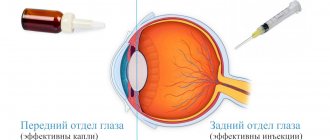
Different retinal diseases require different treatment methods. Some of them are treated exclusively surgically. But a number of diseases can usually be treated in the initial stages with conservative methods - using medications (eye drops, injections).
The main goal of conservative treatment of retinal pathologies is to relieve inflammation, proliferation of newly formed vessels, as well as eliminate degenerative changes and swelling of the retina. In some cases, prescriptions are made for prophylactic purposes (“to strengthen the retina”). At the same time, the use of drugs in the form of drops is not always effective, because they do not penetrate very well into the back of the eye (in this case it is recommended to use injections or tablet forms).
Anterior and posterior parts of the eye
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamic parameters.
The active ingredient in Taufon-Darnitsa eye drops is taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid). This conditionally replaceable sulfur-containing β-amino acid is formed in the human body based on the metabolism of methionine and cysteine and comes from food. Taurine is found in particularly high concentrations in excitable tissue cells and tissues exposed to oxidative stress (CNS and retina, as well as leukocytes, smooth muscle cells and cardiomyocytes).
Taurine plays an important role in many physiological processes: it is involved in cytoprotection and regulation of apoptosis; exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, supporting cell homeostasis under conditions of acute and chronic inflammation/oxidative stress.
Taurine is a free radical scavenger and an effective inhibitor of the generation of reactive oxygen species; enhances the expression and activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase, preventing their damage; improves the condition and function of mitochondria, restoring the activity of the respiratory chain and increasing ATP synthesis.
Taurine stabilizes cell membranes; participates in the regulation of cell volume and modulates the content of other osmolytes, including the intracellular concentration of free calcium; necessary in the processes of immunomodulation, as well as glucose metabolism; There is evidence of the effects of taurine as a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator.
Taurine modulates protein phosphorylation and cell signaling, regulates the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy processes. Taurine-mediated changes in transcription factor content have been reported.
Taurine is found in high quantities in the retina, vitreous body, lens, cornea, iris and ciliary body. The highest concentration of taurine was observed in the photoreceptors of the retina. Taurine inhibits lipid peroxidation processes caused by light exposure. The taurine content in the retina is critical for the development of photoreceptors and the viability of ganglion cells, and is also necessary to prevent the development of neurodegenerative processes and other pathological conditions in the tissues of the eye. Taurine deficiency is associated with damage to retinal neurons.
Pharmacokinetic parameters. The specific effect of taurine when instilled into the eye is observed in the eye tissues. When used in therapeutic doses, the drug practically does not enter the systemic circulation.
Intraocular injections
Intravitreal injections are the injection of a drug directly into the eye cavity (into the vitreous body). Such injections are performed for hemorrhages (partial hemophthalmia), wet form of macular degeneration, retinal edema, the appearance of newly formed vessels and other serious eye diseases.
In our clinic, intravitreal injections are performed by ophthalmologists with extensive experience in complex intraocular injections in sterile procedure rooms, in compliance with appropriate medical protocols. Such therapy for retinal pathologies, using effective medications, allows one to preserve visual function and also achieve a significant improvement in visual acuity.
Lucentis
The active component of the drug is ranibizumab, a substance that suppresses excessive angiogenesis (the formation of pathological blood vessels), which is characteristic of age-related macular degeneration. In addition, it helps relieve macular edema, normalizing the thickness of the retina. The drug quickly penetrates completely into the layers of the retina, reducing the size of the lesion, preventing possible hemorrhages and further progression of the growth of newly formed vessels with a pathological wall. More about Lucentis >>>
Eilea
The active substance of Eylea is aflibercept. Its action is aimed at inhibiting the progression of age-related macular degeneration (wet form). In addition, it has the ability to act effectively and safely in reducing visual acuity in the case of diabetic macular edema and edema caused by retinal vein occlusion.
The innovative drug Eylea has a long-lasting effect, so injections can be performed less frequently than with Lucentis, which is much more convenient for patients. More about Eylea >>>
Ozurdex
It is used in cases of macular edema caused by occlusion of the retinal veins. The drug is produced in the form of a thin implant in the form of a rod, which is inserted into the vitreous body. The implant contains the potent steroid dexamethasone, which begins to be released inside the vitreous in small portions. This innovative method of dosed delivery of a medication to the affected area significantly increases the duration of action of the hormone, which can last up to six months. Read more about Ozurdex >>>
Parabulbar and intravitreal injections are performed under sterile conditions
Application
Locally for adults. Before the instillation procedure, heat the tube to 37 °C (hold it in the palm of your hand).
Cataract: 2-3 drops 2-4 times a day for 3 months. Repeat at intervals of 1 month.
Eye injury: 2-3 drops 2-4 times a day for 1 month.
Retinal dystrophy, penetrating injuries of the cornea: 0.3 ml of 4% solution is administered subconjunctivally once a day for 10 days. The course is repeated after 6–8 months.
Open-angle glaucoma: 2-3 drops into the conjunctival sac 2 times a day (20-30 minutes before using timolol eye drops). The duration of treatment is individual (determined by the doctor).
My eyes are watering
Watery eyes or lacrimation
- a condition when tears accumulate in the conjunctival cavity and flow over the edge of the eyelid.
As a result, eyelid skin irritation, redness, and maceration occur. Constantly flowing tears cause discomfort and irritation. Why do my eyes water and what should I do?
The eyes water only for three reasons: A.
The lacrimal glands produce an excess amount of tear fluid
.
B. Violation of the lacrimal ducts
.
C. Violation of the composition of tears
.
Tear is necessary for constant hydration of the cornea. With a lack of tears, the cornea dries out, becomes cloudy and the person loses vision. This disease is called corneal xerosis. Therefore, to maintain good vision, tear secretion is necessary. Interestingly, approximately 250 ml of tear fluid is produced per day
in each eye.
The same amount of tears is removed from the eye along the lacrimal ducts, which include the lacrimal canaliculus, lacrimal sac and nasolacrimal duct. Each human eye has a lacrimal gland, which is located in the upper outer part of the eye and 18-20 small additional lacrimal glands in the transitional conjunctival fold of the upper eyelid, at the top of the eyelid on the inside. Under normal conditions, only the accessory lacrimal glands constantly function and secrete tears. This tear is completely enough for a person to moisturize the cornea. The main lacrimal gland is activated when the cornea dries out, is irritated by a foreign object, or is subject to psychological (neurological) irritation. My eyes are watering, what could be the reasons? A. Causes causing hypersecretion of the lacrimal glands:
1. “Dry eye syndrome” 2. Dry air 3. Foreign body in the cornea or conjunctiva 4. Chemical irritation of the cornea 5. Inflammatory process in the conjunctiva (conjunctivitis) 6. Inflammatory process of the eyelids (blepharitis) 7. Irritation of the nerves innervating the lacrimal glands, a neurological cause of lacrimation 8. Violation of the psychosomatic state
B. Causes causing disruption of the outflow of tears:
1. Atony (flabbiness) of the lower eyelid 2. Blockage of the lacrimal ducts 3. Inflammatory process in the lacrimal ducts 4. Narrowing of the lacrimal ducts 5 Inversion or eversion of lacrimal openings.
6. Compression of the lacrimal canaliculi by swelling of the eyelids C. Reasons leading to disruption of the composition of tears:
1. Meibomitis - inflammation of the meibomian glands
A. Reasons causing hypersecretion of the lacrimal glands:
1
.
"Dry eye syndrome." Paradoxically, “dry eye syndrome” is one of the two most common causes of lacrimation.
It would seem that a “dry eye” requires hydration and cannot be the cause of excess tears. But it is the drying of the cornea that triggers hypersecretion of the lacrimal gland, which produces a larger volume of tears than the lacrimal ducts can drain. Treatment
: Drops of artificial tears, restoring the tear film and, most importantly, its normal composition, will help get rid of lacrimation in this case.
Massage of the meibomian glands is also recommended to restore their normal functioning. Dysfunction of the meibomian glands leads to disruption of the composition of tears and, as a consequence, to “dry eye syndrome.” It is also necessary to humidify the air in the room, especially in winter. The relative power of air for the normal functioning of the lacrimal organs must be more than 50%. 2 . Dry indoor or outdoor air
causes tears to dry out and the cornea to become dry.
This effect is especially pronounced in countries with hot climatic conditions accompanied by persistent winds. The mechanism of additional tear production is triggered, which is produced in excess, and lacrimation occurs. It should be noted that frosty air is much drier in its physical characteristics than warm air. Therefore, outside in the cold, accompanied by the wind, the tears also quickly dry out and, as a result, an additional increased secretion of tears from the lacrimal gland occurs, which makes the eyes become very watery. Treatment
: maintain relative humidity in the room more than 50%, avoid prolonged stay outside in conditions of too dry, warm or frosty air accompanied by strong winds.
3 .
A foreign body in the cornea or conjunctival cavity , most often an eyelash, leads to disruption of the corneal epithelium, causing “corneal” syndrome, which is always accompanied by redness and severe watering of the eyes.
Treatment
: it is necessary to remove the foreign body and use means that improve the regeneration of the cornea for its speedy recovery: eye drops or gel “Korneregel”, eye ointment “Solcoseryl”, eye drops “Citral” 2-3 times a day.
Once the cornea is restored, the lacrimation will stop. Along with drugs that improve regeneration, it is recommended to use eye drops to prevent secondary infections, such as: Tobrex, Albucid 20%, Levomycetin - 1 drop 3 times a day. 4 .
Chemical irritation of the cornea by substances in the air leads to a reflex increase in lacrimation for increased protection of the cornea, to prevent the negative effects of chemicals on the eye lens, which are washed away by the copious secretion of tears.
We know that our eyes water when we peel onions. This is the most typical example of lacrimation from chemical exposure to the eyes. The same thing happens in a room where there is an excess of ammonia, tobacco smoke, and other active chemicals. Treatment
: It is necessary to rinse the eyes with warm water and leave the room.
For prevention, it is necessary to use safety glasses. 5. Conjunctivitis
, or inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye, also causes the eyes to water.
In addition to the fact that tears flow, the eyes become red. With bacterial conjunctivitis, pus discharge and swelling of the eyelids occur. Treatment
: it is necessary to determine the cause of conjunctivitis and eliminate it using drugs that suppress the proliferation of viruses or bacteria.
These can be: “tobrex”, “tobradex”, “maxitrol”, “interferon”, “albucid 20%”, “chloramphenicol” - 1 drop 4-6 times a day. 6 .
Blepharitis , or inflammation of the edges of the eyelids, leads to chronic lacrimation, as does the disease itself, which most often has a chronic course.
Lacrimation in blepharitis is associated with swelling of the eyelids and difficulty in the outflow of tears through the lacrimal canaliculi. Treatment
: Treatment of the underlying condition of blepharitis will help get rid of watery eyes in this case.
7 . Irritation of the nerves innervating the lacrimal glands
, a neurological cause of lacrimation.
The innervation of the lacrimal gland is very complex. Four nerves provide its sensitive and secretory functions. This is the “Lacrimal nerve” - the first branch of the trigeminal nerve, a branch of the facial nerve, as well as nerve fibers of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. Irritation of these nerve fibers can cause hypersecretion of the lacrimal gland. Irritating factors include tumors, inflammatory diseases on the face, and injuries. Treatment
: neurologists can tell you what to do in this case to stop lacrimation.
8. Violation of a person’s psychosomatic state
is a common cause when the eyes water in excess and tears flow like a river.
Anger, fear, sadness or grief irritate the sympathetic nervous system, releasing the so-called “stress response hormones” - adrenaline, norepinephrine - into the blood. As is known, the lacrimal gland is innervated by the sympathetic nervous system and therefore, when it is irritated, increased tear production occurs. The stronger the stress response, the greater the irritation of the sympathetic nervous system and the more tears flow. Treatment
: drugs that stabilize the nervous system and reduce stress.
“Novopassit”, “Valerian extract” are very suitable. Causes causing disruption of tear outflow:
1.
The second most common cause of lacrimation is atony (decreased tone) of the lower eyelid
. The tear flows from the conjunctival cavity through the lacrimal punctum located on the lower eyelid. Normally, the eyelid has good tone and the point is adjacent to the eyeball.
With age, muscle tone changes, tone decreases, the eyelid becomes flabby and a small gap forms between the eye and the eyelid.
The lacrimal punctum moves away from the eyeball, the tear cannot find its outflow path and overflows the edge of the eyelid. This happens when the eyes water due to age-related disorders in the body - atony of the lower eyelid. Treatment
: treatment in this case can only be surgical.
There are two directions of treatment: expansion of the lacrimal punctum or excision of part of the lower eyelid to increase its tone and return to its original state, when the lacrimal punctum is again adjacent to the eyeball and the tear outflow path is restored. 2. Blockage of the lacrimal ducts
can occur at any stage.
In adults, blockage of the tear ducts most often occurs. The cause of blockage may be discharge from conjunctivitis, blepharitis, mascara and other similar reasons. Disruption of the outflow in the lacrimal sac occurs after inflammatory diseases of the lacrimal ducts, dacryocystitis, canaliculitis. In such cases, the products of inflammation remain in the lacrimal sac and obstruct the outflow of tears. Diagnosis is made by taking x-rays with a contrast agent filling the tear ducts. Treatment
: Violation of the conductivity of the lacrimal canaliculi is carried out by dilating and washing them.
As a rule, such procedures give a lasting positive effect. 3. Inflammatory process in the lacrimal ducts
.
Dacryocystitis is inflammation of the lacrimal gland. Dacryocystitis is characterized by the accumulation of inflammatory products in the lacrimal sac, its swelling, redness and pain in the area of the internal commissure of the eyelids. At the same time, tears, as a rule, “run in a stream.” Canaliculitis is inflammation of the tear ducts. Diagnosis of canaliculitis is difficult, since there are no external signs of inflammation other than lacrimation. Treatment
: Treatment must be carried out in a specialized surgical facility, since for successful treatment of dacryocystitis it is necessary to create a path for the outflow of inflammatory fluid of the lacrimal sac, which is carried out surgically.
4. Narrowing of the lacrimal ducts
, or their stricture, is, as a rule, a consequence of inflammatory processes of the eye - conjunctivitis, inflammation of the eyelids, blepharitis.
Damage to the epithelial wall of the lacrimal ducts due to infection leads to narrowing of the lumen and disruption of the outflow of tears. Treatment
: Bougienage of the lacrimal and nasolacrimal ducts.
If there is no effect, they resort to plastic surgery. 5. Inversion or eversion of the lacrimal openings
is a consequence of injury or very severe inflammation of the eyelids.
As a result of the scarring process, the lacrimal punctum is displaced, and tears cannot flow down the lacrimal ducts. The eyes are very watery. Treatment
: Cosmetological treatment of volvulus or eversion of the lacrimal punctum can only be surgical.
6. Compression of the tear ducts by swelling of the eyelids
is the most common cause of
watery eyes in the morning
.
If your eyes are very watery in the morning, pay attention to whether you have swelling of your eyelids and face. Low mobility of a person at night and a violation, especially with age, of the water-salt balance leads to stasis (slowing down of the flow) of fluid in the body, which accumulates in tissues rich in fiber, which include the eyelids. Excessive accumulation of interstitial fluid compresses the tear ducts and can lead to severe watery eyes in the morning, which goes away as the person stays awake and moves. Nocturnal lymphostasis, which occurs for a variety of reasons from cardiac dysfunction, renal failure to varicose veins, can be the reason why tears flow in the morning. Treatment:
if, in addition to tears in the morning, you notice swelling of the eyelids, then it is necessary to carry out active physical exercises, at least for a few minutes. Muscle work will improve lymphatic drainage, swelling of the eyelids will subside and lacrimation will stop. In order to more accurately understand the malfunctions of the body, it is necessary to consult a therapist, who, based on examinations, recommends consultation with a specialist.
C. Reasons leading to disruption of the composition of tears:
1. Meibomitis (meibomitis) - inflammation of the meibomian glands
Meibomite is the third most common cause of watery eyes.
The meibomian glands are found in the intermarginal margin of the eyelids (the edges of the eyelids that touch when the eyes close). The meibomian glands produce a special viscous secretion that is found in the superficial layer of the tear. The tear consists of 99% water, so it dries quickly. The secretion of the meibomian glands prevents this process. When the meibomian glands become inflamed, the composition of the secretion changes or is completely absent when the glands are clogged with inflammatory products. In this case, the biochemical composition of the tear changes and the tear dries very quickly on the surface of the cornea, irritation occurs and, as a result, increased tear production, the eyes begin to water during this process. Treatment
: massage of the edges of the eyelids is necessary (5-7 days) with the use of anti-inflammatory ointments: “tetracycline”, “gentamicin”, “hydrocortisone”. Treatment always has a positive result.
10.08.2021
Author, Ph.D. Oleg Getto
special instructions
In the case of treatment of open-angle glaucoma, taufon is used 20–30 minutes before the use of timolol eye drops.
If it is necessary to combine several drugs for topical use in the eyes, the interval between their administration should be 10–15 minutes (ointment last).
There is no data on the use of Taufon during pregnancy and lactation, in childhood, as well as when driving vehicles and operating other mechanisms.
However, if transient blurred vision develops after using the drug, you should wait until visual function is fully restored before starting to drive a vehicle or operate other machinery.
How to understand when it's time to take vitamins to improve vision
As a rule, eye vitamins are recommended for people suffering from visual impairment, those who spend a lot of time at the computer (students, office workers), patients with macular degeneration of the retina, cataracts, as well as people over 40 years of age. However, even if you don't fall into one of these groups, you may still need vitamins for your vision. Especially if you begin to notice one of the following signs:
- decrease in field of view . In this case, the clarity of the image deteriorates when looking away in any particular direction. For example, you can see objects directly in front of you well, but as soon as you look to the side, objects become blurry;
- decreased visual . The need to find effective medications containing vitamins for the eyes may be indicated by a condition in which certain objects that you previously saw clearly become less clearly visible. This can apply to both nearby and far away objects. Sometimes the disorder affects only one eye. In this case, it is enough to close your eyes several times and evaluate your visual acuity;
- dryness, itching, burning, pain in the eyes . If you find these symptoms in yourself, this does not mean that your visual acuity problems are progressing, but they often signal the presence of certain eye diseases or eye strain. Thus, when the ability to focus on a specific object deteriorates and a feeling of “sand” appears in the eyes, conditions can develop that, without correction, can lead to consequences that require a more radical approach than simply taking vitamins to restore vision.
Note!
Description of the drug Taufon-Darnitsa cap. eye. solution 40 mg/ml vial. 10ml on this page is a simplified author’s version of the apteka911 website, created on the basis of the instructions for use.
Before purchasing or using the drug, you should consult your doctor and read the manufacturer's original instructions (attached to each package of the drug). Information about the drug is provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as a guide to self-medication. Only a doctor can decide to prescribe the drug, as well as determine the dose and methods of its use.