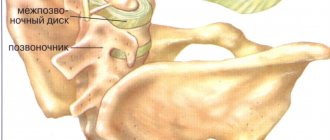
Osteochondrosis in the chest, in comparison with other forms of the disease, develops quite rarely. It is important to identify it at the first stage so that the destructive process in cartilage does not lead to dangerous complications.
The joint and spine clinic "ArthroMedCenter" offers effective treatment for thoracic osteochondrosis in Moscow at affordable prices! "ArthroMedCenter" is a medical institution that specializes in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. We offer not only qualified assistance from specialized specialists, we offer an innovative method of treating osteochondrosis of the thoracic region - MBST therapy!
Thoracic osteochondrosis: symptoms, sensation, factors in the formation of the disease
Let's take a closer look at the symptoms and treatment methods for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine. Most often, the formation of the disease in the thoracic region is caused by insufficient load on the muscles (physical inactivity), which causes excessive stress on the discs between the vertebrae.
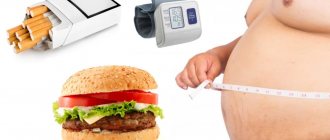
The formation of osteochondrosis in the chest can begin under the influence of the following factors:
- bad habits;
- scoliosis and poor posture;
- genetic predisposition;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- frequent significant physical activity;
- history of spinal injuries;
- great stress and psychological stress.
The functions of the discs between the vertebrae in the sternum are equally negatively affected by increased physical activity and lack of movement.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine: symptoms
Thoracic osteochondrosis is characterized by pronounced symptoms - all sensations are very strong. Therefore, there is no need to delay the treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region. This pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pain syndrome in the sternum of an acute nature, which occurs when staying in one position for a long time. Painful sensations may develop due to sudden movements or heavy lifting.
- A feeling of constriction, both in the back and in the sternum. Breathing becomes difficult - if you inhale or exhale deeply, pain occurs.
- Hypesthesia of some areas of the body. This phenomenon is observed when the nerve receptors located in the spinal canal are damaged.
- Inability to sharply turn the body or stretch the arms and raise them to the top. Any of these movements results in severe pain.
- Painful manifestations of a dull nature in the shoulder blades and between them.
- Due to insufficient blood supply, the feet become cold.
- Chills and goosebumps appear all over the body.
With osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine, the symptoms are determined by how advanced the disease is. Moreover, against the background of this pathology, dysfunction of other organs is possible. As a result, the following symptoms may develop:
- intercostal neuralgia;
- feeling of burning and itching in the feet;
- flatulence, problems with stool, gagging or heartburn;
- peeling of the skin, thinning and brittle nails;
- dysfunction of the reproductive/genital organs;
- in some cases there is a lack of oxygen.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is also characterized by acute and prolonged pain in the form of attacks. With exacerbation of the disease, the symptoms become as vivid as possible. If the disease has reached an acute stage, the patient must be hospitalized.
Coronary pathology
This reason is not the most common, but the most dangerous is when the thoracic aorta or coronary artery is dissected, torn, or otherwise damaged.
Coronary insufficiency
The patient feels sudden, very severe pain. It burns in the chest all the way to the back. Pain in the peritoneum pulsates. Hemorrhage may occur in the pleural area or chest space.
Important! If pain of a similar nature occurs, it is necessary to immediately hospitalize the patient and provide him with emergency care.
As first aid, pain relief with alkaloids is used. Then the operation is performed.
Also, chest pain projected to the back can cause a heart attack, called a posterior one. It occurs as one of the consequences of coronary artery dissection. In this case, the pain is unbearably strong, and specifically in the thoracic spinal region.
Important! Here the minutes count, and if the patient is not helped immediately, death may occur.
Video - Acute coronary insufficiency. Angina pectoris
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis using MBST therapy
ArthroMedCenter became the first Russian spine and joint clinic to use MBST technology: all the attention of doctors is focused on ensuring that patients get rid of problems and disorders of the musculoskeletal system. MBST therapy allows you to eliminate the cause of disorders of the musculoskeletal system, and not only relieve the patient from the unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
The principle of operation of this therapeutic method is based on the fact that tissue metabolism is regulated by electric and magnetic fields. And if in a healthy organ or system the processes of regeneration, that is, renewal, occur independently, then in case of dysfunction they require impulse influence from the outside. In MBST therapy, magnetic resonance is used as such an impulse, which sends signals to the tissues affected by the disease, reproducing the signals of a healthy body system. Normalized metabolism allows you to resume the regeneration process in the cells of cartilage, bone tissue, tendons, etc.
After 8-10 sessions, not only the destruction process stops, but also the restoration of damaged tissues. The effect lasts for more than 5 years without surgery or long-term medication!
Dorsagia and Dorsago
Against the background of thoracic osteochondrosis, one can often notice the formation of vertebral syndromes: dorsalgia and dorsago.
Dorsago is the instant formation of acute pain in the sternum. As a rule, this condition is observed in those who remain in one position for a long time, for example, sitting. The syndrome can develop during the process of standing up after a long stay at the table in an unchanged position. Dorsago is characterized by the appearance of unbearable pain and limited movement in the spine.
Unlike dorsago, dorsalgia develops gradually. With this syndrome, slight pain and discomfort appears in the affected area of the ridge. An increase in pain is observed when taking a deep breath and bending the body.
The muscles become tense and movements in the spine become limited. Typically, the pain increases in the evening and goes away in the morning after a 10-minute walk.
The presence of other pain syndromes against the background of osteochondrosis in the thoracic region.
With this pathology, other pain syndromes may develop, which complicate the accurate diagnosis of the disease. When the disease spreads to the area of the upper thoracic segment of the sternum, pain appears in the esophagus, larynx, and a “lump in the throat” is felt. If the lesion is located in the mid-thoracic segment, discomfort occurs in the right hypochondrium.
When the pathology spreads to the area of the lower thoracic segment, pain in the peritoneum develops, similar to signs of a disease in the intestines.
It is worth noting that there is no relationship between the pain syndrome due to thoracic osteochondrosis and the patient’s nutritional quality. Moreover, pain can appear regardless of the time of year. Although the pain associated with this disease can increase in the evening and during physical overload. By morning, the discomfort usually disappears or subsides.
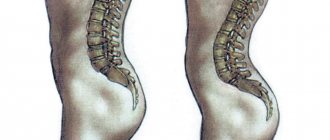
Scoliotic deformities
All diseases that result in poor posture cause pain in the thoracic spinal area. This can be observed in young people, with osteoarthritis or Scheuermann-Mau disease, as well as with kyphosis, kyphoscoliosis and any form of scoliosis.
Scheuermann-Mau disease: general information
Scheuermann-Mau, kyphosis
Prices for orthopedic corsets and posture correctors
The pathology begins in the joints connecting the ribs. Their tissues become coarser, lose elasticity, and weaken their connective functions. Potassium salts are deposited on the vertebral bone, forming an osteophyte. This growth begins to pinch the nerve, compressing the intervertebral canal. A pain syndrome develops - from mild to unbearable, localized in the interscapular area.
Possible consequences
During the development of thoracic osteochondrosis, various complications may appear regarding internal organs. Most often, the development of diseases of the heart and blood vessels is noted. This is due to irritation of nerve receptors in the chest and neck area.
Occasionally the appearance of:
- disturbances in the functioning of the duodenum;
- problems with digestion;
- dyskinesia in the gallbladder.
To avoid the development of such health problems, treatment for osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine should be started on time.
Prevention
Since preventing the disease is much easier than treating it, preventive measures against the occurrence of osteochondrosis are relevant for almost every person over thirty. The main thing is to lead an active life, not experience excessive abnormal stress, and exercise in a balanced manner. Sudden movements, a static sitting position, lifting weights with a jerk - all this can provoke osteochondrosis.
An active lifestyle will help maintain spinal health into old age.
A healthy diet will also help prevent degenerative changes. The occurrence of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis can be promoted by high-calorie food, its excess, plus lack of activity. If you take care of your health, engage in moderately active sports, and perform preventive exercises, your body will be able to resist osteochondrosis on its own, and the disease will not overtake you.
Diagnostics
Before starting treatment for osteochondrosis in the chest, a comprehensive diagnosis of the patient is carried out. It includes:
- Visual examination and questioning of the patient. If the disease has reached stage 2-3, noticeable deformation of the skeleton occurs. The doctor must collect anamnesis to exclude or confirm hereditary factors that can provoke the occurrence of thoracic osteochondrosis.
- Laboratory testing of blood and urine.
- X-ray examination to determine the presence and size of osteophytes and the height or contours of the intervertebral discs. X-rays also allow us to determine the size and location of the hernia, and changes in disc shape.
- Carrying out discography allows you to determine the outlines of the nucleus pulposus. This procedure is carried out with the introduction of a contrast agent.
- Computed tomography is used in rare cases, since the diagnosis is characterized by strong radiation that negatively affects the patient.
- An ECG is done to exclude or confirm the presence of cardiac ischemia.
Timely diagnostic measures allow for effective treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region
Before starting therapy for thoracic osteochondrosis, the doctor determines the causes of the disease, considers the symptoms that appear against the background of the disease, and only then prescribes treatment. This disease requires an integrated approach to treatment. A conservative treatment method for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region involves a combination of drug therapy with physiotherapeutic procedures.
In case of exacerbation of the pathology, it is recommended to maintain bed rest, use painkillers and other medications that are effective for such pathology. Medicines are selected by the doctor for any patient personally, taking into account the characteristics of his body and the clinical picture of the disease. Typically, for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, the following may be prescribed:
- analgesics to get rid of acute pain in the sternum, which leads to dysfunction in the respiratory organs and causes significant discomfort when moving;
- drugs to relieve muscle spasms;
- medications with a high content of B vitamins;
- medications with herbal components that retain fluid in intervertebral discs affected by osteochondrosis.
How to treat referred back pain, which doctor to consult
Therapy is prescribed by a specialized specialist. To start, you can see a therapist. Treatment tactics are selected based on the underlying disease that was the source of visceral pain in the ribs. The gastrointestinal tract is examined and treated by a gastroenterologist. A hepatologist specializes in hepatobiliary pathologies. Vertebrogenic pain due to neuralgia and spinal destruction is relieved by a neurologist or vertebrologist. A urologist deals with dysfunctions of the urinary system. A gynecologist helps solve “women’s problems”.
Preventive actions
To prevent the development of problems with the spine, the following preventive measures must be observed:
- lead an active lifestyle: swim in the pool, run in the morning, do exercises;
- if you are engaged in a sedentary job, you should try to sit with a straight back and relaxed shoulders;
- sedentary work should be carried out on a chair with a back that will support the spinal column;
- To ensure that the spine is in the correct position during the night's rest, it is recommended to acquire an orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- avoid lifting heavy objects, but if this is unavoidable, then lift them smoothly;
- it is recommended to pump up the abdominal muscles;
- you need to use only shoes that are comfortable to wear;
- You should include foods enriched with vitamins and microelements in your diet.
It is quite difficult to protect yourself from the development of thoracic osteochondrosis, but nothing is impossible. If any signs of pathology are detected, you should immediately seek help from a specialist to determine the nature of the symptoms that have arisen. It is possible that the reason may lie not in the spine, but in dysfunction of other internal systems and organs.
If the previously listed rules are observed, the possibility of developing thoracic osteochondrosis is reduced to a minimum.
Moscow, metro station Dubrovka, st. Sharikopodshipnikovskaya, 6/14
| Loading map... |
Other reasons
These mainly include pathologies of internal organs, such as:
- herpes;
- shingles;
- polio;
- liver diseases;
- gallbladder problems;
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes;
- pancreatic problems;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- drops in the kidneys;
- appendicitis;
- vasculitis;
- oncology.
What to do for pain in the thoracic spinal area
You should consult a doctor if the pain is intense and does not go away. When contacting, carefully describe your symptoms. Manual diagnostics and a series of examinations will be prescribed, including MRI, cardiogram, and tests.
The primary diagnosis is carried out by a therapist. He then refers the patient to other specialists.
Primary diagnosis is carried out by a therapist
If we talk about preventive measures to prevent pain in the thoracic spinal area, they are as follows.
- Hardening.
- Cold and hot shower.
- Charge every day for at least a third of an hour.
- Lack of excess weight.
- Balance in nutrition.
- Orthopedic furniture for sleeping (mattress) and work.
- Align your back and maintain good posture.
- Lifting weights competently.
- No injuries.
- Playing sports with a trainer.
Orthopedic chair
Is it possible to help yourself with back pain opposite the sternum? There are warming compresses and ointments, exercises and decoctions. But it is best to use them after the doctor has authorized the appointment, so you will have to find a way to show up to him.