Gabriglobin-IgG
Instructions for use:
GABRIGLOBIN®-IgG, solution for infusion
Registration number
LS000412 dated 06/09/2010.
Trade name
Gabriglobin®-IgG.
INN. Human immunoglobulin is normal. Dosage form. Solution for infusion Composition. One bottle contains: Immunoglobulin G - 1.25; 2.5; 5.0 or 10.0 g. Maltose - 2.5; 5.0; 10.0 or 20.0 g. Water for injection 25; 50; 100 or 200 ml. Description. Transparent, colorless or yellowish liquid. Pharmacotherapeutic group. MIBP, immunoglobulins. ATX code:
J06BA02.
Pharmachologic effect. The drug is an immunologically active protein fraction isolated from human plasma or serum of donors tested for the absence of antibodies to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV1) and HIV2), the hepatitis C virus and the surface antigen of the hepatitis B virus. The drug is not subjected to chemical or enzymatic treatment, contains sodium chloride, preservatives and antibiotics. Stabilizer - maltose. The active component of the drug is immunoglobulin G, which has antibody activity against various viruses and bacteria. The drug also has nonspecific and immunoregulatory activity, manifested in increasing the body's resistance and anti-inflammatory effect. The anti-complementary properties of the drug are eliminated by special processing of the semi-finished immunoglobulin in a slightly acidic environment with subsequent stabilization, which allows you to completely preserve all the biological functions of immunoglobulin G and its half-life from the body. The technological process for obtaining the drug includes a special stage of inactivation of possibly present viruses. Pharmacokinetics. With intravenous infusion, bioavailability is 100%. Immunoglobulin G crosses the placenta and enters breast milk. The proven maximum serum IgG concentration is maintained for 21 days. In patients with primary hypo- or agammaglobulinemia, the biological half-life is more than 32 days. Indications for use. Primary antibody deficiency syndrome: agamma- and hypogammaglobulinemia (congenital form, period of physiological deficiency in newborns); secondary immunodeficiency, antibody deficiency syndrome with normal levels of immunoglobulins, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS); blood diseases, systemic connective tissue diseases; severe forms of any bacterial, toxic and viral infections; postoperative complications accompanied by bacteremia and septic condition; prevention of opportunistic infections and postoperative complications; replacement and immunomodulatory therapy. Contraindications. Immunoglobulin is not administered to persons with a history of allergic reactions to blood products and with IgA immunodeficiency. (In cases of severe sepsis, the only contraindication for administration is anaphylactic shock to blood products with a history.) For persons suffering from allergic diseases (bronchial asthma, atonic dermatitis, recurrent urticaria), or prone to allergic reactions, the first administration of the drug is carried out against the background of antihistamines. During the period of exacerbation of the allergic process, the drug is administered according to the conclusion of an allergist. Method of administration and dose. Immunoglobulin is warmed to a temperature of 30-35 °C immediately before administration. Administered intravenously, in the first 10-15 minutes at a rate of 15-20 drops per minute, then at a rate of 30-40 drops per minute. Faster administration may cause the development of a collaptoid reaction. A single dose of the drug depends on the indications for use and is usually 0.05-0.2 g/kg body weight. The course of treatment consists of 3-10 transfusions. The frequency and frequency of transfusions is determined individually, depending on the severity of the disease. In some cases, in severe septicotoxemic conditions or severe forms of bacterial and viral infections, the daily dose of the drug can be increased to 1-2 g/kg body weight (20-40 ml/kg). For systemic connective tissue diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, etc.), the drug is administered in doses of 0.2 - 0.4 g/kg (4-8 ml/kg) of body weight per day daily for 3-10 days. For idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, the drug is administered at a dose of 1.0 g/kg (20 ml/kg) body weight for 1-2 days. The course of treatment can be repeated. For agamma- and hypogammaglobulinemia, the drug is administered in doses to compensate for the deficiency of circulating IgG, controlling the level of serum immunoglobulins (usually at a dose of 0.6 g/kg, or 12 ml/kg). The interval between administrations of the drug is 1-2 months. The drug is used only in a hospital setting, subject to all aseptic rules. The drug is not suitable for use if the integrity of the bottles is damaged, if there is no labeling, as well as if the color of the drug has changed, if the expiration date has expired, or if it has been improperly stored. Partially used drug cannot be stored. Side effect. As a rule, there are no reactions to the administration of Gabriglobin-IgG. Individuals with altered reactivity may develop allergic reactions of various types, and in extremely rare cases, anaphylactic shock. Persons who received the drug must be under medical supervision for an hour. Antishock therapy must be available in the room where the drug is administered. If adverse reactions develop (nausea, pain in the lumbar region, tachycardia, shortness of breath, decreased blood pressure), reduce the rate or temporarily stop administering the drug. If the symptoms of an anaphylactoid reaction do not go away on their own, antihistamines, glucocorticosteroids and adrenergic agonists are used. Overdose. Interaction with other drugs has not been described Gabriglobin-IgG should not be mixed with various saline solutions. Transfusion therapy with immunoglobulin can be combined with antibiotics, hormones, cytokines, and bacteriophages. Live viral vaccines for parenteral use should not be used for at least 3 months after immunoglobulin administration. Storage conditions. In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature of 2 to 10 ° C. Release form. In bottles with a capacity of 25 or 50, 50 or 100, 100 and 250 ml, containing 25, 50, 100 or 200 ml of the drug. Each bottle with instructions for use in a cardboard pack. Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies. By doctor's prescription. Manufacturer. CJSC "Immuno-Gem", Moscow.
Israfilov A. Comparative analysis of immunoglobulins for intravenous administration. 2006. Presentation. ppt
Samsygina G. A. Immunoglobulins for intravenous administration in pediatrics
Beloborodov V.B. The place of immunoglobulins in the treatment of sepsis. ppt
Clinical use of immunoglobulins for intravenous administration. Collection of scientific articles Edited by Doctor of Biological Sciences V.V. Anastasieva. — Nizhny Novgorod state enterprise for the production of bacterial preparations — the company “Imbio”.
Human immunoglobulin is normal. Preparations for intramuscular and subcutaneous administration / A. G. Israfilov, M. M. Alsynbaev, V. A. Trofimov, L. K. Lapteva. – Ufa: RIO branch “Immunopreparat” of the Federal State Unitary Enterprise “NPO “Microgen” of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, 2008. – 130 p.
Buy Gabriglobin IgG (human immunoglobulin normal) solution d/inf 50ml in pharmacies
Gabriglobin Buy Gabriglobin in pharmacies Gabriglobin in the medicine directory DOSAGE FORMS lyophilized powder for the preparation of intravenous solution 2.5g
MANUFACTURERS Ivanovo Regional Blood Transfusion Station (Russia)
GROUP Immunoglobulins
COMPOSITION Active ingredient: Normal human immunoglobulin.
INTERNATIONAL NON-PROPENTED NAME Human immunoglobulin normal
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION Immunostimulating. Increases the level of antibodies in the body. With intravenous infusion, bioavailability is 100%. Redistribution of the drug occurs between the plasma and the extravascular space, and equilibrium is reached after approximately 7 days. In individuals with normal serum IgG levels, the biological half-life averages 21 days, while in patients with primary hypo- or agammaglobulinemia it is 32 days. Contains a wide range of opsonizing and neutralizing antibodies against bacteria, viruses and other pathogens. In patients suffering from primary or secondary immunodeficiency syndromes, it provides replenishment of missing IgG antibodies, which reduces the risk of infection.
INDICATIONS FOR USE Replacement therapy for the prevention of infections in primary immunodeficiency syndromes: agammaglobulinemia, common variable immunodeficiencies associated with a- or hypogammaglobulinemia; deficiency of IgG subclasses, replacement therapy to prevent infections in secondary immunodeficiency syndrome caused by chronic lymphocytic leukemia, AIDS in children or bone marrow transplantation, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Kawasaki syndrome (in addition to treatment with acetylsalicylic acid), severe bacterial infections, including sepsis (in combinations with antibiotics) and viral infections, prevention of infections in premature infants with low birth weight (less than 1500 g), Guillain-Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, autoimmune neutropenia, partial red cell aplasia of hematopoiesis, thrombocytopenia of immune origin, incl. h. post-transfusion purpura, isoimmune thrombocytopenia of newborns, hemophilia caused by the formation of antibodies to coagulation factors, myasthenia gravis, prevention and treatment of infections during therapy with cytostatics and immunosuppressants, prevention of recurrent miscarriage.
CONTRAINDICATIONS During the first day after administration of the drug, a slight increase in body temperature and allergic reactions are possible. Sometimes headache, dizziness, dyspeptic symptoms, arterial hypo- or hypertension, tachycardia, and shortness of breath occur. In extremely rare cases, due to individual intolerance, anaphylactic reactions may develop. Hypersensitivity to human immunoglobulins, especially in patients with IgA deficiency due to the formation of antibodies to it.
SIDE EFFECTS Headache, nausea, dizziness, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, arterial hypo- or hypertension, tachycardia, cyanosis, shortness of breath, feeling of constriction or pain in the chest, allergic reactions; rarely - severe hypotension, collapse, loss of consciousness, hyperthermia, chills, increased sweating, fatigue, malaise, back pain, myalgia, numbness, hot flashes or a feeling of cold.
INTERACTION Transfusion therapy with intravenous immunoglobulin can be combined with other drugs, in particular antibiotics. The introduction of immunoglobulins can weaken (for 1.5-3 months) the effect of live vaccines against viral diseases such as measles, rubella, mumps and chicken pox (vaccinations with these vaccines should be carried out no earlier than 3 months later). After the administration of large doses of immunoglobulin, its effect can last in some cases up to one year. Do not use simultaneously with calcium gluconate in infants.
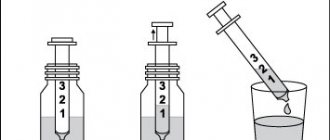
METHOD OF APPLICATION AND DOSAGE Intravenously, drip at a rate of 30-40 drops per minute. The dosage regimen is set individually depending on the indications, the severity of the disease, the state of the immune system, and individual tolerance. Immunoglobulin immediately before administration is dissolved in water for injection in the volume indicated on the label. Typically, a single dose of the drug is 0.05-0.2 g/kg body weight (2.5-10 g). The course of treatment consists of 3-10 transfusions, performed every 24 hours (depending on the severity of the disease). For systemic connective tissue diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitis, etc.), the drug is administered in doses of 0.2 - 0.4 g/kg body weight per day daily for 3-10 days. For agamma- and hypogammaglobulinemia, the drug is administered in such doses to compensate for the deficiency of circulating IgG, controlling the level of serum immunoglobulins. Courses of treatment are repeated after 2-3 months. In some cases, in severe septicotoxemic conditions, the daily dose of the drug can be increased to 1 g/kg body weight. Immunoglobulin for intravenous administration is used only in a hospital setting, subject to all aseptic rules.
OVERDOSE No data available.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS For persons suffering from autoimmune diseases (blood diseases, connective tissue diseases, nephritis), the drug should be administered against the background of appropriate therapy. Immunoglobulin passes into breast milk and may help transfer protective antibodies to the newborn. After administration of the drug, the patient's condition should be monitored for at least 30 minutes. Antishock therapy must be available in the room where the drug is administered. When anaphylactoid reactions develop, antihistamines, glucocorticosteroids and adrenergic agonists are used. A temporary increase in the level of antibodies in the patient’s blood after the administration of immunoglobulin can cause false positive results of serological tests. The rate of intravenous administration should not be exceeded due to the possibility of developing collaptoid reactions.
STORAGE CONDITIONS At a temperature of 2-8 °C. In the refrigerator (not recommended to freeze).