Oftan Timolol eye drops 0.5% fl-cap 5ml
Compound
1 ml of the drug contains:
For a dosage of 2.5 mg/ml:
Active substance
Timolol maleate 3.42 mg (equivalent to timolol 2.50 mg).
Excipients
Benzalkonium chloride 0.10 mg, sodium hydrogen phosphate 8.10 mg, disodium phosphate dodecahydrate 29.30 mg, sodium hydroxide until the pH of the solution is 6.5-7.0, water for injection up to 1.0 ml.
For a dosage of 5 mg/ml:
Active substance
Timolol maleate 6.84 mg (equivalent to timolol 5.0 mg).
Excipients
Benzalkonium chloride 0.10 mg, sodium hydrogen phosphate 6.10 mg, disodium phosphate dodecahydrate 30.50 mg, sodium hydroxide until the pH of the solution is 6.5-7.0, water for injection up to 1.0 ml.
Pharmacokinetics
When applied topically, timolol maleate quickly penetrates the cornea. After instillation of eye drops, the maximum concentration of timolol in the aqueous humor of the eye is reached after 1-2 hours.
80% of timolol, used in the form of eye drops, enters the systemic circulation through absorption through the vessels of the conjunctiva, nasal mucosa and lacrimal tract. Excretion of timolol metabolites is carried out primarily by the kidneys.
In newborns and young children, the concentration of timolol as an active substance significantly exceeds its maximum concentration (Cmax) in the blood plasma of adults.
Indications for use
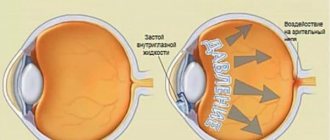
-Increased intraocular pressure (ophthalmohypertension),
- open-angle glaucoma,
-glaucoma in the aphakic eye and other types of secondary glaucoma,
- as an additional means for reducing intraocular pressure in closed-angle glaucoma (in combination with miotics),
-congenital glaucoma (if other means are ineffective).
Contraindications
Systemic effects characteristic of beta-blockers may develop: dizziness, headache, arrhythmia, bradycardia, bronchospasm, nausea and vomiting. Treatment: immediately rinse eyes with water or saline solution,
symptomatic therapy.
Directions for use and doses
At the beginning of treatment, 1-2 drops of Oftan Timolol 2.5 mg/ml or 5.0 mg/ml into the affected eye 2 times a day.
If intraocular pressure normalizes with regular use, the dose should be reduced to 1 drop once a day in the morning.
Treatment with Oftan Timolol is usually carried out over a long period of time. A break in treatment or a change in the dosage of the drug is carried out only as prescribed by the attending physician.
Storage conditions
Store at temperatures from 15 to 25 degrees. WITH.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
3 years.
After opening the bottle - 1 month.
Do not use the drug after the expiration date indicated on the package.
special instructions
Visual impairment, dizziness and fatigue may occasionally occur when using Oftan Timolol eye drops. During the treatment period it is necessary to observe
caution when driving vehicles and when working with complex equipment that requires increased concentration, speed of psychomotor reactions and good vision (within 0.5 hours after instillation into the eye), since the drug can reduce blood pressure, cause fatigue and dizziness. Monitoring of effectiveness is recommended approximately 3-4 weeks after the start of therapy (no earlier than 1-2 weeks). With long-term use of timolol, the effect may weaken.
When using it, it is necessary to monitor the function of tear secretion, the condition of the cornea and evaluate the size of the visual fields at least once every 6 months.
Oftan Timolol contains the preservative benzalkonium chloride, which can cause eye irritation and can be absorbed by soft contact lenses, causing discoloration and adverse effects on eye tissue. Contact lenses should be removed before using the drug and, if necessary, put them on again no earlier than 15 minutes after instillation.
When transferring patients to timolol treatment, it may be necessary. correction of refractive changes caused by previously used miotics.
Oftan Timolol, like other beta-blockers, can hide possible symptoms of low blood sugar in patients with diabetes.
In case of upcoming surgery under general anesthesia, it is necessary to discontinue the drug 48 hours before surgery, as it enhances the effect of muscle relaxants and general anesthetics.
Description
Transparent, colorless solution.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
On prescription
Dosage form
eye drops
Manufacturer and organization accepting consumer complaints
Santen, JSC
Pharmacodynamics
Timolol is a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker. It does not have intrinsic sympathomimetic and membrane-stabilizing activity.
When applied topically as eye drops, timolol reduces both normal and elevated intraocular pressure by reducing the formation of intraocular fluid. Does not affect pupil size and accommodation.
The effect of the drug appears 20 minutes after instillation into the conjunctival cavity. The maximum decrease in intraocular pressure occurs after 1-2 hours and persists for 24 hours.
Side effects
Local reactions:
Blurred vision, irritation and hyperemia of the conjunctiva, burning and itching of the eyes, lacrimation, swelling of the corneal epithelium, punctate superficial keratopathy, corneal hyposthesia, dry eye syndrome, blepharitis, conjunctivitis and keratitis. With long-term use, ptosis and, rarely, diplopia may develop. When performing fistulizing (penetrating) antiglaucomatous operations, choroidal detachment may develop in the postoperative period.
Systemic reactions:
The cardiovascular system
: bradycardia, bradyarrhythmia, decreased blood pressure, collapse, heart block, transient cerebrovascular accidents, exacerbation of chronic heart failure.
Respiratory system
: shortness of breath, bronchospasm, pulmonary insufficiency.
central nervous system
: headache, dizziness, weakness, confusion, hallucinations, insomnia, onirodynia, anxiety, mood changes. Allergic reactions: generalized or local rash, itching.
Skin
: alopecia, psoriasis-like rashes and exacerbation of psoriasis. Genitourinary system: Peyronie's disease
Other systemic reactions
: paresthesia, nasal congestion, myasthenia gravis, decreased potency, nausea, diarrhea, chest pain, ringing in the ears.
If side effects occur, you should contact your doctor as soon as possible.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
There is no sufficient experience with the use of the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but it has been established that timolol passes the placental barrier and enters breast milk. As prescribed by the attending physician, Oftan Timolol can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding, unless the expected therapeutic effect for the mother justifies the potential risk to the fetus and child.
If the drug was used immediately before childbirth or during breastfeeding, newborns should be closely monitored for several days after birth and during the entire period of treatment of nursing mothers with Oftan Timolol.
Interaction
Combined use of Oftan Timolol with eye drops containing adrenaline may cause pupil dilation.
The specific effect of the drug is a decrease in intraocular pressure, which can increase with the simultaneous use of eye drops containing epinephrine and pilocarpine.
Two different beta blockers should not be instilled into the same eye.
Arterial hypotension and bradycardia may increase with simultaneous use of Oftan Timolol with calcium antagonists, reserpine and systemic beta-blockers.
CYP2D6 inhibitors such as quinidine and cimetidine may increase plasma concentrations of timolol.
Concomitant use with insulin or oral antidiabetic agents may lead to hypoglycemia.
Timolol enhances the effect of muscle relaxants, so it is necessary to discontinue the drug 48 hours before the planned surgery under general anesthesia.
These data may also apply to medications that were used shortly before.
Overdose
Systemic effects characteristic of beta-blockers may develop: dizziness, headache, arrhythmia, bradycardia, bronchospasm, nausea and vomiting. Treatment: immediately rinse eyes with water or saline solution,
symptomatic therapy.
Timolol maleate
Like other ophthalmic drugs, timolol undergoes systemic absorption.
When beta-blockers are used topically, the same adverse reactions may occur as when they are used systemically. For example, severe respiratory reactions and cardiac events have been reported with both systemic and topical use of timolol, including death due to bronchospasm in patients with bronchial asthma and, less commonly, death due to heart failure (see section "Contraindications"). .
Heart failure
To maintain blood circulation in persons with impaired myocardial contractility, sympathetic stimulation is necessary. The use of beta-blockers may aggravate the course of heart failure.
In patients without a history of heart failure, long-term myocardial suppression with beta-blockers may in some cases lead to the development of heart failure. When the first signs of heart failure occur, timolol should be discontinued.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Patients with COPD (for example, chronic bronchitis, emphysema) of mild to moderate severity, bronchospastic diseases, including a history (other than bronchial asthma (including a history), in which the use of timolol is contraindicated), the use of beta-blockers, in including timolol, is generally not recommended.
Extensive surgical interventions
The need and desirability of discontinuing beta-blockers before undergoing major surgery has not been definitively established. Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade impairs the heart's ability to respond to beta-adrenergic receptor-mediated reflex stimuli, which may increase the risk of complications of general anesthesia.
In some patients who continued the use of beta-blockers during general anesthesia, a prolonged severe decrease in blood pressure occurred. The difficulty of resuming and maintaining heart contractions was also noted. In this regard, patients referred for elective operations are advised to gradually discontinue the use of beta-blockers. During surgery, if necessary, the effects of beta-blockers are stopped by high doses of adrenergic agonists.
Diabetes
Patients with spontaneous hypoglycemia or diabetes mellitus (especially those with an unstable course) using insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents should use beta-blockers with caution. Beta blockers may mask the signs and symptoms of acute hypoglycemia.
Thyrotoxicosis
Beta blockers can mask certain clinical symptoms of hyperthyroidism (for example, tachycardia). The use of beta-blockers in patients who may develop thyrotoxicosis should be used with caution, avoiding abrupt withdrawal, in order to prevent the development of thyrotoxic crisis.
General recommendations
Due to the potential effect on blood pressure and heart rate, beta blockers should be used with caution in patients with cerebrovascular insufficiency. If symptoms of cerebrovascular accident develop after initiation of timolol therapy, alternative therapies should be considered.
Cases of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multi-dose containers for ophthalmic drugs have been described. These containers were unintentionally contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had concomitant corneal diseases or disruption of the integrity of the epithelial surface of the eyeball.
In patients taking medications that reduce the formation of intraocular fluid (for example, timolol), cases of choroidal detachment after filtration surgery have been reported.
Angle-closure glaucoma
The main goal of treatment for patients with angle-closure glaucoma is to open the angle of the eye, which requires contraction of the pupil. Timolol does not affect the pupil, therefore the use of timolol in monotherapy for the treatment of angle-closure glaucoma is not allowed.
Anaphylaxis
The use of beta-blockers in patients with atopy or a history of severe anaphylactic reactions to various allergens may provoke more severe reactions in response to accidental, diagnostic or therapeutic administration of allergens. Such patients may respond poorly to normal doses of epinephrine to relieve anaphylactic reactions.
Muscle weakness
The use of beta-blockers increases muscle weakness in myasthenia gravis (for example, increased diplopia, ptosis and general weakness). Some patients with myasthenia gravis and other myasthenic diseases have experienced an increase in muscle weakness when taking timolol.
Excipients
Timolol maleate contains benzalkonium chloride, which can cause eye irritation, be absorbed by soft contact lenses, causing discoloration, and have adverse effects on eye tissue. Before using the drug, contact lenses should be removed and reinserted if necessary, no earlier than 15 minutes after instillation.