Otolaryngologist for adults and children
Son of the gods
Stanislav Vladimirovich
25 years of experience
Otorhinolaryngologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences, member of the European Rhinological Society (European Rhinologic Society)
Make an appointment
The most common complication of ARVI in both children and adults is sinusitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of one or more nasal paranasal sinuses.
- Patients complain of nasal congestion, discharge, heaviness and discomfort in the frontal or paranasal areas of the face, and body temperature often rises.
- Pain with sinusitis is often pulsating in nature, it intensifies with sudden movements and tilting of the head. The disease is not mistakenly considered dangerous, but it significantly worsens the quality of life. Without adequate treatment, sinusitis easily becomes chronic, and in some cases complications may develop that can have serious consequences.
Symptoms and signs of sinusitis
Sinusitis is one of the most common diseases. Timely diagnosis and therapy can quickly get rid of pain and other unpleasant sensations, but advanced cases are difficult to treat. It can occur in an acute form with an increase in temperature and characteristic signs, or in a sluggish form.
The following symptoms are observed with sinusitis:
- prolonged runny nose, congestion in both or one nostril, clear or greenish-yellowish discharge, sometimes with blood clots, worsening in the morning;
- a feeling of dryness that persists throughout the day;
- irritation in the larynx area in the evening and at night, causing a dry cough;
- swelling, pain, increased sensitivity in the paranasal and frontal areas;
- decreased sense of smell;
- high temperature in acute form, low-grade fever (37–37.5°) in chronic form;
- increased fatigue and irritability, decreased appetite.
Are you experiencing symptoms of sinusitis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
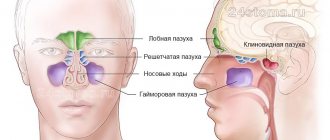
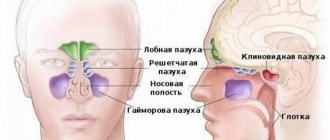
A special case of sinusitis is sinusitis, and they should not be confused. To understand the essence of the terms, you should turn to anatomy. Sinuses are air cavities in the nasal area, primarily necessary for warming and humidifying the inhaled air.
Humans have paired sinuses:
- maxillary (maxillary);
- frontal;
- ethmoid, as well as single wedge-shaped.
All of them are interconnected by channels and covered with a mucous membrane. When the inflammatory process develops, the mucous membrane swells and blocks the channels, causing the fluid to stagnate and cause discomfort. Depending on the location of the inflammation, they distinguish between sinusitis - inflammation in the maxillary sinuses, frontal sinusitis - in the frontal sinuses, ethmoiditis - in the ethmoid sinuses, sphenoiditis - in the sphenoid sinus.
Sinusitis can be left- or right-sided, as well as bilateral.
Reasons for development
Most often, sinusitis in adults occurs due to a viral infection, less often due to a bacterial or fungal infection. The mucous membrane of the sinuses is covered with ciliated epithelium, which traps bacteria, viruses and dust that come with the inhaled air. Normally, mucus is quickly removed, preventing pathogens from starting their activity. But if this mechanism fails, the mucous membrane is not promptly renewed, and viruses manage to penetrate the epithelial cells. Inflammation begins, the vessels enlarge, which leads to increased permeability, and nasal discharge appears. The drainage of the sinuses is impaired, and this creates ideal conditions for a bacterial infection to join the viral one in the absence of adequate treatment. With bacterial sinusitis, nasal discharge acquires a yellowish tint, with purulent sinusitis it becomes greenish.
In addition, the disease can occur for a number of other reasons. Among them:
- adenoid vegetations (pathological enlargement of the tonsils, making nasal breathing difficult);
- allergy expressed by rhinitis;
- anomalies of the nasal septum, polyps, trauma;
- dental caries, complications after dental surgery;
- stress (psychosomatic factor).
Sinusitis can be acute (lasts less than 12 weeks, there is a high temperature and general intoxication of the body), recurrent (up to 4 cases per year) and chronic (lasts more than 12 weeks). Without proper treatment, acute sinusitis can easily turn into a chronic form with mild symptoms, during which periods of remission and relapses are observed.
Frequently Asked Questions About Chronic Sinusitis
People who are faced with an ENT disease want to know the answers to some questions related to getting rid of an otolaryngological problem.
How to cure chronic sinusitis once and for all?
To eliminate the disease, you should contact our medical center, equipped with modern equipment. Highly qualified doctors working at the Yuzhny clinic use methods provided in international practice to cope with the problem:
- rinsing the nose, including the paranasal sinuses according to Proetz;
- antifungal or antibacterial therapy;
- anti-inflammatory drugs, including corticosteroids;
- antihistamines;
- intranasal injections of drugs;
- endonasal novocaine blockade;
- anemization of the mucous membrane.
When is surgery needed?
In difficult cases, for example, when the nasal septum is deviated, conservative therapy is ineffective. Therefore, surgeons provide assistance. An operation performed to eliminate chronic sinusitis will eliminate the obstruction in the nasal cavity that prevents the complete cleansing of the sinuses. The procedure is carried out using an endoscope. It is an optical device that allows visual control of all actions.
Thanks to our reliable equipment, it will be possible in a short time, without incisions and harm to the patient’s health, to cope with the nuances of the abnormal structure of the nasal cavity, to cut out overgrown bone tissue, thick sections of the mucous membrane, cysts, and polyps.
The procedure involves inserting a special tube into the nose. On its sides there are 1-2 channels where surgical instruments are inserted. The video surveillance system helps the doctor examine the problem area and remove altered tissue and pus.
What to do if you have sinusitis?
An unadvanced disease can be corrected using conservative methods that can overcome infection, pain, and inflammation.
It is necessary to ensure that the mucus is removed freely, that is, the drainage of the sinuses is restored. This is achieved by vasoconstrictor drugs that eliminate swelling, which leads to the gradual release of stagnant contents. You can do inhalations. A nebulizer gives the best results. The drug is administered in pulsation mode and has the form of microscopic particles - this ensures access of active substances to distant inflamed areas. The therapy does not cause pain, its duration is 7-10 days. Washing is also performed using:
- Sinus catheter YAMIK. A large negative pressure is created in the nose, which allows the pus to be pumped out. Then the antibiotic is administered in liquid form. Usually 3-5 manipulations are performed.
- Suction aspirator “Cuckoo”. The first step is to narrow the blood vessels in the nasal cavity using a nasal spray. The second stage is the introduction of the medication into one nasal passage and suctioning it through the other. During the procedure, the patient has to say “ku-ku”. The third stage is the administration of the drug.
Before a specialist chooses how to treat chronic sinusitis, he will find out what reason caused the stagnation of the contents. Bacterial damage is treated with antibacterial drugs. If you use antibiotics for a virus, the functioning of the immune system will be disrupted, the microflora will change, and the pathological process will become chronic. Allergies will have to be treated with antihistamines. When an acute form is observed, absorbable agents are prescribed to prevent adhesions.
Physiotherapeutic procedures indicated:
- use of ultra-high frequencies (UHF);
- using current to administer medications (electrophoresis);
- complex effect of ultrasound and drugs (phonophoresis);
- applying electrodes to the inflamed area to reduce pain (diadynamic currents);
- laser exposure (quantum rays).
What are the first signs of chronic sinusitis in adults and children?
Signs of the disease in both young patients and adults are:
- prolonged runny nose (secretion is separated, where pus or blood is observed);
- periods when one or the other nostril is blocked;
- in the evening and at night there is a dry cough;
- feeling that the nasopharynx is dry;
- in the morning the runny nose becomes stronger;
- decreased sense of smell;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- the skin on the face becomes sensitive;
- refusal to eat;
- severe pain in the head, which is affected by the places where the problem area is located (it becomes stronger with physical activity).
Risk factors and complications
Acute sinusitis with high fever develops in people with weakened immune systems and chronic diseases. It is more severe in people who do not adhere to the principles of a healthy diet, have bad habits, in particular, smokers, do not play sports and are not hardened. The development of the disease is facilitated by such anatomical features as an enlarged nasal concha and narrowed nasal passages, which make it difficult for mucus to pass through.
Against the background of reduced immunity, a fungus can also settle in the nasal cavity, especially if it has already affected the nails or skin on the hands or feet.
Improper treatment of sinusitis leads to complications. Among them:
- infection entering the general bloodstream;
- damage to other tissues and organs located in the skull (especially dangerous for the eyes and inner ear);
- deterioration of the sense of smell, up to its complete disappearance.
To prevent the development of complications, you should avoid self-medication and strictly follow your doctor’s recommendations. Purulent discharge is of particular concern.
Complications of chronic rhinosinusitis
Prolonged inflammation carries many dangers, since the sinuses are close to such important structures as the eyes and brain:
- Meningitis (inflammation of the membranes of the brain and spinal cord);
- Sepsis. Generalized infection;
- Other infectious complications. Sometimes the inflammation spreads to the bones (osteomyelitis) or skin (cellulitis);
- Orbital complications. If the infection enters the eye socket, it can cause decreased vision or permanent blindness.
- Partial (or complete) loss of smell. The difficulty of odorants entering the olfactory cleft and inflammation of the olfactory nerve can lead to temporary or permanent loss of odor perception.
Diagnosis of sinusitis
Sinusitis is treated by an otorhinolaryngologist, but in the case of psychopathic factors, it is necessary to involve a psychotherapist. The doctor listens to the patient's complaints and examines his nose (performs rhinoscopy) using special mirrors. A source of local light helps him in this - a head reflector-mirror. In addition, the larynx and pharynx, as well as the ears, are examined using ear specula.
To accurately assess the condition of the nasal sinuses and diagnose the disease, the following types of research are used:
- rhinoscopy - performed using a rhinoscope to examine the nasal septum, determine the degree of swelling and irritation of the mucous membrane;
- endoscopic examination using optics - shows the presence of an inflammatory process in the sinuses, polyps and other pathologies, the condition of the mucous membrane and nasal septum;
- radiography – records foci of inflammation;
- computed tomography – in addition to areas of inflammation, reveals complications;
- puncture - taking samples from the nasal sinuses to test for the presence of a bacterial infection.
Instrumental research methods
- Rhinoscopy. Anterior rhinoscopy against the background of diffuse congestive hyperemia and edema of the nasal mucosa reveals a typical sign of purulent rhinosinusitis - the presence of pathological discharge in the anastomosis area of the affected paranasal sinuses. With sinusitis and frontal sinusitis, the discharge can be seen in the middle nasal passage, and with sphenoiditis - in the upper.
- Endoscopic examination requires a minimum of time and is painlessly tolerated by the patient. The study includes three main points: sequential examination of the lower, middle and upper nasal passages. The method allows you to identify an additional anastomosis of the maxillary sinus. With a choanal polyp, a formation is detected, the stem of which comes from the anastomosis of the maxillary sinus.
- Diaphanoscopy. Illumination of pericutaneous formations or cysts with a narrow beam of light. Allows to identify a decrease in pneumatization of the maxillary and frontal sinuses.
- Ultrasound is a fast, non-invasive method that is used mainly for screening purposes, to diagnose inflammatory diseases and cysts of the maxillary and frontal sinuses. Both special devices for scanning the paranasal sinuses and standard equipment are used. The sensitivity of ultrasound in diagnosing sinusitis is lower than that of X-ray and CT.
- X-rays of the paranasal sinuses are usually performed in the nasomental projection. To clarify the condition of the frontal and sphenoid sinuses, an additional study can be carried out in the nasofrontal and lateral projections. X-ray of the ethmoid bone sinuses is not very informative. Poor quality radiography often leads to diagnostic errors.
- CT , which is performed in a coronal projection, is the most informative method and is gradually becoming the “gold standard” for studying the paranasal sinuses. CT not only makes it possible to establish the nature and extent of pathological changes in the paranasal sinuses, but also reveals the causes and individual features of the anatomical structure of the nasal cavity and sinuses, leading to the development and recurrence of rhinosinusitis. High-resolution CT allows you to visualize structures that are not visible with conventional radiography.
- MRI , although it provides better visualization of soft tissue structures, is not one of the main methods for diagnosing rhinosinusitis. This method gives virtually no idea of the patency of the air spaces connecting the paranasal sinuses with the nasal cavity. MRI is indicated only in certain situations - for example, if a fungal infection of the paranasal sinuses is suspected or the possible tumor nature of the disease, as well as with orbital and intracranial complications of rhinosinusitis. MRI is the most informative method for differential diagnosis between a cerebral hernia (meningoencephalocele) and a tumor or inflammatory process in the roof of the ethmoidal labyrinth.
- Diagnostic puncture and probing make it possible to assess the volume and nature of the contents of the affected sinus and indirectly obtain an idea of the patency of its natural opening.
To assess the patency of the anastomosis of the punctured sinus, a simple scheme is used, taking into account 3 degrees of violation of the patency of the anastomosis (see table). To do this, using a syringe connected to a needle or drainage tube, the contents are first aspirated, and then the sinus is washed.
Assessment of the patency of the natural anastomosis of the paranasal sinuses
| Normal patency of the anastomosis | During aspiration, air or liquid contents of the sinus enter the syringe; when rinsing, the liquid flows freely into the nasal cavity |
| Obstruction of the 1st degree | During aspiration, negative pressure is created; during rinsing, the liquid freely enters the nasal cavity (valve mechanism and negative pressure in the sinus) |
| Impairment of patency II degree | Aspiration from the sinus is impossible; rinsing is possible only by increasing pressure on the syringe plunger |
| Level III obstruction | Neither aspiration nor lavage of the sinus is possible: there is a complete blockage of the anastomosis |
How to cure sinusitis in adults
This disease can be catarrhal, purulent, mixed type.
With catarrh, profuse discharge and swelling of the sinuses are observed. With proper treatment, recovery occurs relatively quickly.
With purulent sinusitis, bacteria and other pathogenic microorganisms develop in the appendages. The temperature rises, general intoxication is observed, and the discharge becomes greenish. Without adequate treatment, inflammation can spread to bone tissue.
If the causative agent is a virus, the symptoms resemble a cold: discomfort in the throat, runny nose, stuffy nose, cough. In this case, antibiotics are not prescribed. The main therapy is bed rest, plenty of warm fluids, and saline nasal sprays for rinsing. At high temperatures, antipyretic drugs are prescribed. Normally, recovery occurs within 7–10 days; if the process is prolonged, the alarm should be sounded.
If the nasal discharge has become thick, with a greenish-yellow tint, and the swelling does not go away, antibiotics may be prescribed after additional examination. In this case, the person recovers in 10–14 days.
Sinusitis can be allergic - the disease becomes chronic and manifests itself throughout the year. Treatment involves identifying the allergen and taking antihistamines. It is possible to prescribe immunotherapy.
Previously, in the treatment of sinusitis, vasoconstrictor drops were widely used, which temporarily reduced swelling of the mucous membrane. But it turned out that their long-term use (over 5 days) worsens the condition of the ciliated epithelium and leads to the development of drug-induced rhinitis. And children may even experience symptoms of poisoning. Considerable problems also arise due to the uncontrolled use of antibiotics and antiviral drugs.
When drug therapy does not give the expected results, a surgical procedure is performed - puncture. A puncture is made to remove accumulated fluid, and then the sinuses are washed with antiseptic solutions. Elimination of curvature of the septum, removal of polyps and tumors also cannot be done without surgical intervention. Physiotherapeutic procedures may be additionally prescribed during treatment: heating, laser and magnetic therapy.
Only a doctor can choose the right remedy for sinusitis, taking into account the research results. There is no universal pill for this disease; the approach to each patient is individual.
Odontogenic sinusitis
A special place is occupied by odontogenic maxillary sinusitis, which occurs due to problems with teeth. It can be perforated, as well as chronic, often purulent.
Main reasons for development:
- caries and periodontitis;
- osteomyelitis, suppurating cysts of the upper jaw;
- perforation of the maxillary cavity, the presence of root remains due to the removal of severely neglected teeth;
- unerupted teeth;
- careless work of the dentist when filling dental canals.
It also happens that the roots of the tooth grow into the maxillary sinus, and granulomas and subperiosteal abscesses appear at their tips.
The disease is diagnosed using radiographic or tomographic examination.
Its distinctive features are:
- unilateral damage to the maxillary sinus (during infection, bilateral sinusitis mainly develops);
- absence of anatomical predispositions to development - deviated nasal septum and other anomalies.
Treatment is carried out only surgically.
Prices
| Service | price, rub. |
| Collection of material for histological examination (Biopsy) | 4000,00 |
| Collection of material for bacteriological research | 350,00 |
| Diagnosis of disorders of the separation mechanism of the hypopharynx | 1250,00 |
| Consultation with an otolaryngologist, candidate of medical sciences | 2600,00 |
| Consultation with an otolaryngologist | 1800,00 |
| Repeated consultation | 1300,00 |
| Inhalation (ultrasonic) device Omron nebuliser | 350,00 |
| Steam inhalation | 350,00 |
| Toilet cavity boil/nasal abscess | 3000,00 |
| Radio wave nasal polypotomy (multiple polyps, one side) | 21800,00 |
| Radio wave coagulation of eroded vessels of the nasal septum | 6000,00 |
| Radio wave coagulation of blood vessels for recurrent nosebleeds | 14500,00 |
| Radio wave coagulation of the inferior turbinates | 18200,00 |
| Primary surgical treatment of nasal wounds up to 1.5 cm | 2500,00 |
| Primary surgical treatment of nasal wounds over 1.5 cm | 2900,00 |
| Puncture of the maxillary sinus (on one side) | 2100,00 |
| Removal of a foreign body from the nasal cavity | 1450,00 |
Home Remedies for Sinusitis
During the acute period of illness at home, it is recommended to only rinse the nose with an isotonic (0.9%) saline solution or a decoction of medicinal herbs and drink more warm teas.
- Decoctions can be prepared from St. John's wort, eucalyptus, sage, calendula, which have antibacterial properties, as well as chamomile, mint, linden, which have an antispasmodic effect. The decoction must be freshly prepared.
- Vials of sterile saline solution of the required concentration are sold at the pharmacy. At home, 9 grams of table or sea salt are dissolved in 1 liter of boiled water.
- When the acute period is over, you can do steam inhalations with eucalyptus and menthol oils. For this purpose, an inhaler or an aroma lamp is used. It is recommended to avoid drinking coffee and alcoholic beverages, which remove fluid from the body. Tea with honey, rose hips and/or ginger is beneficial. Massage of the paranasal sinuses and breathing exercises give a good effect. You can warm your nose, but this is contraindicated in case of fever and purulent sinusitis.
Myths and dangerous misconceptions about treating sinusitis
There is an opinion that sinusitis is a minor disease that will end in a week without treatment. However, it is worth remembering: the nasal sinuses are located close to the brain and eyes, to which the inflammatory process can spread under unfavorable circumstances. It should also be borne in mind that sometimes the natural opening connecting the cavities of the sinuses and nose is blocked, then there is no discharge at all. In this case, puncture and x-rays are used for diagnosis.
Another myth is related to punctures. They say that after one puncture you will have to do this procedure constantly. But today this is done quickly and painlessly, under local anesthesia. The puncture site heals without changing the anatomy of the sinus.
Sinusitis during pregnancy
Due to hormonal changes during pregnancy, almost 30% of women experience swelling and congestion in the nasal mucosa. This makes it difficult for mucus to come out and creates ideal conditions for bacteria to multiply in the sinuses. Increased stress on the immune system leads to a weakening of the defense mechanism, which may result in infectious rhinosinusitis. Disturbances in nasal breathing, up to its complete blockage, lead to insufficient saturation of the mother’s blood with oxygen, which can lead to fetal hypoxia. This is especially dangerous in the first trimester of pregnancy, when vital organs are forming. If sinusitis is infectious in nature, intoxication of the whole body begins. The maxillary and frontal sinuses are most often affected.
It is impossible to fully treat sinusitis during pregnancy, since many drugs have a negative effect on the fetus. Therefore, in order to avoid the addition of a bacterial infection and the development of complications, at the first signs of ARVI and allergic rhinitis, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The main method of treating sinusitis during pregnancy is to rinse the nose with a water-salt solution and decoctions of medicinal herbs to remove mucus, reduce swelling, and restore drainage function. Dry heat and inhalations are also recommended, but all therapeutic techniques should be discussed with a doctor.
X-rays cannot be taken during pregnancy, so diagnosis is made based on palpation and rhinoscopy. Allergic sinusitis and vasomotor rhinitis are excluded, and in the case of infectious sinusitis, the type of pathogen is determined. Pregnant women can undergo a puncture under local anesthesia. A sample is taken for bacteriological culture, and then the sinuses are washed with antiseptic solutions. In cases of severe bacterial sinusitis, it is possible to prescribe antibiotics that have minimal risk to the fetus.
How and why OBRS develops
Death of ciliated cells
An important role in protecting the nasal cavity from infections is played by mucociliary clearance - a mechanism for removing mucus, dead cells and microorganisms from the respiratory tract. It is provided by the cells of the ciliated epithelium, which lines the inside of the upper respiratory tract. Cilia direct mucus and foreign substances into the external environment.
With ARVI, massive death of epithelial cells occurs. The number of cilia decreases, which contributes to a decrease in mucociliary clearance and creates conditions for stagnation.
Impaired sinus aeration
Anomalies in the structure of the respiratory tract and swelling of the mucous membrane prevent the outflow of mucus from the paranasal sinuses and disrupt their normal ventilation. Stagnation promotes the introduction and proliferation of microorganisms. This is how sinusitis develops.
Formation of bacterial films
An important role in the chronicization of the inflammatory process is given to biofilms, which shield microorganisms as a shield from immune cells and antibiotics.
First, bacteria attach to the mucous membranes of the body and multiply, forming a colony, then form a protective shell. Under it, their vital activity continues even during the period of remission of the disease. Microbes are able to exist for many years, going beyond the biofilm, causing exacerbations of the disease and creating new inflammatory foci.
Bacterial biofilms have the ability to protect themselves from the effects of antibiotics (causing antibiotic resistance), antiseptics, and factors of the human immune system
Sinusitis in children
The maxillary sinuses are fully formed by the age of 7, so children most often have frontal sinusitis and ethmoidal sinusitis. Their symptoms are the same as those of adults, but they are more pronounced. The disease begins with nasal congestion and dry cough in the evening (night). Then a headache appears and appetite decreases.
In children under one year of age, ethmoiditis is especially severe. There is severe intoxication, swelling and copious discharge. The risk of infection of the bronchopulmonary system and even the development of sepsis cannot be ruled out.
In children from 1 to 3 years old, infection of the eyes is also possible, in children 4–7 years old – damage to the maxillary sinuses, and in older children – inflammation of the frontal part.
Factors predisposing to the development of rhinosinusitis
- Rhinitis.
- Intolerance to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Anomalies in the structure of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses (deviated nasal septum; bulla of the middle turbinate; additional anastomosis of the maxillary sinus, etc.).
- Immunodeficiency states (X-linked agammaglobulinemia; common variable immunological deficiency; deficiency of IgG subclasses; selective IgA deficiency; hyper-IgM syndrome; HIV).
- Diseases accompanied by a slowdown in MCT (Kartagener's syndrome; Young's syndrome; cystic fibrosis).
- Wegener's granulomatosis.
- Hyperplasia of the pharyngeal tonsil, adenoiditis.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease.
- Fistula between the oral cavity and the maxillary sinus.
Prevention
To prevent sinusitis, you should maintain your immune status at the proper level. To do this, it is recommended to lead a healthy lifestyle, enrich the menu with vegetables and fruits, harden yourself, and play sports. Sinusitis often occurs after ARVI and influenza, so it is advisable to get vaccinated before the start of the epidemic period. When the first signs of sinus inflammation appear, you should consult a doctor for adequate treatment to prevent the disease from becoming chronic. In addition, it is important to promptly identify and correct defects of the nasal septum (curvatures), due to which the passage of mucus may be difficult, as well as regularly sanitize the oral cavity.
Sinusitis
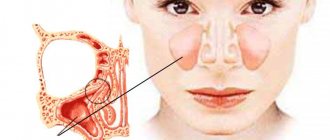
Sinusitis is one of the most common types of sinusitis. This disease is accompanied by inflammation in the maxillary and maxillary cavities. During inflammation, swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, which blocks the opening from the sinus to the nasal cavity. Mucus begins to accumulate in the sinus space, pathogenic bacteria multiply, and pus appears. Inside the cavity, pressure occurs on the vessels, and the person begins to feel pressing pain at the site of accumulation of pus.
Chronic sinusitis is the result of a long inflammatory process, when a person has had sinusitis for more than 2 months. The patient develops general weakness, nasal discharge has an unpleasant odor, the sense of smell is impaired, and a night cough appears. Chronic sinusitis is characterized by inflammation of only one sinus, right or left. Pressure in the sinus can cause a deviated nasal septum.
Symptoms of sinusitis
The following symptoms are characteristic of sinusitis:
- increased body temperature;
- copious discharge, nasal congestion;
- disturbances of smell;
- weakness;
- headache radiating to the forehead, bridge of the nose, teeth;
- pain that intensifies when tilting the head and pressing on the sinus;
- constant, intense pain;
- a feeling of fullness in the forehead and cheeks, aggravated by tilting the head, coughing and sneezing;
- photophobia and lacrimation.
Signs of sinusitis
If after a flu or cold the temperature rises again, your health worsens, severe pain appears when tilting your head and when pressing on the sinuses, then you need to urgently consult an otolaryngologist. These could be manifestations of sinusitis! Sinusitis in adults is often advanced, since adults are usually in no hurry to see a doctor.
Treatment of sinusitis
Antibiotics for sinusitis are used only after a complete examination of the patient, based on the characteristics of his body and possible allergic reactions.
Antibiotics are not advisable in case of sinusitis of allergic or fungal origin. For mild sinusitis, inhalations, rinses and immunotherapy are also sufficient.
1 Rhinoscopy in MedicCity
2 Video endoscopy of the nasopharynx in MedicCity
3 ENT office in MedicCity