at the request of the patient, images can be obtained on electronic media, CD/DVD disks, the next day after the examination.
Detailed information and registration for research can be obtained by calling the department, 414-79-01
PET CT
Diagnosis of gout
The diagnosis and treatment of gout is carried out by a rheumatologist, internist or general practitioner (family doctor). Most often, the patient comes not at the onset of the disease, since the symptoms of acute gouty arthritis quickly disappear, which can be regarded by a person as recovery, but during one of the subsequent exacerbations. The doctor conducts a conversation with the patient, during which the fact of an acute joint attack in the past, the presence of characteristic complaints, as well as risk factors for the development of pathology are established. The phenomena of bursitis and tophi - the main objective manifestations of gout - are more often found on the leg. The diagnosis can be confirmed by a comprehensive examination of the body using laboratory and instrumental methods. If gout is suspected, the following tests are performed:
- Clinical blood test. During an attack of gouty arthritis, an acceleration of the COE, an increase in the number of leukocytes and a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left are possible.
- Determination of urate in blood serum. About 70% of patients with an exacerbation of gout have a high level of uric acid - more than 0.42 mmol/l in men and 0.36 mmol/l in women.
- Determination of uric acid in daily urine. The method is used to assess the risk of kidney stones.
- General urine analysis. It is carried out for the purpose of diagnosing diseases of the urinary system that contribute to the development of gout or are its complication.
- Examination of synovial fluid. Biomaterial is collected for analysis using puncture of the affected joint. The presence of monosodium urate crystals in the joint fluid makes it possible to confirm gout, and its sterility during bacterial culture excludes infectious causes of arthritis.
- Microscopic examination of a biopsy sample from tophi. When viewed through a polarizing microscope, urates appear as needle-shaped crystals with a pointed end. This method is also highly specific in diagnosing gout, like the previous one.
Instrumental diagnosis of gout may include research methods such as:
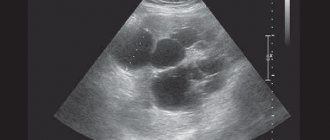
- Ultrasound of affected joints;
- MRI and CT;
- X-ray diagnostics.
X-rays at the onset of the disease are carried out for the purpose of differential diagnosis with other arthropathies, but there are no specific signs of gout. Only when the pathology becomes chronic can one see intraosseous tophi and marginal bone erosions in the photographs.
Ultrasound examination of joints before the development of chronic gout is effective only during exacerbations.
MRI makes it possible to detect tophi inside the joints even before they appear under the skin, making it possible to begin specific therapy for hyperuricemia earlier. The method is used in differential diagnosis with other diseases, as well as to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. CT, in comparison with other imaging methods, allows for more accurate differentiation of tophi masses.
Early diagnosis of diseases: why it is important and why it is needed
Detection of a disease before its initial signs appear is a chance to avoid it altogether, as well as eliminate the risk of developing parallel ailments that have a devastating effect on a person’s performance, psyche, and quality of life. Early diagnosis makes it possible to timely identify and block various dangerous diseases, in particular cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Treating such diseases at an early stage can save lives and significantly save money on their treatment. What is early diagnosis? This is a comprehensive program of tests and research, which a specialist selects individually for each patient depending on his age, gender, and nature of complaints. Early diagnostic methods are studies of various organs in order to determine possible pathologies. The purpose of the method is to: • make the correct diagnosis; • determine the location of the pathology and its level of severity; • check hormone balance; • find out whether there is a lack of vitamins necessary for the body. Who is recommended for regular preventive diagnostics: • People who are overweight, have bad habits, have weak immunity; • Elderly persons; • Persons with chronic diseases; • Workers of hazardous industries; • Citizens living in environmentally unfavorable conditions; • Persons with a hereditary predisposition to certain diseases. A special risk group is people over 40 years of age. Starting from this time, regular examinations for the presence of the beginnings of oncological processes are recommended. For women, this measure is aimed at timely detection of breast cancer, and for men, prostate or testicular cancer. Statistics show that cancer can be successfully cured if it is detected early. Consultations with a mammologist, mammography and ultrasound of the mammary glands can protect against the development of a dangerous disease. Also, all women, regardless of age, must periodically undergo cytological examination. Men are advised to visit a urologist and undergo blood tests for male diseases. In addition, all people, regardless of gender, are not required to be tested for sexually transmitted infections. Married couples who are planning to have a child are recommended to undergo a series of examinations to determine the possible risks of developing pathologies in the fetus and take measures to avoid them. The M-Vita medical center near the Khovrino and Rechnoy Vokzal metro stations offers a wide range of services related to the early diagnosis of various diseases. Patients can choose a convenient time for examinations. At the same time, the time spent on procedures will not harm professional activities. The main goal is to keep your health under control and gain confidence in the future. In the laboratory of the M-Vita clinic, you can undergo tests of varying degrees of complexity, and if problems are identified, the medical center’s specialists are ready to provide competent medical care.
Treatment of gout
The main principle of treating the disease is to reduce hyperuricemia. This is facilitated by changing the patient’s lifestyle and reviewing the diet. Correction of hyperlipidemia, arterial hypertension, hyperglycemia, weight loss and smoking cessation are recommended. A diet for gout involves eliminating foods that are rich in purines or retain them in the body:
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- seafood;
- meat;
- spicy, hot and smoked foods;
- chocolate, ice cream;
- salty cheeses;
- caffeine, cocoa, strong tea;
- alcohol.
Endogenous purines increase when consuming large amounts of animal protein, so the daily requirement for a patient with gout is considered to be no more than 1.5 g per 1 kg of the patient’s body weight. Dairy products with low fat content, such as kefir, cottage cheese, yogurt, help remove uric acid from the body. Polyunsaturated fatty acids, for example, those found in olive oil, have a similar effect. Also, if you have gout, you must follow a drinking regime - at least 2.5 liters of water per day.
It is advisable to begin drug treatment of gout on the first day of the onset of acute arthritis. To stop an attack, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, colchicine and glucocorticosteroid drugs are used locally or systemically. Hypouricemic therapy is prescribed after laboratory and instrumental confirmation of the diagnosis. It is aimed at:
- reduction of uric acid to the target level - 0.36 mmol/l;
- reduction of foci of urate accumulation in the body;
- reduction in the size of tophi;
- reduction in the frequency of attacks of gouty arthritis.
Allopurinol is considered the drug of choice for this. If it is intolerant, it is possible to use a selective xanthine oxidase inhibitor, febuxostat. Losartan, Amlodipine and Fenofibrate also have a moderate uricosuric effect. Diuretics are used with great caution, only for health reasons. Surgical removal of tophi is carried out only when severe complications occur, for example, carpal tunnel syndrome, spinal compression.