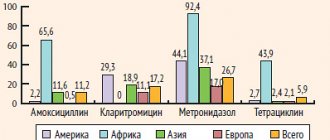
Polyoxidonium, 10 pcs., 12 mg, tablets
Pills.
Orally
and
sublingually
, 20–30 minutes before meals, daily 1, 2 or 3 times a day.
Adults - in doses of 12 or 24 mg, adolescents - in doses of 12 mg. The method and dosage regimen is determined by the doctor, depending on the diagnosis, severity and severity of the process.
Sublingual:
- for inflammatory processes of the oropharynx (bacterial, viral and fungal in nature):
1 table each 2 times a day every 12 hours, for 10–14 days. For severe forms of herpetic and fungal infections of the oral cavity - 1 table. 3 times a day every 8 hours for 15 days;
- for chronic diseases of the paranasal sinuses and chronic otitis media:
1 table each 2 times a day every 12 hours, for 5–10 days;
- for chronic tonsillitis:
1 table each 3 times a day every 8 hours for 10–15 days;
- for chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract:
adults - 2 tablets. (24 mg) 2 times a day, adolescents - 1 tablet. (12 mg) 2 times a day, every 12 hours, for 10–14 days;
- for the prevention of influenza and acute respiratory infections:
immunocompromised persons who suffer from acute respiratory infections more than 4 times a year; in the pre-epidemic period, adults - 2 tables. (24 mg), adolescents - 1 tablet. (12 mg) 2 times a day every 12 hours, for 10–15 days.
Orally:
— for chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract:
adults - 2 tablets. (24 mg) 2 times a day after 12 hours, for adolescents - 1 tablet. (12 mg) 2 times a day, every 12 hours, for 10–14 days.
Lyophilisate for the preparation of solution for injection and topical use
Adults
Parenteral, intranasal
. Methods of application are selected by the doctor depending on the severity of the disease and the age of the patient.
IM or IV (drip):
the drug is prescribed to adults in doses of 6–12 mg 1 time per day, daily, every other day or 1–2 times a week, depending on the diagnosis and severity of the disease.
For intramuscular administration, the contents of the ampoule or bottle are dissolved in 1.5–2 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution or water for injection. For intravenous (drip) administration, the drug is dissolved in 2 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution, Hemodez-N, Reopoliglucin or 5% dextrose solution, then sterilely transferred into a bottle with the indicated solutions of 200–400 ml.
The prepared solution for parenteral administration cannot be stored.
Intranasally:
a dose of 6 mg is dissolved in 1 ml (20 drops) of distilled water, 0.9% sodium chloride solution or boiled water at room temperature.
Recommended treatment regimens for adults
Parenterally:
- for acute inflammatory diseases:
6 mg daily for 3 days, then every other day with a general course of 5–10 injections;
- for chronic inflammatory diseases:
6 mg every other day for 5 injections, then 2 times a week for a course of at least 10 injections;
- for tuberculosis:
6–12 mg 2 times a week for a course of 10–20 injections;
- in patients with acute and chronic urogenital diseases:
6 mg every other day for a course of 10 injections in combination with chemotherapy;
- for chronic recurrent herpes:
6 mg every other day for a course of 10 injections in combination with antiviral drugs, interferons and/or inducers of interferon synthesis;
- for the treatment of complicated forms of allergic diseases:
6 mg, course of 5 injections - the first 2 injections daily, then every other day. For acute allergic and toxic-allergic conditions, administer 6–12 mg intravenously in combination with other antiallergic drugs;
- for rheumatoid arthritis:
6 mg every other day - 5 injections, then 2 times a week for a course of at least 10 injections.
In cancer patients:
- before and during chemotherapy to reduce the immunosuppressive, hepato- and nephrotoxic effects of chemotherapy drugs - 6-12 mg every other day for a course of at least 10 injections, then the frequency of administration is determined by the doctor depending on the tolerability and duration of chemotherapy and radiation therapy;
— for the prevention of the immunosuppressive effect of the tumor, for the correction of immunodeficiency after chemotherapy and radiation therapy, after surgical removal of the tumor, long-term use of the drug Polyoxidonium® is indicated (from 2-3 months to 1 year) - 6-12 mg 1-2 times a week.
In patients with acute renal failure:
prescribed no more than 2 times a week.
Intranasally
6 mg/day is prescribed for the treatment of acute and chronic infections of the ENT organs, to enhance the regenerative processes of the mucous membranes, to prevent complications and relapses of diseases, to prevent influenza and acute respiratory infections. 3 drops in each nasal passage every 2–3 hours (3 times a day) for 5–10 days.
Children
Parenteral, intranasal, sublingual
. Methods of application are selected by the doctor depending on the diagnosis, severity of the disease, age and body weight of the patient.
Parenterally
the drug is prescribed to children from 6 months at a dose of 3 mg (im or intravenous drip 0.1–0.15 mg/kg) daily, every other day or 2 times a week in a course of 5–10 injections (dose calculation is indicated in the table ).
For intramuscular administration, the drug is dissolved in 1 ml of water for injection or 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
For intravenous drip administration, the drug is dissolved in 1.5–2 ml of a sterile 0.9% solution of sodium chloride, Reopoliglucin, Hemodez-N or 5% dextrose solution, sterilely transferred to a bottle with the indicated solutions with a volume of 150–250 ml.
Intranasal and sublingual:
daily at a daily dose of 0.15 mg/kg for 5–10 days. The drug is administered 1–3 drops into one nasal passage or under the tongue after 2–3 hours. To prepare a solution for intranasal and sublingual use, a dose of 3 mg is dissolved in 1 ml (20 drops), a dose of 6 mg is dissolved in 2 ml of distilled water, 0.9% sodium chloride solution or boiled water at room temperature. One drop of the prepared solution (50 μl) contains 0.15 mg of the drug Polyoxidonium®, which is prescribed per 1 kg of child’s body weight.
Store the solution for sublingual and intranasal use in the refrigerator for no more than 7 days. Before use, the pipette containing the solution must be warmed to room temperature (20–25 °C).
Recommended treatment regimens for children:
- for acute inflammatory diseases:
0.1 mg/kg every other day for a course of 5–7 injections;
- for chronic inflammatory diseases:
0.15 mg/kg 2 times a week for a course of up to 10 injections;
- for acute allergic and toxic-allergic conditions:
IV drip at a dose of 0.15 mg/kg in combination with antiallergic drugs;
— for the treatment of complicated forms of allergic diseases in combination with basic therapy:
IM 0.1 mg/kg in a course of 5 injections with an interval of 1–2 days.
Intranasally
administer 1–3 drops into one nasal passage every 2–3 hours (2–4 times a day). For intranasal and sublingual administration, the calculation of the daily dose for children is presented in the table.
| Child's body weight, kg | Number of drops per day | Volume of injected solution, ml |
| 5 | 5 | 0,25 |
| 10 | 10 | 0,5 |
| 15 | 15 | 0,75 |
| 20 | 20 | 1,0 |
Sublingual:
for all indications - daily at a daily dose of 0.15 mg/kg for 10 days, for the treatment of intestinal dysbiosis for 10-20 days. Place 1-3 drops under the tongue every 2-3 hours.
Suppositories
Rectally
or
vaginally
1 supp.
(6 and 12 mg) 1 time per day. The method and dosage regimen is determined by the doctor depending on the diagnosis, severity and severity of the process. Polyoxidonium® can be used rectally
or
vaginally
daily, every other day or 2 times a week.
Polyoxidonium®, suppositories 12 mg
used in adults rectally or vaginally.
Rectally:
1 time per day, 1 sup. (after bowel cleansing).
Vaginally:
for gynecological diseases, 1 supp. Once a day (at night) it is inserted into the vagina in a lying position.
Polyoxidonium®, suppositories 6 mg
used: in children over 6 years old rectally - 1 supp. 1 time per day (after cleansing the intestines), in adults - rectally (after cleansing the intestines) or vaginally (in the vagina in a lying position) as a maintenance dose - 1 supp. 1 time per day (at night).
Standard scheme
use of Polyoxidonium® - 1 supp. (6 or 12 mg) 1 time per day, daily for 3 days, then every other day with a course of 10–20 supp. If necessary, the course of treatment is repeated after 3–4 months.
For patients receiving long-term immunosuppressive therapy, cancer patients with an acquired defect of the immune system - HIV, who have been exposed to radiation, long-term maintenance therapy with Polyoxidonium® is indicated for 2-3 months to 1 year (adults - 12 mg, children over 6 years - 6 mg 1–2 times a week).
Recommended regimens for use as part of complex therapy:
— for chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases:
in the acute stage - according to the standard regimen, in the remission stage - 1 supp. after 1–2 days, the general course is 10–15 supp.;
— in acute infectious processes and to activate regenerative processes (fractures, burns, trophic ulcers):
1 sup. daily, course of treatment - 10–15 sup.;
- for tuberculosis
: according to the standard regimen, the course of treatment is at least 15 supp., then it is possible to use maintenance therapy - 2 supp. per week for a course of 2–3 months;
— against the background of chemotherapy and radiation therapy of tumors
: 1 sup. daily 2-3 days before the start of therapy, then the frequency of suppository administration is determined by the doctor depending on tolerability and duration of chemotherapy and radiation therapy;
— for rehabilitation of frequent (more than 4–5 times a year) and long-term ill persons and for rheumatoid arthritis
: 1 sup. every other day, course of treatment - 10–15 supp.
— for the correction of secondary immunodeficiencies, incl. arising due to aging
: 1 sup. (12 mg) 2 times a week, course - at least 10 supp. 2–3 times a year.
As monotherapy:
- for seasonal prevention of exacerbations of chronic foci of infection, prevention of recurrent herpes infection
: every other day for adults - 6–12 mg, for children - 6 mg. Course - 10 supp.
— for the correction of secondary immunodeficiencies, prevention of influenza and acute respiratory infections
: according to the standard scheme.
— for gynecological diseases
(rectal or vaginal)
: according to the standard regimen.
Pharmacological action, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Polyoxidonium has detoxification and immunocorrective effects. It increases the body's immune defense and helps it more effectively fight diseases of viral, fungal and bacterial etiology.
The mechanism of action of the drug is based on the ability of the main substance to influence natural killer cells and phagocytes, as well as stimulate antibody formation.
Taking Polyoxidonium together with other medications makes treatment more effective, reduces its duration, and sometimes allows you to completely stop using antibacterial, bronchodilator and hormonal drugs.
The main active ingredient has a high bioavailability of up to 90%. Azoximer bromide quickly enters and distributes into tissues. Excreted from the body through the kidneys.
Indications and contraindications
Depending on the dosage form, Polyoxidonium can be prescribed for various pathological conditions. Doctors recommend taking the tablets for:
- Diseases of an inflammatory and infectious nature localized in the mouth, sinuses, ear, and upper respiratory tract.
- Secondary immunodeficiencies as a prophylactic agent during periods of increased incidence of viral and bacterial infections.
Indications for use of lyophilized powder:
- Intravenous or intramuscular administration for diseases of inflammatory or infectious nature.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (if the patient was treated with drugs that suppress the immune system).
- Tuberculosis.
- Allergic diseases complicated by severe, recurrent infection.
- After radiation or chemotherapy for oncological conditions.
- Reducing nephro- and hepatotoxicity of drugs.
- Prevention of influenza and acute respiratory viral infections during epidemics.
- Complicated bronchial asthma.
- Atopic dermatitis accompanied by purulent infection.
- Gastrointestinal diseases with dysbacteriosis.
Indications for the use of rectal and vaginal suppositories are the same as for lyophilisate. In addition, they are used to treat a wide range of gynecological pathologies (erosion, colpitis, endometritis, etc.).
There is only one contraindication to the use of Polyoxidonium. It should not be taken only by persons with high hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. It is also rarely prescribed to pregnant women due to the lack of data on the effect of the drug on the fetus.