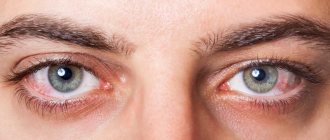
The lacrimal organs are a system of the appendage apparatus of the eye that protects the eyes from drying out, produces tear fluid and drains it into the nasal cavity.
Lacrimal organs are divided into tear-producing ( tear-secretory ) and lacrimal-draining organs .
The tear duct consists of the main lacrimal gland and several additional ones located in the conjunctival sac.
The lacrimal ducts include: lacrimal openings, lacrimal lake, lacrimal stream and other formations along which tears move before entering the nasal cavity.
1
Diseases of the lacrimal organs. Diagnosis and treatment
2 Diseases of the lacrimal organs. Diagnosis and treatment
3 Diseases of the lacrimal organs. Diagnosis and treatment
Reasons for appearance
Dacryocystitis occurs in the presence of physiological pathologies, namely congenital narrowing of the duct (stenosis). Sometimes doctors detect a complete blockage of the tear duct.
- Trauma to the eyes or paranasal sinuses.
- Inflammatory process of the nose, which provokes swelling of the tissues around the eye.
- An infectious process caused by bacteria and viruses, which leads to blockage of the duct.
- Getting foreign particles into the eye or working in dusty and smoky rooms. As a result, the channel becomes clogged.
- Allergy to exposure to an irritant.
- Reduced protective properties of the body.
- Overheating and hypothermia.
- Presence of diabetes mellitus.
Very often this pathology occurs in newborn babies. This is due to the structural features of the tear ducts. When the baby is in amniotic fluid, the tear duct is closed with a special membrane, which must rupture during or after childbirth. This process does not occur if pathology occurs. Tears collect in the canal and this provokes an inflammatory process. It mainly develops in women. Men are also no exception, but this pathology is detected very rarely in them. The reason is differences in the structure of the lacrimal canal. Women use cosmetics, most of which cause inflammation.
Dacryocystitis of newborns
Dacryocystitis of newborns is one of the most common problems in pediatric ophthalmology: to varying degrees, the disease manifests itself in 6-20% of infants. The treatment of dacryocystitis in newborns in our clinic is carried out by pediatric ophthalmologists who have confirmed certificates and are able to work not only with adults, but also with children. By contacting us, you can be sure that your children will be treated using modern equipment, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body.
Symptoms of the disease
Tears are necessary for the normal functioning of the visual organs. They moisturize the cornea of the eye, protect against mechanical irritants, and perform an antibacterial function. Sometimes tears stop flowing, this is the first sign of obstruction of the lacrimal canal. Treatment is one way to cope with the problem and prevent the development of canaliculitis. Sometimes massage of the tear duct helps.
- painful and unpleasant sensations in the eye area;
- redness of the skin around the eye;
- feeling of squeezing and bursting;
- swelling of the skin;
- lacrimation;
- edema;
- vision problems;
- increased secretion of mucus, which smells bad;
- formation of pus;
- high body temperature;
- intoxication of the body.
The acute stage of dacryocystitis appears as an inflammatory process affecting one eye. In the chronic stage, the tear duct swells, the eye turns red and the number of tears increases.
If you experience such symptoms, you should consult a doctor. Blockage can occur in both acute and chronic stages. The accumulation of tear fluid increases the likelihood of infectious processes.
Lacrimal gland disorders
Disorders of the lacrimal gland manifest themselves in increased tear production ( hyperfunction ) or insufficient production of tear fluid ( hypofunction ).
Increased lacrimation may occur due to bright light, strong wind, cold and other external irritants, or as a result of disturbances in the innervation of the eye. A characteristic sign of lacrimal duct pathology is increased lacrimation (epiphora).
Hypofunction of the lacrimal glands (or “dry eye syndrome”) is one of the manifestations of Sjögren’s syndrome. It also occurs in endocrine and autoimmune diseases, in patients on hormone replacement therapy, in people who work for a long time behind a monitor, in smokers.
Diagnostics
Dacryocystitis is detected without much difficulty. At the appointment, the doctor performs a visual assessment of the eye and palpation of the lacrimal sac.
- Test using paint. The eye is instilled with a solution containing a dye. If pigment appears in the eye after a few minutes, this indicates a blockage of the tear ducts.
- Probing. Using a probe with a needle, the ophthalmologist penetrates the duct, which helps to expand it and get rid of the problem.
- Dacryocystography. Carrying out an X-ray examination with the introduction of a dye. In the picture you can see the structure of the eye system and identify the problem.
- Patency can also be checked with the West test. A cotton swab is placed in the nasal passage, on the affected side. Collargol is instilled into the eye. The condition is considered normal when after 2 minutes the tampon turns dark. If the swab remains clean or stained after 10 minutes, there is a problem.
How to distinguish dacryocystitis from conjunctivitis
Dacryocystitis in newborns is often confused with conjunctivitis. They have similar symptoms but completely different causes. And the treatment for these diseases is different, so do not try to diagnose yourself and start taking medications. This should be done by a doctor. Come to us if your baby shows the first signs of illness. You can make an appointment from home: by phone or on our website.
Popular questions
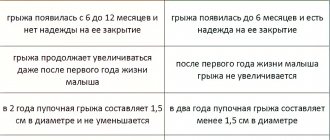
I heard that in the West they do not recommend probing until the child is one year old, since the nasolacrimal duct can suddenly open on its own. Is it so?
In 70-90% of children, spontaneous opening of the nasolacrimal duct does occur during the first year of life. Therefore, most Western ophthalmologists recommend conservative treatment if the symptoms are mild. However, when signs of inflammation are obvious, and massage and rinsing do not improve the child’s condition, surgical expansion of the nasolacrimal duct is required.
Are there any complications after probing?
Any operation, even something as simple as probing, is always associated with a certain risk of complications. When probing, this causes bleeding, creation of a false passage, damage to the epithelium of the lacrimal canal, which increases the risk of scarring and a negative outcome of the operation. The likelihood of such consequences is extremely low and is usually associated with errors during the procedure. To reduce the risk, you should carefully choose a clinic and a pediatric ophthalmologist.
Treatment
Eyes are the mirror of the soul. When an eye problem arises, there is no need to take risks. Treatment should be prescribed by a doctor after preliminary diagnosis. The treatment method is selected depending on the form and cause of the pathology that provoked it, and age characteristics.
- Rinsing the eyes with antibacterial and disinfectant solutions.
- The use of special drops and ointments.
- Massage procedures and compresses to help clean the canal.
Eye rinsing with antiseptic solutions is carried out several times a day. The procedure is performed by an ophthalmologist in a hospital setting.
Ointments and drops that have an antibacterial effect:
- Phloxal . Antibacterial drug with a wide spectrum of effects. Fights the inflammatory process. The course of treatment is 10 days, two drops twice a day.
- Dexamethasone . Drops with an antibacterial effect. Effective against infectious processes. Instill 5 times a day. The required dosage and course of treatment are selected by the doctor individually for each patient.
- Levomycetin is a hormonal drug. Used for allergic reactions and inflammations.
- Ciprofloxacin . Prescribed for infections of the lacrimal duct. Buried every three hours.
The drugs have contraindications and side effects. Drug therapy is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
If the treatment does not have a positive effect, bougienage is performed - cleaning the tear duct from purulent contents; The disease can be quickly dealt with only if treatment is started in a timely manner. If symptoms are negative, you should visit an ophthalmologist.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of this disease, it is recommended to follow these rules:
- Avoid unsanitary conditions: it is important that all items used to care for the baby are clean.
- Parents should always wash their hands before handling their baby.
- If the eye is watery, bandages should not be used, as this can lead to complications.
- If symptoms of dacryocystitis develop, you should immediately show the child to a doctor and consult with him about your further actions.
- It is important to promptly treat all colds and follow the recommendations of a specialist.
- Adults should use only high-quality cosmetics that have not expired.
- You should protect your eyes when performing work where there is a risk of injury, and also protect your eyes when playing sports.
Radical ways to fight
If there is no positive effect from drug treatment, or if the cause is a tumor or cyst, surgical treatment is performed.
Surgical intervention happens:
- Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy I. A device with a camera is inserted into the duct. A puncture or incision is made using an endoscope. A special valve is created, the main purpose of which is drainage. The recovery period is 7 days. In parallel, antibiotic therapy is carried out to prevent the risk of developing an inflammatory process. The main advantage is the absence of visible marks after the operation.
- Balloon dacrycytoplasty is an intervention that, due to its safety, is performed even on newborns. A conductor with a reservoir filled with liquid is inserted into the channel. Allows you to expand the area, thereby breaking through it. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia. During the rehabilitation period, special drops and antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Patients and methods
We observed 56 patients who were divided into 2 groups. The 1st (control) group included patients with chronic dacryocystitis ( n
=22), who were treated in an ophthalmology clinic without the involvement of an otorhinolaryngologist, who performed transcanalicular laser dacryocystorhinostomy.
The 2nd (main) group included patients with chronic dacryocystitis and concomitant pathology of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses ( n
= 34), who underwent endonasal endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy. These patients were treated at the otorhinolarynology clinic. An ophthalmologist was involved in diagnosing the disease and performing surgical interventions.
The clinical examination of patients in group 1 included a standard set of ophthalmological examinations (testing visual acuity, refraction, assessing the transparency of optical media and the condition of the fundus, perimetry and tonometry, biomicroscopy, dacryocystography with simultaneous visualization of the paranasal sinuses), allowing to assess the condition of the organ of vision. To assess the active function of lacrimal drainage, color tubular and color nasolacrimal tests were used.
Clinical examination of patients in group 2, in addition to the methods listed above, also included anterior rhinoscopy and optical endoscopy of the nasal cavity, anterior active rhinomanometry, computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses with contrasting of the lacrimal ducts. To assess the function of active lacrimal drainage, color tubular and color nasolacrimal tests were also used.
Massage
Prepare your hands before the procedure: wash, disinfect or wear gloves.
Massage scheme:
- Press on the outer corner of the eye, turn your finger towards the bridge of the nose.
- Gently press and massage the lacrimal sac, removing purulent masses from it.
- Instill a warm solution of furatsilin and remove the discharge.
- Carry out pressing and massaging movements along the tear ducts.
- Jerky movements along the nasolacrimal sac with some force to open the canal and extract the discharge.
- Instill a solution of chloramphenicol.
Pathogenesis
Normally, the tear fluid produced by the lacrimal glands washes the eyeball and flows to the inner corner of the eye. It is there that the so-called lacrimal openings are located, which lead to the lacrimal canaliculi. If there is no pathology, the tear first enters the lacrimal sac, and then through the nasolacrimal duct into the nasal cavity. If the nasolacrimal duct is obstructed, the lacrimal drainage process is disrupted and tears accumulate in the lacrimal sac. This is a cylindrical cavity that is located at the top of the nasolacrimal duct. When tears stagnate, the lacrimal sac becomes infected, which leads to the development of inflammation in it.
In children, dacryocystitis develops due to the fact that at the time of birth, a membrane (muco-gelatinous plug) remains at the mouth of the nasolacrimal duct, which prevents the normal process of tear outflow. In most cases, after birth in children, the patency of the lacrimal ducts is restored spontaneously. However, sometimes the stagnant contents of the lacrimal ducts with pus enter the conjunctival sac, which provokes a pathological process.
Folk remedies
After prior approval from a doctor, traditional medicine is successfully used at home.
Folk remedies:
- Aloe. For inflammation, it is good to instill freshly prepared aloe juice, half diluted with saline solution.
- Eyebright. Cook in the same way. Use for eye drops and compresses.
- Chamomile. Has an antibacterial effect. You need to take 1 tbsp. l. collection, boil in a glass of boiling water and leave. Use to wash eyes.
- Thyme . Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, the infusion is used for dacryocystitis.
- Kalanchoe. Natural antiseptic. Cut off the leaves and keep in the refrigerator for two days. Next, extract the juice and dilute it in a 1:1 ratio with saline. This remedy can be used to treat children. Adults can instill concentrated juice into the nose, 2 drops each. The person begins to sneeze, during which the tear duct is cleared of pus.
- Leaves from a rose . Only those flowers that are grown on your own plot are suitable. You will need 100 gr. collection and a glass of boiling water. Boil for five hours. Use as lotions.
- Burda ivy-shaped . Brew a tablespoon of herb in a glass of boiling water, simmer for 15 minutes. Use for rinsing and compresses.
- Bell pepper . Drink a glass of sweet pepper fruit every day. adding a teaspoon of honey.
Diet
Diet 15 table
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 2 weeks
- Timing: constantly
- Cost of food: 1600-1800 rubles per week
A baby whose tear sac is inflamed should receive breast milk like all newborns. As for the advice about dropping breast milk into the eye, you shouldn’t follow it. Such use of breast milk can be not only useless, but also harmful, because in this case the risk of infection with pathogenic bacteria increases.
Adults can eat their usual food, trying to formulate a diet so that it is both varied and nutritious.
Risk group
People ask me who is most susceptible to this disease? Most often women aged 35 to 70 years are affected. This is explained by the genetic characteristics of the female body - narrower tear ducts compared to males. In addition, women use cosmetics and, with insufficient hygienic care, can cause an infection in the eye.
Also at risk are people with weak immune systems, newborns and infants.
Predisposition to dacryocystitis is sometimes “written on the face.” People with a characteristic appearance - a round skull, a flattened nose, an oblong face - are more susceptible to the disease. In such patients, the complex anatomy of the nasolacrimal ducts and lacrimal gland becomes a predisposing factor.
In representatives of the Negroid race, dacryocystitis almost never occurs due to wider nasolacrimal ducts.
Dacryocystitis in adults has an unusual pattern - the left nasolacrimal duct is mainly affected. The fact is that the lacrimal glands are asymmetrically located: on the left side the distance is smaller, and the duct is narrower than on the right.
With timely consultation with a doctor and the absence of secondary pathologies, the disease in children and adults has a favorable prognosis. But in advanced cases, the infection may spread and dangerous complications may arise, even with the risk of death.
Unsuccessful surgical interventions caused by late consultation with a doctor and ignoring clinical recommendations can also lead to complications.
During the treatment of dacryocystitis, other ophthalmological interventions (cataract surgery and laser vision correction) are postponed until complete recovery from dacryocystitis.
List of sources
- Kataev M.G. External dacryocystorhinostomy // Modern methods of diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the lacrimal organs: scientific and practical. conf.: Sat. scientific Art. - M., 2005. - P. 121-126.
- Ophthalmology: national guide / ed. S.E. Avetisova, E.A. Egorova, L.K. Moshetova, V.V. Neroeva, Kh.P. Tah-chidi. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008. - 944 p.
- Strogal A.S. Efficiency of treatment of congenital dacryocystitis // Ophthalmol. Journal 1983. No. 7. pp. 437-438.
- Cherkunov B.F. Diseases of the lacrimal organs: Monograph. - Samara: GP Perspective, 2001. - 296 p. (140-152).