Otitis is one of the most common diagnoses in the daily practice of an otolaryngologist. In acute otitis media, we observe an inflammatory process affecting one of the parts of the human hearing organ. The appearance of acute pain in the ear is the main symptom signaling the onset of inflammation.
The disease is common among both children and adults. Although children are at increased risk of developing acute inflammation. This is due to the structural features of the child’s ear and weak, fragile immunity.
Diseases of the hearing organ, like any other disease concentrated in the head area, must be treated carefully and responsibly, since an infection through the bloodstream can easily reach the brain and cause irreversible consequences. Therefore, it is necessary to treat an acute inflammatory process as soon as the first prerequisites for the disease appear. Treatment of the disease should be carried out in a hospital, under the supervision of a competent doctor.
In this article we will look at how the disease develops, what treatment methods are available today, how complications of otitis manifest themselves and how to avoid them.
Types of disease
Inflammation that occurs in the organ of hearing can be chronic or acute. In acute cases of otitis, the disease lasts for up to three weeks, in chronic cases - more than three months. The chronic process starts when treatment of the acute form of otitis was not carried out or was not carried out at the proper level. There is also an intermediate form - subacute, when the duration of the disease ranges from three weeks to three months.
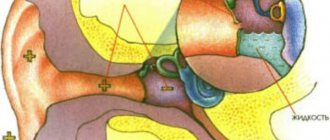
The human hearing organ is divided into three parts: the outer, middle and inner ear. Otitis may appear in each of these areas. Based on the location of the inflammation, acute otitis media is distinguished, and inflammation of the inner ear, otherwise known as labyrinthitis.
External manifestations of inflammation, in turn, are divided into limited, manifesting mainly in the form of a boil of the auricle, and diffuse otitis media. With diffuse otitis, a significant area of the outer ear is affected.
Acute inflammation of the middle ear involves the tympanic cavity of the ear, the auditory (Eustachian) tube and the mastoid process. This type of hearing disease is the most common.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
The disease of the internal part is called labyrinthitis (this part of the ear is called the labyrinth because of the similarity of its shape to the cochlea). As a rule, inflammation covers the internal part if the treatment of inflammatory disease of the middle ear was carried out late or the treatment for otitis media was chosen incorrectly.
Based on the causes of occurrence, infectious otitis media is distinguished, caused by various pathogens, and non-infectious (for example, arising due to exposure to allergens or ear injuries).
Otitis in acute form can occur in catarrhal (without the formation of secretion in the ear cavity), exudative (with the formation of fluid in the tympanic cavity) and purulent (with the presence of purulent masses) forms.
Structure of the human ear
The human ear consists of three sections. The outer section consists of the auricle and the auditory canal, which ends in the eardrum. The middle ear conducts sound impulses and is formed by the tympanic cavity between the opening of the temporal bone and the eardrum. The hammer, one of the sound ossicles, is attached to the eardrum. When exposed to sound waves, the hammer vibrates. These vibrations are transmitted along a chain to other sound bones: from the malleus to the incus, then to the stapes and to the inner ear.
The inner ear is located deep in the temporal bone and is a complex system of canals. Special hair cells located on the surface of the canal convert mechanical vibrations into nerve impulses, which are transmitted to the corresponding parts of the brain. Otitis can spread in different parts of the ear, so there are external, middle and internal types of pathology.
Acute otitis media of the middle ear: what causes inflammation?
The inflammatory process is always caused by pathogenic microorganisms, which means that the prerequisites for their activation must be present in the body. The causes of otitis media are:
- hypothermia;
- diseases caused by infection (flu, ARVI, measles);
- inflammatory processes of the ENT organs (the tympanic cavity is connected to the nasopharynx via the Eustachian tube, it is not surprising that the infection from the nasopharynx easily penetrates into the middle ear);
- improper nose blowing;
- hypertrophy of adenoid vegetations;
- rhinitis, sinusitis;
- allergic reactions;
- deviated nasal septum;
- foreign object in the ear;
- damage to the hearing organ.
Causes
Otitis of the inner ear causes the spread of an infection of viral or bacterial origin. Often the cause is a previous upper respiratory tract infection (influenza, acute respiratory infections, ARVI).
Causes causing the disease:
- streptococcal infection;
- meningococcal infection;
- pneumococcal infection;
- influenza virus.
Another cause of the disease is ear injury. Injuries can be mechanical, chemical or thermal.
Outer and inner ear: causes of inflammation
Otitis externa can develop due to improper ear hygiene. If you don't take care of your ears, dirt will accumulate in them, and this is a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria. Excessive hygiene is also harmful: earwax is a natural barrier against the penetration of bacteria into the ear. If you diligently clean the ear canals every day, a person loses this barrier and opens the way for pathogens. Another mistake that leads to acute ear inflammation is cleaning the ears with sharp objects that are not intended for this (toothpicks, matches, hairpins). Such actions can lead to damage to the auricle, which in turn leads to infection entering the wounds. Another factor is dirty water that gets into the ear, which contains pathogens. “Swimmer’s ear” is another name for this type of disease.
As we have already said, inflammation of the internal region occurs due to undertreated otitis media, if due attention has not been paid to the treatment of otitis media. Bacteria can also get here from the meninges, for example, with meningitis. This type of inflammation can be caused by injuries and fractures of the skull or temporal bone.
In order to recognize the disease in time and choose the right treatment, you need to be able to identify its signs.
Prevention
There are no specific preventive measures to avoid suppurative otitis media. To reduce your risk of getting sick, strengthen your immune system and promptly treat any ENT infection you encounter. An important point: treatment should not only be timely, but of high quality: no self-medication, only competent assistance from an otolaryngologist. There is no need to start the disease. At an early stage, any disease is much easier to treat: in many cases, the accumulation of purulent masses in the middle ear could be easily avoided by contacting an ENT doctor in time.
If you or your loved ones are faced with hearing problems, do not waste time: make an appointment by calling +7 (495) 642-45-25 and come.
We will definitely help you!
Symptoms
The acute course of the disease is characterized by a rapid onset and pronounced symptoms.
With a disease of the outer ear, a person experiences pain inside, which intensifies when pressing on it from the outside. Acute pain occurs when swallowing and chewing food. The ear itself swells and turns red. The skin of the auricle is itchy, the patient's complaints are reduced to a state of stuffiness and ringing in the ear.
In acute otitis media, the main sign of inflammation is the sudden appearance of sharp shooting pains, which become stronger by night. The pain can radiate to the temples, left or right frontal parts, to the jaw - it is very difficult to endure even for an adult, not to mention children. The following symptoms are also characteristic of acute otitis media:
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
- fever (up to 39°C);
- tinnitus;
- hearing loss;
- lethargy, malaise, loss of appetite;
- in the exudative form, discharge comes from the ear (usually this discharge is transparent or white);
- Acute purulent otitis media is characterized by suppuration from the ear.
The main symptom of labyrinthitis is dizziness. They can last a few seconds, or they can last for several days.
If you notice one or more of the symptoms described above, you should immediately consult a doctor for treatment.
Symptoms of labyrinthitis
With labyrinthitis (otitis of the inner ear), there is a complex disorder of the vestibular apparatus, loss of orientation in space, dizziness, and tinnitus. If the disease progresses significantly, it is difficult for a person to take a vertical position (stand up, sit down), and there are significant restrictions in the control of his movements.
Symptoms of the disease:
- sweating;
- nausea and vomiting;
- loss of coordination;
- noise in ears;
- dizziness;
- tachycardia;
- pale skin.
Also, labyrinthitis is often accompanied by Vertigo syndrome (sensation of rotation), high body temperature (up to 38 degrees), fainting, slurred speech, vomiting, partial or complete hearing loss, and tinnitus.
Stages of disease development
Treatment of acute otitis lasts from one to three weeks. There are several stages in the development of the disease. But it is not at all necessary that the patient will go through all of them. If treatment for infectious otitis is started on time and the acute disease is treated by a competent ENT doctor, recovery will not take long.
So, the course of the disease is conventionally divided into several stages:
- Catarrhal. Pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively multiply, triggering an inflammatory process in the ear. At this time, catarrhal edema and inflammation are observed.
- Exudative. Inflammation leads to active formation of fluid (secret). It accumulates and pathogenic microorganisms continue to multiply here. Timely treatment at this stage will allow you to cure otitis media, avoiding complications.
- Purulent. Acute purulent inflammation is characterized by increased formation of purulent masses in the middle ear cavity. They accumulate, the patient experiences pressure from the inside. The state of congestion does not go away. This phase usually lasts from several days to several hours.
- Perforated. At this stage, accumulated pus causes a rupture of the eardrum, and purulent masses emerge from the tympanic cavity to the outside. At this moment, the patient begins to feel noticeable relief, the high temperature decreases, and the pain gradually disappears. It happens that the eardrum is unable to rupture, then the doctor manually punctures the eardrum (paracentesis) and thereby releases purulent masses out into the ear canal.
- Reparative phase - the release of pus is completed. The hole in the eardrum closes. As a rule, after proper symptomatic treatment, the patient quickly recovers.
Diagnostics
For an experienced otolaryngologist, diagnosing the disease is not difficult. When making a diagnosis, the ENT doctor relies on the patient’s complaints and the results of otoscopy (examination of the hearing organ). The patient may be referred for a number of laboratory tests that will confirm or refute the presence of inflammation. To assess the degree of hearing impairment, audiometry or tuning fork testing is performed. To assess the condition of the components of the middle ear, tympanometry is performed. In severe cases, the patient is sent for X-ray, CT, MRI.
Complications and preventive measures
As a rule, if you start treating the disease on time, treatment of acute purulent otitis, exudative or inflammation of any other kind, you can avoid any complications.
However, if treatment is not carried out and the disease progresses, the diagnosis can become chronic. The most serious consequences are: meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess, facial neuritis, hearing loss. But these dangerous conditions can only appear when patients persistently neglect treatment for otitis media.
Preventive measures include the fight against existing foci of inflammation in the body, competent and timely treatment of ENT diseases, proper ear hygiene and, of course, strengthening the immune system.
Symptoms of purulent otitis media
A distinctive sign of the disease, which distinguishes it from non-purulent otitis media in adults and children, is discharge of purulent exudate from the ear. This sign is not always present. Suppuration is possible only when pus ruptures the eardrum. If the eardrum has not ruptured, the purulent accumulations cannot leave their location, which can lead to possible complications.
Another sign of suppurative otitis media is ear pain. It can be either tolerable and non-intense, or simply unbearable.
During the period of inflammation, body temperature may rise, although this is not a mandatory sign.
Patients also note hearing loss, ear congestion and headaches.
It is more difficult to understand that a child has developed otitis media, since children cannot clearly explain what and how it hurts. In infants, diagnosis is even more difficult. But based on his behavior, one can suspect ear inflammation: the baby is capricious, has become whiny, and refuses milk.
The disease occurs in stages: inflammation goes through several stages. These stages of otitis differ from each other in symptoms.
Carrying out treatment
It is much easier to cure acute otitis media if treatment for the disease begins as early as possible. Treatment should be carried out under the supervision of an otolaryngologist. Complex treatment includes the following activities:
- for acute pain, taking analgesics is indicated to relieve pain;
- to bring down the temperature you need to take antipyretic drugs;
- in difficult cases, antibiotic treatment is carried out;
- local treatment consists of using special ear drops, which are prescribed individually in each case. Self-selection of drops, as well as antibacterial drugs, is fraught with dangerous consequences for health.
- Antihistamines help relieve swelling;
- a good effect is achieved during physiotherapeutic procedures;
- surgical intervention: opening of the eardrum (paracentesis) is carried out if spontaneous rupture has not occurred.
All ENT doctor’s prescriptions must be followed in full: after all, following treatment recommendations is the key to a quick recovery.
Classification of the disease according to the nature of its course.
There are many classifications of diagnosis. We will dwell on a few in more detail.
Based on duration, the disease is divided into three forms: acute, subacute and chronic. The acute form lasts no more than three weeks. If the disease does not go away within three months, then we are dealing with a subacute variation of the disease. Chronic inflammation is characterized by sluggish symptoms that prevent an adult from leading a full lifestyle for more than six months in a row.
Based on the type of causative agent of the disease, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- bacterial - when the cause of infection is bacteria;
- viral - provoked by viruses;
- fungal - the causative agents are fungi;
- allergic - manifests itself against the background of the action of allergens;
- traumatic - due to damage to the hearing organ (more often occurs when improperly manipulating a cotton swab when cleaning the ears or a pressure drop during diving or air travel).
There is an exudative type of disease, when fluid is released from the ear cavity, catarrhal (no discharge, but severe swelling is present) and purulent. Purulent otitis is accompanied by discharge from the organ of hearing and is fraught with complications.
If the inflammatory process occurs in the right ear, we talk about right-sided inflammation, if in the left ear, we talk about left-sided inflammation. The most difficult course is for bilateral ear lesions.
What not to do during treatment
Some patients are overly self-confident and believe that a disease such as otitis media can be easily cured with the help of folk remedies and “grandmother’s” recipes. A wide variety of methods are used. This is a huge misconception!
The first mistake is that no foreign objects should be placed in the ear canal. Some are trying to use phytocandles, others, for example, geranium leaves. Such measures are fraught with the fact that leftover leaves may get stuck in the ear, which will provoke increased inflammation.
The second mistake is the use of heat and warming compresses for the purulent form of the disease. Some people replace compresses with a heating pad. At this stage of the disease, thermal heating will only increase the proliferation of bacteria.
The third mistake is trying to instill various oils or variations of alcohol into the ears. If during such treatment a perforation of the eardrum occurs, such instillations will not only cause pain, but will also cause scarring in the middle ear and eardrum.
What is prohibited for otitis media
- Under no circumstances should foreign bodies be introduced into the ear (geranium leaves, ear phyto-candles). This will make diagnosis difficult and may lead to a worsening of the condition (for example, leaves that have not been removed begin to rot and become a source of infection).
- If the pain is severe, do not apply a heating pad to your ear or apply warm compresses. This is dangerous if purulent inflammation has begun in the ear. Compresses can only help at stages 1-2 of the disease.
- You should not put melted oil in your ear: if there is a perforation, the oil will end up in the tympanic cavity.
- You should not put camphor oil or camphor alcohol into your ear - it can burn the walls of the ear canal and irritate the eardrum, which will increase ear pain.
At MedicCity you will be denied professional help for otitis media and other ENT diseases. Our otolaryngologists will conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient and prescribe a treatment regimen, depending on the cause and stage of the disease. However, the success of treatment depends no less on the patient himself: the sooner he consults a doctor, the more effective the result will be and the lower the likelihood of complications. It is also important to follow preventive measures. So, in the cold season, to prevent otitis media, it is important to wear a hat, protect your ears from drafts, and of course, boost your immunity!
Otitis, or when the ear hurts
Otitis is a disease of one or more parts of the ear - external, middle, internal - of an infectious, allergic, mechanical or other nature, occurring acutely or chronically. People of both sexes and all ages are affected, but due to the anatomical features of the ear, children are more likely to experience otitis than others. Diagnosis and treatment are within the competence of an ENT doctor.
The main thing: otitis media is a serious disease; if not treated correctly, it leads to the development of dangerous complications. Self-medication is unacceptable
Make an appointment with an ENT specialist
Treatment of chronic otitis in adults.
Chronic inflammation of the ear canal is diagnosed if the disease does not stop for more than a month. The chronic development of inflammation is divided into three types:
- Purulent chronic otitis (divided into mesotympanitis and epitympanitis). With mesotympanitis, chronic inflammation affects only the tympanic cavity; with epitympanitis, the bone is also involved.
- Chronic exudative otitis - this chronic form of the disease is characterized by the concentration of secreted exudate in the tympanic cavity for a long time, since the eardrum is not perforated.
- Chronic adhesive otitis - this chronic form is characterized by soldering together of the auditory ossicles and eardrum - this greatly reduces hearing.
Therapy for chronic purulent otitis includes a complex of therapeutic measures with medications.
If the patient has a ruptured eardrum, it is necessary to avoid contact of the ear with water by covering it with a cotton pad.
A chronic disease in the acute stage is treated with conservative methods, which include rinsing the ear with an otolaryngologist, using antibacterial drops (attempts to prescribe medications for yourself or adjust the therapy prescribed by a doctor are unacceptable! The cost of incorrect manipulations in this case is your hearing!).
If it is not possible to cure chronic otitis media with medications, adult patients will be offered surgery, the essence of which is to restore the integrity of the eardrum and prevent further inflammation and infection, thereby stopping chronic inflammatory processes in adults.
Exudative otitis media in chronic form is treated with shunting: a Teflon tube, hollow inside, is inserted into the tympanic cavity through an incision in the eardrum, through which liquid is removed and a medicinal solution is placed.
It is also possible to cure chronic inflammation in adults with adhesive inflammation through surgery.
It is very important, when starting to treat a disease, to eliminate foci of chronic inflammation in the nasal cavity and nasopharynx.
Treatment in our clinic.
Dear friends! Please do not forget that if you do not seek help in a timely manner, you will advance the disease and may cause the inflammatory process to become chronic. If the problem of chronic or acute otitis is not addressed in time, serious complications may occur (for example, brain abscess, meningitis or encephalitis).
Our profile is the treatment of ENT diseases, and otitis media is one of them. Our clinic is known for its proprietary treatment methods. We work with the most modern equipment, and our doctors are graduates of the best medical universities in the country with extensive experience.
Please come to us! We will help you effectively cope with your problem and will definitely tell you what measures should be taken to prevent otitis media in order to avoid unpleasant symptoms in the future.
We will always be happy to help you! You are welcome!