What is periodontitis
Periodontitis is one of the most common dental diseases. Symptoms of periodontitis can affect many people to varying degrees for a variety of reasons.
But, despite this, many people often do not pay special attention to the first signs of this disease, as a result of which periodontitis can worsen and develop into severe forms of the disease, which, in turn, most often leads to the loss of a tooth or even several teeth, and as well as other complications.
Periodontal tissue surrounds the root of the tooth and is designed to hold the teeth firmly in place. In other words, periodontal tissues include vessels, hard fibers and channels involved in the process of feeding hard tissues.
Periodontal pathology is an inflammation of its tissues, the cause of this inflammation is the penetration of infection into the periodontal tissue. Periodontitis often occurs as a result of a complication of gum disease such as gingivitis, or due to untreated caries.
Periodontitis in severe advanced form and in the acute phase is accompanied not only by bleeding gums, but also by purulent discharge and ulceration of the gums (formation of ulcers on the gums).
If periodontitis starts and treatment is not started on time, the inflamed gum tissue begins to peel off from the roots of the tooth, causing the teeth to become loose, and if treatment is not started, the teeth may begin to fall out.
Also, periodontitis can develop during pregnancy, since during pregnancy there is a temporary decrease in natural immunity, while the progression of the disease in the first stages is often characterized by a latent course.
In this case, as a treatment, dentists try, if possible, to limit themselves to the use of gentle medicinal treatment methods, and continue treatment after the woman is ready for more serious therapy.
Diagnostics
The presence of at least one of the above symptoms should be a reason to contact the clinic, where a more thorough examination will be carried out. Doctors at our clinic only need a simple examination to make a preliminary diagnosis. A comprehensive diagnosis of periodontitis includes a number of diagnostic procedures that are necessary to clarify the extent of the disease and differentiate it from other diseases. Diagnostic procedures:
- Probing of periodontal pockets.
- Orthopantomogram is necessary to assess the degree of destruction of the jaw bones.
- Calculation of periodontal indices.
- Bacterial culture or PCR of the detachable gingival pocket.
- Schiller-Pisarev test.
To clarify the cause of periodontitis, you may need the results of other examination methods: biochemical and general blood tests, glucose level testing, and others. Gastroenterologists and endocrinologists are often involved as consultants, since without adequate treatment of somatic pathology, the treatment of periodontitis is very difficult.
How does periodontitis occur?
As a result of several scientific studies, statistics were collected that showed that people between the ages of 30 and 40 most often experience periodontitis.
At the same time, these data do not allow us to assert that the occurrence of periodontal pathologies is directly dependent on a person’s age.
How to reduce the risk of periodontitis
To minimize the possible occurrence of periodontitis, you need to undergo preventive examinations with a dentist every six months, lead a healthy lifestyle, eat right and carefully observe oral hygiene.
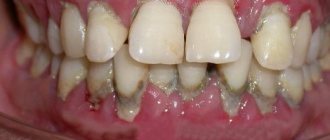
Symptoms of periodontitis
The manifestations of periodontitis depend on how advanced the disease is. The main symptoms of periodontitis include the following:
- bleeding gums;
- plaque in the root area of the teeth and under the surface of the gums;
- the occurrence of bad breath;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- redness of the mucous membrane due to the onset of the inflammatory process;
- blue mucous membrane due to inadequate blood supply to the gum area;
- the presence of pockets with purulent contents;
- pain during chewing and brushing teeth;
- exposure of tooth roots;
- change in the color and viscosity of saliva.
Gums are bleeding - contact a periodontist
If you notice the slightest symptoms of periodontitis, immediately go to the doctor. The first sign is regular bleeding of the gums after mechanical impact.
If there is a single bleeding, there is no reason for serious concern: to strengthen the gums, you can change the toothpaste to a special product for the treatment and prevention of periodontitis, or use a strengthening gel or balm. But if bleeding becomes regular, you need to see a specialist.
If the disease progresses, some teeth may need to be removed. Therefore, the earlier the diagnosis is made and treatment is started, the greater the chances of completely getting rid of periodontitis without negative consequences.
Advanced periodontitis
Advanced periodontitis in the absence of timely initiation of treatment leads to the appearance of typical complications that have a detrimental effect on the condition of the body as a whole - the patient’s body temperature rises, headaches occur, general weakness appears, appetite and mood decrease.
Causes of periodontitis development
Periodontitis can occur for many reasons, the main ones being:
- untreated caries;
- advanced gingivitis;
- improper oral hygiene;
- lack of daily oral hygiene;
- using a toothbrush that is too hard, which injures the gums;
- incorrect, incorrectly and poorly installed fillings;
- the presence of subgingival deposits;
- improperly manufactured dentures that injure the mucous membrane;
- improper hygiene of dentures or lack of such hygiene;
- congenital prerequisites;
- complications after treatment of jaw fractures;
- jaw injuries;
- some types of malocclusions.
Also, the development of periodontitis can be caused by the presence of common general somatic diseases, such as:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- disruptions in the digestive system;
- insufficient function of the salivary glands;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- disruption of the normal functioning of the hormonal system;
- severe stress;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- temporary drop in general immunity.
For what other reasons can periodontitis develop?
However, it is worth noting that with all the variety of possible causes for the development of periodontitis, according to statistical data obtained as a result of many studies conducted around the world, the main cause of periodontitis is the lack of oral hygiene or its poor or improper implementation. And, as a consequence, lack of oral hygiene leads to the formation of plaque, and then the formation of hard dental deposits (tartar). Everything else is just provoking factors.
Classification and forms of periodontitis
Before starting treatment for periodontitis, the dentist conducts a diagnosis, the purpose of which is to determine the form and stage of the pathology. Based on the study of the characteristics of the course of the disease, the following types of periodontitis are distinguished:
Acute stage of periodontitis: this stage is characterized by the rapid development of foci of infection, which in a short period of time can lead to serious complications. The gums begin to bleed heavily, and acute painful sensations appear when pressing on areas of inflammation, brushing teeth, or eating hard foods.
Within a very short time (several days), periodontitis can lead to the rapid formation of significant abscesses and the subsequent formation of fistulas.
Chronic form of periodontitis: when periodontitis is chronic, the pathology usually does not manifest itself with such pronounced symptoms as in acute cases. The patient may not experience any discomfort or experience minor discomfort, but this fact does not mean that the inflammatory process does not occur and does not develop.
Mild degree
As usual, mild degrees are not given any importance. A subgingival pocket is formed near the dental unit, where microorganisms accumulate. There are signs of periodontal inflammation, and on the Rg image there is destruction of bone tissue by 1/3 of the root, gum pockets up to 3.5 mm. In the cervical area of the teeth, hard deposits are observed, the gums are loose, slightly inflamed and swollen. There is slight bleeding when cleaning, and discomfort when chewing solid food. Mobility and movement of teeth is not observed at this stage.
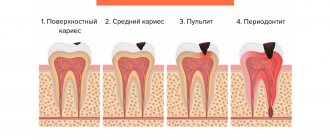
Stages of development of periodontitis. Localization of infection in periodontitis
Localized form of periodontitis: The onset of this type of periodontitis is usually caused by minor trauma to the mucosa. The localized form, in the absence of dental care, can progress to the next stage of the disease.
Generalized form of periodontitis: inflammation in the generalized form of the disease, inflammation develops along the entire length of the alveolar ridge. Experts in the field of periodontology argue that this form can quickly develop and become more complicated due to weakened immunity, for example, with a cold, hypothermia, infection with another infection, or self-medication with antibiotics.
Forms of periodontitis
According to the severity of periodontitis, there are: mild form, moderate form, severe form. At the beginning of the pathological process, slight bleeding, slight pain, and the formation of small periodontal pockets are observed. In the moderate form of the disease, large gaps appear in the periodontal pockets, and the teeth become mobile and loose. With the development of severe periodontitis, deformation of the interdental septa, decay of collagen fibers and root tissues are observed. Periodontal pockets become large, they contain purulent contents, and teeth fall out.
Average degree
With moderate severity, periodontal pockets up to 5 mm are observed. The x-ray shows damage to the bone septa on half the root. In the oral cavity, upon examination, there is a sufficient number of dental deposits, mobility of teeth I-II degrees, inflammation of the gums. A small amount of pus may ooze from under the gums. When the process worsens, slight mobility and displacement of units occurs.
Patients complain of pain in the gums; pain and bleeding when eating; the necks of the teeth are exposed; a reaction to cold and hot food is formed.
What are the treatment options for periodontitis?
First of all, it should be noted that self-treatment of periodontitis at home without consulting a dentist often leads to neglect of the disease, complications and dangerous consequences. The treatment of periodontitis should only be carried out by a dentist, preferably a specialized specialist - a periodontist.