Dorsalgia is a set of symptoms that are united by stinging or burning pain of varying intensity in the back area. There are several types of dorsalgia: cervical, thoracic and sacral. The causes of back pain are many different diseases of a vertebral or non-vertebral nature.
Dorsalgia is a group of disorders characterized by mild, moderate or intense pain that occurs in the muscle nerves or joints located in the dorsal region.
The pain can be constant or intermittent, localized to one area or scattered over a wide area. It can be stinging or burning. If the pain is associated with the cervical spine, it can develop into intense pain, accompanied by a feeling of dumbness.
Dorsalgia of the thoracic region
With dorsalgia of the thoracic region, the patient, as a rule, complains of pain in the chest area, aggravated by palpation or movement of the body; there is aching pain under the shoulder blades; pain when moving your arms, bending or turning your body, when you inhale and exhale deeply, between the ribs, there is a feeling of squeezing in the chest. Dorsalgia of the thoracic region occurs as a result of such a common disease as osteochondrosis. But the most common cause of the disorder is a sedentary lifestyle.
Effective methods of treating dorsalgia in Samara
- shock wave therapy
- dosed traction and massage using the Ormed device
- manual therapy
- kinesio taping
- carboxytherapy
- ozone therapy (intravenous administration of ozonized saline solution and subcutaneous local administration of ozone)
- mesoinjection therapy with vascular drugs
- chronomagnetic complex "Multimag"
- physiotherapeutic techniques (high-top, ultrasound, electrophoresis)
- medical therapeutic blockades
- Peripheral magnetic stimulation (PMS)
Dorsalgia of the cervical region
With cervical dorsalgia, compression of the roots, compression of blood vessels, compression of the spinal cord may occur, and may be accompanied by mixed paresis of the arms. The patient complains of pain in the neck, upper shoulder, posterior surface of the shoulder, scapula, and hypotension of the shoulder muscles. The pain can be shooting or chronic. Cervical dorsalgia does not cause sensory impairment. The causes of this type of dorsalgia can be various factors, among them: osteochondrosis, microtrauma of joints and tendons.
Symptoms
Back pain that lasts more than 3 weeks with the presence of functional impairment requires special attention, since it is necessary to identify serious causes of such pain, for example, malignant formations (metastases to bone tissue), inflammatory processes (for example, spondylodiscitis), instability of segments ( e.g. spondylolisthesis) or local compression (spinal or foraminal compression). Typically, serious causes of back pain occur in 5% of cases. The greatest alertness in case of pain for three weeks should be in relation to non-mechanical causes of pain - malignant diseases and infections. Typically, intense back pain at rest is most often a sign of a serious illness (cancer or infection). The presence of serious causes of pain (specific pain) in the back may include the following symptoms (red flags):
- Paroxysmal pain or pain associated with visceral disorders.
- A history of cancer, chronic fatigue, weight loss.
- Fever or immunodeficiency.
- Old age and the presence of osteoporosis.
- Progressive neurological deficit or dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
- Severe stiffness in the morning as the main complaint.
- For nonspecific mechanical back pain, the following red flag symptoms are significant:
- Dissociation between verbal and nonverbal expressions of pain
- Affective description of pain.
- Low pain modulation with prolonged intensity.
- Presence of previous trauma.
- Signs of depression (difficulty falling asleep, waking up earlier, decreased interest in life) and anxiety.
- The need for the use of psychoactive substances
- A history of unsuccessful surgical or conservative treatment.
What is dorsopathy and how to treat it?
Recently, we have published a number of articles devoted to the pathology of the spinal column and methods of its treatment. Have you heard about the disease, which translated means “back pain”?
Dorsopathy. We talk about what is hidden behind this term with Natalya Vladimirovna Umerenkova, a leading specialist in the neurology department of Clinic Expert Kursk LLC.
- Natalya Vladimirovna, what is dorsopathy and how often in your practice do you meet patients with this diagnosis?
This is not just one disease, but a collective concept that includes various pathologies of the spine and paravertebral structures (ligaments, muscles). They themselves can be specific diseases (for example, osteochondrosis, ankylosing spondylitis and others), but the general name for them is “dorsopathy”. In addition, the appearance of such definitions in domestic medicine is apparently associated with the desire to eliminate or reduce terminological discrepancies with foreign classifications (in particular, with the International Classification of Diseases).
We encounter dorsopathies almost every day: we can say that this is one of the common reasons for turning to neurologists and specialists in related specialties - neurosurgeons and orthopedists.
- What types and forms of dorsopathies are there? How is a disease coded in the International Classification of Diseases?
There are various classifications of them. If you adhere to ICD-10, then these are entire blocks of diseases. These include deforming dorsopathies, which include, for example, various spinal deformities, osteochondrosis, displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other, and others.
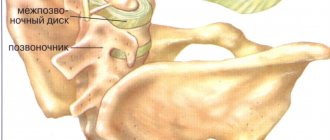
Another group is spondylopathies: ankylosing spondylitis, Forestier disease, disc damage in spinal tuberculosis, and brucellosis. The third is other dorsopathies: this includes, for example, pathology of intervertebral discs and dorsalgia.
According to another classification, diseases are divided into vertebrogenic (spondylogenic, associated with the spine itself) and non-vertebrogenic (muscles or ligaments suffer).
There is dorsopathy of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral spine. There is a variety of it with radicular syndrome.
The code for dorsopathies according to ICD-10 is M40-M54.
- What symptoms are characteristic of dorsopathy?
Its signs are very diverse, so I will name the main ones.
This is a pain syndrome in any part of the spine, in the area of the shoulder girdle and shoulder, buttocks, legs; weakness or excess tension in muscles, limbs, decrease in their volume; sensory disturbance; limitation of movements, daily activity, vertebral artery syndrome.
- What is the triggering factor for the development of dorsopathy?
There are also many of them. This is a hereditary factor, poor nutrition, metabolic disorders and excess weight. Also, the causes of dorsopathy can be infectious processes, age-related changes, spinal injuries, poor posture, flat feet, a sedentary lifestyle, or excessive physical and static stress, suboptimal lifting of weights (for example, by jerking or from an incorrect position), vibration, pregnancy and even smoking.
- How is this disease diagnosed?
It depends on the symptoms the patient has and his complaints. Diagnostic examination is, first of all, the task of the doctor. Only he, during the patient’s appointment, will be able to reliably and competently determine the volume of diagnostic studies that is advisable to carry out in each specific case.
To confirm the diagnosis of dorsopathy, a neurological examination is certainly performed. Additional methods include radiography, including functional tests, magnetic resonance and computed tomography, myelography, electroneuromyography, and laboratory tests. If necessary, consultations with related specialists are carried out - for example, a neurosurgeon, orthopedist, rheumatologist, phthisiatrician.
- Dorsopathy is a diagnosis for adults? Or can it occur in children?
This pathology is typical for almost all age groups. Of course, in the structure of dorsopathy, other diseases will be more common in children than in adults and the elderly.
- What is included in treatment measures for dorsopathy?
Here it is probably appropriate to talk about the standards of treatment for individual diseases included in the group of dorsopathies.
If we, for example, take one of the most common syndromes in the structure of dorsopathies - pain syndrome - then the principles of treatment include the correct motor regimen (currently, according to modern ideas, early activation of the patient is used (feasible loads are selected, bed rest is not recommended), prescribing analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, medications to relax muscles (the so-called muscle relaxants). Also, for dorsopathy, physiotherapy (including massage), manual therapy, acupuncture, physical therapy are used. Of course, the use of any treatment methods must be clearly justified, must there are no contraindications.
- How effective is the use of manual therapy in patients with dorsopathy?
It all depends, in particular, on the specific diagnosis (for some dorsopathies it may be contraindicated), the severity of the disease, and the qualifications of specialists. For the most part, even when indicated, manual therapy is not used in isolation, i.e. it is combined with various other treatment methods, including medications.
- If dorsopathy is not treated, is it fraught with complications?
Depends on the specific disease, its severity and the treatment provided (or lack thereof). Some dorsopathies can regress on their own. In other cases, for example, with pain syndromes, chronization of manifestations and progression of pathological structural and functional changes are possible.
- What specialty does the doctor treat dorsopathy? And does dorsopathy require dynamic monitoring?
Most often, patients have an initial appointment with a therapist, general practitioner or neurologist. Depending on the established diagnosis, the patient will be treated by a specialist of the appropriate profile: neurologist, neurosurgeon, orthopedist, rheumatologist, infectious disease specialist, phthisiatrician.
Dorsopathy certainly requires dynamic monitoring. This is required both during treatment and after it, to assess its effectiveness. In addition, in many cases, the formed structural changes do not regress, i.e. they tend to persist and, if risk factors are not eliminated, lead to progression of the underlying disease.
- Is rehabilitation carried out for dorsopathy and if so, what does it include?
Undoubtedly. Depending on the type of disease, manual therapy, physiotherapy (including massage), kinesitherapy, and swimming can be used. Preventive measures aimed at eliminating risk factors for the development of dorsopathies are of great importance.
For reference:
Umerenkova Natalya Vladimirovna
In 2004 she graduated from Kursk State Medical University.
In 2004-2005, she completed an internship in neurology at the above-mentioned university.
Since 2015, he has been working at Clinic Expert Kursk LLC, and is a leading specialist in the neurology department.
Other interviews with N.V. Umerenkova:
How to relieve tension headaches?
How to get rid of stuttering in adults?
Spinning until you drop!
Treatment
Bed rest is necessary only for acute radiating pain (for example, sciatica) and should not last more than 1-3 days, as this avoids the progression of a decrease in physical activity and the appearance of pathological behavioral dominants. With all nonspecific myofascial pain, lack of physical activity will have a devastating physiological effect, leading to muscle and other soft tissue wasting, joint hypomobility, decreased muscle strength, and bone demineralization. Therefore, bed rest is generally not recommended. Patients are advised to maintain normal physical activity as much as possible. Bed rest leads to the patient developing a fear of movement and the formation of a pathological behavioral cycle.
Drug treatment is often prescribed for dorsalgia and, moreover, long-term unreasonable prescription of NSAIDs is carried out, which not only do not have a pathogenetic effect, but also cause a lot of side effects. The use of NSAIDs is justified for acute pain and for a short period of time. For dorsalgia (nonspecific pain), central muscle relaxants are also prescribed to relieve muscle spasm. If we are talking about chronic pain syndrome, the prescription of antidepressants is justified, since in chronic pain syndrome the central link of pain sensations is in the foreground. Strong analgesics such as opioids are indicated for pain caused by spinal cancer or serious degenerative changes.
Blockades with the introduction of local anesthetics and steroids are quite effective if there are clear indications for their use (for example, blockades in the area of trigger points or paravertebral blockades).
For dorsalgia, non-drug treatment methods, such as physiotherapy, massage, manual therapy and exercise therapy, have become widely used. The use of a complex of these treatment methods often allows one to achieve good results (stable remission).
Therapeutic exercises for dorsalgia
To consolidate the effect of treatment, it is necessary to perform a set of simple exercises daily to maintain and strengthen the muscle corset:
- Spread your arms to the sides. Loosen them a little at the elbows for complete relaxation. Slowly move your arms forward, while tilting the entire shoulder area (about 10 times).
- Lying on your back, bend your knees, then straighten them. Slowly move your legs to the sides, perform circular movements.
- Perform circular movements with your head, first clockwise and then counterclockwise.
Diagnostics
Intense pain at rest for 3 weeks and the presence of “red flag” symptoms usually suggest the presence of a serious illness (tumors or infections). In such cases, it is necessary to conduct instrumental research methods (visualization) using methods such as radiography, MRI, CT (MSCT). If there are signs of progressive neurological deficit, then imaging should be used as quickly as possible and the patient should be transported to a clinic where studies (MRI, CT, radiography) can be performed. X-rays can diagnose fractures, cancer, metabolic changes in bone tissue, infections and inflammatory changes in bone tissue. But it is often necessary to use more informative diagnostic methods, such as MRI or CT, especially when it is necessary to visualize in more detail changes in bone tissue and, especially, in soft tissue. In this regard, MRI is the most informative research method, allowing high-quality visualization of even minor morphological changes in both soft and bone tissues, this is especially necessary if it is necessary to diagnose damage to the nervous tissue of the muscles of the disc ligaments.
If it is necessary to identify focal changes in tissues, scintigraphy can be prescribed, which makes it possible to verify oncological or infectious diseases.
ENMG makes it possible to determine conduction disturbances in nerve fibers and is often used to monitor the dynamics of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment.
Laboratory research methods are used when it is necessary to verify inflammatory oncological and infectious processes.
Chronic vertebrogenic dorsalgia
Like any other chronic pain, pain with chronic dorsalgia goes through several stages in its development:
- arising from the primary focus - the site of injury (acute pain), if the cause of acute pain is not treated, the pain receptors continue to be irritated and send continuous impulses to the central nervous system (spinal cord and brain);
- over time, from continuous incoming information, the cells responsible for conducting and analyzing these impulses in the brain become hyperexcitable and undergo restructuring (central sensitization), a secondary focus of pathological impulses is formed and a change in the psycho-emotional perception of pain (subacute and chronic pain).
Chronic pain is considered after 12 weeks (3 months).
Causes of chronic dorsalgia
Various reasons contribute to the development of pathology in the body:
- myofascial syndrome;
- degenerative-dystrophic processes (osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis, spondylosis);
- intervertebral hernias and protrusions;
- genetic predisposition;
- vertebral displacement;
- compression of nerve endings;
- spinal injury or surgery;
- endocrine disorders;
- psychogenic pain;
- congenital malformations;
- excess weight.
Proper nutrition for dorsalgia
Nutrition is a very important factor in the prevention of dorsalgia, since it is the lack of substances necessary for bone and muscle tissue that can become the impetus for the development of negative processes in the body. Basic rules of dietary nutrition:
- Limit salt intake into the body.
- Introduce restrictions on the consumption of smoked and fatty foods.
- Eat meat no more than 2 times a week, if possible replace it with seafood and fish.
- It is recommended to eat jellied meat, jelly, and broths.
- The basis of the diet consists of vegetables and herbs.
- Be sure to include dairy products and eggs in your dishes.
What is chronic dorsalgia?
Dorsalgia (literally translated from Latin dorsum - back, algos from Greek - pain) is a collective concept of back pain of various origins. This diagnosis occurs quite often. According to statistics, up to 80% of people have experienced back pain at least once in their lives; Most people experience back pain occasionally, while for some it is chronic. Chronic nonspecific back pain (chronic dorsalgia) is most often localized in the lumbosacral region and in the back of the neck.