Compound
Each filter bag contains 1.5 grams of plant material from bearberry leaves in powder form.
The leaves of the plant contain 8-25% ericoline arbutin glycoside ), about 30% tannins of the pyrogall group, flavonoids ( isoquercitrin , quercetin , hyperoside , quercitrin , myricitrin and myricetin ), ursolic acid , hydroquinone in free form, essential oils and a number of acids ( ascorbic acid , formic acid , cinchonic acid ). The leaves contain a fairly large amount of iodine , essential amino acids and nitrogenous substances.
History and scientific research of bearberry
- The first mentions of the medicinal properties of bear's ear date back to the 12th century - then it was already used in England: in the Old English medicinal book “Meddygon Myddfai” a description of the properties of the plant is given.
- In medieval medicine of the Armenian peoples, torment was used as an astringent for diarrhea and hemoptysis.
- Bearberry received recognition in Germany as a medicinal plant only in the 18th century.
The German public health service recognizes bear's ear as one of the effective remedies for the treatment of inflammatory processes of the urinary tract.
- Instructions for the use of bearberry in scientific and practical medicine in France date back to the 20s. 20th century The famous herbalist in this country, Leclerc, recommended the plant as a diuretic and anti-inflammatory drug for pathologies of the kidneys, bladder and prostatitis.
- In folk medicine of Siberia and the North of Russia, bearberry was used for pathologies of the urinary system, for the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases - syphilis and gonorrhea. Moreover, in a number of localities in Russia the plant is still used for this purpose.
- In Lithuanian folk medicine, the plant was used in the treatment of chronic diarrhea, hypertension, neuroses, to tone the body, and eliminate inflammatory processes.
- Tibetan healers use the leaves of the plant for heartburn, Graves' disease, and gastritis.
- Ukrainian herbalist Nosal V. recommends plant preparations for urinary incontinence at night in children.
- Czech scientists have developed a technology for culturing mesophilic cells of bearberry leaves. However, arbutin and other phenol glycosides do not accumulate with this method, and the active base is represented by triterpene compounds derived from oleanolic acid.
- In 1974, at the Chemical-Pharmaceutical Institute of St. Petersburg, a method was developed for obtaining a liquid concentrate from a plant leaf that contained up to 15% arbutin. In experiments conducted on laboratory rats, it was found that the drug increased diuresis by 37%.
- In vitro experiments have proven that plant leaf extracts inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus aureus, Enterobacter aerogenes, Enterococcus faecalis, Bacillus subtilis, Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli, Proteus vulgaris, Proteus mirabilis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Serratia marcescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus mutans and Mycoplasma hominis .
- In 2001, Japanese scientists found that bearberry extract increases the sensitivity of St. aureus (methicillin-resistant strains) to β-lactam antibiotics.
pharmachologic effect
Bearberry leaves contain a number of organic acids and a set of flavonoids , but the main therapeutic effect is provided by the arbutin glucoside contained in the plant. After entering the human body, arbutin, as a result of hydrolysis, breaks down into hydroquinone (diatomic phenol) and glucose. Hydroquinone has an antiseptic effect and has a diuretic and diuretic effect .
The most active process of arbutin breakdown is observed in the urinary tract (alkaline hydrolysis, contact with uric acid), therefore the main properties of bearberry leaves are used in the treatment of nephrological pathologies ( pyelitis , nephritis , urethritis , cystitis and other inflammatory processes in the bladder or renal system) . The medicinal properties of bearberry leaves have also been used for diseases of other organs and systems ( gastritis , goiter , etc.).
Bearberry decoction contains tannins, which have an astringent effect in the digestive tract. Experiments on rats showed that the plant is also an antihypoxic agent (the survival rate among animals increased under hypoxic ).
Hydroquinone is able to increase the activity of redox processes. Under its influence, O-methyltransferase is blocked, which makes it possible to prolong the action of adrenaline . Experimental studies have shown that hydroquinone has a positive effect on metabolism, the ability of tissue to absorb oxygen, normalizes the level of glutathione , potassium and glucose in the blood, neutralizes diabetic ketoacidosis , and in a number of shock states exhibits a hypertensive effect .
Bearberry: contraindications for use
Bearberry herb has some restrictions for use. Before starting treatment, you should definitely talk to your doctor. During the consultation, the doctor will tell you what bearberry is, what it helps with, and how it should be taken correctly.
Based on urine and blood tests, the doctor will give permission or prohibition to use the herb. It can only be consumed under the supervision of a specialist, strictly following the prescribed dose.
Bearberry leaf has the following contraindications:
- lactation;
- renal failure;
- short-term constipation;
- allergy;
- individual intolerance to plant components.
Additionally, bearberry is prohibited for children under 12 years of age. If you use a large amount of the product, serious side effects may occur:
- nausea and gag reflexes;
- fever;
- pain in the back;
- diarrhea;
- dehydration of the body;
- worsening inflammation;
- the appearance of vascular fragility;
- decreased cardiac tone;
- blood pressure disorders.
When used correctly in combination with classical medicine, medicinal decoctions from bearberry will help get rid of the symptoms of diseases and reduce the damage done to the body.
You should know that bearberry, a photo of which is easy to find on the Internet, is not taken together with antibiotics. The use of tinctures from the plant with alcohol during a diet for weight loss can provoke disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys. Despite the fact that bearberry extract does not stop the effect of vitamin complexes, it removes them along with the liquid. Therefore, be sure to discuss their combination with your doctor.
Bearberry, the use of which has a positive effect on the body at the correct dosage, is also not recommended for use if:
- perforated ulcer;
- acute urolithiasis problems;
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- leukemia;
- advanced psoriasis;
- disturbances in the functioning of excretory processes;
- excessive body weight.
Bearberry can be prescribed to pregnant women, but the course is selected on an individual basis, since a double load is placed on the female body. The herbal medicine is prescribed, but with a reduced dosage.
Bearberry leaves, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
The medicinal plant is used in medicine in the form of a decoction or infusion 40 minutes after eating. Depending on the severity of the underlying disease, 45-75 ml per day is prescribed. Duration of therapy is 20-25 days. The course can be repeated after 10 days. You can take no more than 4 courses per year. It is recommended to shake the decoction and infusion thoroughly before ingestion. The prepared solution can be stored for 2 days in a cool place.
Preparation of the decoction: 1 filter bag is placed in a special container (glass, enamel), poured with boiled hot water in a volume of 200 ml and covered with a lid. Keep in a boiling water bath for 30 minutes. After cooling, the solution is filtered and the plant material is squeezed out. The volume of the resulting solution is adjusted to 200 ml with boiled water. The infusion is prepared according to a similar scheme, only heating is carried out for 15 minutes, and cooling until squeezing and filtering is carried out for 45 minutes.
Bearberry description of appearance
Photo: Yandex.Pictures
Bearberry is an evergreen creeping subshrub, its creeping shoots can reach a length of up to 1.3 meters.
Bearberry has oblong, ovate leaves. Their length is from 1 to 2 centimeters and their width is 4–8 millimeters. The leaves are thick, leathery with short petioles.
The top of the leaf is dark green, shiny, with visible veins. The lower part of the leaf is lighter.
The flowers are small, white-pink, and pitcher-shaped. The anthers of the stamens are dark red, jagged along the edge, and pubescent inside. At the ends of the branches, the flowers are collected in clusters into drooping inflorescences.
Bearberry fruits are small red-wax-colored spherical berries. They are the size of lingonberries, or slightly larger. The berries have a fresh, sweet, tart-sour taste. Bearberry blooms from April to June, and the berries ripen closer to autumn.
Bearberry is not a poisonous plant, but its berries are inedible.
Analogs
Level 4 ATX code matches:
Renel
Samprost
Lingonberry leaves
Uriflorin
Gentos
Bioprost
Testis compositum
Birch buds
Lespefril
Prostopin
Lespeflan
Phytonephrol
Lespenefril
Canephron N
Vitaprost Forte
Vitaprost Plus
Vitaprost
Brusniver
Speman Forte
Speman
Uriflorin.
What it looks like and where it grows
Bearberry is a perennial evergreen plant that belongs to the Heather family.
- The shrub is low-growing: from 5 to 30 centimeters in height.
- Thin fluffy stems of brownish-green or brownish-red color branch, lie on the ground, take root on their own and form new growth - a creeping carpet. The length of the stems reaches one and a half meters.
- The oblong leaves of the grass are obovate in shape, tapering towards the base, and rounded at the top. They are attached to the stem using a short cutting. The leaves are dark green, with a pronounced shine on top, matte and lighter below. Visible veins appear on them. Arranged alternately. After two years they die, fall off, and new ones grow in their place.
- The plant blooms in April, the flowering period ends in June. It is interesting to watch the bearberry bloom. Small white and pink flowers are collected in tassel inflorescences that droop to the ground. The corolla of the flower is in the form of a jug with stiff hairs inside and has five folded denticles. The “pitchers” are pollinated by large insects, generously sharing nectar and pollen with them.
- The drupe berries of the grass ripen in late summer - early autumn. The dark red fruits, 0.5 cm to 1 cm in diameter, contain a mealy, dry pulp reminiscent of oatmeal - hence the name - with five seeds.
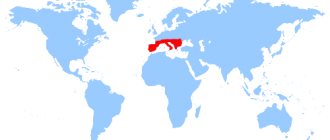
Northern Europe, North America are the places of distribution of the plant. Bear berries are found in the center and south of Europe: in the Alpine mountains, on the Balkan Peninsula, and the Apennine Peninsula. In Russia, bearberry has chosen the Center, the Urals, Siberia, the Caucasus, and the Far East. Bear's ear grass grows in sandy areas of the tundra. The plant prefers sandy soils with good access to sunlight. In addition to sunlight, the bear's ear needs enough moisture. Insufficient moisture affects the growth of the plant - it slows down: the leaves of the grass become coarser and brown, the stems dry out.
For development and growth, bearberry needs the soil to be enriched with mycorrhizal fungi, because the plant contains endotrophic and exotrophic mycosis.
Bearberry is found in pine forests, deciduous forests, among sparse birch-larch crops, in clearings, burnt areas, and chooses seaside rocks and gravelly areas. The bear's ear does not like competitors, so it forms entire clumps and displaces other plants from its range. Gardeners and landscape designers appreciated the decorative properties of the unpretentious plant. Bear ears are used to decorate embankments, grottoes, and slopes in park areas. Rock gardens and botanical gardens cannot do without plants.
How to distinguish bearberry from lingonberry
Upon careful examination of the two plants, it becomes clear what the difference is between bearberry and lingonberry.
- Lingonberries choose moist, fertile soil, while bearberry can grow on dry, poor soil.
- The height of the bushes is different: lingonberry grows only up to 15 centimeters, bearberry - twice as tall.
- The root system of the bear's ear does not cooperate with fungi; in lingonberries, mycorrhiza of the fungus and the root is possible.
- The leaves of plants differ from each other. In bearberry they are stringy, reminiscent of bear ears - which is implied in one of the names. Lingonberry leaves are more elongated, the lower surface is strewn with dark speckles.
- Bearberry fruits are insipid and lack taste. Lingonberries have sweet and sour berries. Their shape is also different: spherical for the lingonberry, with a small hole in the center for the bear’s ear. The ripeness of lingonberry fruits is determined not only by their red color, but also by their softness. In bearberry, ripe berries remain firm.
There is a chemical way to test dried medicinal raw materials. A grain of iron sulfate is added to the water infusion. The red color of the mixture will indicate that the infusion is made from bearberry. Ferrous ammonium alum will make the bear's abalone infusion dark blue, and the lingonberry infusion - black and green.
Is it possible to eat bearberry berries?
Due to the unpleasant taste of the bear's ear berries, they are not eaten. This is good because they are dangerous for humans - you can be poisoned by them. Excessive consumption of leafy infusion of the herb also leads to unpleasant consequences: digestive disorders, poisoning.
Reviews of Bearberry Leaves
Infusion and decoction allow you to quickly relieve the unpleasant symptoms that accompany most diseases of the urinary tract: itching and pain when urinating, discomfort in the lumbar region. Patients note a significant improvement in overall well-being after the first doses of the solution. Reviews of allergic responses in predisposed patients are rare. Bearberry leaves are a good addition to the main treatment of urinary tract diseases.
The difference between bearberry and lingonberry
Photo: Yandex.Pictures
The fact is that bearberry is very similar to lingonberries, one might say they are similar, like twins. But there is still a difference!
- There are no dots on the underside of the bearberry leaf.
- At the base the leaves are more elongated and narrowed.
- The edges of the sheet are not folded.
- Bearberry berries are denser, have a seed inside, and look mealy when crushed.
Price for bearberry leaves, where to buy
The cost of 1 package of filter bags in Russia is about 100 rubles. The price may vary depending on the number of bags of raw materials, the region of sale and the pharmacy chain selling the medicinal product.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
ZdravCity
- Bearberry leaves powder 1.5 g 20 pcs. Ivan-tea JSC
64 rub. order - Bearberry leaves PharmaColor 1.5g filter pack. 20 pcs. JSC Krasnogorskleksredstva
74 RUR order
- Bearberry leaves PharmaColor pack 50 g JSC Krasnogorskleksredstva
74 RUR order
- Bearberry leaves crushed pack 50 gIvan-tea JSC
64 RUR order
show more
Side effects and special instructions
When treated with plant preparations in large doses, there may be an exacerbation of inflammatory phenomena in the urinary organs and the development of renal symptoms, which is associated with prolonged irritation of the renal tubules.
It is also possible to develop vomiting, nausea, chills, fever and diarrhea.
- To reduce the likelihood of side effects when treating bearberry, it is recommended to use it in combination with plants (in the form of collections) that have anti-inflammatory and diuretic properties.
- Also, during the period of treatment of urinary tract pathologies with plant preparations, protein products should be excluded, since they oxidize the urine. The bulk of the diet should be plant foods. To ensure that the urine pH remains alkaline, before taking bearberry preparations, you need to drink a solution prepared from 1 glass of water and 1 tsp. soda
- During treatment, you should not take medications that contain alkalis and alkaloids.
Bearberry in cosmetology
In cosmetology, the leaves of the bear's ear herb are actively used to maintain beauty, youth of skin and hair. The plant removes pigmentation, brightens the skin and fights its problems, strengthens the hair.
- To remove pigmentation, use a decoction: 3 tbsp. spoons of grass leaves are poured with half a liter of water, heated in a water bath, and filtered. The cooled broth is used to wipe the areas with pigmentation several times a day.
- A decoction of the leaves of the plant can be used to wipe inflamed areas of the skin.
- For the face, the antioxidant quality of bearberry is used, which helps protect the skin from dryness, fight fine wrinkles, revitalize and rejuvenate it.
- To strengthen hair, use a decoction of the leaves of the bear's ear herb, which is used to rinse your hair after washing.
- Using a concentrated infusion of plant leaves, hair is lightened.
The cosmetic industry produces cosmetics based on bear's ear. For example, Clean Line has a cream that caters to dry, sensitive skin. "Credo Natural" produces a cream for cleansing pores.
Diuretic collection
Excess fluid is removed from the body using a diuretic mixture consisting of bear's ear leaves (2 parts) and juniper fruits (1 part). A tablespoon of the composition is poured into 250 ml of hot water, infused for 20 minutes, and filtered. To prepare a diuretic collection, you can take bear's ear leaves (3 parts), licorice roots (1 part), cornflower flowers (1 part). One tablespoon of plant material is scalded with 300 ml of boiling water and infused for about half an hour. The infusion is taken 15 ml three times a day on a full stomach.
Botanical description
Bearberry is a perennial evergreen low shrub. The stems are creeping (30-150 cm), highly branched with reddish-brown bark that peels off easily, bearing numerous branches (especially at the ends). Young branches are green or greenish-brown, finely pubescent.
Bearberry leaves are alternate, small, shiny, thick, leathery, entire, obovate, with a rounded apex, tapering towards the petiole. Wrinkled on both sides with depressed reticulate veins. Length: 1-2 cm, width: 0.5-1.2 cm. Color: dark green above, lighter below. Life expectancy is 2 years, by the end of the third they die.
Bearberry flowers are small, pitcher-shaped on short pedicels, collected in groups of 2-10 in drooping racemes at the tops of the shoots. Color: white, pale pink.
The fruit is a round drupe with 1-5 seeds. Taste: fresh-sweet, mealy. Color: red.
Bearberry blooms in May-June, the fruits ripen in July-August. It reproduces mainly vegetatively, less often by seeds.
Bearberry Traditional medicine recipes
For nervous diseases
Collecting bearberry and motherwort has a good effect as a sedative for various diseases of the nervous system. 1 tbsp. pour 600 ml of bearberry leaves and motherwort grass. water, bring to a boil and simmer over low heat until a third of the liquid has evaporated. Strain.
This is a daily portion that should be drunk, divided into three doses.
For prostatic hypertrophy
Bearberry leaf powder, take 1 tsp. in the morning on an empty stomach and in the evening before bed.
For cystitis
Make a collection of the following medicinal plants: bearberry (leaves) - 25 gr., hernia - 25 gr., parsley - 5-7 gr., celandine (grass) - 5 gr.
Pour 350 ml of raw materials. boiling water, cover with a lid, insulate and leave for 40-50 minutes. Strain.
Take 50 ml. three times a day before meals. The course of treatment is 10 days.