Oftan dexamethasone
Oftan dexamethasone is a local glucocorticosteroid for use in ophthalmic practice. Has anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effect. It interacts with protein receptors in target tissues, thereby controlling the processes of transfer of genetic information from DNA through RNA of corticosteroid-dependent genes to polypeptides and proteins and influencing the formation of protein structures. Maintains lysosomal enzymes of leukocyte membranes in a stable state. Prevents the formation of proteins of the kinin-kallikrein system, division and migration of white blood cells. Suppresses the formation of antibodies and disrupts the mechanism of antigen recognition by lymphocytes. All of the above effects cause suppression of the inflammatory response in tissues. The duration of the anti-inflammatory effect after using a single dose of the drug is from 4 to 8 hours. When drops are instilled into the conjunctival sac, systemic absorption occurs only to a small extent. The drug has good local absorption ability and easily penetrates the outer layer of the cornea and connective membrane to achieve a therapeutic concentration in the aqueous humor of the chambers of the eye. Dexamethasone undergoes metabolic transformations by microsomal liver enzymes. Elimination from the body occurs along with feces. The half-life is approximately 3.5 hours. The drug is prescribed for non-purulent inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (incl.
including allergic genesis), cornea, eyelid margins, sclera, episcleral tissue, iris of the eyeball, ciliary body, superficial damage to the cornea, inflammation of the choroid (the thin pigmented vascular layer of the eye) and retina, binocular damage to the eye that develops after damage uveal tract with subsequent damage to the second eyeball. In the acute phase of the disease, Oftan dexamethasone is instilled 1-2 drops every 1-2 hours. After the condition has stabilized, the drug is used less frequently - in the same dose, but 3-5 times a day. The maximum duration of a medication course is 2-3 weeks. Typical side effects: a burning sensation that develops immediately after instillation and spontaneously passes without any therapeutic intervention, allergic reactions. If the recommended duration of use is exceeded, the risk of developing disturbances in the regulation of ophthalmotonus increases as a result of previous various eye diseases and glucocorticosteroid cataracts. The dexamethasone contained in Oftan as an auxiliary component benzalkonium chloride can cause local irritation. The medicine is not intended for use in pediatrics. If the duration of the medication course exceeds 2 weeks, you should periodically check the fluid pressure inside the eye and monitor the condition of the cornea.
Oftan Dexamethasone eye drops 1 mg/ml 5 ml No. 1 dropper bottle
Content
Indications Contraindications Side effects Interaction Method of administration and dosage Overdose Precautionary measures Special instructions Expiration date
Indications
- Acute and chronic inflammatory processes: non-purulent forms of conjunctivitis, keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis and blepharitis, scleritis and episcleritis, iritis, iridocyclitis and other uveitis of various origins, superficial corneal injuries of various etiologies (chemical, physical or immune mechanisms) after complete epithelization of the cornea, inflammation of the posterior segment eyes (choroiditis, chorioretinitis), sympathetic ophthalmia.
- Allergic conjunctivitis or keratoconjunctivitis.
- Prevention and treatment of inflammatory phenomena in the postoperative and post-traumatic period.
Contraindications
Keratitis caused by Herpes simplex, chicken pox and other viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva, mycobacterial eye infections, fungal eye diseases, acute purulent eye diseases with damage to the corneal epithelium, corneal epitheliopathy, increased intraocular pressure, hypersensitivity to any of the components of the drug.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
It is possible if the expected effect of therapy exceeds the potential risk to the fetus (to date, there are no clinical trial data regarding the use of the drug during pregnancy, lactation, or in children).
Side effects
A quickly passing burning sensation.
With long-term use, secondary glaucoma and steroid cataracts may occur, therefore, when using the drug for more than 2 weeks, and in patients with a history of glaucoma, it is recommended to regularly monitor intraocular pressure.
Interaction
May enhance the effect of phenytoin, barbiturates and warfarin. Reduces the effectiveness of CCB, quinidine and erythromycin (induces the CYP3A4 isoenzyme). With the usual regimen of topical administration, the dose is insufficient to cause induction or saturation of liver enzymes.
Directions for use and doses
Conjunctivally. 1-2 drops into the conjunctival sac 3-5 times a day.
The course is no more than 2–3 weeks.
Overdose
When applied topically, an overdose is unlikely.
Precautionary measures
Use for 2 weeks or more should be carried out under the control of intraocular pressure.
If a bacterial or fungal infection is present, treatment should be carried out in combination with appropriate antimicrobial therapy.
Before instillation, contact lenses should be removed and reinserted 15 minutes after using the drug (to avoid precipitation of the preservative benzalkonium chloride on them).
Due to possible lacrimation after instillation, it is not recommended to use the drug immediately before driving a vehicle or servicing mechanical equipment.
special instructions
Eye drops in an opened bottle should be used within 1 month.
Storage conditions for the drug Oftan® Dexamethasone
At a temperature of 2–8 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
2 years. After opening the bottle - 1 month.
Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
OFTAN DEXAMETHASONE (drops)
I received recommendations on how to behave so as not to harm him and a list of eye drops:
1. Levofloxacin 0.5% - 4 times a day, 1-2 drops, for two weeks. 2. Bromfenac 0.09% - 1-2 drops once a day, for four weeks. 3. Dexamethasone 0.1% - 4 times a day, 1-2 drops, for four weeks.
I want to talk about the latter in more detail. Usually, I take medications over the Internet, or using information from the Internet, but this time I went straight from the room to the pharmacy at the hospital. I didn’t want to “wander around” with a red eye and a post-operative bruise even on the Internet. Showed the pharmacist the discharge summary with the name of the prescribed drops and item “”3. Dexamethasone...” received “Santen eye drops”Oftan Dexamethasone”.
To my question about the quality of this drug, she replied that it is “the best of the Dexamethasone group.” Made in Finland. “”In your case, it is responsible for protecting the eye from inflammation and allergic reactions. It must be stored in the refrigerator at a temperature of 2-8 degrees Celsius, i.e. in the refrigerator, but not in the freezer. It is necessary. I’ll write “cold” directly on the box,” the woman pharmacist continued. ""But! Before dripping, do not heat it for a long time. Just hold it in your hands - tightly grasping the bottle. Warm it up a little with your palms, drop it in and return it to the refrigerator. Then you will maintain the effectiveness of the active substance."
This information was quite enough for me. Thanked. I paid 220 rubles for the bottle and went home, fortunately I live nearby.
It started dripping immediately. Here is a bottle - the dropper is not pierced - the hole has already been formed. You unscrew the cap and immediately drip the first time without any preparatory operations. Even if, on the advice of the pharmacist, you warm the bottle with your palms, they will still be cool and you will feel it. But I didn’t notice anything bad about it. Well, cold and cold.
Once the bottle is opened, it can be used for a month. This is a standard requirement for almost all eye drops. When using, do not touch the eye with the dropper, as well as with your hands. These are basic sanitation standards and must be strictly observed in relation to the eyes.
The effectiveness of the drug is evidenced by the fact that all inflammation that arose immediately after the operation disappeared quite quickly. The redness of the eye has gone. The “mote in the eye” effect no longer occurred. But, I think, in my case, these drops, apparently, are necessary not for any kind of treatment, but specifically for prevention.
You can learn more about indications for use, contraindications and other issues from the attached instructions.
With this, let me take my leave. Do not be ill. All the best. Goodbye.
Oftan-dexamethazon (Oftan-Deksametazon)
Dexamethasone
Indications for use:
Addison's disease, congenital adrenal hypoplasia, adrenal insufficiency (usually in combination with mineralocorticoids), adrenogenital syndrome, thyroiditis (acute, subacute), hypothyroidism, tumor hypercalcemia, shock (anaphylactic, post-traumatic, postoperative, cardiogenic, blood transfusion, etc.), rheumatoid arthritis in the acute phase, acute rheumatic carditis, collagenosis (rheumatic diseases; disseminated lupus erythematosus, etc.), inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the joints (arthritis, tendovaginitis, bursitis, epicondylitis, styloiditis, osteochondrosis, osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, etc.), myositis, infectious-allergic bronchial asthma, status asthmaticus (IV, IM), allergic and anaphylactoid reactions, incl. caused by drugs, dermatitis (contact, atopic, exfoliative, blistering, herpetiformis, seborrheic, etc.), psoriasis, eczema, exudative erythema multiforme, pemphigus, mycosis fungoides, erythroderma and other skin diseases, cerebral edema (with tumors, cranial -brain injury, neurosurgical intervention, cerebral hemorrhage, encephalitis, meningitis, radiation damage to the lungs (IV, IM), ulcerative colitis, hepatitis, sarcoidosis, berylliosis, disseminated tuberculosis (only in combination with anti-tuberculosis drugs), disease Leffler and other severe respiratory diseases, anemia (autoimmune, hemolytic, congenital, hypoplastic, idiopathic, erythroblastopenia), idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (in adults), secondary thrombocytopenia, lymphoma (Hodgkin, non-Hodgkin), leukemia, lymphocytic leukemia (acute, chronic), agranulocytosis, plasmacytoma and other blood diseases, nephrotic syndrome, severe infectious diseases (with mandatory combination with antibiotics), multiple sclerosis, non-purulent and allergic eye diseases (conjunctivitis, keratitis, iritis, iridocyclitis, blepharitis, blepharoconjunctivitis, episcleritis, scleritis), inflammatory processes after eye injuries and operations, sympathetic ophthalmia, diagnosis of adrenocortical insufficiency, pituitary short stature (in children), affective disorders, incl. for depression.
Contraindications for use:
Hypersensitivity, systemic mycoses, amoebic infections, active forms of tuberculosis, infectious lesions of joints and periarticular soft tissues, the period before and after preventive vaccinations (especially antiviral ones), obesity of III-IV degree (inside); eye drops - viral, including lichen simplex, chickenpox, fungal and tuberculous eye infections, acute purulent eye infection (in the absence of antibacterial therapy), diseases of the cornea with epithelial defects, trachoma, glaucoma.
Restrictions on use:
Peptic ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract, gastric and duodenal ulcers, esophagitis, gastritis, intestinal anastomosis (in the immediate history), congestive heart failure, arterial hypertension, thrombosis, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, acute renal and/or hepatic failure, psychosis, convulsive conditions, myasthenia gravis, open-angle glaucoma (oral, parenteral), AIDS, pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Side effects:
Sodium and water retention, loss of potassium and calcium, edema, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (with exacerbation of peptic ulcer up to perforation, bleeding), hemorrhagic pancreatitis, atony of the gastrointestinal tract, increased appetite, nausea and vomiting, hepatomegaly, muscle weakness , myopathy, osteoporosis, pathological fractures, tendon ruptures, arrhythmia, bradycardia, increased blood pressure, congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction and dystrophy, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, hyperglycemia, hyperlipoproteinemia, negative nitrogen balance, dysmenorrhea, growth retardation in children, hirsutism, decreased immunity, suppression of regenerative and reparative processes, dizziness, headaches, mood disorders, psychosis, increased intracranial pressure, convulsions, thinning and vulnerability of the skin, petechiae, ecchymoses, stretch marks, erythema and changes in facial pigmentation, increased sweating, increased intraocular pressure, exophthalmos, thrombosis and thromboembolism, withdrawal syndrome (malaise, pain: headaches, in the abdomen, joints and muscles), depression, secondary adrenal insufficiency; rarely - allergic reactions (rash, itching).
Interaction with other drugs : Reduce the therapeutic and toxic effects of barbiturates, phenytoin, rifampicin (accelerate metabolism), somatotropin, antacids (reduce absorption), increase - estrogen-containing oral contraceptives, the risk of arrhythmias and hypokalemia - cardiac glycosides and diuretics, the likelihood of edema and arterial hypertension - sodium-containing drugs or supplements, severe hypokalemia, heart failure and osteoporosis - amphotericin B and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, risk of erosive and ulcerative lesions and bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract - NSAIDs. When used simultaneously with live antiviral vaccines and against the background of other types of immunizations, it increases the risk of viral activation and the development of infections. Weakens the hypoglycemic activity of insulin and oral antidiabetic agents, the anticoagulant activity of coumarins, the diuretic activity of diuretics, and the immunotropic activity of vaccinations (suppresses antibody formation). Worsens the tolerance of cardiac glycosides (causes potassium deficiency), reduces the concentration of salicylates and praziquantel in the blood.
Overdose:
Treatment: with the development of adverse events - symptomatic, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome - administration of aminoglutethimide.
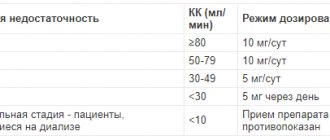
Method of administration and dosage: Orally, parenterally, locally. The dose is set individually, depending on the disease and condition of the patient. Orally (during or after meals) once, in the morning (small dose) or in 2-3 doses (large dose): 2-3 mg to 4-6 mg (10-15 mg) per day, after achieving the effect, the dose is gradually reduced to maintenance - 0.5-1 mg, (2-4.5 mg or more) per day; treatment is stopped gradually (at the end, several injections of corticotropin are prescribed. Children - 0.25-25 mg, or 0.0833-0.3333 mg/kg or 0.0025-0.0001 mg/m2 per day in 3-4 doses per day depending on age.Parenteral: IV, slow stream or drip (in acute and emergency conditions) or IM 4-20 mg (up to 80 mg) 3-4 times a day, maintenance doses 0.2-9 mg per day, course 3-4 days, then - oral administration. Children - IM, 0.02776-0.16665 mg/kg every 12-24 hours. Intra-articular (into the lesion) or periarticular (into soft tissue): adults and adolescents - 0.2-6 mg (2-8 mg), repeated at intervals of 3 days to 3 weeks as needed; maximum dose for adults - 80 mg per day. For shock (adults) - IV, 20 mg once, then 3 mg/kg over 24 hours as a continuous infusion or intravenously once 2-6 mg/kg, or intravenously 40 mg every 2-6 (4-6) hours. For cerebral edema (adults) - 10 mg IV, then 4 mg every 6 hours IM until symptoms disappear; the dose is reduced after 2-4 days and gradually - over 5-7 days - treatment is stopped. For adrenal insufficiency (children) - IM 0.0233 mg/kg (0.67 mg/m2) per day in 3 injections every third day, or daily 0.00776-0.01165 mg/kg (0.233 -0.335 mg/m2) per day. Conjunctivally: for acute conditions - 1-2 drops every 1-2 hours, then - after 4-6 hours; in other cases - 1-2 drops 3-4 times a day; course - from 1-2 days to several weeks.
Precautions: Use with caution for nonspecific ulcerative colitis, intestinal diverticulitis, hypoalbuminemia. Prescription in case of intercurrent infections, tuberculosis, septic conditions requires preliminary and subsequent simultaneous antibacterial therapy. It is necessary to take into account the increased effect in hypothyroidism and cirrhosis of the liver, aggravation of psychotic symptoms and emotional lability at their high initial level, masking of some symptoms of infections, the likelihood of relative adrenal insufficiency persisting for several months (up to a year) after discontinuation of dexamethasone (especially in the case of long-term use) . Breastfeeding is stopped for the period of treatment. During a long course, the dynamics of growth and development of children are carefully monitored, an ophthalmological examination is systematically carried out, and the condition of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system and blood glucose levels are monitored. Stop therapy only gradually. It is recommended to be careful when performing any kind of surgery, the occurrence of infectious diseases, injuries, avoid immunization, and avoid drinking alcohol. In children, in order to avoid overdose, the dose is calculated based on the body surface area. In case of contact with patients with measles, chickenpox and other infections, appropriate preventive therapy is prescribed.