Liver cancer is a malignant tumor that quickly grows in size and metastasizes. It may be primary or represent metastases from other organs. The disease is asymptomatic for a long time or manifests itself with nonspecific symptoms.
Yusupovskaya's oncologists diagnose liver cancer using the latest research methods. To treat the disease, the most effective antitumor drugs are used, which have a minimal range of side effects. Surgeons use innovative surgical techniques. Medical staff provides professional patient care.
Causes
Primary liver cancer occurs on average 30 times less frequently than secondary liver cancer. As a rule, a malignant liver tumor occurs against the background of the presence of another oncological process in the body and its metastasis (for example, cancer of the uterus or stomach with metastases to the liver). Liver cancer occurs as often at 30 years old as at 50 and 60 years old - this disease has no age categories. The liver is susceptible to active metastasis due to intense blood circulation in this organ. There are a number of risk factors that influence the formation of malignant neoplasms in the liver:
- chronic inflammation of the liver. Cirrhosis, hepatitis C and B significantly increase the risk of developing cancer in the liver;
- alcoholism. Uncontrolled alcohol consumption destroys liver cells, providing favorable conditions for the formation of malignant neoplasms;
- poor nutrition and, as a result, excess weight. Excessive fat accumulation and slow metabolism increase the risk of cancer. The liver ceases to cope with the volumes of consumed hydrogenated fats and gradually loses its functions;
- hemochromatosis. This diagnosis involves a disorder of iron metabolism in the body, as a result of which its accumulation occurs in the gastrointestinal tract;
- heart failure;
- parasite infection;
- diabetes;
- syphilis;
- cholelithiasis;
- exposure to radiation and oncogenic viruses;
- disruption of the endocrine, lymphatic and circulatory systems;
- disturbances in the functioning of the biliary tract;
- accumulation of the contrast agent Thorotrast in the body. It can persist in the body for many years and eventually cause liver tumors;
- taking medications that have a toxic effect on the liver;
- smoking. Smoking negatively affects human health, and especially the functioning of the liver;
- elderly age. With age, organs stop working as well as in youth - the metabolic rate decreases and the likelihood of developing cancer becomes higher;
- burdened heredity.
Typically, malignant liver tumors develop under the influence of several causes and provoking factors.
Make an appointment
Prevalence and frequency
In terms of frequency of detection, liver cancer ranks 5th among all cancers in men and 8th in women. Primary, that is, one that initially develops from liver cells (hepatocellular liver cancer), is quite rare. Much more often, secondary metastatic cancer is found in the liver. Such cases are detected 20–30 times more than cases of primary cancer.
Liver metastases are approximately 30 times more common than primary cancer. The main tumor is located in another organ. Most often, cancer of the colon and rectum, lung, breast, stomach, pancreas, as well as melanoma and neuroendocrine tumors metastasize to the liver.
Secondary lesions can be located in any part of the liver. Sometimes there is only one metastasis, but in most patients they are multiple, located in both lobes.
Get a treatment program
Symptoms
In the first stages, liver cancer is practically asymptomatic. The patient may be concerned about weakness and fatigue, but this, as a rule, does not raise suspicions of liver cancer. Basically, the tumor begins to appear after spreading beyond the liver or metastasizing to other organs. The main clinical manifestations of liver cancer are:
- pain in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- increased body temperature;
- a feeling of heaviness that worsens after eating;
- causeless weight loss;
- decreased appetite;
- yellowness of the skin and sclera;
- nausea, vomiting, belching of air;
- tendency to diarrhea or constipation;
- palpable hard nodule in the liver area;
- an increase in abdominal volume due to the accumulation of pathological fluid;
- light colored stool;
- dark color of urine;
- anemia;
- skin itching;
- nosebleeds or gastrointestinal bleeding.
In order to establish a diagnosis as early as possible, you should contact a gastroenterologist when the first signs of liver dysfunction appear. After the examination, the patient will be consulted by an oncologist. Early diagnosis of malignant liver tumors allows for adequate therapy that increases life expectancy.
Symptoms in women
Symptoms of liver cancer in women are no different from general symptoms. Doctors say that the danger for females lies in the later manifestations of the disease. Characteristic changes for women are:
- the appearance of male pattern hair;
- deepening of the voice;
- decreased libido;
- lumps in the chest and armpits.
Rehabilitation
For a quick and successful recovery after liver cancer surgery, clinical recommendations are:
- in maintaining vital functions of the body;
- in constant monitoring of liver function and blood counts;
- in careful care of postoperative sutures and drainages;
- in the timely administration of blood substitutes, hemocorrectors and other drugs;
- in adequate intravenous nutrition followed by transition to regular nutrition.
Classification
Primary liver cancer mainly develops from hepatocytes - liver cells, or from bile duct cells. Experts distinguish several types of liver tumors:
- carcinosarcoma;
- sarcoma;
- liver lymphoma. Occurs due to the proliferation of atypical lymphocytes. This neoplasm is distinguished by its rapid growth and spread of metastases to distant organs;
- Hepatocellular carcinoma is an extremely rare form of tumor in the liver. The main cause of this type of cancer is cirrhosis or hepatitis B and C;
- cystadenocarcinoma. The structure of this neoplasm is similar to the structure of a cyst. The main manifestations of the disease are severe, sharp abdominal pain and dizziness. Cystadenocarcinoma tends to grow quickly, as a result of which it often causes compression of neighboring internal organs;
- hepatoblastoma is a tumor characteristic of childhood. Characterized by weight loss with a disproportionate increase in the abdomen;
- cholangiocellular liver cancer (portal liver cancer). A rather rare form of cancer associated with a mutation in the cells of the bile ducts. It is usually detected in the later stages, when treatment no longer brings results;
- angiosarcoma. Liver cancer is the most difficult and practically untreatable cancer. Metastases from angiosarcoma spread very quickly, preventing doctors from stopping or slowing down their growth. The reason for the appearance of this tumor is prolonged contact with poisonous and toxic substances in production;
- liver melanoma. One of the most severe liver tumors. Mainly occurs due to metastasis of another tumor or due to the development of melanoblastoma;
- fibrolamellar carcinoma. This liver tumor manifests itself as severe pain in the epigastrium and upper abdomen if the tumor has grown to a size of 20 centimeters or more. Treatable in early stages;
- undifferentiated sarcoma. In this case, the liver tumor grows and develops rapidly, spreading metastases to neighboring organs. It is often discovered in childhood and has virtually no treatment.
Timely diagnosis ensures a quick diagnosis, which is extremely important for cancer. You should not put off going to the doctor, because this is what can save your life.
Make an appointment
Primary and secondary cancer
In diagnosing liver cancer, in order to select a treatment method, it is important to identify its primary and secondary types.
Primary cancer is a pathology formed in the cellular structures of the gland. We are talking about stages 1 and 2 of the disease.
Primary cancer is:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common;
- Hemangiosarcoma - forms and develops in the blood vessels supplying the liver;
- Angiosarcoma - occurs infrequently, but is characterized by formation in people under 30 years of age;
- Cholangiocarcinoma - occurs in the bile duct;
- Hepatoblastoma – formed during fetal development;
- Hepatocellular carcinoma – more often found in men, appears in the liver epithelium.
A more severe form is secondary cancer. If it is present, metastasis processes are detected, i.e. These are stages 3 and 4 of the disease. As already noted, at this stage the disease is difficult to treat.
Unfortunately, the doctor has to deal with secondary cancer much more often than with primary cancer (95% to 5%), which means that the process of treating a patient causes many problems.
Angiosarcoma of the liver
An extremely aggressive malignant neoplasm that occurs upon contact with toxic chemicals (arsenic, copper, vinyl chloride) and upon exposure to radioactive radiation - liver angiosarcoma. Often, tumor growth begins against the background of accumulation in the body of Thorotrast, which was previously taken as a contrast agent when performing x-ray studies.
The symptoms of angiosarcoma are non-specific - the patient may experience abdominal pain, bloating, fever, loss of weight and appetite. During palpation, a compaction may be felt; during auscultation, the doctor may hear characteristic noises. It is difficult to establish a diagnosis at an early stage of development of the pathological process, since the onset of the disease is not accompanied by clinical signs of a malignant tumor.
Angiosarcoma is detected using the same methods as other types of liver malignancies. X-rays show thorotrast in the liver and spleen. During diagnostic laparoscopy, surgeons perform a biopsy and send areas of pathologically altered tissue for histological examination. Since angiosarcoma is detected at a late stage, patients are given palliative care in a hospice setting.
Liver cancer in ICD
In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, malignant liver tumors are assigned code C22 - “malignant neoplasm of the liver and intrahepatic bile ducts.” This section includes seven subsections:
- C22.0 - hepatocellular carcinoma (hepatocellular carcinoma);
- C22.1 - cancer of the intrahepatic bile ducts;
- C22.2 - hepatoblastoma;
- C22.3 - angiosarcoma;
- C22.4 - other types of sarcomas (tumors of connective tissue) of the liver;
- C22.7 - other specified malignant tumors of the liver;
- C22.9 - unspecified malignant tumors of the liver.
Liver hemangioendothelioma
The clinical picture of liver hemangioendothelioma does not differ from other types of tumors. At first, the disease is asymptomatic, but later characteristic signs of liver cancer appear - yellowing of the skin, fever, weakness, fatigue, sudden and rapid weight loss. Often this disease entails particularly extensive internal bleeding. Scientists attribute this to damage to neighboring blood vessels by neoplasms and deterioration of blood clotting.
Effective methods of treating hemangioendothelioma are:
- radiation therapy. This technique is applied to primary pathology; a repeated course of radiation therapy in case of relapse is ineffective;
- surgical intervention. It is the most effective method of treating liver tumors, as it allows you to eliminate the source of the disease. However, surgery is not a guarantee of complete recovery, since metastases cannot be removed surgically;
- chemotherapy. This method involves the use of drugs that destroy malignant cells. Chemotherapy is fraught with a deterioration in the patient’s general well-being and is mainly used in cases of inoperable recurrent tumor.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital Oncology Clinic use only the most modern treatment methods in their practice, which can improve the patient’s quality of life.
About the disease
A malignant formation is formed from hepatocytes and endothelium of blood and lymphatic vessels. According to statistical studies, the disease ranks 7th in the structure of cancer formations. Every year, more than 790 thousand new cases are diagnosed worldwide. Secondary metastatic neoplasms occur approximately 20 times more often than primary cancer. The disease progresses aggressively with a poor prognosis - without timely treatment, life expectancy does not exceed 1-2 years.
Causes
The reasons that provoke the development of liver cancer are a number of pathologies:
- viral hepatitis B, C, D, F;
- chronic diseases of the liver and biliary tract (cirrhosis, cholelithiasis, hemochromatosis);
- toxic damage to the liver by combustion products of oil and its derivatives, coal, household garbage, excess oils when frying fish and meat;
- abuse of alcohol and tobacco products;
- toxins from fungi and molds growing on grains, nuts and fruits with a high oil content;
- taking anabolic steroids and hormonal contraceptives;
- autoimmune diseases;
- diabetes;
- syphilis;
- poor nutrition.
The development of the disease is also facilitated by genetic predisposition and parasitic infection.
Types of Liver Cancer
The classification of a neoplasm depends on the type, location, stage, severity, and presence of metastases. A distinction is made between primary oncology, which develops directly in the liver, and secondary, caused by metastasis from another organ. Primary cancer is divided into types:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma . Formed as a result of the degeneration of hepatocytes, it is diagnosed in 70-90% of the total number.
- Fibrolamellar carcinoma. Children and persons under 35 years of age are susceptible. Affects small areas without affecting the entire organ. With timely diagnosis, there is a high chance of successful treatment.
- Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (Klatskin tumor). Affects the bile ducts.
- Cystadenocarcinoma . Diagnosed mainly in women, due to malignancy of a benign cystadenoma or congenital cyst. It has a polycystic structure with localization in the right lobe.
- Hepatoblastoma . Develops in children under 4 years of age. With early diagnosis, there is a high survival rate (more than 90%).
- Angiosarcomas and hemangiomas . The blood vessels of the liver are affected. They are characterized by rapid growth and are usually diagnosed in late stages.
Metastases
Metastases are the main danger of any cancer, since they are almost impossible to stop or prevent their spread.
Metastases of primary liver cancer can spread to the stomach, brain, lungs, esophagus, veins and arteries, heart muscle, blood vessels, bones and spine. Metastases from the liver enter the body in the following ways:
- through lymph flow;
- through the circulatory system;
- through growth beyond the liver and damage to neighboring tissues and organs.
Unfortunately, metastases occur in 40% of liver cancer cases and often affect vital organs, which are subsequently extremely difficult to treat.
Risk factors
Regardless of whether liver cancer has metastasized or not, it is still necessary to resort to urgent treatment. It is important to diagnose a malignant tumor on time. Therefore, a routine medical examination never hurts. There is a group of people who are more predisposed to developing this cancer. The most common form of liver cancer is a consequence of cirrhosis. Other risk factors include:
- excess weight.
- diabetes mellitus (type 2).
- use of anabolic steroids.
- exposure to toxic substances (aflatoxin, vinyl chloride, arsenic).
- smoking addiction.
- certain rare diseases (tyrosinemia, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, porphyria cutanea tarda, etc.)
Complications
The uncontrolled course of liver cancer is dangerous due to the occurrence of complications. Their appearance depends on many factors. Possible complications include:
- bleeding from the tumor;
- suppuration of the tumor focus;
- impaired outflow of bile due to compression of the bile ducts;
- circulatory disorders due to compression of the abdominal organs by large tumor sizes;
- ascites.
The listed symptoms require immediate diagnosis and surgical intervention. Without this, death is possible.
Make an appointment
Kinds
Primary liver cancer is divided into the following types:
- hepatocellular - formed from hepatocytes - cells of the liver parenchyma;
- cholangiocellular - from epithelial cells of the biliary tract;
- fibrolamellar – growing from fibrous tissue cells, usually found in children and young people up to 35 lei;
- cystadenocarcinoma is a tumor formed from a congenital cyst and is characteristic mainly of women;
- angiosarcoma - a neoplasm from the cells of the hepatic vessels, characteristic of elderly people who have been in contact with arsenic compounds, vinyl chloride and other toxic substances for a long time;
- hepatoblastoma is a tumor that develops in children under 4 years of age from liver blast cells;
- undifferentiated sarcoma is a type of cancer with a very rapid progression and extremely difficult to treat.
Diagnostics
Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination that allows you to quickly establish a diagnosis of liver cancer and verify the type of tumor. It includes the following studies:
- Complete blood count – the number of leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases;
- Biochemical blood test - the level of bilirubin, ALT, AST increases;
- Determination of the level of specific tumor antigen (tumor marker) ACE.
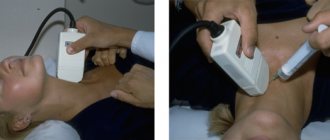
Using ultrasound, which is performed using expert-class equipment with high resolution, the location and size of the tumor are determined. Ultrasound is used both for primary diagnosis and for the purpose of dynamic monitoring of the condition of the tumor.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are performed to clarify the size of the formation, the degree of invasion into surrounding tissues and organs, and distant metastases.
Laparoscopy is performed to clarify the spread of the tumor process. During the examination, the surgeon performs a biopsy - sampling tissue sections for histological examination.
Stages
Determining the stage of the disease using clinical, instrumental and laboratory tests allows doctors at the oncology clinic to develop optimal tactics for patient management.
- In the first stage of liver cancer, the size of the tumor does not exceed two centimeters. There are no clinical symptoms. In some cases, patients experience increased fatigue and discomfort in the right hypochondrium.
- At the second stage of the disease, the size of the tumor reaches five centimeters. Invasion of atypical cells into blood vessels is observed. Patients are bothered by heaviness and dull aching pain in the right hypochondrium. As the pathological process progresses, the pain intensifies.
- The third stage of liver cancer is accompanied by the spread of the tumor to other organs and tissues. Severe pain syndrome forces the patient to see a doctor.
- Stage four liver cancer is characterized by multiple metastases to other organs. Due to increased pressure in the portal vein, the veins on the anterior wall of the abdomen and chest dilate. Patients are concerned about severe pain and constipation. Their abdominal volume increases due to the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity, body weight decreases, and emotional lability occurs.
Treatment
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital Oncology Clinic take an individual approach to the choice of treatment methods for each patient diagnosed with liver cancer. The complex of treatment measures depends on the following factors:
- location of the pathological focus;
- stage of tumor development;
- presence or absence of metastases;
- patient's condition;
- accompanying illnesses.
The decision on the need and expediency of a particular method of therapy is made after a thorough diagnosis. Treatment for liver cancer includes:
- Medications. The active ingredients of medications have a toxic effect on cancer cells. In this case, healthy tissues are not damaged. Chemotherapy for liver cancer has no curative effect.
- Radiation therapy. Local impact on the tumor leads to a decrease in its size. As a result, the pain syndrome decreases. Radiation therapy is used at all stages of liver cancer treatment.
- Ablation. The essence of the method is the introduction of ethanol into the tumor formation. Then the pathological focus is exposed to microwave radiation. Ablation is effective for liver cancer that is less than 3 cm in diameter.
- Vascular embolization. Blood circulation in the tumor area is disrupted due to the introduction of special drugs into the vessels. As a result, the formation decreases in size. Vascular embolization is effective for tumors up to 5 cm in diameter. This method is often used in conjunction with other types of liver cancer treatment.
- Surgical intervention. In the presence of operable cancer, tumor removal or liver transplantation is indicated.
About the treatment of liver cancer at Euroonco
Treatment of liver cancer is generally one of the most difficult tasks in oncology. I learned this when I was diagnosed with T2N0M0 - the second stage of liver cancer in the regional center. This was very unexpected, since apart from fever and complete loss of appetite, I did not have any special symptoms at all. The doctor is a good friend of mine and based on some of his symptoms, he sent me for a blood test for alpha-fetoprotein and an ultrasound. Based on the results, he advised me to go to a good private oncology clinic. I chose Euroonco. And he did absolutely the right thing. There they examined me further and found out that there was only one lesion, albeit a large one, and the tumor itself did not extend beyond one third. The resection was performed by Dr. Pylev. Everything went very well. As for how I feel, everything is fine. I know that everything will be fine. Thank you!
What diet is recommended for liver cancer?
The diet for malignant liver tumors should be varied, include all the necessary nutrients, vitamins and minerals, and correspond to the functional capabilities of the liver. Malnutrition is a very common problem in hepatocellular carcinoma, but it is not always given the attention it deserves. Due to the fact that the patient’s body does not receive the necessary substances, the quality of life decreases and the prognosis worsens.
In such patients, nutritional status should be regularly monitored. They need a special diet that is as complete as possible, but at the same time does not put extra stress on the liver. The patient should receive:
- Sufficient amount of protein: 1–1.5 g per kilogram of body weight.
- Sufficient amount of fats, at least 50% of which must be of vegetable origin.
- Sufficient amount of carbohydrates.
Liver cancer patients are advised to eat lean meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, various vegetables and fruits, grains, beans, cereals, olive oil and corn oil. Drinks allowed are juices, water, and milk. Products must be prepared by boiling or baking: fried foods are contraindicated. You should try to completely eliminate salt: use various spices instead. Preservatives, chemical additives, and alcohol are prohibited. If liver function is severely impaired, protein foods should be limited as much as possible.
The main principle of creating a diet for the treatment of liver cancer, as well as for any other cancer, is variety, completeness, and naturalness. This means that the patient should fully receive all the necessary substances and microelements necessary for the functioning of the body. At the same time, food should put as little stress on the affected liver as possible. In such conditions, the patient menu looks something like this:
- Fruits, berries, juices from them and vegetables, except tomatoes - without restrictions. Particular attention should be paid to beets - a very healthy product for the liver.
- Soups - milk, cereal, vegetable.
- Products of lactic acid and mixed fermentation.
- Sea fish and seafood.
- White meat.
- Bread made from wholemeal wheat flour.
- Cereal flakes, nuts, grain sprouts, herbal infusions and green tea.
How long do people live with liver cancer?
Doctors focus on the five-year survival rate. It refers to the percentage of patients who are alive 5 years after their cancer diagnosis. Five-year survival depends on the stage of the tumor:
- For a localized tumor limited to the organ (liver cancer stages 3, 2 and 1) - 31% (for liver duct cancer - 15%).
- For a tumor that has spread to neighboring organs and lymph nodes (stages IIIC and IVA) - 11% (for liver duct cancer - 6%).
- For liver cancer with metastases - 3% (for liver duct cancer - 2%).
Is prevention possible?
Since the main risk factor for liver cancer is infection—viral hepatitis B and C—prevention measures should primarily be aimed at preventing infection. The main risk factors: promiscuous and unprotected sexual intercourse, injections with unsterile, used needles.
Reducing the risk of liver diseases, including cancer, helps to give up bad habits, maintain a healthy weight, timely treatment and observation by a doctor for hemochromatosis and other hereditary diseases that increase the risk of cancer.
Nutrition
The patient's condition improves with a special diet. The cooks at the Yusupov Hospital prepare dishes from high-quality products that do not contain nitrates, GMOs or carcinogenic food additives. In case of uncontrolled weight loss, increase daily caloric intake at the expense of protein products. When preparing dishes, preference is given to gentle culinary technologies: boiling, stewing, steaming and grilling, baking in the oven.
The following foods are excluded from the patient's diet:
- store-bought sauces;
- smoked meats and pickles;
- rich broths;
- margarine and other heavy fats;
- fresh baked goods;
- alcoholic drinks;
- strong tea and coffee.
Forecast
Since liver cancer is often diagnosed at the final stage of the tumor process, the prognosis for recovery is pessimistic in most cases. Palliative therapy is aimed at reducing the severity of symptoms of the disease and alleviating the general condition. In the presence of concomitant pathologies, death occurs 6 months or 1 year after diagnosis. The average life expectancy after the onset of this disease is about 2 years with properly selected effective treatment.
Prevention
You can reduce your risk of developing liver cancer by following the following medical recommendations:
- exclude alcoholic drinks;
- control weight;
- observe safety precautions when working with toxic substances;
- avoid unprotected sexual intercourse;
- do not take drugs;
- apply tattoos or make-up only in trusted salons;
- Vaccine against hepatitis B on time;
- undergo an annual preventive examination with a doctor.
Treatment of liver cancer at the Yusupov Hospital is prescribed by qualified oncologists depending on the nature of the tumor, its type and stage. All therapeutic procedures are carried out under the strict supervision of medical personnel, ready to provide assistance at any moment. In our clinic you can undergo any types of examinations using professional modern equipment.
Make an appointment
Patient reviews
| More information about liver cancer treatment at Euroonko: | |
| Liver cancer treatment | |
| Oncologist-gastroenterologist | 5100 rub. |
| Emergency oncology care | from 12100 rub. |
Bibliography:
- The prognostic value of tumor cells blood circulation after liver surgery for cancer lesions - Patiutko IuI, Tupitsyn NN, Sagaĭdak IV, Podluzhnyĭ DV, Pylev AL, Zabezhinskiĭ DA. — Khirurgiia (Mosk). 2011. [1]
- Surgical and combined treatment of multiple and bilobar metastatic affection of the liver. — Patiutko IuI, Sagaĭdak IV, Pylev AL, Podluzhnyĭ DV. — Khirurgiia (Mosk). 2005. [2]
- Modern approaches to the treatment of colorectal cancer metastases in the liver - A. L. Pylev, I. V. Sagaidak, A. G. Kotelnikov, D. V. Podluzhny, A. N. Polyakov, Patyutko Yu.I.,.. - Vestnik surgical gastroenterology - Number: 4, 2008 Pages: 14–28.
- Ten-year survival of patients with malignant liver tumors after surgical treatment - Yu. I. Patyutko, A. L. Pylev, I. V. Sagaidak, A. G. Kotelnikov, D. V. Podluzhny, M. G. Agafonova, - Annals of Surgical Hepatology 2010.
- Surgical and combined treatment of patients with metastatic liver and lymph nodes invasion by colorectal cancer — Patiutko IuI, Pylev AL, Sagaĭdak IV, Poliakov AN, Chuchuev ES, Abgarian MG, Shishkina NA. — Khirurgiia (Mosk). 2010. [3]
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78