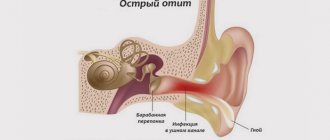
Acute tracheitis
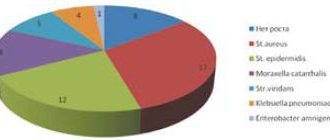
1. Infections caused by the following microorganisms:
- Streptococci.
- Haemophilus influenzae.
- Klebsiella.
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Moracella.
- Anaerobic bacteria.
- Viruses (influenza, parainfluenza and others).
2. Toxic effects on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract of toxic substances (gasoline fumes, paints, chemicals and others).
3. A breakdown in the immune system causes acute allergic tracheitis.
Folk remedies
Effective folk remedies for tracheitis:
- Marshmallow root. Available in syrup form. The basis of the drug is plant mucilage. It softens the throat, eliminating pain and promoting mucosal restoration. A protective film is formed on the surface of the epithelium, which reduces the irritating effect during a coughing attack. Marshmallow root also contains substances that thin phlegm and promote its removal.
- Marshmallow root. Available in syrup form. The basis of the drug is plant mucilage. It softens the throat, eliminating pain and promoting mucosal restoration. A protective film is formed on the surface of the epithelium, which reduces the irritating effect during a coughing attack. Marshmallow root also contains substances that thin phlegm and promote its removal.
- Heat the milk, put a teaspoon of butter and half a teaspoon of soda into a cup, drink the mixture in small sips.
- Oak bark. The main therapeutic effect of the bark is associated with tannins (their concentration can reach 20%). They promote the desquamation of epithelium affected by microbial agents and the improvement of the mucous membrane.
Compresses stand apart in folk medicine. It makes sense to administer them when there is no fever, the cough has become productive, but night attacks torment the patient, that is, approximately starting from the fourth day of illness. The compress for tracheitis is applied for 20 minutes an hour before bedtime. Under no circumstances should you put a compress on your throat, so as not to catch the thyroid gland. Only on the chest.
Compress recipes:
- A tablespoon of honey and 3 drops of eucalyptus essential oil.
- A tablespoon of dry mustard, two teaspoons of honey, 20 ml of sunflower oil, 3 drops of fir oil.
- Boil two potatoes, mash, add a spoonful of sunflower oil.
Symptoms of tracheitis
Every person is familiar with a painful dry cough, especially at night. This is a typical sign of the disease. A cough with tracheitis is often preceded by a sore throat. The sputum produced after a coughing attack is very scanty.
Another characteristic symptom is pain and burning behind the sternum during coughing. This symptom (especially if the patient is not treated) becomes so painful that the person begins to limit his breathing, taking shallow breaths so as not to provoke another coughing attack. This significantly worsens the psychosomatics of tracheitis.
Other symptoms that accompany tracheitis include the following:
- fever and general weakness as a sign of any infectious process;
- signs of respiratory failure (noisy inhalation and exhalation, retraction of the intercostal muscles during inhalation, pallor of the skin);
- symptoms of concomitant nasopharyngitis (nasal discharge, lack of nasal breathing, sore throat);
- when the vocal cords are involved in the process - hoarseness or complete loss of voice.
If tracheitis is the result of an exclusively viral process, then the sputum released during coughing has a transparent mucous appearance. Thick gray-yellow sputum indicates the development of purulent tracheitis. This symptom is very important to consider when prescribing specific therapy.
The symptoms of chronic tracheitis do not differ from acute tracheitis, only periods of exacerbation are replaced by relative health. The disease lasts a long time. Chronic tracheitis takes a long time to treat and is not always successful, since it is often impossible to get rid of the provoking factor (smoking, smog and exhaust fumes). The causative agents are often opportunistic bacteria that are present in the body in small quantities and normally. These pathogens are resistant to antibiotics and exist, among other things, inside the cells of the tracheal mucosa.
Tracheitis is of particular concern to some patients. Tracheitis during pregnancy brings many exciting moments for expectant mothers. What medications are best for treatment, is tracheitis contagious for a baby, and so on. Any infectious disease in a pregnant woman (including tracheitis) is more severe and requires greater caution and proper treatment. The causative agent of tracheitis can penetrate the placenta and infect the fetus, the process can quickly “descend” into the bronchi and lungs. Therefore, pregnant women at the first signs of tracheitis should immediately consult a doctor.
The question of how dangerous tracheitis is for a child always worries parents. In children, inflammation spreads more quickly to adjacent parts of the respiratory tube. Acute inflammation of the larynx may develop - false croup (with attacks of suffocation that are life-threatening) or bronchopneumonia.
Symptoms of the disease in children are the same as in adults. The difference is in the severity of the general condition. The child's temperature rises to higher numbers, and the symptoms of intoxication are more pronounced. Coughing attacks disrupt sleep and make children moody. Young patients are more likely to develop signs of respiratory failure.
The disease in adults has a relatively favorable course. With proper therapy, after a few days the cough becomes moist, the general condition improves and the patient recovers without any special consequences. The exception is patients with bad habits (smoking, alcohol) or who are constantly in unfavorable conditions (in polluted places, in smoky, stuffy rooms). In such cases, the acute process is more difficult to treat, more often leads to complications and becomes a chronic process.
General tips on how to help the body cope with illness
For any disease of the respiratory tract, including tracheitis, you should follow some simple rules.
- Drink more warm liquids: fruit drinks and heated mineral water without carbon, decoctions of rose hips, raspberries and linden blossoms. This will not only help relieve intoxication, but will also help thin the sputum.
- Eat high-calorie, vitamin-rich foods. During illness, the body needs nutrients to repair tissue and maintain the functioning of the immune system.
- Stop smoking and ask family members to smoke only outside the home.
- Eliminate irritating factors: smoke, dust, strong odors. During illness, it is advisable not to use household chemicals and temporarily stop using perfumes and eau de toilette.
- Ventilate the room and maintain a sufficient level of humidity. Dry air irritates the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract and provokes coughing attacks.
With timely treatment, tracheitis resolves within 10–14 days, without leaving any consequences and without subsequently limiting the ability to work.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of tracheitis is usually made based on a detailed analysis of complaints and examination of the patient. The diagnostic search is aimed mainly at determining the type and cause of the inflammatory process. Here are some studies that are prescribed for a patient with suspected inflammation of the trachea:
- general blood test - allows you to immediately determine the viral or bacterial nature of the disease;
- swab from the throat and nose - detects the pathogen and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs;
- sputum collection and examination for Mycobacterium tuberculosis;
- laryngotracheoscopy - allows you to timely detect the transition of an acute process to a chronic one based on the specific type of tracheal mucosa;
- consultation with an allergist and conducting allergy tests (if a corresponding cause of tracheitis is suspected);
When diagnosing, you should remember about other diseases that are accompanied by a dry debilitating cough: pulmonary tuberculosis, whooping cough, diphtheria, stenosing laryngitis, foreign body, lung cancer.
Prevention
In order to prevent acute tracheitis, it is necessary to exclude the main risk factors contributing to the development of the disease. You should start by strengthening your immune system. It is important to establish a diet and eat foods rich in vitamins and protein. Alcohol consumption should be kept to a minimum. Moderate physical activity will provide tangible benefits: exercise in the gym, swimming, running are suitable. Smoking should be stopped altogether, this is especially important for people with a predisposition to respiratory diseases.
The functional state of the nervous system plays a major role in strengthening the immune system, so stress and conflict situations should be avoided. It is necessary to get enough sleep: while some people need seven hours of sleep a day, others need at least nine. In this matter, focus on your well-being.
It is important to avoid hypothermia. It makes sense for people living in environmentally unfavorable regions to think about changing their place of residence, since constant exposure to chemicals on the respiratory system will sooner or later lead to unpleasant consequences. Even with minor diseases of the respiratory system, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe treatment and help avoid the disease from becoming chronic.
Diagnosis in children
When examining children, much attention is paid to objective examination data. The child often cannot describe his complaints, so the doctor conducts a more thorough examination.
When auscultating the chest, harsh breathing is heard. Wheezing is not characteristic of tracheitis (if they are found in a child, they indicate the development of bronchitis or pneumonia).
In children, an X-ray of the lungs is more often prescribed, since there is a greater likelihood of the process “lowering” into the bronchi and lungs.
Examination of the larynx using a laryngoscope allows you to timely diagnose the spread of edema to the vocal cords and avoid a dangerous complication for the child - false croup.
First signs
Usually tracheitis begins according to a similar scenario with acute respiratory infections. First, the patient has a runny nose and a dry cough. A person may complain of weakness, sore throat, pain in the head. Hyperthermia up to 38-39 degrees can last up to 3 days, but sometimes it may not increase at all or rise to subfebrile levels of 37.5-38.0.
In young children, when tracheitis begins to develop, wheezing that can be heard at a distance may occur in the morning. Such wheezing usually goes away after the patient has cleared his throat. Shortness of breath with tracheitis, as a rule, does not occur.
Complications
We have already mentioned some dangerous complications of tracheitis. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Development of bronchial tracheitis and pneumonia. A frequent complication of incorrect, untimely therapy and in patients with a weakened immune system. The differences between tracheitis and bronchitis are as follows: the patient’s general condition worsens, intoxication, shortness of breath and other signs of respiratory failure increase, and a creak appears in the lung after tracheitis. This complication requires immediate hospitalization of the patient in a hospital.
- False croup in children. Due to the anatomical narrowness of the glottis in a child, the spread of edema to the mucous membrane of the larynx leads to acute attacks of suffocation. Such a complication is a reason to immediately call an ambulance.
- Bronchial asthma is a severe complication of allergic tracheitis.
Treatment of tracheitis
Treatment of acute and chronic tracheitis is a complex process that requires the prescription of specific medications depending on the cause of the disease, the stage of the process, the presence of complications and concomitant diseases. This task is successfully coped with in medicine.
In our center, the patient undergoes a comprehensive diagnosis, which allows us to prescribe exactly those drugs that will affect the immediate cause of the disease. Competent doctors must take into account the individual characteristics of the patient (presence of concomitant diseases, individual intolerance to drugs, possible side effects).
This approach allows you to quickly get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease and prevent tracheitis from becoming a chronic process.
Classification
Acute tracheitis is determined by several criteria at once. When classified according to etiology (the cause of the disease), the following forms are distinguished:
1. Infectious. Occurs when pathogenic microflora enters the body from the outside or the inflammatory process spreads from the nasopharynx (with laryngitis or rhinitis) into the lower respiratory tract. This form of tracheitis, in turn, is divided into three types:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- mixed.
2. Non-infectious. It develops when inhaling cold or too hot air, as well as from irritating exposure to chemicals.
3. Allergic. Occurs when allergens (pollen, animal hair, etc.) enter the respiratory tract with the subsequent development of an allergic reaction.
4. Infectious-allergic. In the infectious form of tracheitis, allergic reactions to microbial antigens occur.
Additional criteria for the classification of acute bronchitis²:
1. According to pathogenesis (mechanism of disease development). There are two forms:
- primary (independent disease);
- secondary (the disease occurs as a complication of other pathological conditions).
2. By type of functional impairment. Simply put, in this case the classification criterion is a violation of the flow of air into the lungs. There are also two forms here:
- non-obstructive (the flow of air into the lungs is not impaired, and the course of the disease is relatively favorable);
- obstructive (pulmonary insufficiency is noted, the disease is severe with a tendency to relapse).
3. By the nature of the flow. Based on the duration and propensity of the disease to relapse, experts distinguish three forms:
- acute current (typical course, duration no more than 14 days);
- protracted (duration up to 2 months);
- recurrent (the disease reoccurs at least 3 times a year).
4. By the nature of inflammation. Depending on the severity of the inflammatory process, two forms are distinguished:
- catarrhal (sputum is mucous and watery);
- purulent (sputum contains impurities of pus).
5 facts about the disease
- Preschool children suffer from acute tracheitis more often than adults.
- Boys get sick 3 times more often than girls¹.
- The disease is characterized by seasonality: in the winter months, the incidence increases several times⁵.
- Acute tracheitis does not always occur as an independent disease: very often it is a consequence of a previous acute respiratory viral infection5.
- Tracheitis affects not only people, but also animals. For example, illness can occur in dogs due to the pressure of a leash that is too tight.