Causes and consequences of heat stroke
The effect of high temperature and high humidity on the body is very negative. Heatstroke can occur on the street, indoors, in a bathhouse, sauna, in vehicles, etc. In this case, the body loses a significant amount of water and a malfunction in thermoregulation occurs. Factors influencing the development of heat stroke:
- long exposure to heat;
- work near a source of high temperature;
- clothing that prevents sweat from evaporating;
- failure to replenish water balance in the heat;
- physical activity at high temperatures.
Medicine distinguishes heatstroke into several degrees of severity.
- Signs of a mild form: lethargy, fatigue, drowsiness.
- Moderate symptoms: those described above, plus increased body temperature, nausea, fainting, increased sweating, nosebleeds, and severe thirst.
- A severe form of heatstroke is a dangerous condition for the body. Confusion occurs, there is no sweating, the skin is dry and hot, arrhythmia, damage to the heart muscle is possible, the kidneys are under severe stress.
A victim who has been in the sun may show signs of both heatstroke and sunstroke.
Sunstroke: what it is, symptoms and treatment (first aid) in adults
Sunstroke: what it is, symptoms and treatment (first aid) in adults
In this article we will talk about sunstroke - its symptoms and treatment in adults. The consequences of prolonged exposure to the sun are dizziness, weakness, fainting, throbbing pain in the back of the head and temples.
A person can become ill not only in an open space, but also in the evening after 9 hours. A feeling of complete exhaustion, loss of capacity, an increase in body temperature to 40 degrees - this is the result of a long stay under the scorching rays of the sun. With a fever, the victim often becomes delirious, his consciousness begins to become confused, blood flows from the nose and his ears become blocked.
Sunstroke - what is it?
In medical terminology, there are two types of overheating:
- Thermal. A person becomes ill from the rapidly rising temperature outside, in a stuffy, unventilated building, and his whole body suffers.
- Solar. It occurs from the negative influence of ultraviolet radiation on the patient’s head. In this case, normal blood circulation in the brain stops, sweating increases, and dehydration of the body occurs. Radical infrared radiation is aimed not only at human skin, but also affects internal organs. All this causes general intoxication of the body, which leads to a deterioration of the entire condition.
It is especially dangerous to abuse the sun's rays for children, the elderly, patients suffering from heart disease, alcoholics, and people with a poor thermoregulation system. Their blood pressure rises greatly from overheating, which can provoke a hypertensive crisis. This, in turn, leads to cardiac arrest. There are often cases when the ambulance unsuccessfully carries out resuscitation measures, and the victim dies.
Symptoms, signs of sunstroke and first aid
When overheated, everyone's body reacts differently. It depends on individual characteristics, age, and concomitant diseases. Some people get sick right on the beach or street, others get sick after a few hours.
Doctors divide the disease into three types:
- Mild degree of sunstroke. With this form, an adult exhibits the following symptoms:
- pulse and breathing increase;
- the pupils of the eyes dilate;
- he is tormented by endless thirst;
- becomes very weak;
- headache occurs;
- there is a feeling of nausea;
- not enough air.
- Average degree. How does sunstroke manifest? The victim experiences the following symptoms:
- the temperature quickly rises to 40 degrees;
- he is unable to move, loses concentration when moving;
- dizziness appears, which ends in fainting;
- throbbing pain in the back of the head increases;
- plugged ears;
- vomiting begins;
- weakness appears in the arms and legs;
- palpitations occur;
- blood flows from the sinuses.
- Severe form. The patient's condition deteriorates sharply. In front of passers-by, he begins to blush, then turn pale and his lips appear blue. Then the symptoms quickly increase:
- consciousness changes;
- hallucinations and delirium occur;
- involuntary urination occurs;
- there are body spasms;
- coma occurs.
When you see the first signs of sunstroke in an adult, to avoid death, urgently call an ambulance.
The effect of the sun on children
The vulnerable group includes children under four years of age. Their thermoregulation structure has not yet been formed. Lack of fluid in the body leads the child to hyperthermia; he is unable to cope with the high temperature of the external environment. Therefore, parents are not advised to go outside in scorching heat to avoid causing sunstroke.
Symptoms of overheating in a child:
- Body fever.
- Hysterical behavior in a child. He is very irritated, cries a lot, and is demanding of his mother's attention.
- Then, after a state of overexcitation, in the evening he becomes very weak and lethargic.
- Refuses to eat.
- Nausea and vomiting begins.
- Diarrhea may occur.
- At a temperature of 40 degrees, loss of consciousness is possible. This is a very risky moment, when the child turns blue, becomes covered in droplets of cold sweat, and becomes delirious. Here it is worth urgently calling a doctor or an ambulance. Parents cannot cope on their own without medical workers.
Causes of body overheating
- Staying in the heat for a long time without a hat.
- Clothes made from close-fitting synthetic fabric.
- Abuse of alcoholic beverages in hot weather.
- Concomitant chronic illnesses, such as vegetative-vascular dystonia, diabetes mellitus, excess weight, endocrine disorder, hypertension, heart and kidney failure.
- Humidity reaching up to 100 percent.
- Eating fatty foods.
- Lack of fluid.
- Drug use.
- Taking medications that negatively affect the body's temperature regulation, such as antidepressants, amphetamines, diuretics, antihistamines.
- Nervous stress, work overload.
- Physical work under the scorching sun.
- A feature of the body when a person sweats little.
Treatment
If you witness a person’s poor health, do not pass by. Don’t be nervous, concentrate on the problem, call a doctor or emergency room. While the car is getting to you, consult the emergency doctor by phone. Remember what you were taught in school and put your skills into practice.
We will briefly talk about providing first aid to a sunstroke victim:
- Transfer the patient to a cool, shaded place that is well ventilated (tree, large bush). If a person feels sick indoors, open the windows and doors wide and turn on the air conditioner.
- Unbutton the neck and chest. It is advisable to free your torso from constricting clothing.
- Do not rush to give antipyretic medications before the doctor arrives; it is better to wipe your palms and soles with vinegar.
- Constantly give the victim cool water, still mineral water, tea with lemon, or unsweetened compote.
- If the patient loses consciousness, let him smell a cotton swab soaked in ammonia.
- When a person, in addition to sunstroke, has received skin burns, it is better to wrap him in a wet cloth.
- It is necessary to place the patient on his side so that if he feels sick, he does not choke on vomit.
- It is recommended to apply cool compresses of water to the back of the head and forehead. They need to be changed as the towel warms up. Ice should not be applied, so as not to provoke vascular spasms, which will aggravate the situation of the victim.
- Give a sedative.
- Fan him constantly with a newspaper, magazine, or whatever you have on hand.
- If a violation of the respiratory system is detected (the patient does not have enough air) and sharp pain in the heart area, urgently perform mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration and cardiac massage. With such actions you will not miss precious minutes before the ambulance arrives, and save the person’s life.
Emergency room doctors assess the patient’s condition and determine the degree of overheating based on symptoms and complaints. With a mild form of sunstroke, he is sent home for treatment. He must remain in bed for several days until blood circulation and biochemical processes in the body return to normal.
With moderate to severe overheating, an adult is taken to the hospital to the therapeutic department, and complex treatment is carried out there.
Medicinal methods of therapy
For conscious patients, medical workers perform pre-medical procedures:
- To prevent muscle cramps, immediately inject 1 ml of a 0.5% solution of Relanium.
- An intramuscular injection of diazepam or seduxen will help relieve anxiety.
- An intravenous injection of analgin lowers the temperature and relieves headaches.
- A drip infusion of 0.9% sodium chloride, 1000 ml, is made into a vein.
- Place an enema for a few minutes with warm water.
- If respiratory function is impaired, then tracheal intubation is urgently performed and transferred to a ventilator.
- To ensure stable blood flow through the vessels, an injection of prednisolone is prescribed.
- To restore peace of mind, the patient is prescribed antipsychotics (Droperidol, Aminazine, Etaperazine, Fluanxol) in a small dose.
After all the procedures performed, the doctor sees how the patient’s well-being improves. If he returns to normal, he is sent for home treatment under the supervision of a local therapist.
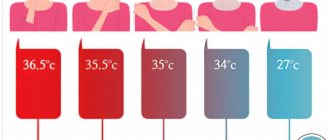
The victim is hospitalized in serious condition and sent to the intensive care unit. In such patients, the body temperature reaches 40 degrees and is not reduced with the help of antipyretic drugs. Therefore, it is immersed in a bath filled with warm water and taken out when the liquid cools to 36 degrees. The patient cannot move independently, he has involuntary urination, so a nurse looks after him during his illness. With timely and competent treatment, the victim is transferred from intensive care to a regular ward after 5-7 days.
To maintain the patient’s immune system, the immunomodulatory drug “Cytovir-3” can be recommended. For adults it is available in tablet form, and for small children - syrup with various fruit flavors.
During illness, the body's protective function is greatly weakened; for a quick recovery process, it is necessary to take a course of Cytovir-3. It consists of three mutually combining components:
- bendazole, which causes the production of endogenous interferon in human blood, restores immunity;
- thymogen enhances the effect of bendazole and affects the T-link of the immune system;
- ascorbic acid has an anti-inflammatory effect, normalizing the walls of blood vessels.
"Tsitovir-3" does not give side effects, it only temporarily lowers blood pressure, which returns to normal after half an hour.
Home therapy
We talked about the causes, symptoms of sunstroke, and drug treatment in adults. If you or your loved ones feel unwell, do not forget about proven folk remedies. They will help cope with depression:
- Come home, lie down without a pillow, raise your legs above your head. This will help improve blood circulation.
- You need complete rest, try not to get nervous.
- To prevent dehydration, drink at least 3 liters of fluid per day.
- Water-containing vegetables and fruits (cucumbers, watermelons, oranges, melons, pears) are also suitable for this purpose.
- Remove clothes and periodically wipe the chest, neck, and face with a wet towel.
- Among the medications, it is worth using “Regidron”, it will help restore the water-salt balance in the body.
- Rub half of the onion on your feet and palms.
- Take a sedative (30 drops of valerian tincture per 100 grams of water or motherwort).
- Eliminate alcohol and cigarettes, which can cause a spike in blood pressure.
- Reduce physical activity.
- Stop playing sports temporarily.
- Don't go outside unnecessarily.
How to avoid sunstroke
When it gets hot outside, make it a rule to take preventative measures. This way you will maintain your health and not waste your invaluable rest on treatment in a hospital ward.
To do this you need:
- Review your wardrobe, buy loose-fitting cotton clothes. This fabric cools the body, absorbs droplets of sweat and allows normal air circulation.
- Don't go outside without covering your head. Suitable for this: cap, bandana, scarf, Panama hat, straw hat. When swimming in a pond, do not take off your hat, as the water attracts the sun's rays.
- Carry with you a small bottle of cool water, fruit juice, compote. Eliminate carbonated and alcoholic (vodka, beer, energy drinks, wine) drinks from your diet. They are provocateurs of cerebral vascular spasms.
- Use sunscreen and glasses while tanning.
- Move your work schedule to an earlier time, for example, do business outside from 6 a.m. When the sun is at its peak, take a break and go to a cool room.
In our article, we revealed the definition of sunstroke in an adult and told what to do if you overheat. To avoid unpleasant complications, call an ambulance and follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Causes and consequences of sunstroke
Sunstroke can only happen to someone who is exposed to sunlight, as opposed to heat. This happens when the head is uncovered, the blood vessels of the brain dilate, capillaries can burst, which leads to excessive fluid flow to the head and damage to the nervous system. Also, sunstroke may not occur immediately, but after several hours. Its symptoms:
- dizziness and headache;
- high temperature, sweating;
- vomiting, diarrhea.
In particularly serious cases, a person may lose consciousness. There are also three types of consequences of such a blow: in the first case, breathing and the heart can stop, in the second - cardiac arrest and coma, and in the third - the appearance of hallucinations, delirium and even paralysis.
How many days do the effects last?
If sunstroke was mild and its consequences were not pronounced, then within a day the victim’s condition will normalize, although general weakness may be present for another 2-3 days. A more severe form of the painful condition requires the provision of qualified medical care, hospitalization of the victim, and in this case the recovery period can last 7 days - 1 month.
If a person falls into a coma, even doctors cannot predict the period of rehabilitation and recovery. It all depends on the general state of health, the age of the victim, and the level of the immune system.
Difference between heatstroke and sunstroke
Infrared radiation coming from the sun can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, causing changes in parts of the brain. Excessive blood supply to the brain leads to compression of all cells. The nerve plexuses stop receiving adequate amounts of oxygen. If the condition persists for a long time, tissue necrosis and pulmonary edema may occur.
Heat stroke affects not just the brain, but all systems of the body. Excessive heating of the body can be stopped if a person changes his environment when unpleasant symptoms occur. In all cases, a person can be helped; for this it is necessary:
- isolate the victim from the sun;
- give air access;
- apply a cold compress to the forehead;
- give ammonia to smell, drink cool water;
- in serious cases, call an ambulance.
If you have a high temperature, antipyretic medications will not help; you need the help of a doctor. It is easier to prevent these conditions by observing the prevention of heat and sunstroke
What are the dangers of sunburn?
A mild degree of sunburn does not cause serious consequences, but the most severe sunburns cause long-term non-healing skin defects - ulcers and erosions. If a mild degree of sunburn is often repeated, then this also poses a danger to humans and leads to the appearance of skin lesions - malignant neoplasms, photodermatoses, sunburns of varying degrees of severity.
First steps when providing assistance
In case of sunburn, the damaged areas of the body are cooled and moisturized, and special remedies are taken to relieve pain.
1. Cooling. Just like any burn, the affected area for a sunburn should be cooled. For these purposes, lotions and compresses with ordinary running cold water are used. Use chilled black chalk, ice cubes, aloe juice, tomato and cucumber juices. Antiseptic lotions - a weak solution of potassium permanganate, chlorhexidine, furatsilin - give a good effect. As it heats up, the compress cloth must be wetted.
2. Moisturizing and subsequent treatment. Cooled skin must be moisturized, otherwise it will dry out and become inflamed again.
Precautionary measures
To avoid unwanted effects from the sun and heat, you need to protect your head. When going outside, you should wear a hat. On the street you should avoid sunny places, being mostly in the shade. Without any special reason, in very hot weather, you should not leave the house or do so before 12 o’clock and after 16-17 o’clock. When going outside, you need to take still water and wet wipes for your face with you. On the beach - use sunscreen, do not be in direct sunlight, do not drink alcohol or fatty foods.
A person often feels ill in the hot summer on crowded buses or minibuses. Here you can use this life hack: buy a bottle of water from the refrigerator in advance and, while in transport, apply it to the side of your neck (to the jugular vein), so the blood will enter the brain cooled. This should be done without having chronic throat diseases.
Providing first aid
Actions for sunstroke and heatstroke begin with transporting the victim to a place that is protected from thermal influences. It is necessary to lay the victim so that his head is higher than his body. The victim must be provided with unimpeded access to oxygen and clothing must be loosened. The victim's skin can be cooled by wiping with water, and a cold compress can be placed on the head. It is important to provide the victim with a cold drink, and in severe cases, perform artificial respiration.
Problems from the head
There are several factors that contribute to the development of heat and sunstroke. Knowing about them, you can avoid serious complications. Firstly, you need to ensure that your head does not overheat outside - in particular, wear hats. When it comes to clothing, choose loose, loose pieces that don't cling to your body. When indoors, do not forget to ventilate and cool it. Secondly, in order for the body to successfully cope with stress, doctors advise not to drink alcohol or smoke. It is also worth limiting the intake of medications that can dull sensations and cause drowsiness.
Try to avoid stress and nervous tension. This is especially important for people who are overweight, have cardiovascular and endocrine diseases, and neurological problems. Provide yourself with free access to cool drinking water. Drink fluids in sufficient quantities and as often as possible (in the heat - at least two and a half liters of water per day).
Children are at particular risk. Unlike adults, they cannot track the nuances of their physical state and often find it difficult to describe what is happening to them. If a child becomes lethargic in the heat, complains of a headache and poor health, then this is most likely not just mood swings.
Babies' bodies are not able to regulate their temperature on their own, so it is better for them to be in the shade. To replenish your water balance, it is better to drink not soda or juice, but simply still water.
Main symptoms
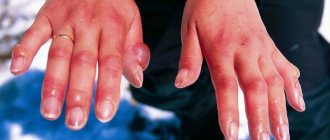
Signs of heat stroke increase gradually as overheating increases. The skin becomes red and hot; in the first stages of the condition, profuse sweating appears, which is subsequently replaced by dry skin. General weakness, dizziness, double vision and difficulty focusing appear. Breathing becomes more frequent, its rhythm is disrupted, and shortness of breath develops. The pulse quickens and weakens. Nausea and vomiting, convulsions and hyperthermia occur, confusion of consciousness appears, including hallucinations.
The classic form of heatstroke occurs in mild, moderate and severe forms. Their symptoms coincide with those of sunstroke, differing only in the generalization of the process: neurological symptoms are accompanied by more severe disorders of the cardiovascular, respiratory, endocrine and urinary systems.
Other forms of heat stroke are also encountered in clinical practice:
- hyperthermic (pyretic), the main symptom of which is intense heat (39-42°C);
- asphyxial, characterized primarily by respiratory distress;
- dyspeptic (gastroenterological) with severe nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and urinary retention;
- cerebral (paralytic), the main symptom of which is convulsions and disturbances of consciousness caused by oxygen starvation.
Without specialized assistance, the severity of the condition progressively increases. It can result in the development of cerebral and pulmonary edema, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, intracranial hemorrhage, heart and kidney failure.