Cervical osteochondrosis is a disease that affects the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. Cervical osteochondrosis refers to deforming dorsopathies. Involutive changes in the discs are observed as early as 20 years of age. At the same time, they become more sensitive to stress, less elastic, and lose lubricating fluid.
Most often, the pathology occurs in the elderly, but currently there is a significant increase in incidence among children and young people. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital identify cervical osteochondrosis using the latest diagnostic tests. After clarifying the diagnosis, complex therapy is carried out with the most effective medications, physiotherapeutic procedures and innovative methods of physical rehabilitation.
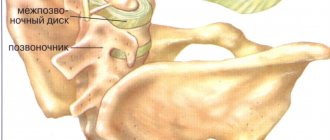
The name of the disease consists of two Greek terms “osteon” (bone) and “chondros” (cartilage). Cervical osteochondrosis begins with changes in the central part of the disc. The intervertebral disc loses moisture and decreases in size, this leads to the convergence of the vertebral bodies and pinching of the nerve roots and blood vessels. The vertebrae receive nutrients from surrounding tissues, which causes harm to the body. Compression of nerves and blood vessels leads to a protective muscle spasm, which, as the disease progresses, becomes a cause of pain.
Which doctor treats this disease?
At the Yusupov Hospital, the treatment of osteochondrosis is the field of activity of neurologists. However, if symptoms of neck osteochondrosis appear, you may contact a general practitioner. A neurologist will select medications for cervical osteochondrosis that have the least burden on the body, which is important during drug therapy.
To determine the presence of a pathological process in cartilage tissue and cervicobrachial osteochondrosis, the patient is sent for a comprehensive examination to the diagnostic center of the Yusupov Hospital. Tactics on how to treat cervical osteochondrosis are being developed in accordance with research results.
Interdisciplinary collaboration also makes it possible to treat the patient's comorbidities. In addition, when contacting the Yusupov Hospital, the patient receives full information support: a treatment plan, an extract on the cost of services, information about consultations with specialists and diagnostic measures.
Make an appointment
Contraindications to osteotherapy.
Osteopathic science uses gentle means of regulating the internal processes of the spinal region. Limitations in its use are due only to the presence of chronic diseases and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Osteopathy is used with caution when:
- Oncological processes.
- Foci of infection.
- Some types of psychiatric disorders
An alternative to osteopathy for these contraindications can be massage or therapeutic exercises.
Causes
Cervical osteochondrosis develops under the influence of various provoking factors. No specific cause of cervical osteochondrosis has been identified. Often the disease is associated with metabolic disorders and aging of the vertebrae.
Researchers suggest that cervical osteochondrosis develops for the following reasons:
- Excessive load on the spine. A high load on the spine is observed when wearing incorrect shoes, flat feet, obesity, and prolonged sitting;
- Metabolic disorders. Deficiency of vitamins, minerals, and calcium metabolism disorders can cause degenerative processes in the vertebrae;
- Congenital and acquired anomalies of the development of the spine and ligamentous apparatus (thickening of the ligaments, lumbarization, sacralization);
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract leading to insufficient absorption of nutrients;
- Infections, intoxication;
- Injuries, bruises, spinal fractures, as a result of which the blood supply and innervation of the spinal column are disrupted, which causes their degenerative disorders;
- Stress;
- Wearing shoes with heels;
- Pregnancy, especially multiple pregnancy;
- Autoimmune connective tissue lesions, pathological structure of collagen types 1 and 2;
- Occupational hazards (lifting heavy loads, prolonged vibration, working in a sitting position with constant head tilt);
- Atherosclerotic and other changes in the vertebral arteries;
- Curvature of the spine (kyphosis, scoliosis, kyphoscoliosis).
An important risk factor for the development of cervical osteochondrosis is family history. This fact proves the presence of osteochondrosis in children when the spine is not yet overloaded.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women
As a rule, symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women appear 5-10 years later than in men. First of all, this is due to the later onset of menopause and anatomical features (including a lighter bone structure).
Before the mass distribution of computers and the demand for “sedentary” professions, the average age of onset of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women ranged from 50 to 55 years. But now the disease has “rejuvenated” to 40-45 years.
Unlike a similar problem in men, symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women often include:
- sudden surges in pressure, especially due to the weather;
- pallor of the face, blue discoloration of the lips and skin;
- decreased sensitivity, up to numbness, of the skin of the face and cervical-collar area, which is accompanied by tingling or goosebumps;
- a feeling of nausea, which is especially intensified in stressful situations.
It should be remembered that cervical osteochondrosis is a disease of the whole body, so it can negatively affect conception and the course of pregnancy. Also, symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in women can cause ovarian dysfunction and disruption of the monthly cycle.
Degrees
Thanks to the special structure of the spine, it is able to perform its functions. The main structural unit is considered to be the spinal motion segment (SMS). It consists of two adjacent vertebrae, an intervertebral disc and a muscular-ligamentous apparatus. Osteochondrosis leads to dystrophic-degenerative processes, first in the intervertebral disc, then in the vertebra. When one vertebra is damaged, its functions are provided by adjacent ones. This leads to increased load and loss of mobility of the affected segment.
Doctors distinguish several stages in the development of cervical osteochondrosis:
- First degree of cervical osteochondrosis. Since the intervertebral disc is deprived of its own blood supply and receives nutrients from surrounding tissues, it is susceptible to degenerative changes. Osteochondrosis at the 1st stage of development is characterized by destruction of the nucleus pulposus and cracks in the fibrous ring. Clinically, this is manifested by acute or persistent local pain in the neck (cervicalgia) and stiffness;
- Osteochondrosis of the second degree of the cervical spine. At this stage, the destruction of the fibrous ring continues, pathological mobility and instability of the vertebrae appear. Patients complain of pain in the neck, aggravated by physical activity, tilting the head or in a certain position;
- The third stage of the disease is characterized by complete destruction of the fibrous ring. The nucleus pulposus is not fixed. Intervertebral hernias may occur, which cause severe pain. At this stage, due to poor fixation of the SMS, spinal curvature may form;
- At the fourth stage of the disease, the intervertebral disc is replaced by connective tissue, and other adjacent segments are affected. Spondyloarthrosis and arachnoiditis develop. The joints become completely immobile - ankylosis develops. Bone tissue grows around the affected area - osteon is formed. With the fourth degree of cervical osteochondrosis, clear symptoms are observed: severe pain that radiates to the arm, sternum, to the area between the shoulder blades, sensitivity disorders.
Possible complications
Lack of timely treatment can lead to serious complications, including:
- bulging intervertebral discs
(formation of hernia/protrusion);
- intervertebral disc rupture,
accompanied by pinching of nerves and blood vessels, which can cause death;
- radiculopathy
(damage to the nerve roots), the formation of osteophytes (spikes on the vertebral body) with the manifestation of numerous paresis and paralysis.
Symptoms and signs
Signs of cervical osteochondrosis in the initial stages may be nonspecific: dizziness, headaches, weakness, crunching when moving the head. As the disease progresses, the following symptoms develop:
- Severe pain in the neck and shoulders;
- Numbness of the hand;
- Dizziness;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Increased sweating.
There are several syndromes that appear with the development of a pathological condition of the muscles of the back and cervical spine:
- Cervical migraine syndrome.
- Vertebral artery syndrome.
- Hypertension syndrome.
- Cardiac syndrome.
- Radicular syndrome.
They occur when nerve endings are injured, arteries and veins are compressed during the development of the disease. The most dangerous complication is considered to be vertebral artery syndrome. There is a disruption of blood flow through the artery supplying the brain and spinal cord. The patient's hearing decreases, vision decreases, and constant dizziness develops. The patient may lose consciousness while moving due to a sudden disruption of blood flow.
As a result of compression of the nerves responsible for the innervation of the muscles of the chest and diaphragm, pain appears in the heart area, not associated with heart disease, but at the same time tachycardia, arrhythmia and hypotension may develop. Compression of the veins leads to the development of hypertensive liquor syndrome. Intracranial pressure increases, nausea, vomiting, and severe headache appear due to impaired blood flow from the brain.
As a result of compression of the neck, radicular syndrome develops - severe pain appears in the neck, shoulders, shoulder blades, and back of the head. With this syndrome, the arms and neck area become numb. With cervical migraine syndrome, the patient experiences severe pain in the back of the head, which is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Reflex syndromes occur when the spinal roots are not yet affected. Patients complain of pain in the neck, head (especially the back of the head), and arms on one or both sides. Reflex pain, unlike radicular pain, is not combined with sensory disturbances. Cervicalgia can be dull and aching. Acute sharp “shoots” of pain are called cervicago. There is muscle spasm and pain, pain in the paravertebral points. Signs of cervical osteochondrosis intensify in an uncomfortable position, when tilting the head, coughing, or physical activity. Signs of epicondylosis, glenohumeral periarthrosis and shoulder-hand syndrome appear due to nerve impulses from the annulus fibrosus of the affected segment, which causes compensatory muscle spasm.
Radicular syndromes are accompanied by impaired motor activity and sensitivity. In this case, nerves and blood vessels are infringed, venous and lymphatic outflow in the pathological focus is disrupted as a result of a decrease in the intervertebral canal. The pain with radicular syndrome is acute and intense. A common cause of pinched spinal nerves is the formation of a hernia. In the area of the pathological focus, muscle tone decreases. With radiculoischemia, in addition to nerves, blood vessels are compressed.
If the phrenic nerve is involved in the pathological process, cardiac syndrome occurs. It manifests itself as a burning, acute pain in the left half of the chest with radiation to the arm and interscapular region. The name of the syndrome is due to the fact that the nature of the pain is similar to an attack of angina. The main difference between pain during angina pectoris is that it is relieved after taking nitroglycerin, can occur at rest and is combined with interruptions in heart rhythm (tachycardia, arrhythmia).
Signs of cervical osteochondrosis depend on the location of the pathological process. When the upper cervical vertebrae are affected, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted due to compression of the cerebral arteries. This leads to headaches (especially in the occipital region), dizziness, fainting, and high blood pressure. Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the inner ear. Patients also experience nausea and vestibular and ocular symptoms.
With combined damage to the vertebrae, they speak of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis. The disease is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Dizziness;
- Pain in the neck and arm;
- Tingling, crawling sensation on the upper limb;
- Intercostal neuralgia.
Make an appointment
What is the danger of cervical osteochondrosis?
Vital arteries and capillaries are located in the cervical areas. There are complaints of headaches and shoulder pain, chronic fatigue and decreased performance. These signs should not be ignored. Treatment not started on time is often accompanied by many unpleasant syndromes:
- lesions of the spine: pinched nerve, resulting in the appearance of hernias, protrusions of a chronic nature;
- disturbances in the functioning of the vegetative-vascular system: high blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, tachycardia;
- hypertension and hypotension: headaches, dizziness, nervous system disorders;
- disturbances of the vestibular apparatus: deterioration of visual and auditory functions, disorientation in space, noise and darkening in the eyes, nausea and vomiting;
- laryngeal syndrome and voice changes;
- endocrine pathologies.
To avoid irreversible consequences, you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible. In the neurosurgical department of Dr. Zavalishin E.E. They use modern methods of diagnosis and treatment of such dangerous diseases as osteochondrosis and intervertebral hernia.
Diagnostics
Cervical osteochondrosis is a chronic disease that can lead to the formation of hernias and compression of the spinal cord. Therefore, it is important to establish an accurate diagnosis in a timely manner and begin therapy. To identify cervical osteochondrosis, the following types of instrumental diagnostics are used:
- Spondylography or radiography of the spine. This research method is painless, highly informative and does not require special training. An X-ray of the spine allows you to evaluate its anatomical and functional features. In the picture, attention is paid to the structure of the vertebrae, their relationship to each other, the distance between them, the lumen of the spinal canal;
- Computed tomography - provides information mainly about the condition of bone tissue, allows you to identify narrowing of the spinal canal and disc herniation;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to determine changes in soft tissues. The MRI image clearly shows changes in the intervertebral discs and spinal cord.
At the Yusupov Hospital, the patient undergoes a comprehensive examination. Doctors take into account the individual characteristics of his body and concomitant diseases. An important advantage of the neurology clinic is the availability of modern, high-quality equipment and specialized specialists: neurologists, neurosurgeons, oncologists.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
If you experience one of the symptoms listed above, it is advisable to immediately seek medical help. The sooner a problem is diagnosed, the higher the likelihood of it being completely eliminated. A neurologist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis of the spine.
After the patient contacts, the neurologist will interview the patient and, based on his complaints, make a conclusion about the presence of the disease. Most often, patients complain of pain, discomfort, and problems with movement of the upper limbs. After the interview, the doctor will conduct a visual examination of the patient. Will be assessed:
- Correct posture;
- At what angle are the shoulder blades, shoulders and ilia bones located?
- The location of the line of the spinous processes along the length of the spine.
A visual examination allows you to determine what pathological processes began in the spine and how much they affected the spine and surrounding tissues.
The final diagnosis is not made solely on the basis of examination and questioning of the patient. Additional examinations are required. Most often, the patient is sent for radiography and computed tomography. If for one reason or another it is impossible to make a final diagnosis, the patient is referred for magnetic resonance imaging. Additional examinations include Doppler sonography; the procedure allows you to find out the state of the circulatory system in the cervical region.
Drug treatment
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine consists of drug and non-drug therapy. Even after complete recovery, to exclude relapses of the disease, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital carry out preventive measures. In the acute period, for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, doctors prescribe medications to patients from the following pharmacological groups:
- Non-narcotic analgesics (analgin, baralgin, trigan). They are taken orally or administered intramuscularly to quickly achieve an effect;
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen, ketanol);
- B vitamins in large doses.
In order to reduce fluid retention in the area of the spinal root and surrounding tissues, diuretics (furosemide, Triampur, Lasix) are used. Antihistamines (diphenhydramine, suprastin, pipolfen) potentiate the effect of analgesics. Muscle spasms are eliminated by muscle relaxants (sirdalud, miorix, mydocalm, flexen). For prolonged severe pain, neurologists perform a nerve block.
To improve metabolic processes in the intervertebral disc, chondroprotectors (alflutop, evalar) are used. These drugs increase the content of glycosaminoglycans, increase the firmness, elasticity and shock absorption of the intervertebral discs.
Anti-dizziness pills
Patients often experience dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis. To reduce them, doctors prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. NSAIDs belonging to different groups differ in their mechanism of action and effect, so only a qualified specialist can determine the appropriate drug.
It is important to remember that medications for cervical osteochondrosis cannot be taken without a doctor’s prescription. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have side effects, so before prescribing them, the neurologist determines the presence of contraindications in the patient and the required dosage. Drugs for dizziness in cervical osteochondrosis can improve the patient’s quality of life.
Injections for osteochondrosis
Injections for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine help relieve pain during an exacerbation. With this method of drug administration, the effect occurs quickly. Neurologists use various injections.
Nurses administer drug solutions subcutaneously, intramuscularly or intravenously. During the period of exacerbation of the disease, drugs that are administered by injection for cervical osteochondrosis have an exclusively symptomatic effect. To treat the disease, contact the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital.
Make an appointment
Headache treatment
Headache is a symptom that occurs with various disorders. However, cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by attacks of intense headaches. Head movements increase symptoms, so to eliminate them, doctors prescribe analgesic tablets and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Treatment of neck osteochondrosis.
Every year the disease gets younger. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine affects people 30-35 years old and even younger. Due to the fact that teenagers spend a lot of time in a static position at the computer, the disease even affects schoolchildren. Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is accompanied by increased intracranial pressure and blurred vision. The pain forces you to see a doctor for treatment. Even the mildest form of osteochondrosis requires work to restore. It is important to objectively assess the nature of the disease.
Each case of the disease is individual, but there are general stages of treatment:
- The initial stage is dedicated to pain relief. There are different ways to block pain: sometimes painkillers are urgently needed before full treatment can begin.
- Disc restoration. Such long work requires patience and perseverance. There is a wide range of medical remedies. The main task is to determine which one to give preference to.
- Activation of blood supply to the affected area. An important stage that promotes better nutrition of tissues and delivery of the necessary amino acids and microelements to them.
- Restoring muscle tone. Provides the ability to correctly position all skeleton fragments.
- Prevention and building a recovery program have a long-lasting effect. Rehabilitation continues even when inflammation is eliminated.
People think that a specialist will first prescribe painkillers. Medicine offers different ways to solve the question: “Which doctor should I contact to correct osteochondrosis?”
The easiest way to relieve suffering is drug treatment. Taking one tablet in a short time treats pain and relieves symptoms. But an expert will tell you that the shortcut is not always the best. Many drugs are designed to act on a specific organ. The nature of their influence on others has not been studied. The biological structure of the spine is a complex system of interconnected elements. For the treatment of osteochondrosis, a universal remedy that treats one and does not harm the other has not yet been invented. But there is a combined approach to eliminating pathologies in cervical osteochondrosis, taking into account the relationship of the elements.
Osteochondrosis demonstrates the importance of comprehensive treatment of the cervical spine. The skeleton, muscles, ligaments, veins, arteries, lymphatic ducts are located in the neck in close proximity to each other and act in complete mutual synchronization.
Osteopathy is a specialization of restorative medicine based on a comprehensive approach to healing the body. Treatment of organs for osteochondrosis is considered in their close relationship. In this medical field, when pain occurs, the task is to eliminate it, treat the disc and generally regulate processes.
Drug-free treatment is aimed at activating protective reserves. An osteopathic doctor stimulates hidden abilities, looks for ways to self-healing and self-regulation. Among several osteopathic branches for cervical osteochondrosis, the following methods are most effectively used in rehabilitation:
structural
fascial
visceral
craniosacral
1. Structural method of treating osteochondrosis.
Structural therapy is most often used in the correction of neck osteochondrosis; it is aimed at regulating the musculoskeletal system. The cervical region is a fragment of the spinal column. Functional failures are caused by damage to the articular processes. The hard base of the skeleton in the neck grows, and osteophytes—growths—appear. Such formations are often called thorns or salt deposits. With such a pathology, you need to consult a specialist. Osteophytes injure soft tissues and discs. During the course of the illness:
- the muscles lose the ability to support the spine and have to resort to a supporting corset.
- the ligaments lose their elasticity, deform the skeleton, the vertebrae fuse and the skeleton loses flexibility.
- The nerve endings are compressed, causing pain.
If you have severe neck pain, you need to get treatment: a neurologist will determine the nature of the pathology.
The structural principle of healing allows you to regulate the imbalance of the internal parts of the spine. No medications are used.
2. Fascial correction method.
Fascial osteotherapy regulates the condition of connective tissue, veins, and arteries. In the presence of osteochondrosis of the neck, this direction is as effective as the structural one. The cartilage and disc tissue interact with the skeleton. Cervical or thoracic osteochondrosis is most often observed due to deterioration of the fibrous substance. To preserve the function of the spine, comprehensive treatment provided by an osteopathic specialist is invaluable.
3. Visceral method of treatment.
Nerve endings, muscles, soft tissues of the neck, blood and lymphatic pathways function within a single system. Constant inflammatory diseases of the throat affect the condition of the cervical area: inflammation spreads to the soft tissues, pain and swelling appear, followed by compression of the spinal cord. The replenishment of intervertebral discs with necessary substances deteriorates - osteochondrosis occurs. Visceral osteoguidance eliminates situations that interfere with the effective interaction of internal organs. Which approach is most preferable is decided by the therapist.
Osteoscience traces the connections between different areas of the human body and regulates their interaction, eliminating disease. A doctor treats cervical osteochondrosis with the help of a patient.
4. Craniosacral method of correction of osteochondrosis.
When correcting osteochondrosis of the neck, the doctor often chooses craniosacral therapy. The theoretical basis of a full-fledged section of restorative medicine lies in the study of skull bones that have the ability to rhythmic micromobility.
Between the hard parts of the skull there is a connecting fibrous layer. It is inactive, but under the influence of impulses a subtle shift of the bone plates occurs. A rhythm failure indicates a deviation in neural connections or a deviation from physiological norms not only in the brain, but also in other organs associated with it.
With the development of osteochondrosis of the neck, a failure of impulses is observed. With such a course of affairs, an imbalance occurs in the movement of fluids inside the skull, dizziness is added, and it is difficult to turn the head. The supply of important substances to the disc pulp is deteriorating.
The current situation is especially bad for the condition of the smallest vertebrae. From an elastic ball acting as a shock absorber, the core of the pulp turns into a hard, rigid substance. The main burden falls on the disk; it collapses within a fairly short time.
Regulation of cranial impulses eliminates the original source of the problem: normalizing the circulation of fluids improves the supply of the disc with the components necessary for life. Manual massage is actively used. Osteochondrosis of the cervical region is receding.
Manual and osteotherapy are unique techniques from the arsenal of restorative medicine, where the doctor treats osteochondrosis using the most sensitive instrument - the hands.
After getting rid of pain, sessions will most likely be needed to consolidate success. In parallel, it is recommended to pass
- Psychotherapy – is implemented in the absence of organic and infectious lesions to relieve stress and adjust to improving the quality of life.
- Diet therapy is an effective action to reduce the force of pressure on the skeleton. A carbohydrate-free diet and limiting fat intake will quickly correct the situation.
- Therapeutic physical education – carried out in a clinical setting under the guidance of a rehabilitation instructor.
- Physiotherapy is an auxiliary tool that is actively used in osteotherapy to stimulate certain areas of self-regulation.
Non-drug therapies
Complex non-drug therapy for cervical osteochondrosis of the spine includes:
- Protective mode - if the roots are pinched, patients lie on a hard surface,
- Massage;
- Physical therapy;
- Spinal traction;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
Massage for cervical osteochondrosis is used to reduce pain and swelling, improve peripheral blood supply, and eliminate muscle spasms. A contraindication to performing this procedure is the presence of acute pain. Massage the neck and back in the direction of lymph outflow. Particular attention is paid to the interscapular and paravertebral zones.
Therapeutic exercises for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are aimed at eliminating muscle spasms and strengthening the muscular frame. Since instability of the vertebrae often occurs in the cervical spine, the exercise therapy instructor conducts individual classes, during which he teaches the patient how to safely perform exercises. Some authors recommend conducting physical therapy classes in a Shants collar.
To improve the mobility of the cervical vertebrae, rehabilitation experts recommend performing the following exercises:
- Flexion and extension of the neck. Bend your head forward toward your sternum without pulling your shoulders forward and then back. Hold the incline for 3 seconds, repeat each exercise 8-10 times;
- Neck turns. Turn your neck first to the left until it stops, then to the right, without changing the position of your shoulders and the level of your chin;
- Lower your head all the way down. Then tilt your head back without changing the level of your shoulders. Hold the position for 5 seconds.
The following exercises have been developed to strengthen the neck muscles:
- Place your hand on the back of your head. Tilt your head back, resting on your hand;
- Place your hand in the temporal region. While tilting your head, resist with your hand;
- Place your hand on your forehead, resisting it, tilt your head forward;
- With your right hand, tilt your head to the side, your left hand should be behind your back. Repeat the exercise on the other hand.
Autogravity therapy is the exact name for the spinal traction procedure. It is carried out using special devices. The goal of therapy is to reduce muscle spasm and restore the correct position of the vertebrae. To avoid complications, spinal traction is performed by a doctor.
To improve blood supply to the pathological focus, relieve swelling and eliminate pain, the following physiotherapeutic procedures are used in the Yusupov Hospital:
- Diadynamic currents. During this procedure, low-frequency currents are applied using a special device, which stimulate the muscles, relieve spasm and pain. They have a positive effect by improving tissue trophism;
- Ultraviolet irradiation. Under the influence of UV radiation, vitamin D metabolism improves, calcium content increases, bone tissue becomes stronger;
- Exposure to ultrasound - used to accelerate blood flow, antispasmodic and reparative effects. Ultrasound is capable of penetrating deep into tissues; sometimes it is used for better absorption of medicinal substances;
- Amplipulse therapy - allows you to relieve pain by blocking nerve impulses from the source of pain.
In the acute period of the disease, which lasts 4-7 days, painkillers, antispasmodics, and irritants are used to reduce pain. The patient is provided with rest. Immobilization of the cervical spine is carried out using a Shants collar. Exercise therapy and massage are contraindicated. Ultraviolet radiation is used.
The duration of the subacute period is 29 days. After complete recovery, the patient should rest for several days. Then you can begin a course of rehabilitation therapy. In the chronic course of the disease, the patient is prescribed muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors, B vitamins, and for pain - analgesics, NSAIDs. Physical therapy classes and massages are provided. The patient is given physiotherapeutic procedures (amplipulse, alternating current exposure), and spinal traction is performed.
At the Yusupov Clinic, doctors have extensive experience in successfully treating cervical osteochondrosis. Patients are given the opportunity to undergo a full course of rehabilitation: physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, spinal traction. The neurology clinic employs specialists of the highest medical category, professors, who use proprietary methods for the treatment of osteochondrosis.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures pursue a number of goals:
- Localization of the inflammatory process;
- Relieving muscle spasm;
- Pain relief;
- Launch of regenerative processes;
- Increasing general and local immunity;
- Restoring the normal position of nerve fibers, eliminating compression and pinching.
Most often, the following procedures are prescribed for cervical osteochondrosis:
- Shock wave therapy. Using a special device, the acoustic wave is directed directly to the cartilage tissue of the spine that has been damaged. As a result, metabolic processes are launched, salt and calcium deposits are destroyed, which interfere with the normal movement of joints and vertebrae. The procedure is characterized by a cumulative effect, often the first results become noticeable only 2-3 months after the start of treatment.
- Acupuncture. Acupuncture is often used to treat and prevent cervical osteochondrosis. It is important that the procedure is performed only by a qualified doctor, otherwise you may not only experience a lack of effect, but also a worsening of the current condition. The essence of the procedure is that special needles are installed on biologically active points, forcing the body to start metabolic processes and stimulate the production of natural painkillers.
- Massage. The main goal is to reduce pain and improve blood circulation in the damaged area of the cervical spine. With proper massage, the muscles acquire the lost tone, and as a result, it is possible to eliminate the risk of relapse of osteochondrosis in the future. When attending the first massage sessions, the patient encounters severe pain; it is important not to stop treatment due to pain, but to go through all the procedures prescribed by the doctor.
Surgery
It is mainly prescribed in advanced stages of the disease, when the use of medications and visits to physiotherapeutic procedures does not bring any results. The indication for surgical intervention is catastrophic narrowing of the spinal canal.
Modern surgical techniques allow the patient to be discharged from the hospital within 3-5 days and begin outpatient treatment of the symptoms of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis. Over the next three months, the patient undergoes rehabilitation.
Physiotherapy
A correctly chosen set of exercises for osteochondrosis can not only improve the patient’s general condition, but also speed up the process of treating the disease. There are several effective exercises:
- Turns and tilts the head in different directions. The exercise is performed in a sitting position, it is important not to jerk, all movements should be smooth with a gradual increase in the number of repetitions and the amplitude of the inclination.
- Tilt the head to the sides with resistance. Body position - sitting at the table, one elbow stands on the table, while the palm presses on the temple. Tilt your head towards your hand, creating slight resistance.
- Shoulder lift. Raise your shoulders as high as possible and hold in this position for a while.
- Self-kneading of the back of the head and neck with your fingertips. It is important that the movements are soft and do not cause pain. You can perform self-massage in any comfortable position.
It is important not to treat cervical osteochondrosis at home without consulting a neurologist; a set of exercises must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Nutrition
Proper nutrition for osteochondrosis is an important condition for achieving remission. The progression of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis stops with diet and therapeutic measures. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital know how to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, so they create a complex of treatment measures, including procedures, exercise therapy, proper nutrition and lifestyle changes.
Many patients turn to neurologists with the question of how to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine and whether there are any dietary restrictions. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital create individual nutrition programs that take into account the patient’s preferences. The diet for osteochondrosis is based on balanced, low-fat foods that are rich in nutrients. The patient's daily diet includes foods high in calcium.
Less common symptoms
The more the cervical spine degenerates, the more likely it is that the spinal canal will narrow and increase the risk of spinal cord compression. If compression of the spinal cord occurs, myelopathy will develop and symptoms such as:
- Difficulty moving arms and/or legs
- Problems with coordination and/or balance
- Loss of bowel and/or bladder control
- Weakness and/or numbness anywhere below the neck
- Shooting pain in the limbs, which may worsen when bending forward
Cervical myelopathy is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. This condition usually occurs in people over 50 years of age.
How to sleep with cervical osteochondrosis
For patients with diseases of the musculoskeletal system, the question of how to sleep properly with cervical osteochondrosis is relevant. Sleeping on your stomach provokes further development of the disease, so it is better to avoid sleeping in this position. The most optimal positions are on the back and side.
Cervical osteochondrosis progresses while resting on a bed with a soft mattress. Therefore, experts recommend giving preference to elastic mattresses, as well as moderately soft pillows. If a patient is diagnosed with cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, experienced specialists at the Yusupov Hospital will tell you which bedding is safe for sleeping.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men usually appear at the age of 40-45 years. Patients often notice them during physical activity (for example, working out in the gym or lifting weights). Delayed self-diagnosis of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men is associated not only with a reluctance to go to the doctor, but also with physiological prerequisites. Men have stronger and thicker vertebrae than women, and the vessels are stronger. Therefore, they may notice discomfort only when changes have already affected the intervertebral discs. Characteristic symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis in men include:
- decreased overall strength and endurance;
- deterioration of libido and erectile dysfunction;
- irritability, sometimes neuroses;
- deterioration of motor skills (“awkward fingers”);
- headaches that do not go away after taking analgesics.
Vertebral hernias with symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are more common in men than in women.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence or progression of cervical osteochondrosis, doctors recommend:
- Maintain correct posture;
- Lead an active lifestyle, take breaks at work;
- Do physical therapy exercises regularly;
- Sleep on a hard and flat surface, orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- Get rid of bad habits, especially smoking;
- Choose shoes taking into account the physiological structure of the foot;
- Do not carry bags on one hand, this leads to curvature of the spine;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right, eat plenty of fruits and vegetables;
- Do not sit for a long time with your head bowed;
- Go swimming.
In order to improve blood circulation, you should regularly undergo therapeutic massage.
Development of the disease
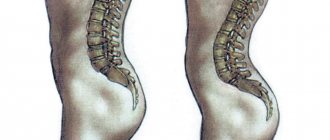
The cervical spine is most vulnerable to various injuries and degenerative changes. This is due to the fact that this segment is the most mobile, and the muscles here are weak. Small cervical vertebrae withstand heavy loads every day, which leads to the gradual destruction of intervertebral discs. The vertebrae put pressure on each other, which causes the cartilage pads between them to lose a lot of fluid and begin to degrade and become deformed.
In addition, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine develops due to insufficient nutrition of cartilage tissue. And the spinal canal in this area is narrow, so it is often compressed, which causes neurological symptoms.
Pathology in women in the early stages is manifested by heaviness in the back of the head, tingling in the hands, etc. Patients often confuse the first signs of the disease with fatigue.
There are a large number of blood vessels and nerve roots located in the neck area; when they are compressed, neurological disorders can also occur. It is especially dangerous if a deformed disc or vertebrae compresses the vertebral artery, which supplies important parts of the brain. When it is compressed, coordination of movements is disrupted, a woman may lose her balance, her vision and hearing deteriorate, and the risk of stroke increases.
Reference. According to statistics, most often cervical osteochondrosis is found in patients aged 25–40 years. This is due to a massive decrease in physical activity and sedentary work. Women are more often diagnosed with the disease than men, as they have more fragile vertebrae and thin bone tissue.
Doctors distinguish 4 stages of osteochondrosis of the spine:
- Stage 1 – the intervertebral disc loses some of its moisture, its height decreases, and cracks may appear on the fibrous ring (outer shell). This is the stage of cervical chondrosis, which is difficult to identify, since it has unexpressed symptoms. The neck quickly gets tired, there is discomfort, heaviness in the damaged area, sometimes there is a slight pain that quickly passes.
- Stage 2 – cracks on the surface of the disc increase, the nucleus pulposus (the gel-like contents of the disc) shifts and can protrude through the damaged areas. This is how protrusions of the cartilage lining appear, which can compress the spinal cord and its roots. Severe pain, weakness, limited mobility periodically appear, and numbness of the face, neck, shoulders, and arms may occur.
- Stage 3 - the protrusion breaks through the outer shell of the disc, thus forming a hernia. The pain becomes more pronounced, and neurological disorders are present.
- Stage 4 – the disc is almost completely destroyed, the vertebrae rub against each other, and bone growths (osteophytes) appear on their edges, which are designed to stabilize the damaged segment. Nerve endings, spinal cord, and blood vessels are infringed. Adjacent joints begin to be damaged. Clinical signs are pronounced.
It is easiest to stop degenerative-dystrophic changes in the first two stages of osteochondrosis of the spine. At stage 3, comprehensive treatment will help stop further destruction of the spinal segment. At the last stage, surgery cannot be avoided.
Treatment in Moscow
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors have been treating cervical osteochondrosis for many years. For the rehabilitation and restoration of performance of patients with osteochondrosis, the rehabilitation clinic has all the necessary equipment. You can find out the cost of treatment on the official website of the hospital.
Make an appointment with a neurologist online or call the contact center phone number. The neurology clinic employs the best doctors in Moscow, leading experts in the treatment of degenerative-destructive diseases of the spine. Patients are offered a comprehensive rehabilitation program, the cost of which is lower than the use of individual procedures.
Make an appointment
Stages of development of osteochondrosis
There are 4 main stages of development of cervical osteochondrosis of the spine:
- Stage 1 – pain, crunching when turning the neck, decreased mobility, headaches, sleep disturbance;
- Stage 2 – thinning of the intervertebral disc capsule, pinching of nerve endings and blood vessels;
- Stage 3 – the occurrence of protrusions, hernias, deformities of the vertebrae, resulting in dizziness, pain, movement coordination disorders, and impaired blood supply to the brain;
- Stage 4 – constant pain, possible neurological complications, loss of consciousness, blurred vision, and even paralysis.
Establishing diagnosis
If you notice symptoms of osteochondrosis, then go to a therapist. After a visual examination, the specialist will refer you to an orthopedist, vertebrologist or neurologist.
The following methods are used to diagnose cervical osteochondrosis:
- X-ray allows us to find out that the patient’s vertebrae are displaced, there are osteophytes on their edges, the distance between the vertebrae has decreased, etc. For this, the study is carried out in different planes. To detail the characteristic changes, the doctor takes targeted photographs.
- CT scan of the cervical spine provides detailed information about pathological changes in the vertebrae. This method allows you to obtain three-dimensional images for a more detailed study; it is used in severe diagnostic cases.
- MRI is used to accurately assess the condition of soft tissues (nerves, blood vessels, ligaments, muscles) in the affected area.
- Electromyography allows you to check the conductivity of the nerve fiber.
Doctors may also prescribe an ultrasound scan (Doppler ultrasound of the main arteries of the brain) to determine the state of blood flow in this area.
Lifestyle recommendations
To quickly get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of osteochondrosis and stop degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical segment, you need to adjust your lifestyle. To do this, the patient must follow these recommendations:
- Go for walks every day, avoid running, jumping and other explosive activities.
- Do not carry heavy objects.
- You cannot sit for a long time; in extreme cases, wear a corset and periodically take a horizontal position.
- Perform special physical exercises for the back muscles at home.
- Sleep on an orthopedic mattress and a special pillow.
- Follow a diet, replenish your diet with foods rich in magnesium, calcium (nuts, dairy products, seafood, legumes), as well as plant fiber, chondroitin (jellied meat, jelly). Avoid fatty, fried, too salty foods and alcohol. Your doctor will advise you in more detail about nutritional rules. But in any case it must be correct.
Hypothermia should not be allowed; warming up will be beneficial in the absence of an inflammatory process.
Surgery
The operation is prescribed in the last stages of osteochondrosis of the spinal cord, which are accompanied by serious destruction of osteochondral structures. Also, surgical intervention cannot be avoided if conservative methods are ineffective or the spinal canal has narrowed significantly.
In the above cases, an anterior cervical discectomy is performed. During the procedure, the doctor immobilizes the damaged segment of the spinal column and removes the hernia that was compressing the spinal nerve. Then the vertebrae between which the disc was removed are fused. If necessary, the space between the vertebrae is filled with a synthetic insert (cage).
After 3–5 days the patient is discharged home. The rehabilitation period is about 12 weeks. To speed up recovery, you need to take medications, wear a corset, lead a healthy lifestyle, go to physiotherapeutic procedures, and eventually perform exercise therapy.
Preventive measures
Ideally, prevention of osteochondrosis of the spine should be done during the period of intrauterine development. The expectant mother must exclude factors that negatively affect the development of the fetus: infections, oxygen starvation, intoxication. If there has been a birth injury, the newborn must undergo treatment.
To reduce the likelihood of developing osteochondrosis of the spine, a woman should follow these recommendations:
- Load your spine evenly, for example, carry a load in both hands or alternately in your right and then your left.
- Don't lift too much weight on your own.
- Try to avoid neck injuries and hypothermia.
- While working in garden plots, take a break every 1.5 hours and lie down to rest for 20 minutes.
- Choose shoes with elastic soles that will soften impacts while running or jumping.
- When sitting for long periods of time, use a high-backed chair with a headrest or wear a corset.
It is also important to eat right, control weight, avoid stress, take vitamin supplements for medical reasons, and promptly treat pathologies that can cause osteochondrosis. During the remission stage, it is recommended to visit sanatoriums to undergo a course of treatment.