Cough
is a reflex reaction of the body to irritation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. The body tries to clear the airways with the help of forced (sharp, intensified) exhalation, which has a characteristic sound. Thus, coughing is a protective reaction of the body. And at the same time, it is a symptom of many diseases. The urge to cough means that free breathing is impaired for some reason, for example, due to the development of inflammation.
Cough comes in different forms. The way we cough can help determine the cause of the cough and diagnose the disease that caused it. It is advisable to pay attention to the main characteristics of a cough in order to tell your doctor about them.
How long does the cough last?
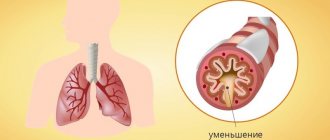
To assess the clinical development of the disease, it is important to determine the nature of the cough. It can be acute, protracted and chronic. A cough is considered acute if it has been present for less than three weeks. Such a cough, as a rule, accompanies the development of acute respiratory diseases and serves to clear the airways of phlegm. Acute cough is usually persistent; that is, while a person is sick, he coughs, and a decrease in the severity of attacks and the cessation of coughing indicates recovery. If the cough returns again after some time, then we are talking about a lingering cough. A cough that lasts from 3 weeks to 3 months is considered to be protracted. Such a cough (a month or longer) means that the disease causing it develops slowly and tends to become chronic. If a cough does not leave a person for more than 3 months, it is classified as chronic. With chronic cough, periods of exacerbation alternate with periods of remission (when there is no cough). Chronic cough is also characterized by fixation - the occurrence of a cough at a certain time of day. Chronic cough is an alarming symptom because it is usually a sign of serious illness. A constant cough loses its useful function and may itself be the cause of the development of certain pathologies.
Symptomatic therapy
Cough caused by natural causes goes away quickly after the irritating factor is eliminated. Until the causes of a pathological superficial cough are clarified, rinsing with antiseptics, local anesthetics (if combined with sore throat and sore throat), moisturizing and softening inhalations can be recommended. Self-administration of antibiotics and antitussives is unacceptable. A persistent cough lasting more than 7-10 days, with increasing shortness of breath and difficulty swallowing, is an indication for emergency medical attention.
Is the cough wet or dry?
A wet (or wet) cough is accompanied by sputum production, which is why it is also called productive. Microbes and their waste products are removed from the respiratory tract with sputum. With a viral infection, the disease often begins with a dry cough
, which subsequently turns into wet. The type of sputum is of great importance. The appearance of pus in the sputum indicates a bacterial infection. An increase in its quantity may indicate an abscess rupture or worsening of the condition. An unfavorable sign is the appearance of blood in the sputum.
Survey
Diagnosis of the causes of a deep dry cough is usually carried out by a general practitioner or family doctor. According to indications, consultations with specialized specialists are prescribed. The primary examination is aimed at assessing the condition of the lower respiratory tract, which is most often affected by symptoms. The primary recommended examination methods are:
- X-ray studies
. Typically, fluorography or plain radiography of the lungs is performed as screening. X-ray diagnostics can detect inflammatory changes, malformations, signs of systemic processes, space-occupying formations in the mediastinum and chest. - Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis
. It is prescribed for prolonged causeless cough, there is information about contacts with patients with tuberculosis infection, and the patient belongs to risk groups. A tuberculin test or molecular genetic test is indicated. - Serological studies
. Due to the absence or meager volume of expectorated sputum, microbiological culture is usually ineffective. Therefore, to exclude a possible infectious process, RIF, ELISA, and PCR diagnostics are more often performed.
A general blood test is performed to identify acute bacterial inflammation, in which the ESR increases, leukocytosis is noted, a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, as well as allergic processes occurring with eosinophilia. At the next stages of diagnosis, additional pulmonary examination methods are often prescribed (bronchography, bronchoscopy, examination of external respiratory function, ultrasound of the pleura and mediastinum, tomography of organs located in the chest, etc.), and allergy tests.
Chest X-ray is used to detect pathological processes
Causes of cough. Diseases that cause cough.
The cause of cough may be:
- acute respiratory infections (flu, ARVI);
- diseases of the upper respiratory tract (chronic rhinitis, chronic sinusitis, pharyngitis) - in this case, coughed up mucus enters the respiratory tract from the nasopharynx;
- laryngitis;
- acute or chronic tracheitis;
- acute or chronic bronchitis;
- pneumonia (pneumonia);
- pleurisy;
- bronchial asthma;
- tumor processes (including lung cancer);
- tuberculosis;
- heart failure;
- ascaridiosis (infection with roundworms);
- smoking;
- inhalation of polluted air (cough is common in representatives of some professions - miners, joiners, carpenters);
- taking certain medications used to treat heart disease and hypertension.
Comparison criterion 2 - cough character
Paroxysmal cough
most often occurs in the first days of illness, becoming more active in the evening and at night.
The attacks follow one after another, there is no way to clear the throat, and between these moments it can be difficult to take a breath. The cause of the problem is dry airways and lack of mucus. The throat becomes irritated and attacks occur again and again. A recurrent cough
can occur suddenly and persist for both short and long periods.
If you notice that you cough from time to time, but for quite some time, then you need to find the reason. It could be an allergy to animals, dust or flowers, sometimes even to the presence of a certain person or to a certain situation. This cough is usually called psychosomatic. A short or one-time cough
can occur when you inhale smoke or any other irritants or when pieces of food get into the respiratory tract.
Child's cough
In children, the cause of cough can also be:
- whooping cough;
- measles;
- mouth breathing. If a child constantly has a stuffy nose and is used to breathing through his mouth, cold and dry air entering the respiratory tract that has not passed through the nasal sinuses can cause irritation of the mucous membrane and cough;
- entry of a foreign body into the respiratory tract. In this case, the cough begins suddenly, the child turns red and begins to choke. It is necessary to help the child cough up a foreign object, for which you should press his chest and stomach to a hard surface, tap between his shoulder blades, or hold him upside down and shake him, tapping on his back. If help fails, the child should be taken to the hospital immediately.
Cough due to postnasal drip
Cause of Drip syndrome
is a secretion that, when you have a runny nose, flows from the nasal cavity into the pharynx, its laryngeal part. The cough is reflexive in nature and appears as a result of mechanical irritation of the pharyngeal receptors. In this case, it is necessary to treat rhinitis that caused postnasal drip syndrome. And, of course, treatment depends on the genesis of this rhinitis. For non-allergic rhinitis, vasoconstrictors and antihistamines are prescribed. The combination of these drugs reduces swelling and mucus production. In the case of allergic rhinitis, glucocorticoids and cromoglycates in the form of a nasal spray are usually used.
A cough is a reason to see a doctor
Cough is a very common symptom. Very often it is combined with other symptoms such as a runny nose, fever, sore throat or chest pain. In such cases, we usually resort to medical help in a timely manner.
But in other cases, cough may be the only symptom: other symptoms are completely absent or appear vaguely. And then the illusion arises that there is nothing serious and you don’t need to see a doctor. In this case, the cough is often chronic, since it is the chronic cough that, as a rule, acts as an isolated symptom.
This is a dangerous misconception. Since many serious diseases (tumors, lung cancer) in the initial stages can only manifest themselves as a cough. In case of heart failure, the patient may complain of cough and not pay attention to other symptoms (shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness, hypertension). Therefore, if the cough does not leave you for several weeks ( cough for more than a month
– this is already a lingering cough) or if you notice
an increase in cough in the morning or at night
, be sure to consult a doctor.
If your child coughs, take him to the doctor. Children's immunity is weaker than that of an adult, so more sensitive monitoring is required over the child's health. Perhaps the child is simply clearing his throat (a healthy child can cough up to 10-15 times a day - this is how his body clears the airways of dust and germs), or maybe he develops an inflammatory process in the nasopharynx or nasal breathing is impaired..
Comparison criterion 3 - cough timbre
Dry cough is called barking
, similar, as one might imagine, to the loud barking of a dog.
This situation is due to the fact that the sputum becomes viscous and is difficult or impossible to cough up. A hoarse or hoarse cough
with dull and whistling sounds indicates diseases such as laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis or pneumonia.
With laryngitis and tracheitis, the cough is accompanied by a hoarse voice, and with bronchitis and pneumonia - chest wheezing. A silent cough
may be associated with severe inflammation of the vocal cords. It sometimes occurs in patients with extreme malnutrition or heart failure.
1.General information
Cough is a spastic, repeated contraction of the muscles associated with the respiratory tract. The natural purpose of such a reflex, which most often occurs in response to irritation of the ENT organs and structures of the respiratory system, is to forcefully cleanse the lumen of the airways. A distinction is made between dry (unproductive) and wet cough (productive, colloquially “wet”, “expectorant”, i.e. accompanied by the separation of mucous masses).
Often there is a transformation of a dry cough into a wet one and vice versa.
In general, a persistent, clearly pathological cough is one of the most common reasons for seeking medical help (according to Western data, from 10 to 40 percent of all visits to the doctor are caused by a cough as the only complaint). In this case, dry cough is more common; For patients, it is more uncomfortable, often painful, debilitating and difficult to treat. There are many reasons and factors that cause such conditions; in some cases, these causes are found outside the respiratory system or nasopharynx. Thus, dry cough remains an acute problem for several areas of modern medicine.
Sign up for a consultation
A must read! Help with hospitalization and treatment!
4.Treatment
Obviously, treating a dry cough means asking the question incorrectly. Therapy is always aimed at eliminating the causes, i.e., a pathological process or condition diagnosed during examination. Often the first priority is to change the nature of the cough to a productive, naturally cleansing one; For these purposes, the so-called expectorants or mucoregulators, herbal remedies, physiotherapeutic procedures.
Drugs are often prescribed that suppress the cough reflex itself. It should, however, be understood: given the variety of possible causes described above, as well as the huge range of antitussive medications available in pharmacies without a prescription, self-medication is simply dangerous, and any specific recommendations are inappropriate here. Any prescriptions of this kind should be made exclusively by a doctor and based on the results of an objective diagnosis.
Sign up for a consultation