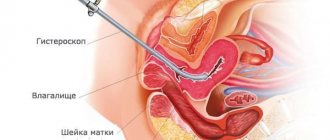
Prices for services
Initial appointment with a gynecologist + ultrasound (assessment of complaints, medical history, examination in a gynecological chair, pelvic ultrasound, consultation)
Primary appointment – visiting a doctor of a specific specialty for the first time. Make an appointment
1800 ₽
Repeated appointment with the gynecologist
With the exception of repeated appointments with doctors: Blatsios N.D., Dzhashiashvili M.D. Make an appointment
1200 ₽
Ultrasound of the pelvis in women (uterine cavity, ovaries)
Make an appointment
1500 ₽
Brownish light discharge in early pregnancy
In addition to implantation 10 days after conception, spotting may appear at 4-12 weeks due to pregnancy pathology:
- Placental abruption;
- Hematoma;
- Presentation;
- Ectopic location of the embryo;
- Intrauterine fetal death;
- Miscarriage.
All of these conditions are characterized by a gradual increase in bleeding, so the discharge darkens or becomes bright red. Along the way, patients note stretching in the lower back and abdomen, spasms and cutting pains. The first 3 cases are corrected with medication, saving the child’s life; the latter require surgical intervention and exclude continuation of the pregnancy.
Attention! For many women, at week 5, the discharge resembles a scanty period. This so-called washing of the fetus indicates a lack of progesterone in the body, which can cause a miscarriage.
About normal discharge
Normally, a woman's vagina should release fluid. But not all discharge is normal. “Good” discharge includes clear, not abundant (from 50 mg per day), odorless mucus. Normal discharge does not cause discomfort, it does not cause itching, burning or irritation of the vagina. If you take a smear for microflora, it should reveal a normal number of leukocytes with a predominance of lactobacilli. Mucus discharge gradually increases in quantity until the day of ovulation (approximately 14 days after menstruation). During this period, the mucus changes its properties. The feeling of moisture in the external genital area at this time is absolutely normal.
But you need to be very careful about brown discharge! A brown, brownish tint to the liquid clearly indicates bloody or bloody additions to the mucus. And this, in turn, may indicate disorders of the female genital area. Further on such violations and their causes.
Brown discharge in women
Often in the practice of a gynecologist, diseases of the female reproductive system are encountered, which are accompanied by pathological discharge.
A woman should be very careful about brown discharge. Such discharge indicates the presence of bloody or bloody additions to it, which is a disorder in the female genital area.
Dark brown discharge is associated with a large amount of blood being released, while a light brown tint means less blood is being released. Discharge of scarlet blood indicates the presence of fresh bleeding (for example, due to injury to the vaginal mucosa during sexual intercourse). The blood does not have time to clot, so it has a scarlet color. Brown discharge is clotted blood.
Blood takes longer to leave the uterus when there is little of it, so it oxidizes in the process, darkening and acquiring a shade of brown and a glandular specific odor. When released, the blood mixes with vaginal lubrication and looks like brown mucus or smear.
Important! If you suddenly notice brown discharge in your vagina, then mark it on your menstrual calendar and pay attention to other symptoms.
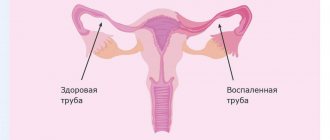
Endometritis
Brown discharge may be a sign of chronic endometritis - inflammation of the endometrium, the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity. Brown discharge with endometritis appears before and after menstruation and often has an unpleasant odor. Sometimes brown mucus appears in the middle of the cycle and is combined with aching pain in the lower abdomen. Chronic endometritis is dangerous during pregnancy; it can lead to miscarriages at different stages. This pathology is due to the fact that the process of attachment of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity and its further development are disrupted.
Chronic endometritis can result from:
- acute postpartum or post-abortion endometritis that has not been completely cured;
- intrauterine interventions;
- imbalance between the body's hormonal and immune systems;
- hidden infections.
Possible pathological causes of brown discharge
Brown vaginal discharge in women can cause the following pathologies:
Endometritis
A sign of chronic endometritis (inflammation of the lining of the uterus) may be brown discharge. Such discharge with endometritis appears before and after menstruation, and sometimes has an unpleasant odor. Brown mucus may appear in the middle of the menstrual cycle and be accompanied by aching pain in the lower abdomen.
Chronic endometritis is dangerous for women who are planning a pregnancy; it can cause miscarriages at different stages. Chronic endometritis is caused by:
- untreated postpartum or post-abortion endometritis;
- intrauterine interventions;
- imbalance between a woman’s hormonal and immune systems;
- hidden undetected infections.
Endometriosis
Bloody or brown discharge is also a major symptom of cervical endometriosis. In this case, pain may not occur. Endometriosis of the cervix is nodular, small cystic formations that grow in the form of red or purplish-blue stripes. After menstruation, such discharge decreases in size and its color becomes lighter.
If endometrial tissue does not leave the body of the uterus when menstruation occurs, it can cause very severe pain in women, brown discharge and problems with fertilization.
Other possible symptoms of endometriosis: nausea, fatigue, diarrhea, pain during penetrative sex and urination, constipation, bloating
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Bleeding and brown discharge can cause STIs. Many diseases in this group (for example, gonorrhea and chlamydia) are asymptomatic in the early stages. Over time, you may experience pain when urinating, a feeling of pressure in the pubic area, vaginal discharge, and bleeding between periods.
Be sure to see your doctor if you think you have contracted an STI. Such infections lead to chronic pelvic inflammatory disease, infertility and chronic pain if left untreated.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
With polycystic ovary syndrome, the menstrual cycle is often unstable, with many women having only 9 periods per year. Due to lack of ovulation, it is not uncommon to experience bloody brown discharge between periods.
Other possible symptoms: darkening of the skin, weight gain, depression, increased anxiety, mood swings, thinning hair and hair growth in atypical areas of a woman's body, headaches, acne.
Ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm similar in shape to a fluid-filled sac that appears on the ovary. If the egg fails to successfully leave the ovary during ovulation, a follicular cyst may form. Such a cyst can form asymptomatically and go away on its own after a few months. Sometimes it increases in size, which can cause brown discharge and other adverse symptoms. Such cysts are dangerous because they can twist or crush the ovary. If a woman suspects that she may have a cyst, she urgently needs to consult a doctor for advice.
Polyp
A sign of a polyp in the uterus may be brown discharge. The cause of the appearance of a polyp may be a pathology of the cervical canal or uterine mucosa against the background of a chronic inflammatory process. Most often, hormonal disorders in a woman’s body cause the appearance of polyps.
Detachment of the ovum
During pregnancy, spotting and bloody discharge is the first sign of abruption of the placenta or ovum, which happened several days or a week ago. Such discharge feels similar to mild contractions, which are accompanied by aching pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region.
Ectopic pregnancy
Brown discharge with ichor may indicate an ectopic pregnancy. In this case, a decrease in blood pressure, pain in the lower abdomen, increased heart rate, and dizziness may be observed.
When a fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tubes rather than in the uterus, the condition is called an ectopic pregnancy.
Other symptoms of ectopic pregnancy: acute pain in the abdomen, pubic area, neck and shoulders, fainting, dizziness, feeling of pressure, unilateral pain in the lower abdomen.
If, in addition to brown discharge, you also experience other symptoms listed above, then you need to call an ambulance to prevent rupture of the fallopian tube and severe bleeding. This is deadly!
Miscarriage
Miscarriages usually occur before the 10th week of pregnancy in 10-20% of women. Heavy bleeding and other rapidly developing symptoms (fainting, dizziness, pain and cramps in the lower abdomen) indicate a miscarriage.
The appearance of spotting in the early stages of pregnancy is often completely normal, but you should definitely report it to your gynecologist.
Lochia (bloody discharge after childbirth)
Bloody discharge that occurs in women for 4-6 weeks after childbirth is called lochia. At first they are very abundant, scarlet with small clots, but after a few days they weaken and turn pink or brown. After 10 days, the discharge becomes yellow or creamy, then disappears completely. If the discharge has large clots, an unpleasant odor and is accompanied by an elevated temperature in a woman, this may be a sign of a bacterial infection. In such a situation, you should immediately consult a doctor!
Hormonal contraceptives
Brown discharge may appear in the first months of taking hormonal contraceptives, which is considered normal. But if this phenomenon continues for more than 3 months, then the hormonal drug requires replacement.
Hormonal disbalance
The thickness of the uterine epithelium is regulated by estrogen. If there is too little of it, then the uterine mucosa is separated during the cycle, which affects the appearance of brown and other atypical discharge.
Low estrogen levels can also cause hot flashes, insomnia, mood swings, depression, difficulty concentrating, genitourinary infections, and weight gain.
Premenopause
Premenopause is the period of time before menopause that begins around age 40. During the premenopausal period, cycle failure may occur and brown, pink and red discharge may appear, which occurs due to changes in estrogen levels. Other possible symptoms: hot flashes, changes in libido, vaginal dryness, irritability and mood swings, insomnia.
Be attentive to your body; you may need urgent medical treatment or consultation with a specialist if you have continued bleeding for a long time.
Endometriosis
Brown or bloody discharge are also the main symptoms of endometriosis of the cervix or uterine body. This does not necessarily cause pain. Endometriosis of the cervix is nodular, small cystic formations or growths in the form of red or purplish-blue stripes. Dark bloody and brown discharge may appear from individual lesions. Endometriosis of the uterine body is the growth of endometrial cells in the myometrium (the muscular layer of the uterus). Pathological discharge decreases in size after menstruation, and its color becomes lighter.
Make an appointment
Is yellow vaginal discharge a cause for concern?
Not every yellow-colored vaginal mucus indicates an intimate infection. Yellowish discharge - cervical mucus - also appears outside the ovulation period. If yellow discharge is not accompanied by any additional symptoms, this is a sign that the bacterial flora of the vagina is in good condition.
Yellow vaginal discharge
In the case of discharge, the occurrence of which is associated with itching, burning in the intimate area, as well as an unpleasant odor, this may indicate the occurrence of cervical erosion.
Yellow and greenish discharge also occurs with trichomoniasis. Other signs of trichomoniasis:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- itching and redness around the vagina and labia;
- frequent urination;
- pain during intercourse;
- Possible menstrual irregularities.
Treatment of this intimate infection requires the use of an antibiotic.
Endometrial hyperplasia
Spotting, bloody, brown discharge at the end of the cycle before menstruation or for a long time after menstruation may indicate endometrial hyperplasia. The causes of hyperplasia can be of different nature. Most often, this pathology develops due to hormonal imbalances, as well as carbohydrate, lipid and other types of metabolism. An important role may be played by hereditary predisposition, the presence of uterine fibroids, cancer of the genital organs and breast, hypertension and other diseases, manifestations of damaging effects during the prenatal period of development, diseases during puberty and the disorders of menstrual and subsequently reproductive function caused by them. The appearance of hyperplasia in adulthood is often preceded by previous gynecological diseases, abortions, and genital surgeries.
Why does spotting appear?
During pregnancy, brown discharge occurs due to a lack of progesterone coupled with muscle hypertonicity. It is important to take action in time, then the daub will stop. If we talk about implantation bleeding as a phenomenon, then it is often one of the early symptoms of pregnancy. Even in the absence of a delay, such discharge will indicate a likely past conception. First, the egg unites with the sperm and a fetal egg is formed, then it penetrates the uterine mucosa and, finally, during this, small vessels are damaged, which causes the coagulation of drops of blood and the appearance of brown discharge. Therefore, if the daub meant pregnancy, then it will go away on its own in a few days. In other cases, as mentioned above, you should definitely visit a gynecologist.
Prevention
To ensure that a woman’s normal discharge does not subsequently outgrow the disease or does not appear due to illness at all, the following preventive measures should be a necessary rule for every woman:
- Regular visits to the gynecologist.
- Healthy lifestyle.
- Adequate use of hormonal drugs.
- Protected sex.
- Personal hygiene must be observed continuously.
- The use of special intimate hygiene products.
If such a symptom appears, you should find out its cause. If physiological factors are excluded, then a gynecologist should get down to business and, having established the origin of the symptom, prescribe the correct treatment. Be healthy!
How can we help?
Take another look at the list of reasons and you will understand that in this case you should under no circumstances rely on the advice of friends for whom some miracle cure helped so well in “exactly the same case.”
If we are talking about an infection, then anti-inflammatory treatment is necessary. A hormonal disorder requires examination of the thyroid gland. In this case, the possible frequency of infectious diseases in childhood (up to 12 years) should be taken into account. Indeed, in this case, it is precisely this circumstance, the so-called infectious index, that is very important for correct diagnosis.