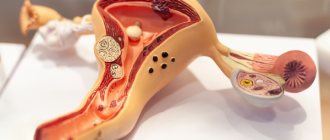
Adnexitis is one- or two-sided inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, caused by various microorganisms. The most common cause of adnexitis is bacteria such as streptococcus, gonococcus, staphylococcus, and E. coli.
There is an opinion that bacterial activity in the body is caused primarily by a decrease in immunity, but no less important reasons can be intestinal dysbiosis, diabetes mellitus, and urinary tract infection. Many microorganisms are constantly present in the female body, and are activated only when the work as a whole fails.
There are acute and chronic adnexitis. Chronic adnexitis is one of the most common gynecological diseases, characterized by frequent relapses. Chronic adnexitis develops in the case of an untreated acute process. Periods of its exacerbation are characterized by a deterioration in general well-being.
The start for the development of adnexitis can be:
- hypothermia
- sex without barrier methods of contraception and during menstruation
- failure to comply with the rules of personal and sexual hygiene
- chronic infections
- overwork
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, constipation
- physical inactivity
- a large number of problems and processes in the female genital area (endometriosis, childbirth, any intrauterine interventions: abortion, hysterosalpingography (examination of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes), diagnostic uterine curettage).
What is adnexitis
The content of the article
Adnexitis (salpingoophoritis) is an inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, which are appendages of the uterus. The process can be one- or two-way.
Treatment of adnexitis is considered a complex area of therapeutic practice, since the development of inflammation can be caused by dozens of different infections introduced into the area of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
Causes of inflammation of the appendages
Inflammation of the uterine appendages occurs due to infectious damage to the membranes of the fallopian tube. Pathogenic microorganisms enter the mucous membrane of the appendages through the blood or lymph flow.
Bacteria can penetrate the appendages by direct, ascending and descending routes.
- Descending route of infection
. In this case, the infection spreads from higher organs down the peritoneum. For example, inflammation can spread from the kidneys with pyelonephritis. - The ascending path
. If the source of inflammation was located below, for example, in the cervical canal. Adnexitis can be a consequence of cystitis. - Straight way.
Some microorganisms (gonococci, chlamydia) can penetrate the mucous membrane of the fallopian tubes directly through natural channels and tissues.
Provoke inflammation of the appendages:
- Chronic intestinal pathologies and chronic inflammation of the genital area;
- Hypothermia of the lower half of the body, leading to inflammation of the genitourinary organs;
- Poor hygiene, unprotected sexual intercourse, or rather, their consequences - STDs;
- Decreased immunity;
- Failure to comply with the deadlines for replacing intrauterine devices;
- Abortion.
If the disease is not treated, the inflammatory process spreads to the pelvic peritoneum and ovaries. Over time, adhesions form in the fallopian tubes, complicating fertilization and leading to female infertility.
General information
Adnexitis can occur in one or two-sided form. The pathology is one of the five most common diseases of the genitourinary system in women. The causative agents of the inflammatory process are microorganisms of various types: bacteria, viruses or fungi. Pathogenic microflora is resistant to the main groups of antibiotics.
Unilateral inflammation is formed as a result of staphylococci and E. coli entering the fallopian tubes, bilateral inflammation - gonococci and tubercle bacilli. The risk of developing the disease increases significantly with hypothermia of the patient's body, the presence of primary infections of the genitourinary system, violation of personal hygiene rules and sexual contacts without the use of barrier methods of contraception.
Symptoms of acute adnexitis
The first sign of an acute form of inflammation of the appendages is sharp or aching pain in the lower abdomen. An additional characteristic sign is irritation of the peritoneum: when pressing with your hand on the abdomen, the pain is weaker than when releasing.
Additional signs of inflammation of the appendages:
- Fever, chills, weakness, dizziness.
- Due to the development of inflammation, leading to enlargement of the organ, kidney and intestinal functions may suffer - constipation, frequent urination, etc.
- If the disease has affected the entire genitourinary system, the urine acquires an unpleasant odor.
- Acute salpingoophoritis is characterized by the appearance of abundant purulent, mucopurulent discharge. They have an unpleasant color and irritate the mucous membranes of the vagina and vulva, causing a burning sensation.
- In blood tests, the doctor will see a picture of inflammation: the ESR is accelerated, the number of leukocytes exceeds the norm.
If the disease is not treated, it will become chronic.
Symptoms
The symptoms of acute adnexitis are specific. Patients experience intense pain in the lower abdomen. Sometimes pain occurs in the perineum and spreads to the anus. The girl’s body temperature increases to 38–39 degrees, and signs of fever appear. Acute urinary retention and bloating are possible. Mucous or purulent contents are discharged from the vagina.
The increase in inflammatory changes provokes the formation of an abscess - a purulent tumor in the ovarian appendages. Sac formation can lead to rupture of the fallopian tube. In this case, purulent contents enter the girl’s abdominal cavity, causing pelvioperitonitis.
In an uncomplicated course of the disease, severe symptoms persist for ten days. The patients' condition gradually improves: the intensity of pain decreases, body temperature normalizes. The result of treatment is the complete recovery of the woman or the transition of the inflammatory process to the chronic stage.
Chronic salpingitis occurs with periodic relapses, leading to the development of adnexitis. Such situations are the result of stress, hypothermia or overwork. Patients suffer from pain and increased body temperature. In some cases, the formation of mucopurulent discharge from the vagina is noted. Within a week, the symptoms completely disappear.
Symptoms of chronic adnexitis
- The pain subsides, the temperature becomes subfebrile (37.1-37.5 degrees). The patient is bothered by dull nagging pain in the lower abdomen.
- If the uterus is involved in the process, algomenorrhea (painful menstruation) and hypermenorrhea (too heavy periods) are observed, and acyclic bloody spotting is possible. Sometimes amenorrhea occurs - the absence of menstrual periods.
With hypothermia, stress, overwork, chronic adnexitis worsens. Often exacerbations are seasonal, occurring in spring and autumn.
ICD
An infectious disease called “left-sided adnexitis” has an individual code in ICD 10.
Left-sided adnexitis according to ICD 10 has the code N70. There is also an alphanumeric coding of this disease in accordance with its form. For example, left-sided acute adnexitis is assigned the number N70.0. left chronic adnexitis has code N70.1. If the etiology of the disease is not clear, it is assigned code N70.9.
Left-sided adnexitis with code N70, regardless of its form, is included in a broader category of the classification medical reference book - “diseases of the female genitourinary system.”
Complications of inflammation of the appendages
Adnexitis is dangerous due to complications, the worst of which for women are:
- A tubo-ovarian abscess is a tumor, the rupture of which causes the deadly disease pelvioperitonitis, a purulent lesion of the pelvic peritoneum.
- Infertility caused by adhesions or hydrosalpinx - accumulation of fluid in the tubal lumen;
- Ectopic pregnancy due to crypts (depressions) in the fallopian tubes;
- Dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse) caused by low-grade inflammation and other reasons.
Treatment of adnexitis
First you need to find out the cause of inflammation of the appendages. For this purpose, tests are carried out for sexually transmitted infections and bacterial flora. Depending on the results, antimicrobial or antiprotozoal drugs are prescribed.
In case of severe intoxication and fever, detoxification solutions and glucose will be administered intravenously. The patient is prescribed vitamins and restorative medications. Additional methods include heating with ozokerite, mud therapy, magnetic therapy, softening adhesions.
If medications do not help, laparoscopic surgery is performed. The doctor dissects adhesions, cleans purulent foci, restoring the natural patency of the fallopian tubes. Antibiotics are injected directly into the site of inflammation.
During the recovery period, the patient is prescribed hormonal contraceptives; becoming pregnant with inflammation of the appendages is prohibited.
The effectiveness of treating inflammation of the appendages: 4 problems of antibiotic treatment
The main treatment for inflammation of the appendages, including the fallopian tubes, is antibiotic therapy. This is explained by the infectious nature of adnexitis. But according to statistics, the effectiveness of treating tubal inflammation is only 37%. This information is found on the Internet, and many women do not understand what we are talking about in this case, so they refuse antibiotics.
Before drawing conclusions, you need to figure out where this figure came from. Let's start with the fact that statistics take as a basis the results of all clinics - both private and municipal. If somewhere in a village a woman with inflammation of the appendages was prescribed a broad-spectrum antibiotic without identifying the pathogen and its resistance to the drug, and it did not help, these figures will be included in the statistical summary. They will be taken into account when calculating the average result, as well as the data obtained with proper treatment.
- Problem 1
. It is not always possible to identify a specific pathogen in the presence of weak laboratory diagnostics, which is not uncommon in provincial or municipal clinics. Therefore, it is difficult to choose the right antibacterial drug. This significantly reduces the overall percentage of treatment effectiveness. Therefore, you can count on the right treatment by choosing a clinic where you can take all the tests and undergo a pelvic ultrasound with a detailed ultrasound of the appendages, including examination of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. - Problem 2.
The second problem when choosing optimal therapy for adnexitis is the formation of adhesions during a long-term inflammatory process around the lesion. This is a protective reaction of the body, seeking to isolate the infectious focus, protecting healthy tissue from it. Adhesions also prevent the antibiotic from reaching the inflamed area, reducing its effectiveness. The gynecologist must take this factor into account when identifying adhesions on ultrasound and assessing their density. - Problem 3.
Weakening of the immune system during a long course of adnexitis. Immune exhaustion reduces the therapeutic activity of antibiotics. Therefore, treatment should be comprehensive, including the use of immunomodulatory drugs. - Problem 4.
Prolonged inflammation is accompanied by the formation of infection resistance to antibacterial drugs that the woman independently took during this period (including for other reasons, for example, colds).
How to increase the effectiveness of treatment of inflammatory processes in the appendages
The use of antibiotics today is a priority in the treatment of unilateral and bilateral inflammation of the appendages. The likelihood of successful therapy can be increased only by a comprehensive examination of the patient and an accurate determination of the causative agent of the disease, as well as by simultaneously strengthening the immune system.
Prevention
Prevention of salpingoophoritis does not differ from that for other inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs. In order to prevent the development of inflammation of the appendages, it is necessary to abandon casual relationships, use protection during sex, avoid abortions, and prevent the development of postpartum infections.
Women who are sexually active should avoid frequently changing sexual partners. Regular medical examinations are recommended at least every six months. This will allow you to timely diagnose diseases of the genital organs, regardless of their nature, origin, and undergo treatment.
To minimize episodes of exacerbation of the chronic form, you need to avoid physical overexertion, overwork, hypothermia, in general, everything that can weaken the body and reduce its immune defense. Here, secondary prevention of salpingoophoritis comes to the fore—prevention of complications. The patient should follow all the doctor’s recommendations very carefully. It is strongly recommended not to make changes to the therapeutic regimen on your own, to stop taking prescribed medications prematurely, or to reduce or increase the dose or frequency of administration.
If you find signs of any inflammatory gynecological disease, consult a doctor immediately. Treatment can be done at the AltraVita clinic. At the clinic, you can undergo all examinations in the shortest possible time, without wasting time on travel and long queues, because it is equipped with all the necessary diagnostic equipment. Timely treatment will allow you to achieve the fastest possible recovery, as well as avoid complications, including those from the reproductive system.
Why do you need to take contraceptives when treating inflammation of the appendages?
Even if there are no physical manifestations of adnexitis, one cannot neglect the diagnosis. Pregnancy should be excluded for the entire period of treatment of the pathology.
With adnexitis, women who do not use contraceptives have an increased likelihood of getting an ectopic pregnancy. With inflammation of the appendages, the risk increases to 50%. This occurs due to the occurrence of adhesions that prevent the normal passage of a fertilized egg into the uterine cavity.
It is also important to note that even if a normal intrauterine pregnancy does occur with adnexitis, there is a significant risk for the development of fetal pathologies. After all, the main factor of the disease is hidden sexually transmitted infections.
Preventive measures
Prevention of pathology involves women following several simple recommendations:
- undergoing regular gynecological examinations;
- timely treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system;
- use of barrier methods of contraception.
Patients who have undergone abortion or surgery should avoid stress, excessive physical exertion, casual sex, and hypothermia.
Operations for chronic adnexitis
The chronic form of adnexitis without treatment is accompanied by suppuration. With advanced abscesses of the appendages, pills and injections will no longer help, so gynecologists recommend surgery. During intervention, the abscesses are opened and washed.
Now such operations are performed in a minimally invasive way - through laparoscopy. The essence of the technique is the possibility of performing all abdominal manipulations through several tiny holes in the anterior abdominal wall. Mini-instruments and video equipment are inserted into these punctures, making laparoscopy one of the safest surgical techniques.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of salpingoophoritis at the AltraVita clinic begins with a consultation with a gynecologist. At the appointment, the doctor first interviews the patient. The doctor asks whether the woman has chronic diseases, what pathologies of the genitourinary system the patient has had in the past, and so on. This is followed by an examination in a gynecological chair.
After completing the examination, the following procedures are performed to confirm the diagnosis:
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- taking gynecological smears for flora, the presence of infections;
- general blood analysis;
- biochemical screening.
Methods for diagnosing salpingoophoritis
Ultrasound examination allows you to examine the internal genital organs, identify signs of acute or chronic inflammatory process, and assess the condition of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. At the AltraVita clinic, ultrasound is performed transabdominal and transvaginally. In the first case, the examination is carried out through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. To ensure that the internal genital organs are clearly visible on the screen, a woman should drink several glasses of water an hour before the procedure. A filled bladder will serve as a kind of acoustic window, conducting ultrasonic waves deep into the pelvis. During a transvaginal examination, a sensor is inserted into the vagina. This technique is more informative and does not require preparation. To prevent the spread of infection, a condom is placed over the sensor.
Microscopic and bacteriological examination of discharge allows us to identify the true causes of salpingoophoritis, determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibacterial agents and select treatment with the most effective drugs.
A general and biochemical blood test allows you to assess the general condition of the patient’s body who has been diagnosed with this disease, identify concomitant diseases, abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs and systems.
According to the patient’s indications, the level of hormones in the blood is determined, CT and MRI, and hysteroscopy are performed. A comprehensive diagnosis of salpingoophoritis allows you to accurately determine the form and nature of the disease, significantly increasing the chances of a good clinical outcome.
Where to cure inflammation of the appendages in St. Petersburg quickly and without complications, prices
Specialists at the Diana Medical Center in St. Petersburg are ready to deal with the problem at all stages - conduct all tests and ultrasound, effective conservative treatment or intervention. The European level of medical service and the most modern equipment allow us to make the treatment process effective and safe.
The cost of treating adnexitis is quite affordable: an appointment with a gynecologist - 1000 rubles, ultrasound of the appendages - 1000 rubles, taking blood for analysis - 170 rubles. The full cost of diagnosing and treating inflammation of the appendages depends on the stage and extent of the process, so contact our clinic as early as possible.