The relevance of optimizing treatment regimens for asthenic conditions is associated with their wide prevalence both among patients with mental disorders - 15-18% [1, 2] and among patients in the general somatic network - 9.2-65% [1, 3]. Asthenia occurs in the structure of a number of psychopathological syndromes: depression, conditions considered within the framework of neurotic, stress-related and somatoform disorders, as well as pseudoneurotic disorders in schizophrenia. Accordingly, when choosing treatment regimens for asthenic syndrome, the determining factor is the nature of the underlying disease (for affective pathology, the drugs of choice are antidepressants, for schizophrenic disorders - atypical antipsychotics).
Asthenic syndrome is a significant destabilizing factor that affects performance and social adaptation. One of the main complaints in asthenic disorders of any etiology is difficulties in concentrating and concentrating, decreased focus of thinking. In this regard, it is important to prescribe drugs from the group of nootropics. Pharmacological effects such as improving memory, increasing mental and physical performance, a moderate activating effect in combination with neuroprotective effects are especially relevant in the treatment of patients with asthenic complaints. In these cases, nootropics can be combined with both antidepressants and antipsychotics.
In connection with the above, it seems advisable to use the drug nooclerin (deanol aceglumate), which has nootropic, neurometabolic, as well as psychoharmonizing and mild antiasthenic effects [4, 5] for the correction of asthenic and cognitive disorders as part of the complex therapy of borderline mental pathology.
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness and tolerability of nooclerin in patients with asthenic syndrome and impaired cognitive functions in the structure of mental pathology of the borderline circle.
Objectives of the study: 1) evaluate the effect of nooclerin on the dynamics of asthenic disorders; 2) evaluate the effect of nooclerin on the dynamics of cognitive functions; 3) to study the tolerability and psychotropic effects of nooclerin used in combination with other drugs (antipsychotics, antidepressants, tranquilizers) in the treatment of asthenic syndrome as part of the underlying disease.
Deanol aceglumate
International name of the medicinal substance:
Deanol aceglumate The list of drugs containing the active substance Deanol aceglumate is given after the description.
Pharmacological action:
Nootropic drug, chemical structure is close to natural brain metabolites (GABA, glutamic acid).
It has a cerebroprotective effect, restores mental activity, improves learning, facilitates the processes of fixation, consolidation and reproduction of a memory trace. Stimulates tissue metabolism processes, increases the amplitude of the transcallosal potential, improves the organization of the basic EEG rhythm and smoothes out interhemispheric asymmetry. It has a positive effect on neurotic conditions in elderly and senile people that have developed against the background of organic brain failure; with alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Pharmacokinetics:
TCmax in the central nervous system after oral administration is 0.5-1 hour, penetrates into the liver, lungs, heart, and kidneys in smaller quantities. T1/2 - 24 hours, excreted by the kidneys.
Indications:
Astheno-depressive states (borderline states, psychoorganic syndrome, schizophrenia, alcoholism);
neuroleptic syndrome (correction of mild and moderate manifestations); alcohol withdrawal syndrome (with a predominance of somatovegetative and asthenic disorders); intellectual-mnestic disorders; psychosomatic disorders; the period of convalescence after a TBI; vascular diseases of the brain (especially in elderly and senile people). Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity, infectious diseases of the central nervous system, febrile conditions, blood diseases, psychotic conditions, renal and/or liver failure, epilepsy, pregnancy, lactation.
Side effects:
Allergic reactions, headaches, sleep disturbances, constipation, weight loss, itching, in some cases - depression (in the elderly). Overdose.
Symptoms: increased side effects. Treatment: discontinuation of the drug, taking activated carbon. If necessary, hospitalization. Interaction: The
effect of drugs that stimulate the central nervous system may be enhanced.
Special instructions:
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Preparations containing the active substance Deanol aceglumate:
Demanol, Nooclerin
The information provided in this section is intended for medical and pharmaceutical professionals and should not be used for self-medication. The information is provided for informational purposes only and cannot be considered official.
Material and methods
An open, controlled, randomized study was conducted at the Department of Borderline Mental Pathology and Psychosomatic Disorders of the Scientific Center for Mental Health (NCMH).
60 patients with asthenic and cognitive disorders comorbid with mental pathology who were undergoing inpatient treatment were examined.
Inclusion criteria:
1) men and women aged 18 to 65 years; 2) the presence in patients of clear manifestations of asthenia, such as fatigue, weakness, increased irritability, drowsiness; 3) impairment of cognitive functions: decreased memory, attention, productivity of thinking; 4) patients with the following mental pathology when diagnosed according to ICD-10: category F48.0 - neurasthenia; pathology of the affective spectrum from the headings F32 (depressive episode), F33 (recurrent affective disorder), F34.1 (dysthymia) and other pathology from the heading of chronic affective disorders; conditions classified as neurotic, associated with stress and somatoform disorders (F40-F49); personality disorders (PD), accompanied by severe asthenic symptoms (somatopathic PD); pseudoneurotic syndrome (schizotypal disorder - F21); 5) informed consent signed by the patient to participate in the study.
Exclusion criteria:
1) acute mental pathology; 2) organic mental pathology; 3) somatogenic asthenia (asthenia caused by somatic pathology); 4) concomitant somatic pathology in the stage of decompensation; 5) addiction to psychoactive substances; 6) a history of a tendency to allergic reactions, including hypersensitivity to the components of the drug Nooclerin.
Nooclerin was prescribed in combination with antipsychotics, antidepressants and tranquilizers. In accordance with the study protocol, the prescription of drugs belonging to the pharmacological group of nootropics and drugs with nootropic effects, vasoactive drugs and drugs that improve cerebral circulation (including nutritional supplements) was prohibited. If necessary, the use of cardiotropic, antihypertensive and other somatotropic drugs was allowed, which were used by 30 patients from the nooclerin group and 30 from the control group.
In accordance with the study protocol, the drug nooclerin was used in the form of an oral solution of 200 mg/ml (100 ml bottle). It was prescribed for the entire study period at a dose of 2 g per day according to the following scheme: 1 g (or 1 measuring spoon containing 5 ml of solution) 2 times a day - morning and afternoon, but no later than 16:00 and no earlier. than 4 hours before bedtime, taking into account drug tolerability. The duration of therapy was 30 days. The condition of the patients was assessed before the start of treatment (baseline examination), on the 15th and 30th days. A general somatic examination, assessment of laboratory parameters of blood, urine, blood pressure, heart rate and ECG were carried out.
The effectiveness of the study drug was assessed on the above days using the following questionnaires and tests: MFI-20 asthenia scale, MMS cognitive assessment scale, CGI-S clinical global impression scale. The assessment of tolerability, safety and impact on the course of the underlying disease of the study drug was carried out based on the patient's complaints, his general clinical condition, as well as the qualification of the emotional state according to the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D).
The asthenia scale MFI-20 (The Multidimensional Fatigue Inventory) allows you to obtain a subjective quantitative assessment of the overall severity of asthenia and its various aspects. This scale consists of 20 points reflecting different components of asthenic disorder: general asthenia, physical asthenia, decreased activity, decreased motivation and mental asthenia. The highest score reflects the maximum severity of asthenia. The scale score is the sum of the scores of its individual components and can vary from 5 to 25 points.
The MMSE Cognitive Assessment Scale is a specialized questionnaire for assessing the general state of the cognitive sphere. Includes questions to assess environmental awareness, attention, speech, reading, counting, memory, understanding of oral and written language, as well as spatial-visual orientation. The scale contains 30 questions and is used for diagnosis (screening) and measurement of the dynamics of cognitive impairment in various diseases and disorders, in particular dementia.
The CGI-S Clinical Global Impression Scale is based on the clinical experience of the clinician using it. The scale measures the severity of symptoms of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment in patients with mental pathology. According to the CGI-S, 1 point is normal, not sick (no symptoms, no disease), 2 points is a borderline state (minimal symptoms, maintaining the ability to perform effectively), 3 points is a mild degree of disease (weak severity of symptoms, subjective malaise, slight impairment or preservation of functions), 4 points - moderate severity of the disease (some symptoms are pronounced, moderate impairment of functions), 5 points - severe disease (obvious symptoms, very significant functional impairment), 6 points - severe disease (very noticeable symptoms, inability to perform functions in most areas of activity), 7 points - patients with the highest severity of the disease (extremely severe symptoms, complete disability, need for outside care).
The Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D) is one of the most common quantified scales used to assess the severity of depressive symptoms. The Hamilton scale consists of 21 items, 2 of which (16th and 18th) contain 2 parts (A and B), which are filled out alternatively. Hamilton scale parameter estimates are based on data from a clinical interview. When interpreting the data, it must be remembered that points from 18 to 21 do not reflect the severity of depressive symptoms themselves, and the sum of points on the first 17 points of the Hamilton scale, in relation to ICD-10, corresponds to: 7-16 points - mild depressive episode ; 7–27 points – moderate depressive episode; above 27 points - a severe depressive episode (G.P. Panteleeva, 1998).
A total of 60 patients were included in the study and were divided into two groups. Group 1 - main - 30 patients who were prescribed nooclerin at a dose of 2 g per day; Group 2 - control - 30 patients, in whose treatment regimen nooclerin was not included.
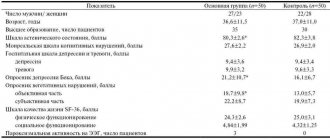
As can be seen from table. 1, the average age of patients in the main group was 45.3±10.6 years, in the control group - 50.1±11.3 years. The ratio of men to women in group 1 was 7:23, in the control group - 4:26. The sample patients had higher (1st group - 56%, 2nd group - 46%) and secondary specialized (1st group - 44%, 2nd group - 54%) education. The majority of patients in group 1 (63%) and half of patients in group 2 (50%) were professionally employed. The majority of patients in both groups 1 and 2 were married at the time of the examination - 18 (60%) and 20 (66%), respectively. Thus, no statistically significant differences were found in the sociodemographic indicators of the study groups.
Table 1. Sociodemographic characteristics of patients
The nosological distribution of patients in groups is presented in Table. 2.
Table 2. Distribution of nosological forms in the main and control groups, %
The average duration of asthenic syndrome in patients of the main group was 3.2±1.4 months, in the control group - 4.1±2.3 months. The average duration and number of depressive states experienced did not differ significantly when comparing the main and control groups - 6.44±2.37 and 5.93±1.94, respectively. There were no statistically significant differences in the clinical characteristics of patients in the study groups.
The examined patients most often suffered from hypertension - 11 (36.3%) in the main group and 13 (43.6%) in the control group. The second place in prevalence among patients included in the study was occupied by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) and biliary tract - chronic gastritis, chronic colitis, cholelithiasis (10 (33.5%) - in the main group, 11 (36.3%) %) - in the control group). In addition to hypertension and gastrointestinal diseases, diseases of the musculoskeletal system (osteochondrosis of the spine) occurred in both groups: in 7 (23.3%) patients of the main group and 5 (16.2%) patients in the control group. And only in isolated cases were patients observed by neurologists with a diagnosis of cerebrovascular disease of the brain: 3 (7%) - group 1, 1 (3.9%) - group 2.
In accordance with the study protocol, combination therapy with antidepressants, neuroleptics and tranquilizers was allowed. Patients in the study and control groups most often received combination therapy with aripiprazole and fluvocasmine, aripiprazole and sertraline, flupentixol and fluvoxamine in tablet forms, as well as a course of intravenous drips of clomipramine and diazepam. These data are presented in table. 3.
Table 3. Concomitant psychotropic therapy in the study groups