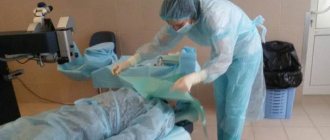
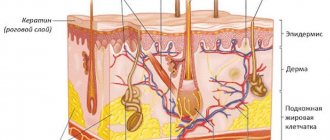
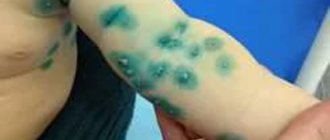
At the age of 30-40, small red moles begin to appear on the body. However, they are not moles in the true sense as they are made up of many small blood vessels. These formations are called angiomas.
Rice. 1. Angioma on the body
The exact cause of the appearance of angiomas on the body is unknown, however, bad heredity plays a large role. That. if your fathers and mothers had similar formations on their bodies, then the likelihood of them appearing on you is very high.
Rice. 2. Multiple angiomas - vascular tumors
Angiomas on the body usually do not develop into malignant tumors. However, if they appear, it is worth consulting with a dermatologist and dermatosurgeon to rule out the presence of melanoma or another type of skin cancer. This is because melanoma and Merkel carcinoma (neuroendocrine skin cancer) can appear as small red papules that can be easily confused with angiomas.
Rice. 3. Red mole - angioma
During the consultation, a specialist doctor will help you determine the diagnosis and advise whether it is worth removing your existing skin lesions.
Classification of vascular tumors
Angiomas are classified according to different criteria. Vascular neoplasms differ in structure, localization, prevalence and morphological structure. A detailed classification of angiomas is presented in the table.
| Classification sign | Type of angioma |
| Morphological structure | hemangiomas - develop from blood vessels |
| lymphagiomas - formed from lymphatic vessels | |
| Cellular structure | monomorphic - consist of cells of the same type |
| polymorphic - combines several different cell types | |
| Type of angiomas | simple (capillary) - occurs due to the proliferation of small vessels - capillaries |
| cavernous - consists of wide spongy cavities filled with blood, has a tuberous surface | |
| branched - represents a branched network of dilated capillaries | |
| combined - combine simple and cavernous types | |
| Localization | brain - vascular angiomas located in the substance of the brain |
| skin - red or blue-purple moles on the body | |
| liver - single or multiple vascular neoplasms, can be located in different parts of the organ | |
| spine - affects one or more vertebrae, predominantly in the thoracic and cervical regions | |
| kidneys - formed from the veins and arteries that supply the organ; the size of the tumor varies widely | |
| and other organs - since angiomas are formed from lymph and blood vessels, they can affect any organ |
Angiomas: causes of appearance
Until now, scientists cannot name the exact reasons for the appearance of vascular formations. Doctors agree that vascular pathology begins during embryonic development. Infectious diseases suffered by the mother can affect this. Toxicosis, anemia of a woman during pregnancy, and serious hormonal fluctuations also contribute to the appearance of abnormalities. Acquired angiomas occur due to sunburn, liver disease, skin injuries, and increased fragility of blood vessels.
Brain angioma
An angioma of the brain is a proliferation of arteries or veins of an organ, turning into a tangled ball of indeterminate shape. The tumor is benign, but if it develops rapidly, it poses a danger to human health and requires immediate treatment.
Causes of vascular brain tumors
The exact reasons for the development of the disease are still not clear, but experts identify a number of factors that provoke the development of cerebral angioma:
- genetic predisposition;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- central nervous system infections;
- cerebral edema;
- multiple sclerosis.
The vast majority (about 95%) of cerebral angiomas are congenital, and only a small proportion of tumors appear during life.
Symptoms of brain angioma
Vascular brain tumors develop extremely slowly, so there are usually no symptoms for several years. The disease makes itself felt only when the tumor reaches a significant size and begins to compress the surrounding tissue. Symptoms largely depend on the location of the tumor.
Most often, patients complain about:
- severe bursting headache;
- dizziness;
- vomiting;
- convulsions;
- decreased visual acuity;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- deterioration of memory and attention.
A characteristic set of symptoms helps doctors determine the location of the tumor. Symptoms of cerebral angioma are nonspecific, so an examination is required to make a correct diagnosis.
Diagnosis of vascular tumor
A diagnosis of cerebral angioma can only be made based on data from hardware studies. Laboratory diagnostics in this case is ineffective. If angioma is suspected, patients are prescribed:
- MRI of the brain with contrast – allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer image of the organ; the contract substance illuminates the area under study, which improves the quality of the images and improves visualization;
- angiography - the essence of the method is the intravenous administration of a contrast agent followed by radiography;
- Computed tomography of the brain, just like MRI, is a layer-by-layer scan of an organ, but differs in that the method is based on X-ray radiation.
It is thanks to the advent of modern diagnostic methods that doctors are able to make an accurate diagnosis even with a small tumor size.
Treatment of cerebral angioma
For small tumors and slow growth, therapeutic methods of treatment are used. However, conservative therapy is aimed only at eliminating symptoms. Patients are prescribed painkillers and sedatives, and drugs to normalize cerebral circulation.
The only effective treatment is surgery. Removal of brain angioma is carried out in different ways. The choice of surgery is determined by the location of the tumor and its size. For superficial neoplasms, excision of the choroid plexus is performed. If the tumor is localized in the deep structures of the brain, other methods are used. For example, blockage of afferent vessels of a tumor or angioplasty. Minimally invasive surgeries are highly effective and safe; their only drawback is their relatively high price.
Prevention of cerebral angioma
There is no specific prophylaxis to prevent cerebral angioma, but you can reduce the risk of developing vascular pathologies by following simple recommendations:
- give up bad habits: smoking and drinking alcohol;
- regularly monitor blood pressure;
- lead an active healthy lifestyle;
- to harden;
- Follow your doctor's instructions for infectious diseases.
If you have frequent headaches, it is important not to self-medicate by taking analgesics, but to consult a doctor and undergo an examination to exclude vascular pathologies.
According to many researchers, angiomas appear during fetal development. Therefore, pregnant women need to take care of their health, take vitamin and mineral complexes and follow the doctor’s recommendations. This will be the best prevention of angioma in your unborn child.
Features of treatment
The method of getting rid of a tumor largely depends on its size and shape.
Small tumors (up to 5-6 cm in volume) do not require special action. They are monitored and ultrasonic controlled after 3 months from the moment of detection. In the absence of any dynamics, ultrasound diagnostics are prescribed every 6-12 months.
The need for surgical removal is determined individually. This course of events leads to:
- rapid growth of liver hemangioma - more than 50% of the original size per year;
- volume more than 5-6 cm;
- bleeding of atypical tissue;
- aggressive manifestation of symptoms;
- inaccurate determination of the benignity of the tumor.
Skin angioma
Almost every person has a certain number of new growths on their skin - moles. They differ in color, shape and size. Red moles are angiomas. Most often they are congenital, but can also appear during life.
Causes of red moles
There are several reasons why skin angioma develops. Red moles in newborns appear as a result of maternal illnesses during pregnancy: ARVI, influenza, pyelonephritis.
The provoking factors of acquired skin angioma are:
- hormonal disorders;
- prolonged exposure to UV rays;
- skin injuries.
In old age, skin angioma develops due to the expansion and proliferation of blood vessels. People with fair skin and hair are most susceptible to the disease.
Symptoms of skin angioma
Skin angioma appears as reddish or purplish-blue spots; they can be located separately from each other or form clusters of several moles. New growths have clearly defined edges, usually rise above the surface of the skin, and are painless. When you press on the angioma, it turns pale as it is filled with blood. When the pressure is removed, it returns to its normal color. Small angiomas do not cause any discomfort, but require constant monitoring as they can develop into malignant tumors. This is especially true for polymorphic angiomas.
Diagnosis of skin angioma
A visual examination allows a diagnosis of skin angioma to be made. Characteristic features of the neoplasm are a typical color and disappearance when pressed. If a skin angioma is detected, it is recommended to undergo a full diagnosis of the body to exclude vascular neoplasms in other organs: magnetic resonance and computed tomography, radiography and angiography.
Treatment of vascular skin tumors
The need and tactics of treatment are selected depending on the location of vascular moles, their size and the dynamics of the disease. Single small angiomas that do not cause discomfort and are not prone to proliferation do not require treatment.
Doctor intervention is required in the following situations:
- the mole is located on the neck, head or in places where there is a high risk of damage;
- the neoplasm increases in size and is often injured;
- there is a risk of the tumor developing into a malignant one.
Treatment is selected depending on the location of the tumor. Surgery is performed when the angioma affects the deep layers of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Superficial tumors are removed using a laser. Sometimes infrared coagulation, cauterization with carbon dioxide and cryodestruction (exposure to low temperatures) are used to remove angioma. These methods are only suitable for small flat tumors located on the surface of the skin.
Prevention of skin angioma
It is impossible to prevent the appearance of congenital angiomas. To detect angioma at an early stage, conduct periodic examinations of the entire body. If you discover new moles, be sure to consult a dermatologist.
In recent years, there has been an increase in skin diseases, including angiomas. In pursuit of a beautiful tan, girls often forget about basic safety rules. Prolonged exposure to the sun and frequent visits to the solarium are dangerous to your health!
What if you have an angioma?
If you have an angioma, it should still be removed. Removal can be done with a coagulator or radio knife, but in most cases they leave a noticeable scar on the skin. This is explained by the fact that angioma consists of vessels, and the coagulator and radio knife cannot separate the vessels from other tissues and cauterize everything. It is better to remove angiomas on the body using a laser, since a laser beam of a certain wavelength is capable of destroying only tumor vessels without affecting neighboring tissues.
Liver angioma
Liver angioma is a neoplasm, the causes of which are still unknown. The tumor can appear at any age; the most frequently reported cases of visiting a doctor are people aged 30 to 50 years. Women are more susceptible to the disease; angioma occurs in them five times more often than in men. Vascular tumors of the liver are always benign; to date, there have been no cases of tumors developing into cancer.
Causes of liver angioma
As noted above, at the moment the causes of liver angioma are unknown to medical science. A number of researchers identify the use of hormonal drugs, hereditary predisposition and congenital developmental anomalies among provoking factors.
Symptoms of vascular liver tumor
There are no specific signs of the disease. As a rule, liver angioma does not manifest itself in any way and is discovered by chance during a medical examination during routine examinations. With large tumors, patients may complain of minor pain in the right hypochondrium and a feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. However, similar symptoms appear in a number of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In any case, if you periodically or constantly experience discomfort in the abdominal area, you should consult a doctor to find out the cause.
Diagnosis of liver angioma
It is not possible to detect liver angioma during examination. Laboratory parameters of blood, urine and feces also, as a rule, remain within normal limits.
The following studies are used to diagnose the disease:
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT);
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- hepatic angiography.
The listed diagnostic methods allow us to obtain reliable data on the size and location of the tumor.
Treatment of vascular liver tumor
In most cases, liver angioma is small and does not cause any discomfort. A vascular tumor does not develop into cancer and rarely increases in size. Upon initial detection, it is recommended to undergo a re-examination after a year. If the size of the tumor does not change during this time, then further observation and treatment is not required.
For a long time, there were no therapeutic methods for treating vascular liver tumors. But several years ago, researchers found that some antitumor drugs effectively act on liver angioma, and their use can reduce the size of the tumor.
Surgical treatment for liver angioma is indicated only in the most extreme cases, when the tumor is large and causes significant discomfort to the person. Doctors pay close attention to cavernous angiomas, since there is, albeit a small, risk of tumor rupture, which can lead to internal bleeding. But here, too, the issue of surgical intervention is always decided individually, since the risk of tumor rupture does not exceed 3%, and the percentage of complications after surgery is twice as high.
Prevention of liver angioma
It is impossible to insure against liver angioma, since the exact reasons for its development are not clear. However, with a high degree of probability, hormonal drugs influence tumor growth. Therefore, you should not abuse medications containing hormones unless necessary. This is especially true for athletes - bodybuilders and powerlifters, who often take steroid-based drugs to improve physical performance. Taking hormones in sports should be justified and approved by doctors after undergoing an examination.
Liver angioma does not require a strict diet, but it is recommended to reduce the following foods in the diet: fatty meat, smoked meats, pickles, spicy seasonings, fast food, alcoholic beverages.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of liver hemangioma do not appear immediately. Due to the small size of the formation, even in laboratory conditions it is not always possible to notice the presence of new cells. The same applies to clinical manifestations.
When the tumor grows to a size of 10 cm, features uncharacteristic of a healthy state can be detected:
- increase in liver volume;
- nausea, slight vomiting;
- unpleasant, painful sensations under the ribs on the right side.
All these symptoms arise as a result of the fact that the neoplasm puts pressure on neighboring organs and compresses nearby vessels.
In some cases, liver hemangioma may manifest itself after trauma to the abdomen (such as a strong blow) or intense physical exertion of the body. When it ruptures due to strain, it causes internal bleeding and acute pain in the abdominal area.
Are you experiencing symptoms of liver hemangioma?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Spinal angioma
Spinal angioma most often forms in the thoracic, less often cervical and lumbar, parts of the spine. Many people have vascular tumors, especially after the age of forty. Spinal angiomas are not dangerous; single small tumors do not require any treatment.
Causes of spinal angioma
The reasons for the proliferation of blood vessels are still unknown to science. In most cases, spinal angiomas are discovered in adulthood during preventive examinations. But despite this, some researchers believe that they are congenital or appeared at an early age. Before the advent of computed tomography, large spinal angiomas were detected on X-rays, but even then very rarely. Most of the small tumors went unnoticed. People lived with them all their lives and did not even suspect their existence.
Symptoms of vascular tumors of the spine
Most often, spinal angiomas do not manifest themselves throughout life.
In rare cases, when the tumor is large enough, the following symptoms may appear:
- pain in the spine (localization depends on the location of the tumor);
- numbness of the limbs;
- decreased sensitivity below the tumor site;
- dysfunction of the organ innervated by the damaged nerve.
Symptoms of spinal angioma are nonspecific and may indicate other neoplasms, therefore, if the listed signs appear, it is necessary to undergo an examination to clarify the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of spinal angioma
Examination and laboratory tests do not allow diagnosing vascular neoplasms of internal organs.
The following hardware methods are used to diagnose spinal angioma:
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT);
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- X-ray (little informative, requires additional research).
The most effective diagnostic methods are MRI and CT. They allow you to determine the location and size of the tumor and decide on the need for treatment.
Treatment of spinal angioma
The need for medical intervention is determined depending on the size of the tumor, neurological symptoms and dynamics of the disease. If the angioma does not cause discomfort and retains its original size, then no treatment is required. It is enough just to undergo a diagnostic examination at least once a year.
Large tumors that threaten to rupture or fracture the vertebrae are removed using embolization - the vessels feeding the angioma are clogged. Radiation therapy is often used to treat vascular tumors. Powerful radiation destroys tumor cells. In case of compression of the spinal cord with impaired motor functions, surgical removal of the angioma is used.
Prevention of vascular neoplasms of the spine
To date, no effective measures have been developed to prevent spinal angioma, since the mechanism of its formation has not been fully studied. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, and hardening will help maintain the health of your blood vessels and reduce the likelihood of developing not only angioma, but also other vascular diseases.
Diagnostics of education
In exceptionally extreme cases, only by chance, liver hemangioma in a child or adult can be detected at an early stage. In the vast majority of cases, it is found when the size reaches serious volumes.
The following diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder and liver (may show a round tumor with clear boundaries);
- MRI of the biliary tract and liver (in addition to the outlines of the formation, it will also show its contents);
- MSCT of the abdominal cavity (layer-by-layer will demonstrate the boundaries and contents of the tumor).
When a tumor is detected, it is necessary to determine its qualitative characteristics. To confirm hemangioma, angiography of the celiac trunk is performed; static liver scintigraphy may also be needed. To determine the degree of benignity (malignancy) of atypical cells, hepatoscintigraphy is prescribed.
Along with this, clinical tests are carried out:
- liver tests;
- complete blood count, blood biochemistry;
- blood test for genetic markers.
Kidney angioma
Kidney angioma develops from the blood vessels that supply the organ, is benign, and has a low tendency to grow. However, renal angiomas require observation, since there is still a minimal risk of the tumor degenerating into a malignant one.
Causes of kidney angioma
As is the case with angiomas of other organs, the factors causing the appearance of vascular neoplasms of the kidneys are not fully understood.
Among the main causes of kidney angioma, researchers identify:
- genetic predisposition;
- congenital developmental anomalies;
- hormonal disorders;
- injuries;
- infections of the genitourinary system.
Many scientists are inclined to believe that most vascular tumors appear during fetal development or in early childhood.
Symptoms of vascular kidney tumors
When small in size, renal angiomas do not reveal themselves in any way. Symptoms of the disease occur only with large tumors.
Most often, patients with renal angioma complain of:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- urinary disorders;
- increased blood pressure;
- weakness and fatigue.
Similar symptoms are typical for other kidney diseases, so additional testing is required to make a diagnosis.
Diagnosis of kidney angioma
The following research methods allow diagnosing renal angioma:
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- computed tomography (CT);
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- angiography;
- intravenous urography.
All of these methods are informative and help to accurately determine the location and size of the angioma. Usually one or two tests are enough to make a diagnosis.
Treatment of kidney angioma
The choice of treatment method for renal angioma is determined depending on the prevalence of the tumor process and the growth rate of the tumor. Small isolated angiomas require only observation. In most cases, they do not grow or increase significantly in size and therefore do not require treatment. In rare cases, when an angioma grows rapidly and the patient’s condition worsens, medical intervention cannot be avoided.
Currently, modern methods are used to treat renal angioma: embolization and cryoblation. In the first case, doctors block the vessels feeding the tumor; in the second, they act on the tumor cells with low temperatures. Both methods are highly effective and can reduce or completely destroy the tumor. Surgery to remove a kidney angioma is performed as a last resort, only for very large tumors with the threat of rupture and internal bleeding.
Note! In the vast majority of cases, the prognosis for renal angioma is favorable. However, even after removal of the tumor, relapses are possible, so patients with this disease are recommended to undergo kidney examinations at least once a year.
DIAGNOSIS OF ANGIOMA
Examination under a magnifying glass or dermatoscope makes it easy to diagnose angioma; the pressing method differentiates it from other formations (when pressed, the vessels become empty and the angioma becomes discolored). For small, slow-growing angiomas in hidden areas of the body, ultrasound every six to twelve months is important to monitor the growth of the formation.
Why is it worth having angiomas removed by a specialist and why are they dangerous?
First of all, angioma spoils the appearance, especially if it is on a visible part of the body or on the face. It is difficult to remove angioma at home due to the risk of bleeding, infection and scar formation. It should also be taken into account that in adults, unlike children, angiomas do not go away on their own and are the result of problems with the liver or hormonal levels; it is necessary to look for the underlying cause of angiomas, especially multiple ones, which is what our specialists do.
Angiomas are dangerous because they can fester and thrombose; in places of friction they empty, thereby self-healing, but lead to bleeding. Large angiomas become “traps” for platelets, and the patient develops thrombocytopenia – a tendency to bleed, which is especially dangerous when operations, childbirth, etc. are necessary. Prolonged pressure of a large angioma on the underlying tissue leads to disruption of their anatomy and functioning.
Do not be afraid of malignancy of angioma, this is an extraordinary phenomenon with a negligibly low frequency!
Absolute indications for removal of angiomas
- Rapid tumor growth in area and tissue depth.
- Tendency to frequent bleeding and ulceration.
- Location in places subject to constant friction - in the neck, back of the head, genitals, on the back.
- Loss or decrease in the functions of the affected organs (localization of angiomas on the eyelids, nose, lips, ears).
- Inconvenience during physical activity, wearing shoes and clothes.
Prevention of vascular neoplasms of the kidneys
There is no specific prevention of angiomas.
Recommendations are general in nature only and include:
- rejection of bad habits;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- hardening;
- avoidance of traumatic situations;
- timely treatment of infectious diseases.
Many people, upon hearing the diagnosis of angioma, feel fear. In most cases, this occurs due to ignorance and lack of information about the disease. Angioma does not pose a health hazard, but requires observation. Modern medicine has effective methods for treating angiomas, so even with large tumors, there is no need to panic, but you just need to follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Angiomas in children
Angioma in children is usually diagnosed at birth or during the first weeks of life. Girls get sick twice as often as boys. Angioma in a child goes through several stages. In the first few months, the formation actively grows, the size of the spot increases. At the next stage, growth stops. By the age of 9, in 90% of cases, self-healing occurs - spontaneous involution of the pathology. The stain disappears, leaving no traces in its place.
Unfortunately, in some cases, benign formation is accompanied by the following complications:
- ulceration and bleeding of the skin as a result of trauma, for example, due to rubbing with a diaper when the formation is located on the leg or buttock;
- formation of scars at the site of healing ulcers after ulceration of the skin at the site of formation;
- dysfunction of internal organs due to the germination of the formation or compression of them by its boundaries;
- When the formation is located on the forehead, ophthalmological diseases develop.
Important: Very often, angioma in a child is located on the face, neck, or chest. This leads to a pronounced cosmetic defect.
It is recommended to observe uncomplicated disease in children. To do this, during the appointment, photographs of the formation are taken using a dermatoscope. At subsequent appointments, images can be compared to analyze the behavior of the formation.
Treatment of angioma
Treatment of angioma is aimed at stopping its growth, eliminating the pathological process and normalizing the functioning of the vascular network. Indications for urgent intervention are:
- extensive tissue damage;
- rapid growth of the tumor;
- localization in the neck, head;
- frequent bleeding;
- dysfunction of the organ in which the angioma is located.
Watchful waiting is justified only if regression of a vascular benign tumor is observed.
Among the most common treatments for angiomas:
- Diathermoelectrocoagulation. Cauterization with electric current is indicated if it is necessary to remove hard-to-reach punctate angiomas and angiofibromas. The method cannot be used if the angioma is deep and occupies a large area.
- Laser treatment. Using a laser, the doctor removes pathological tissue layer by layer. The advantage of laser treatment of angiomas is minimal bleeding.
- Radiation treatment. Allows you to achieve good results when removing angiomas of complex anatomical localization.
- Surgery. It is used if the vascular tumor is deep and it is not possible to remove it without affecting the surrounding healthy tissue.
- Cryotherapy. Makes it possible to remove simple small angiomas of any location. During the procedure, liquid nitrogen is applied to the tumor. The method is painless and does not cause bleeding.
- Sclerosing therapy. Seventy percent alcohol is injected into the tumor. The treatment is painful and is suitable if the angioma is located in the deep layers of the skin.
- Hormonal therapy. Relevant if the lesion is extensive, angiomas grow quickly.
- Excision of angiomatous areas followed by reconstruction of the vessel.
- Ligation of the arteries supplying the angioma. A ligature is applied to the end of the artery, as a result of which the neoplasm gradually dies.
It is possible to treat angioma with folk remedies:
- Apply the kombucha to the tumor site and fix it. After a day, replace the compress. The duration of such treatment is 2-3 weeks.
- Dilute a tablespoon of copper sulfate with 100 ml of clean water. Wipe the neoplasm with the resulting liquid 4-5 times a day for 10 days.
- Apply a compress of onion pulp to the affected area of skin for 10 days. Change the bandage every 12 hours.
- Cover the angioma with fresh grated carrots and tie gauze on top. Change 3 times a day.
- Mix fresh celandine juice in a ratio of 1:4 with petroleum jelly and add a drop of 0.25% carbolic acid. Use the ointment daily in the morning and evening.
- If the angioma has affected the internal organs, you can use the following recipe: pour 3 tablespoons of potato flowers into 300 ml of boiling water. Leave in a thermos. Drink half a glass 3 times a day half an hour before meals. The treatment course is 2 weeks.
It should be remembered that any folk recipe can be used only after consultation with your doctor. Some medicinal plants can provoke the growth of angiomas, so preparing decoctions and infusions from them yourself is not recommended.
Danger
A small spot formed on the skin can go unnoticed or be ignored by the patient for a long time. Since it can transform into a malignant formation, the lack of necessary treatment can lead to dire consequences.
Particular attention should be paid to angiomas located in places of increased friction with clothing (neck, chest, abdomen, shoulders), on the scalp. Frequent traumatization can lead to inflammation of a benign tumor and its rapid growth and bleeding.
The greatest danger to life is posed by angiomas of the brain and internal organs. As practice shows, if you do not treat a cerebral angioma, the prognosis is unfavorable - the area of accumulation of blood vessels will increase, which will lead to their rupture, hemorrhage in the brain and death.
Diagnostics
Angiomas located on the surface of the skin are diagnosed during examination and palpation. The characteristic coloring, ability to contract and increase in size when pressed and strained allow the doctor to easily make the correct diagnosis.
If the localization of the lesion is more complex (internal organs, bones, brain), a number of diagnostic measures are required:
Skeletal hemangiomas are identified using x-rays of the spine, ribs, bones, skull and pelvis.
To identify angiomas of internal organs, antiography (contrast x-ray examination of blood vessels) of the kidneys, brain, lungs, etc. is performed.
Pharyngeal angiomas are examined by an otolaryngologist.
Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to determine the exact depth of growth of the angioma, its structure and location features. If a vascular angioma is suspected, the doctor may additionally prescribe a puncture. The resulting yellowish liquid is examined in the laboratory. This makes it possible to differentiate angioma from lymphadenitis, lipoma, cyst, hernia.
Symptoms of angioma
Symptoms of angioma depend on the type of vascular tumor, its size and location. In newborns, it is diagnosed immediately or several months after birth, and can grow very quickly, covering large areas of the skin.
Vascular angiomas can affect:
- Integumentary tissues - skin, mucous membranes of the genitals, subcutaneous tissue. Angiomas are also found in the mouth.
- Musculoskeletal system - muscles, bones. A severe form of the disease includes hemangioma of the vertebral body.
- Internal organs.
If integumentary hemangiomas cause cosmetic defects, then hemangiomas of internal organs provoke the occurrence of disturbances of important functions - urination, breathing, vision, defecation.
Angiomas of muscles and bones are accompanied by:
- skeletal deformation;
- severe pain in the joints;
- frequent fractures;
- radicular syndrome (compression of the spinal nerves).
Venous angiomas of the brain (cerebellum, left/right frontal lobe, etc.) are very dangerous. They lead to subarachnoid hemorrhage and epilepsy. Also, due to compression of the brain vessels by the tumor, the following symptoms may occur:
- convulsions;
- headache;
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness;
- noise in the head;
- taste disturbances;
- speech problems.
During the growth process, angiomas can become inflamed, causing phlebitis and thrombosis. A common complication is bleeding due to trauma.
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.