Synonyms: neutrophil granulocytes, NEUT, neutrophil segmented granulocytes, polymorphonuclear neutrophils
There are six types of neutrophils depending on the stage of their maturation. Immature types include myeloblasts, promyelocytes, myelocytes, metamyelocytes and band cells. The final stage of development is segmented neutrophils (mature cells with a formed nucleus, divided into several segments).
Even at the stages of their initial development, neutrophils are able to resist infection, although mature segmented cells cope with this task much more effectively.
In blood tests of people suffering from severe infectious diseases, immature forms of neutrophils can be detected. This is explained by the fact that in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms, segmented cells die too quickly, and therefore the body is forced to use cells that are not fully mature. But in the blood of a healthy person, predominantly mature neutrophils are found, since they cope well with their task with virtually no help from their young brothers.
Figure 1. Phagocytosis. Image: mikrostoker/Depositphotos
Why is a leukocyte blood formula needed?
The leukocyte formula is the percentage of leukocytes in the blood serum (eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes, basophils, monocytes).
This analysis allows you to determine the current state of the immune system, identify inflammatory processes in the patient’s body and determine the etiology of allergies. It is known that leukocytes protect the human body from dangerous microorganisms. One of the main tasks of leukocytes is the destruction of foreign particles. If an inflammatory process occurs in the patient’s body, it is immediately reflected in the leukocyte count.
Complete blood count (CBC/Diff - 5 fractions of leukocytes) - capillary blood in Moscow from day 1
from 290 ₽
Sign up
Clinical blood test (CBC/Diff - 5 leukocyte fractions) + ESR in Moscow from day 1
from 294 ₽
Sign up
Complete blood count (CBC/Diff - 5 fractions of leukocytes) in Moscow from 1 weekday
from 290 ₽
Sign up
When leukocyte counts change in the blood, it is necessary to determine in which direction the deviation occurs. This study will help you quickly find the problem and make a diagnosis. However, it should be taken into account that changes in blood parameters without in-depth diagnostics are not a characteristic and final sign for making a diagnosis.
Indications for analysis
A general blood test is the most common hematological test, so the range of indications for its use is wide. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell whose main task is to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, the main goal of the analysis for the content of neutrophils is to identify potentially dangerous conditions accompanied by infectious and inflammatory processes. In other words, a blood test for neutrophils can be informative both for colds and for kidney or liver diseases.
When is the test prescribed?
A clinical blood test with a leukocyte formula is indicated for patients with various pathologies. It allows you to assess a person’s health status with a comprehensive and timely diagnosis of diseases, including those occurring in a latent form.
Indications for a clinical blood test with a leukocyte formula are:
- medical examination or routine medical examination;
- preparation for surgical treatment;
- infection or suspected infection;
- suspicion of inflammation or parasitic infestation in the patient’s body;
- allergic reactions;
- prescribing certain medications;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
Before donating capillary blood, it is recommended not to drink alcohol during the day, not to eat for 2-3 hours, not to smoke for 30 minutes and to avoid stress and excessive physical activity.
How to increase the number of neutrophils in the blood
To correct neutropenia, it is necessary to identify its cause. If a decrease in neutrophil levels is caused by taking medications, you should first weigh the possible risks of a decrease in neutrophil levels with the importance of the therapeutic effect of the drugs used. In extreme cases, the drug can be replaced with an analogue that does not affect the level of neutrophils in the blood. The underlying diseases that cause neutropenia are treated with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs.
It is recommended to consume the following products:
- any meat dishes (it is important that they are all well thermally processed);
- hard boiled eggs;
- pasteurized milk;
- cheese (except for varieties with mold);
- potato;
- rice;
- pasta;
- fruits and vegetables;
- alcohol only in consultation with a doctor.
Careful heat treatment of meat and eggs is necessary in order to exclude the possibility of bacteria and microbes entering the body, which actively multiply in poorly fried or undercooked protein dishes.
What are leukocytes?
Leukocytes are cells that are found in very large quantities in the blood and in almost all tissues. Their main function is protective and immune. However, they would not be able to fully perform these functions if they were not divided into several varieties within their group, each of which plays its own special role.
There are five main types of leukocytes in the blood. They are determined in tests in the form of a leukocyte formula, so the level of leukocytes in the blood is assessed not only as a whole. The content of these cells is also always calculated. These include:
- neutrophils;
- lymphocytes;
- monocytes;
- eosinophils;
- basophils.
They have different functions, but they work together, influence each other, transmit information between themselves and more. High or low white blood cells belonging to a certain type in the blood indicate various diseases, so determining their number is very important in medical practice.
Normal for pregnant women
| Trimester | White blood cell count (*109) |
| first | 4–9 |
| second | 4–10 |
| third | 14–12 |
Normal for women
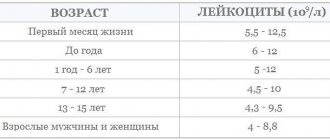
| Age | White blood cell count (*109) |
| up to 16 years old | 4,5–12,5 |
| up to 20 years | 4,2–10,5 |
| from 21 years old | 4–9,0 |
Normal for men
| Man's age | White blood cell count (*109) |
| 12–18 years old | 3,5–8 |
| 18–25 years old | 4–9 |
| 25–40 years | 4–8 |
| Over 40 years old | 3–9 |
Normal in children
| Age | White blood cell count (*109) |
| newborn | 10–30 |
| from the fifth day of life | 9–15 |
| from the tenth day of life to one month | 8,5–14 |
| from month to year | 8–12 |
| from one to five years | 7–11 |
| from 5 to 15 years | 6–10 |
| over 15 years old | 5–9 |
What indicators does the blood test contain?
Donating blood for testing is necessary during planned hospitalization, to assess the effectiveness of the therapy, and during pregnancy. To make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment, the doctor always prescribes a general blood test. Material for research is taken from a finger or from a vein. The second option is preferable, since venous blood more accurately shows the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells.
First of all, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets are analyzed, as well as:
- Hemoglobin level.
- Erythrocyte indices.
- Hematocrit level.
- Reticulocyte count.
Additionally, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), color and blood clotting period are determined.
An extended study involves indicating the leukocyte formula, including the count of eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, band and segmented neutrophils.
Leukocyte formula:
| Index | × 10x9/l | ratio, % | |
| Neutrophils | segmented | 2,1–5,4 | 43–71 |
| stab | 0,4–0,3 | 1–5 | |
| Basophils | up to 0.063 | up to 1 | |
| Eosinophils | 0,02–0,3 | 0,5–5 | |
| Lymphocytes | 1,1–3,1 | 17–38 | |
| Monocytes | 0,08–0,5 | 3–12 | |
Stages of violation
The disease or, more precisely, the pathological condition is accompanied by a decrease in the content of neutrophils. How pronounced a change occurs depends on the primary cause.
As for the stages or severity of the disorder, there are three of them.
Lightweight
Or the very first one. The concentration of granulocytes drops to the level of 1-1.5*109 /l. There are no symptoms yet. The patient does not even suspect that there are any health problems. Minor disorders and changes in well-being are possible.
Neutrophil norms by age in both sexes are described in detail here.
Moderate
The cell concentration drops to 0.5-1*109 /l. Much more noticeable in terms of symptoms. The patient suffers from frequent colds. It is necessary to strengthen the immune system and treat the primary pathological process.
Heavy
It is accompanied by either a complete absence of neutrophils or a significantly reduced number of formed cells. Urgent treatment in a hospital is required. Measures are being taken to strengthen the immune system.
Typically, the disorder develops as a result of immunodeficiency. Viral or otherwise. Possibly with severe radiation sickness.
Attention:
The condition poses a real threat to the health and life of the patient.
Stages are a laboratory indicator. It is examined as part of a general blood test. In case of disorders or disorders that were detected earlier, additional examinations are prescribed.
Neutrophils
Neutrophils come from red bone marrow, they are formed from a single stem cell, which is the ancestor of all blood cells. However, stem cells do not immediately turn into neutrophils. Between these two forms there are several stages, several intermediate forms.
There are 6 types of neutrophils:
- myeloblasts;
- promyelocytes;
- myelocytes;
- metamyelocytes;
- band neutrophils;
- segmented neutrophils.
Most of all is in the blood of the latter. They are present in an amount of 40–75% of the total number of leukocytes. The number of rod-shaped neutrophils is significantly smaller, they can be 1–6%. The number of young cells does not reach 1%.
Additional examinations
Supportive measures are prescribed only by doctors. Among the methods:
- Oral interview with the patient. It is necessary to identify all the symptoms of the pathological process.
- Study of anamnesis.
- General blood and urine analysis. Biochemical methods.
- Allergy tests. Within the framework of which immunological studies are carried out.
- Bone marrow puncture. Quite a risky technique. It is prescribed in extreme cases when there is no other option.
- Immunological tests.
- Chest X-ray.
- Smears from the throat, genitals. From suspected sources of infection.
If neutrophils are low in an adult, this indicates an obvious pathological process: inflammation, poisoning, allergies, disorders of the bone marrow, radiation sickness, or the development of side effects from taking medications.
Monocytes
Monocytes are cells of the immune system that are among the first to respond to the penetration of aggressors into the body. If the forces of local immunity could not contain the attack of bacteria, fungi or viruses, then it is monocytes that are the first to rush to protect health.
Monocytes are formed in the red bone marrow and released into the blood. There they begin to actively function, but this does not last long, only 2-3 days. Then, using their ability to move, they move beyond the vessels through special small pores between the cells and penetrate into the tissue. There, monocytes slightly change their structure and turn into macrophages - more effective phagocytes.
Consequences of deviation of neutrophils from the norm
A change in the level of neutrophils in the blood is a signal from the body about the presence of inflammatory diseases, injuries or poisoning. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the increase or decrease in neutrophils in order to begin treatment in time or eliminate the provoking factor. If this is not done on time, the consequences can be severe (even death). The greatest danger among possible causes is infectious diseases of a bacterial nature, as well as processes of local suppuration and necrotization (death) of tissue.
Eosinophils
Eosinophils are a small number of white blood cells that are found in human blood and tissues. They are an indispensable element that provides immunity.
Like other white blood cells, they are formed from bone marrow, and their progenitor is a single stem cell. The norm is 1–4%.
In total, eosinophils live about 12 days, but do not spend all of this time in the bloodstream. After 3-4 days of ripening, they enter the bloodstream and remain there for only 6-12 hours. Then they pass into the tissues and accumulate in especially large quantities in the lungs, under the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, and in the skin.
When the number of eosinophils increases, the condition is called eosinophilia, and the reverse change is called eosinopenia. As a rule, bright changes are symptoms of diseases, but some physiological fluctuations in their number are possible within normal limits. For example, an increase and decrease in eosinophils can be observed depending on the time of day; at night they are usually most in the blood.
Causes of low levels of neutrophils in the blood
A decrease in the level of neutrophils in the blood is called neutropenia. The cause of this phenomenon can be diseases of various natures, as well as taking various medications.
Reasons for decreased neutrophil levels:
- infectious diseases (viral hepatitis, typhus, influenza, mononucleosis, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic vasculitis, Crohn's disease, etc.);
- radiation sickness;
- blood diseases (leukemia, hemolytic and dyserythropoietic anemia).
Separate mention should be made of medications: taking them can also cause neutropenia. This is a very broad group of medications, which includes:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: analgin, amidopyrine);
- antibacterial drugs (cephalosporins, penicillins);
- drugs to lower sugar (chlorpropamide);
- thyreostatic agents (propylthiouracil, Mercazolil);
- antimalarial drugs of synthetic origin (hydroxychloroquine);
- sulfonamides (sulfapyrazone; sulfasalazine);
- cytostatics (chlorambucil, methotrexate);
- antivirals (ganciclovir, zidovudine).
Figure 3. Blood cells in a healthy person and with neutropenia. Image: Sakurra/Depositphotos
Leukocyte blood count: interpretation of results
Increasing performance
An increase in neutrophils in the blood occurs during infectious diseases and during some specific patient conditions. For example, in acute infectious diseases, candidiasis, rheumatism, tumor processes, lead or mercury poisoning, during diabetes. Also, an increase in the number of neutrophils can be influenced by conditions not associated with diseases, for example: severe physical exertion, stressful situations, overheating or hypothermia.
An increase in the number of lymphocytes indicates the presence of an infectious disease, blood pathology, lead or arsenic poisoning. Some medications can affect the increase in lymphocytes.
A previous infectious disease affects the increase in monocytes. Monocytes increase in autoimmune diseases, in the presence of cancer, and during carbon and phosphorus poisoning.
An increase in eosinophils occurs in response to allergic reactions, when taking certain antibiotics, medications for tuberculosis and convulsive conditions. Parasitic infections, diseases of the skin and respiratory system, and the acute course of an infectious disease can also change the indicators.
Basophils in the blood increase during influenza, chickenpox, tuberculosis, allergic reactions, ulcerative colitis due to increased sensitivity to any food, and an increase may also indicate the presence of cancerous tumors in the body.
Decrease in indicators
If the number of neutrophils decreases, the doctor may suspect that the patient has an infectious disease, hypersensitivity to drugs, anemia and anaphylactic shock.
Lymphocytes decrease in conditions of immunodeficiency, acute inflammatory processes in the body, renal failure and systemic lupus erythematosus.
A decrease in monocytes occurs during oncohematological diseases, purulent infections and aplastic anemia, the use of certain drugs and in a state of severe shock.
The decrease in eosinophils is affected by severe purulent infection and heavy metal poisoning.
Pregnancy, severe stress and the period of ovulation can be a natural cause of a decrease in basophils. Pathological causes include infectious diseases and Cushing's syndrome.
Preparing for analysis
The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach, since food intake causes an increase in the number of neutrophils in the blood. Dinner on the eve of the test is allowed no later than eight o'clock in the evening. 2 days before the study, the patient should follow the following preparation rules:
- stop drinking alcohol;
- limit the consumption of spicy, fried and fatty foods;
- Avoid heavy physical activity and nervous stress.
The morning before the test you should not smoke. It is allowed to drink pure still water.
Figure 2. Preparation for donating blood for analysis.
What does a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left and to the right mean?
Neutrophils form the body's antibacterial and antifungal defenses, and when a certain microbe enters the body, the number of neutrophils increases. In this case, not only their total number changes, but also the number of individual forms of these cells.
Chain of neutrophils arranged according to maturation:
Young - rod-nuclear - segmented.
A shift of the formula to the left is an increase in the number of young cells, and a shift to the right is an increase in the number of old cells.
Reasons for the shift in leukocyte formula
In medical practice, a shift to the left occurs more often. This is affected by the presence of an acute bacterial or fungal infection in the body. The bone marrow is mobilized to protect the body and begins to intensively produce neutrophils. They begin to fight the infection and die in the process. Young cells are produced to replace mature cells. At a certain point, the number of young cells exceeds the number of mature ones.
An increase in segmented neutrophils leads to a shift in the leukocyte count to the right. This occurs not only against the background of an increase, but even more often with a decrease in the number of leukocytes. This is facilitated by long-term chronic infections, in which bone marrow reserves are depleted and young cell forms cease to form. Poisoning, radiation, chemotherapy and radiotherapy, which also suppress the bone marrow, can cause the correct shift.
To prevent changes in the number of leukocytes and changes in the leukocyte formula, you need to monitor your health. To maintain your immune system, you should exercise, maintain a work-rest schedule, eat right, and avoid stressful situations. Also, do not forget about undergoing a routine examination with a therapist.
Special cases of decreased neutrophils
We are talking about genetically determined neutropenia, which is quite rare, but affects the result of a blood test. This:
- benign chronic neutropenia is asymptomatic, there is no danger to life, but when interpreting the analysis, this point is always taken into account;
- cyclic neutropenia occurs in one person per million, does not affect the quality of life, manifests itself in a periodic causeless decrease and then restoration of neutrophils to normal;
- Kostmann's syndrome is a condition when neutrophils are deprived of the opportunity to mature, as a result a person is deprived of natural protection and constantly suffers from all possible infections. Today, provided that the pathology is detected in a timely manner, patients are given courses of drug correction.