The cholinesterase inhibitor Neuromidin is produced in tablets and in parenteral solution based on ipidacrine. The drug has a stimulating effect on the conduction of impulses along the fibers of the nervous system, its interneuronal and peripheral parts. The pharmacy market today provides a large selection of Neuromidin analogues, both in terms of active substance and therapeutic effect.
Neuromidin is used in the treatment of the following pathologies of the peripheral central nervous system:
- neuritis and polyneuritis;
- polyneuropathy of various etiologies;
- myelopolyradiculoneuritis;
- paresis and paralysis;
- myasthenia gravis;
- disturbance of blood microcirculation in parts of the brain;
- memory loss and delayed intellectual development in a child.
Neuromidin is also prescribed as part of combination therapy for multiple sclerosis and in the treatment of head and brain injuries, to stimulate the birth process in pregnant women.
Neuromidin is not used for:
- allergies to the medicinal composition;
- abnormal heart rhythm, angina pectoris;
- epileptic seizures;
- asthma;
- disturbances in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus;
- erosive and ulcerative processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
It is prohibited to use Neuromidin in the form of a solution in the treatment of children under 18 years of age, women with breastfeeding and pregnancy.
In the treatment of polyneuropathy and mononeuropathy of various etiologies, paralysis, paresis, the drug is administered subcutaneously at a dose of 5-15 mg once or twice a day. Myasthenia gravis – parenterally (under the skin) 1-3 times a day, with a single dosage of 5-30 mg. Therapy for multiple sclerosis – 1 tablet up to 5 times a day.
Side effects:
- dyspepsia;
- headache and dizziness;
- bronchospasms;
- disturbance of heart rhythm and blood pressure fluctuations;
- skin allergies - itching, rash, urticaria.
Composition and release forms
The main component of Neuromidin is ipidacrine hydrochloride
, whose Latin name is Ipidacrine.
The auxiliary composition depends on the form of release of the drug:
- In tablets it is starch, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate.
- The injection solution contains hydrochloric acid and water.
The tablets are white, round, flat-cylindrical. They are produced in paper packages of 10 pieces.
The highest concentration of the main component after taking the tablets is achieved after 1 hour, and when administered into a muscle and vein, it is twice as fast.
Ampoules with clear liquid are produced in 5 and 15 ml sizes. Injections can be given either subcutaneously or intravenously.
Axamon
Aksamon is a cheap analogue (synonym) of Neuromidin produced in Russia, which contains the same active substance (ipidacrine). Prescribed for neuritis, Alzheimer's disease, myasthenia gravis, central nervous system lesions and intestinal arrhythmia. The list of contraindications and side effects is the same.
Aksamon is produced in the following forms:
- pills;
- solution for intramuscular and subcutaneous administration (in ampoules);
- substance-powder.
The approximate price for this analogue is 596 – 1089 rubles.
Advantages are price and variety of dosage forms, disadvantage is a greater number of possible side effects.
Therapeutic effect
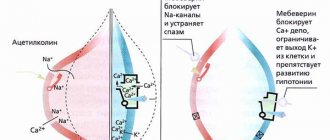
The drug belongs to the group of cholinesterase inhibitors, that is, it reduces the production of a group of enzymes. This is not the only pharmacological function of Neuromidin. It is prescribed for:
- improving the conduction of impulses along nerve fibers and synapses of the nervous system;
- enhancing the effect of a number of hormones on the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract;
- inhibition of developing dementia;
- memory improvements.
Ipidacrine completely disintegrates in the liver and is excreted through the urinary system.
How can I replace Neuromidin?
The choice of analogues of the drug occurs under close medical supervision. It is important to consider contraindications, side effects, and select the exact dosage. An analogue of Neuromidin in ampoules or tablets may have the same or different composition, but the same therapeutic effect.
Axamon
The drug is indicated for neuropathies, polyradiculopathies, paralysis, and intestinal atony. Neuromidin analogue in tablets and ampoule solution improves memory:
- Release form: tablets, solution.
- Price, rub.: 755 for 20 pcs., 1100 for 10 ml.
- Active ingredient: ipidacrine.
- Features: stimulates the conduction of impulses in the neuromuscular synapse and the central nervous system.
- Contraindications: epilepsy, angina pectoris, vestibular disorders.
- Side effects compared to Neuromidin: salivation, diarrhea, jaundice, ataxia, drowsiness, itchy skin.
Article on the topic: Fish oil for pulmonary tuberculosis: the benefits of vitamin D
Amiridine
An anticholinesterase agent is indicated for neuritis, polyneuropathy, myasthenia gravis, demyelinating diseases, and intestinal atony. Amiridine is taken orally 10–20 mg 1–3 times a day for 1–2 months:
- Release form: tablets.
- Price, rub.: 600 for 50 pcs.
- Active ingredient: amiridine.
- Features: stimulates neuromuscular transmission.
- Contraindications: epilepsy, angina pectoris, bronchial asthma, pregnancy, lactation, bradycardia.
- Side effects compared to Neuromidin: hypersalivation, nausea, dizziness.
Kalimin 60 N
An anticholinesterase drug for the treatment of myasthenia gravis is taken orally, 1-3 tablets 1-4 times a day. Characteristics:
- Release form: tablets.
- Price, rub.: 850 per 100 pcs.
- Active ingredient: pyridostigmine bromide.
- Features: reversibly suppresses cholinesterase, enhances the effect of acetylcholine, increases the tone of the bladder and bronchi.
- Contraindications: iritis, bronchitis, myotonia, shock after surgery, pregnancy, lactation, age under 18 years.
- Side effects compared to Neuromidin: allergies, increased sweating, lacrimation, nausea, diarrhea, frequent urination, muscle tremors, accommodation disorders, decreased blood pressure.
Ubretid
The drug has an indirect m-n-cholinomimetic effect. Neuromidin analogues are indicated for postoperative atony and paralytic intestinal obstruction, bladder hypotension, chronic constipation, megacolon, myasthenia gravis:
- Release form: tablets, injection solution.
- Price, rub.: 250 for 20 pcs., 150 for 5 ml.
- Active ingredient: distigmine bromide.
- Features: reversibly inhibits acetylcholinesterase in the synaptic cleft, increases the tone and peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract and bladder.
- Contraindications: vagotonia, hypotension, intestinal hypertonicity, gastric ulcer, myocardial infarction, epilepsy, heart failure, parkinsonism.
- Side effects compared to Neuromidin: nausea, diarrhea, bradycardia, constriction of the pupil, muscle spasms, difficulty swallowing.
Ipigrix
An anticholinesterase agent serves to restore impulse transmission in the peripheral nervous system and improve memory. Ipigrix is indicated for diseases of the central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, intestinal atony:
- Release form: tablets, ampoule solution.
- Price, rub.: 865 for 50 pcs., 810 for 10 ml.
- Active ingredient: ipidacrine.
- Features: stimulates the conduction of impulses along nerve fibers and synapses.
- Contraindications: epilepsy, bradycardia, hyperkinesis, bronchial asthma, pregnancy, lactation, age under 18 years.
- Side effects compared to Neuromidin: diarrhea, dyspepsia, dizziness, drowsiness, weakness, bradycardia, miosis, bronchospasm, tremor, convulsions, sweating, skin rashes.
Prozerin
A synthetic anticholinesterase agent reduces the heart rate, increases the secretion of the salivary glands, and increases the acidity of gastric juice. Prozerin is indicated for myasthenia gravis, paralysis, weakness of labor, open-angle glaucoma, optic nerve atrophy, and bladder tone. The solution is administered subcutaneously at 1–2 mg 1–2 times a day:
- Release form: ampoule solution.
- Price, rub.: 85 for 10 ml.
- Active ingredient: neostigmine methyl sulfate.
- Features: enhances the effect of acetylcholine, restores neuromuscular conduction.
- Contraindications: epilepsy, hyperkinesis, vagotomy, ischemia, bradycardia, arrhythmia, angina pectoris, bronchial asthma, atherosclerosis, thyrotoxicosis, peritonitis, prostate adenoma.
- Side effects compared to Neuromidin: hypersalivation, nausea, flatulence, diarrhea, blurred vision, facial flushing, atrioventricular block.
Article on the topic: Use of Olanzapine: indications, instructions, reviews
Ipidacrine
A cholinesterase inhibitor is indicated for neuropathy, myasthenia gravis, bulbar palsy, Alzheimer's disease, senile dementia, intestinal atony:
- Release form: tablets, solution.
- Price, rub.: 250 for 10 pcs., 200 for 10 ampoules of 1 ml.
- Active ingredient: ipidacrine.
- Features: suppresses enzymatic hydrolysis of acetylcholine, prolongs its effect, reduces blood pressure.
- Contraindications: epilepsy, angina pectoris, bronchial asthma, pregnancy, lactation.
- Side effects compared to Neuromidin: drowsiness, ataxia, convulsions, tremor, miosis, bradycardia, nausea, jaundice, itching, allergies.
List of diseases
Neuromidin is prescribed for the treatment of ailments associated with dysfunction of various parts of the nervous system. Indications for its use are:
WE RECOMMEND THE ARTICLE!
For headaches and circulatory disorders, doctors often prescribe the medicine Piracetam. Read more >>
- neuropathy
- pain that occurs due to excessive excitability of the nerves; - myasthenia gravis
, which is characterized by the occurrence of pathological muscle fatigue; - bulbar syndrome
- cranial nerve palsy; - paresis
, which causes muscle weakness.
The drug is also prescribed during the recovery of the central nervous system after various organic lesions.
"Amiridin"
The drug is available in the form of tablets with ipidacrine as the main component.
The medicine is prescribed to patients for:
- moderate or mild dementia of the Alzheimer's type;
- cerebral palsy;
- disorders of neuromuscular transmission (muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis);
- diseases of the peripheral nervous system (including neuritis, polyneuritis, polyneuropathy, radiculoneuritis);
- damage to the anterior horns of the spinal cord after spinal muscular atrophy, poliomyelitis.
There are also quite a few contraindications for use. Among them:
- presence of allergies to the components of the drug;
- childhood;
- bradycardia;
- bronchial asthma;
- heart failure;
- angina pectoris;
- hyperkinesis;
- epilepsy;
- mechanical intestinal obstruction;
- severe renal and liver dysfunction.
Treatment with Amiridin is also not recommended during pregnancy and lactation.
When is Neuromidin contraindicated?
The drug has a large list of diagnoses that interfere with its use. It includes serious diseases that are aggravated by the use of Neuromidin:
- bronchial asthma;
- chest pain;
- lesions of the vestibular apparatus;
- ulcerative lesions of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract;
- intestinal obstruction;
- epilepsy.
Neuromidin is prohibited for pregnant, lactating women and minor children. It is worth stopping treatment if you are intolerant to the components of the drug.
During treatment, you should not drive a car or operate other vehicles that require attention and quick response.
There are a number of diseases for which Neuromidin is allowed, but with caution. These include pathologies of the heart and lungs.
Contraindications for use
The instructions for use indicate a number of cases when the drug Neuromidin cannot be prescribed to a patient. In particular, this concerns the latter’s presence:
- hypersensitivity to the main or auxiliary components of the drug;
- mechanical obstruction of the urinary tract or intestines;
- vestibular disorders;
- bronchial asthma;
- angina pectoris;
- severe bradycardia;
- peptic ulcer of the duodenum or stomach during the acute stage;
- extrapyramidal diseases with hyperkinesis;
- epilepsy.
In addition, additional medical supervision is necessary if the patient has:
- acute respiratory tract diseases;
- obstructive diseases of the respiratory system;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- lactose intolerance.
Neuromidin injections are not prescribed to patients under 14 years of age.
Instructions for use
The Neuromidin treatment system depends on the patient’s well-being and pathology.
The doctor determines how to use the drug - orally, subcutaneously or intravenously.
Neuromidin is a potent medicine and is only available with a prescription.
For lesions of the nervous system of any etiology, therapy takes place in several stages:
- It begins with injection under the skin or into a vein. The dosage depends on the specific disease: for neuropathy and paralysis - 5-15 mg twice a day for 10 to 15 days, for myasthenia gravis - 15-30 mg twice or thrice for 1-2 months and repeat after a month's rest.
- After a course of injections, a transition to the tablet form is made.
When using, it is worth considering compatibility with other medications. The pharmacological effect of Neuromidin is enhanced by simultaneous treatment with other inhibitors and alcohol. Combinations with nootropic medications are possible.
Modern spinal neurosurgery
Only modern minimally invasive surgical intervention (for example, video endoscopic microdiscectomy, or laser vaporization and nucleoplasty) can remove the hernia defect itself, or prevent its appearance in the case of protrusion. However, the Russian patient knows very well what surgery is. It hurts. This takes you out of normal life for a long time. It may be dangerous. There are so many such “buts” that surgery is considered the last type of treatment, when massage therapists, carboxytherapy sessions, manual therapists and kinesiotherapists stop helping.
Fortunately, in European countries, Israel, and the USA, the approach is completely different. If there are indications, the patient is operated on without pain, and often leaves the hospital on his own feet on the same day or the next. His quality of life is preserved. He is not prohibited from sitting for many days, and he is not forced to relieve himself while standing. Therefore, modern surgery is considered the best, fastest and most effective means of radical treatment. By the way, doctors in many Eastern European countries, for example, the Czech Republic, show excellent results in treating hernias surgically at fairly modest costs.
In Russia, they prefer not to immediately remove the hernial protrusion, but for many years to deal with its consequences and complications - to periodically treat inflammation, pain and swelling of the roots, which persistently arise again and again. And in this respect, the domestic patient resembles an unfortunate driver who, instead of finally changing a punctured tire, is forced to pump it up every half hour of driving. Only, unlike the driver, a patient who has been “treating” a hernia for a long time sometimes spends several times more money than the operation would cost.
Cervical hernia on MRI.
But even among the drugs for relieving swelling, back pain, and excess muscle tension, Neuromidin is not “listed.” However, it is sometimes prescribed for hernias, and is completely unjustified. The situation is aggravated by an unimaginably large number of sites that are written with stunning medical illiteracy. Because if there is a request “How to take Neuromidin for hernias,” then a helpful but illiterate article will immediately appear, which can even harm your health. How to take Neuromidin for hernias? Don't accept it at all. But first things first….
Signs of overdose
Exceeding the dose, which is usually observed with uncontrolled medication use, reveals itself with the following symptoms:
- heavy sweating;
- constriction of the pupils;
- spasms in the bronchi;
- nausea and vomiting;
- lacrimation;
- spasms of the muscles of internal organs;
- jaundice;
- cardiac dysfunction src=»https://karpov-clinic.ru/uploads/postst/2017-10/1508947709_kakie-priznaki-peredozirovki-mogut-byt.jpg» class=»aligncenter» width=»500″ height=»344 ″[/img]
- decreased blood pressure;
- weakness;
- constant desire to sleep;
- partial urination;
- an excited state, during which unreasonable fear and anxiety appear;
- convulsions;
- speech disorders.
To eliminate the result of an overdose, the specialist uses Atropine, Metacin and other m-anticholinergic drugs. Medicines are also used to treat symptoms.
Side effects
But complications are possible not only with an overdose. Some patients experience side effects. For Neuromidin they are as follows:
- increased secretion of saliva and sweat;
- increased heart rate;
- nausea;
- digestive disorders;
- chest pain;
- convulsions;
- itching, rash, swelling and other allergic reactions;
- increased uterine tone;
- general weakness.
Gradual administration of the drug helps to avoid a whole range of side effects. The dose is increased under supervision.
How to save money?
It will not be possible to save on treatment with Neuromidin, since it is an expensive drug. What to do if the treatment course lasts 2 months?
It is better to find analogues that are no less effective, but cost much less.
| Drug name | A country | Main component | Release form, quantity | Price |
| Neuromidin | Latvia | Ipidacrine | Tablets: 50 pcs. 20 mg each | 1187 rubles |
| Neuromidin | Latvia | Ipidacrine | Ampoules: 10 pcs. 15 mg each | 1999 rubles |
| Axamon | Russia | Ipidacrine | Tablets: 50 pcs. 20 mg each | 778 rubles |
| Axamon | Russia | Ipidacrine | Ampoules: 10 pcs. 15 mg each | 1182 rubles |
| Ipigrix | Latvia | Ipidacrine | Tablets: 50 pcs. 20 mg each | 826 rubles |
| Prozerin | Russia | Neostigmine methyl sulfate | Ampoules: 10 pcs, 1 ml each | 73 rubles |
It turns out that analogues are cheaper in tablets. It is also possible to be treated with cheaper Proserin, but it has many more side effects.
Cost of Neuromidin and its analogues
Prices for Neuromidin are in the high price segment. The cost of foreign analogues of the drug is also quite high. The price of domestic Neuromidin substitutes is significantly lower than the original and its foreign generics.
| Name of medications | Dose of the main component (mg) | Number of units per package | Price |
| Neuromidin | 20 | 50 | 1163-1369 |
| Kalimin 60N | 60 | 100 | 499-515 |
| Amiridine | 5 | 1 ml /10 | 656-670 |
| Axamon | 20 15 | 50 1 ml/10 | 759-780 1125-1130 |
| Prozerin | 5 | 1 ml/10 | 87-115 |
| Ubretid | 5 | 50 | 3450-3500 |
| Ipigrix | 20 | 50 | 1189-1200 |
| Nivalin | 10 | 1 ml/10 | 796-888 |