Fallopian tube obstruction is a pathological condition that develops as a result of an inflammatory process in the tube or in the tissues surrounding it. Very often, a woman does not even suspect the existence of the disease until problems arise with conceiving a baby. The causes of obstruction of the fallopian tubes are very different, most often these are infections that are accompanied by an inflammatory process. Also, adhesions can appear after abortion, surgery, or peritonitis. In most cases, the pathology does not affect the woman’s health; the only problem for her is the inability to conceive naturally. Tubal obstruction can be treated conservatively or surgically. If therapy is ineffective, they resort to IVF or other assistive technologies.
Fallopian tube obstruction: infertility
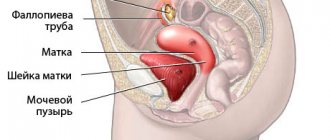
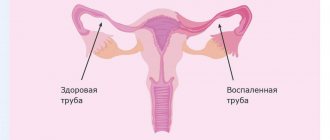
Fallopian tube obstruction is one of the most common causes of infertility. Every month, during ovulation, an egg is released from one of the ovaries. The egg travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus. To fertilize an egg, a sperm passes through the cervix, uterus, and enters the fallopian tubes (where fertilization occurs). Patency of the fallopian tubes allows the egg to travel from the ovary to the uterine cavity, where it can continue its development and give rise to pregnancy.
What are fallopian tube diseases?
The content of the article
Female infertility in 20-30% is associated with impaired functionality or absence of the fallopian tube or both tubes. Epididymis removal is usually associated with an ectopic pregnancy, when a fertilized egg gets stuck inside the tube and begins to develop there.
Inflammatory processes threaten the occurrence of adhesions that block the lumen of the fallopian tube. Also, organ dysfunction is expressed in loss of contractility and peristalsis. Also, fimbriae, the smallest villi at the exit of the fallopian tubes, stick together after inflammation and lose their ability to capture the egg during ovulation.
Options and causes of fallopian tube obstruction
Fallopian tube obstruction varies. The type and degree of blockage of the tube significantly affect the possibility of conception. There are the following options:
- Complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes
- Blockage of one pipe
- Partial gynecological obstruction of the fallopian tubes with movement disorders
- Adhesions around appendages and tubes
- Violation of the motor activity of villi on the funnel of the pipe
The fallopian tubes are paired organs with a diameter of about a centimeter and a length of about 10 centimeters. Inside the tube, the diameter varies, from a millimeter at the entrance to the uterus to a centimeter on the other side. Any inflammatory process in which these organs are involved can cause the formation of adhesions and blockage of the lumen of the tube. So, with one episode of inflammation, the probability of signs of tubal obstruction occurring is 15%, with two – 35%, with three – 75%. Sometimes infectious diseases are practically asymptomatic, which absolutely does not exclude the formation of adhesions. With chronic inflammation with frequent exacerbations, complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes occurs, according to some data, with a probability of 90%.
The most common causes of fallopian tube obstruction resulting from inflammation are chlamydial infection, gonorrhea, mycoplasma, gardnerella, and ureaplasma. Due to the increasing incidence of tuberculosis, this infection cannot be ruled out. Surgery in the pelvis or abdominal cavity can easily provoke obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Pathology often occurs after removal of appendicitis, especially purulent, complicated by peritonitis. Also, signs of obstruction of the fallopian tubes are detected with endometriosis, after abortion or ectopic pregnancies, with tumors or polyps in the uterine cavity and appendages, and abnormal development of these organs.
Laparoscopic surgery - salpingo-ovariolysis
The purpose of the operation is to restore normal topographic relationships by cutting the adhesions around the fallopian tube and ovary, isolating them from each other. Salpingo-ovariolysis is performed either as an independent intervention or as a preparatory step for surgery on the fallopian tubes. The fallopian tube (ovary) is picked up with atraumatic forceps and moved upward if possible. The adhesions are cut with endoscissors after their preliminary coagulation. Rough adhesions are excised and removed from the abdominal cavity. Special precautions are necessary when working near the intestines, ureters, and large vessels. The risk of their damage can be reduced by observing the following conditions: the operation is performed under general anesthesia with sufficient relaxation, the absence of defects in the insulating braid of the instruments, short-term switching on of the electrosurgical unit. After complete release of the fallopian tube from adhesions along its entire length, ovariolysis is performed. In this case, it is imperative to lift the ovary and inspect its surface facing the broad uterine ligament, since adhesions can often be localized there.
Tubal patency test
Today, the following methods are used to detect the patency of the fallopian tubes:
- X-ray hysterosalpingography.
This method of diagnosing the condition of the internal female genital organs allows us to determine the shape of the uterus, the degree of lumen, and the structure of the walls. The study involves the introduction of a contrast agent and an x-ray examination of the internal contour of the uterus and tubes. Unpleasant sensations during the procedure are insignificant; Minor bleeding may occur within a few hours after the procedure. - Echohysterosalpingography (hydrosonography).
The study is carried out using ultrasound, which diagnoses the condition of the uterine cavity and the patency of the fallopian tubes. This method is less painful than x-ray hysterosalpingography, and therefore is used more widely. During echohysterosalpingography, a catheter is inserted into the uterine cavity, through which a contrast agent is infused in a volume of 10-20 ml. Next, the injected fluid penetrates into the fallopian tubes, then into the abdominal cavity, which further proves the patency of the fallopian tubes. In case of obstruction, the contrast agent accumulates only in the tubes. After the manipulation, patients feel some pain, which, as a rule, goes away quickly. - Fertiloscopy.
The method involves inserting a thin optical device through the posterior vaginal fornix. The examination is performed under intravenous anesthesia and lasts from 10 to 15 minutes. Fertiloscopy allows you to make a visual assessment of the condition of the pelvic organs. To diagnose patency of the fallopian tubes, the doctor injects an antiseptic solution - methylene blue - through the uterine catheter. During fertiloscopy, adhesions are separated simultaneously. - Laparoscopy.
Diagnostics provides high accuracy when checking the patency of the fallopian tubes, and also allows you to identify endometriosis, uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts. If tubal obstruction is detected, during laparoscopy this problem can be eliminated by performing tubal plastic surgery or removal of adhesions.
Doctor's opinion
Normally, fertilization occurs in the ampulla of the oviduct, within 24 hours after ovulation.
Moving through the lumen of the tube, the fertilized egg continues to divide and, once in the uterine cavity, it becomes a blastocyst, which, under favorable conditions, penetrates into the endometrium of the uterus, and this is how implantation occurs. Otherwise, if fertilization does not occur, the egg dies. — Shushkova Alexandra Grigorievna Reproductologist, obstetrician-gynecologist.
Test for tubal patency: price
The cost of diagnosing tubal patency depends on the chosen method. Only your attending gynecologist can determine which method is optimal in your particular case. In general, the price of the study consists of the cost of the intrauterine catheter (which, in turn, depends on the manufacturer, the price of the echo contrast gel), the cost of consumables and the cost of the specialist’s work. The price is also influenced by the geographical location and prestige of the clinic. In Moscow, the average cost of diagnosing tubal patency varies from 1,500 to 4,500 rubles.
Hysterosalpingography images
The right fallopian tube is obstructed in the ampullary section.
The left fallopian tube is freely patent.
The "R" on the image indicates the patient's right side.
The arrow indicates an obstruction in the ampullary section of the right fallopian tube.
The right and left fallopian tubes are difficult to pass due to the presence of bilateral valve sactosalpinxes.
The image clearly shows dilated and tortuous fallopian tubes.
The arrow shows the fallopian tube on the left with the presence of a valve sactosalpinx.
The "R" on the image indicates the patient's right side.
The left fallopian tube is freely patent.
The right fallopian tube is obstructed in the intramural section.
The arrow indicates the presence of an obstruction at the mouth of the right fallopian tube.
The letter "R" in the image represents the patient's right side.
The left fallopian tube is obstructed in the ampullary section.
The right fallopian tube is difficult to pass due to the presence of a valve sactosalpinx on the right.
The arrow shows the valve sactosalpinx on the right.
The "R" on the image indicates the patient's right side.
Clinical signs of tubal obstruction and diagnosis
Tubal obstruction has scant symptoms. The manifestations are associated with an exacerbation of the inflammatory process; patients are bothered by various types of pain in the lower abdomen, vaginal discharge, and sometimes fever. A woman can live with a problem for many years without knowing about it. Some patients do not even have a history of surgery or inflammatory diseases. By and large, the pathology does not at all affect general well-being and health (except reproductive health), and is not life-threatening. But very often, obstruction of the fallopian tubes causes infertility; the inability to get pregnant forces patients to consult a doctor.
Since fallopian tube obstruction has mild symptoms, additional diagnostic tests must be performed before prescribing treatment. Ultrasound provides little information. To obtain more data, hydrosonography is done.
A more accurate method is x-ray hydrosalpingography, but this type of diagnosis is performed less and less due to its harm to health. X-ray hydrosalpingography has begun to be replaced by diagnostic laparoscopy, which makes it possible to simultaneously diagnose pathology and eliminate it.
Fallopian tube obstruction: what to do?
Having received a diagnosis of “obstruction of the fallopian tubes,” patients are interested in the question of whether it is possible to eliminate the pathology, or is it better to immediately opt for the method of artificial insemination.
Age plays a big role in resolving this issue. Up to 35 years of age, in the absence of other disorders that prevent pregnancy, you can try to restore the patency of the tubes and become pregnant within a year. As for women over the age of 35 who suffer from long-term infertility and tubal obstruction, here it is worth first of all giving preference to IVF. The fact is that over time, the quality of eggs deteriorates, as a result of which the risk of genetic disorders in the fetus increases. Therefore, it is not considered advisable to waste time trying to restore the patency of the tubes.
Clinical prognosis
In addition to oncological diseases that pose a direct threat to a woman’s life, the most severe pathologies of the fallopian tubes include hydrosalpinx, pyosalpinx and salpingitis. These diseases carry a high risk of developing difficult-to-treat forms of female infertility, and therefore the main efforts should be aimed at their prevention.
Other diseases of the fallopian tubes are successfully treated and have favorable clinical prognoses both in terms of recovery and in the matter of preserving the possibility of subsequent childbearing - of course, subject to timely seeking medical help.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category. Kosolapova Ekaterina Vitalievna
Fallopian tube obstruction - treatment
Treatment is mainly carried out when blockage of the fallopian tubes causes infertility. Conservative medicinal methods or surgical ones are used. If there is minor tubal obstruction, treatment includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, resolving therapy with streptokinase or hyaluronidase. If there is an infection, therapy necessarily includes taking antibiotics or antiviral drugs. Physiotherapeutic procedures give good results.
If tubal obstruction has more severe symptoms, treatment may be invasive. Techniques such as blowing and flushing pipes are now a thing of the past. They too often caused complications, and their effect was questionable. The main method of invasive therapy now is an operation called “laparoscopy”.
Laparoscopy for tubal obstruction
Laparoscopy for obstruction of the fallopian tubes is prescribed from the 7th day of the cycle and no later than the 10th before the onset of ovulation. However, if there are urgent indications, removal of tubes or adhesions can be performed on any day of the cycle. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Manipulations are carried out through several holes in the anterior abdominal wall, 5-7 mm in diameter. A laparoscope equipped with a mini-camera at the end is inserted into one such hole, thanks to which the image is displayed on the screen. A manipulator is inserted into the second puncture, with the help of which the surgeon can move the organs and perform other necessary manipulations. The abdominal cavity is first filled with carbon dioxide in order to improve visibility by raising the abdominal wall.
As a rule, the patient stays in the hospital for no more than a day. Doctors are monitoring her condition and performing ultrasounds. After 2-3 days you can return to work. Drinking alcohol and heavy food is not recommended for 2-3 weeks after surgery. Sexual contacts should also be postponed during this period. As for physical activity, it needs to be increased evenly. It is better to start with walking, gradually increasing their duration.
Please note: if there is significant obstruction of the fallopian tubes, surgery is not always successful. According to statistics, in the first six months after its implementation, only about half of the patients become pregnant. Then this percentage drops, as adhesions can form again.
Sterilization operation
Sterilization of the fallopian tubes, according to L.V. Adamyan (2000), PJ Taylor (1995), is one of the most common gynecological procedures. Indications for surgical sterilization:
- the couple's desire for complete fertility prevention;
- intolerance to other methods of contraception;
- medical indications - diseases of the cardiovascular, endocrine, musculoskeletal systems, mental disorders, hereditary diseases in which pregnancy and childbirth are absolutely contraindicated.
Before the operation, it is necessary to obtain the patient’s personal signature agreeing to sterilization. It is necessary to explain to her that restoration of patency of the fallopian tubes after any method of sterilization is not guaranteed.
With a normal menstrual cycle, surgery should be performed in the early proliferative phase. For women using an IUD, it is advisable to perform it 1 cycle after removal of the intrauterine contraceptive device and prophylactic antibacterial treatment. For patients taking oral contraceptives, sterilization can be performed at any time. The combination of artificial termination of pregnancy and sterilization, in our opinion, is inappropriate.
Currently, there are several options for tubal occlusion. Surgical intervention is performed through 2 approaches: a 5-mm trocar - paraumbilical, 5-mm - in the left (right) iliac region or in the midline above the pubic symphysis. If there is an adhesive process or other complicating issues, a third trocar is introduced.
After fixing the fallopian tube with a clamp, it is monopolarly coagulated over a length of 2 cm, 2-3 cm from the angle of the uterus, followed by dissection with endoscissors to the mesosalpinx, which significantly reduces the risk of recanalization. Coagulation can also be performed using a bipolar electrode in 2 or 3 places.
It is possible to excise a section of the fallopian tube 1-2 cm long after preliminary bi- or monopolar coagulation at a distance of 2 cm from the angle of the uterus.
Fimbriectomy involves coagulation and division of the distal portion of the mesosalpins near the infundibulopelvic ligament and the infundibulum of the fallopian tube.
According to the results of studies by Gomel V., Winston L., J. Hulka J., applying Hulka-Clemens clips to the isthmic part of the tube strictly in a perpendicular direction is a method that ensures the highest efficiency of the refertilization operation. In this regard, when deciding whether to perform sterilization, the patient's future need for a procedure to restore patency of the fallopian tubes should be taken into account.
Yun's ring method involves applying silicone rings using a special tool. The fallopian tube is captured by jaws at the junction of the isthmus and the ampulla, pulled into the lumen of the instrument, the ring is put on the loop of the tube and compresses it. Due to ischemic damage to the tube over a long distance, the likelihood of reversibility of this intervention is very low.
LITERATURE on the topic “Laparoscopic operations on the fallopian tubes”
- Puchkov K.V., Politova A.K., Polyakova O.V. Surgical treatment of infertility using minimally invasive technologies // Treatment of infertility: unresolved problems. – Saratov, 2001. – P. 129-130.
- Puchkov K.V., Politova A.K., Polyakova O.V., Tyurina A.A., Pkhitikova B.Kh. Surgical treatment of female infertility using minimally invasive technologies: method. recommendations. - Ryazan: RyazGMU, 2002. - 37 p.
- Puchkov K.V., Politova A.K., Kozlachkova O.P., Polyakova O.V., Pkhitikova B.Kh. Results of surgical treatment of female infertility using minimally invasive technologies // Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy in gynecology and obstetrics / ed. IN AND. Kulakova, L.V. Adamyan. – M.: PANTORI, 2002. – P.273-274.
- Puchkov K.V., Politova A.K., Polyakova O.V., Ruchkina E.N. Correction of female infertility using minimally invasive technologies // Endoscopic surgery. – 2002. – T.8, No. 3. – P.49.
- Puchkov K.V., Politova A.K., Ivanov V.V., Martynova G.V. Clinical effectiveness of organ-preserving operations in the complex treatment of inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages // New technologies in gynecology / ed. IN AND. Kulakova, L.V. Adamyan. – PANTORI. – M., 2003. – P.187-188.
- Puchkov K.V., Martynova G.V., Politova A.K., Ivanov V.V. Clinical effectiveness of organ-preserving operations in the complex treatment of inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages // Current issues of health of the population of the center of Russia / ed. M.F. Sautkina, O.E. Konovalova. – Ryazan, 2003. – P. 72-74. – (Collected scientific works / Ryazan State Medical University named after I.P. Pavlov; Issue III).
- Puchkov K.V., Kozlachkova O.P., Politova A.K., Polyakova O.V., Ivanov V.V. Surgical aspects of the treatment of tubo-peritoneal infertility // Current problems of pelvic surgery. - M., 2003., pp. 70–73.
- Puchkov K.V., Martynova G.V., Ivanov V.V., Polyakova O.V. Organ-preserving operations in the complex treatment of inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages: assessment of clinical effectiveness // X Russian-Japanese Med. symposium, Yakutsk, August 22 – 25, 2003: abstract. report - Yakutsk, 2003. - P. 629.
- Puchkov K.V., Pkhitikova B.Kh., Shavaeva V.A. Immune status of patients with tubal-peritoneal infertility, the effectiveness of its correction using roncoleukin // Current issues in obstetrics, gynecology and perinatology: materials of the 4th interregion. scientific-practical Conf. - Nalchik, 2004.- P.26-28.
- Puchkov K.V., Ivanov V.V.. Technology of dosed ligating electrothermal effects at the stages of laparoscopic operations: Monograph. - M.: ID MEDPRACTIKA - M. - 2005. - 176 p.
- Puchkov K.V., Politova A.K.. Laparoscopic operations in gynecology: Monograph.- M.: MEDPRACTIKA - M.- 2005.- 212 p.
- Puchkov K.V., Polyakova O.V., Martynova G.V. Surgical treatment of tubo-peritoneal infertility using minimally invasive technologies // Current issues of modern surgery. Regional (Southern Federal District) scientific-practical. conf. surgical doctors, Nalchik, May 26-27, 2006 - Nalchik, 2006.- P. 231-232.
- Puchkov K.V., Polyakova O.V., Martynova G.V. Possibility of increasing the effectiveness of surgical treatment of female tuboperitoneal infertility // Current issues of modern surgery. Regional (Southern Federal District) scientific-practical. conf. surgical doctors, Nalchik, May 26-27, 2006 - Nalchik, 2006.- pp. 232-234.
- Puchkov K.V., Pkhitikova B.Kh., Shavaeva V.A. Immune status of patients with tubo-peritoneal infertility, the effectiveness of its correction using roncoleukin // Current issues of modern surgery. Regional (Southern Federal District) scientific-practical. conf. surgical doctors, Nalchik, May 26-27, 2006 - Nalchik, 2006. - P. 239-241.
- Puchkov K.V., Ivanov V.V., Polyakova O.V. Ways to increase the effectiveness of surgical treatment of female tuboperitoneal infertility // Journal. obstetrics and women's diseases. - 2006. - T. 55 (special issue) - P.34-35.
- Puchkov K.V., Pkhitikova B.Kh., Ivanov V.V. Results of complex treatment of tubo-peritoneal infertility using minimally invasive surgical technologies and immunocorrective therapy of recombinant human interleukin-2 // Endoscopic surgery. – 2007. – T.13, No. 4. – P.36-39.
Fallopian tube obstruction: how to get pregnant
When fallopian tube obstruction is found, what should you do to get pregnant? These questions are often heard in doctors' offices and on online forums. It should be noted that a diagnosis is not a death sentence. Pregnancy with one fallopian tube - healthy, or with partial obstruction - is quite likely. But cases of pregnancy without fallopian tubes naturally have not been recorded. Here we have to resort to assisted reproductive techniques.
The easiest is intrauterine insemination with the sperm of the husband or donor. It will bring results if at least one pipe is in normal condition. Intrauterine insemination is carried out by injecting specially prepared sperm into the uterine cavity. To increase the likelihood of a positive result, ovulation is stimulated. It is necessary that the eggs mature in the ovary on the side where the patent tube is located. This is determined by ultrasound.
Intrauterine insemination costs little and is much cheaper than IVF. The probability of conception with it ranges from 3% to 20%. The procedure is sometimes prescribed after adhesion surgery to increase its effectiveness. Intrauterine insemination, its price may also depend on whether hormonal stimulation of ovulation is carried out. If yes, then the cost will also include the price of the drugs. In most clinics it is 20,000-40,000 rubles.
Hydrosalpinx on ultrasound
Hydrosalpinx is an obstruction of the lumen of the fallopian tube by a hollow formation in which serous fluid (sactosalpinx), pus (pyosalpinx) or blood (hematosalpinx) accumulates. Hydrosalpinx occurs at the site of adhesions, from which a capsule of connective tissue is formed, gradually filling with water. It can burst, and then the contents fall into the fallopian tube. There is a threat of developing an abscess and infection of neighboring organs.
Ultrasound diagnosis of hydrosalpinx is carried out without filling the fallopian tubes with contrast liquid. The appendages are visible only when they are swollen or filled with fluid. On the monitor you can see the expansion of the fallopian tube due to the filling of the capsule with serous substance.
Hydrosalpinx will be visualized on days 5-9 from the beginning of the cycle, but then the data will be unreliable. The procedure is not performed before the 5th day of the cycle, otherwise you may miss an ectopic pregnancy. In the 2nd half of the cycle, the endometrium grows, which also distorts the results.