Oophoritis is a serious pathology, usually accompanied by damage to the fallopian tubes. Most often, this disease is observed in young women of childbearing age. Signs of inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes in women depend on the form in which the disease manifests itself - acute or chronic. If oophoritis is not treated in a timely manner, reproductive function may be impaired. According to statistics, about 20% of women suffering from this disease cannot become pregnant.
What is oophoritis
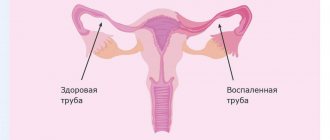
The diagnosis of oophoritis is an infectious-inflammatory process of the ovaries, which can have both an acute and chronic course. Also, oophoritis is divided into a unilateral process, as well as bilateral oophoritis.
In most cases, this pathological condition does not occur as an independent process. Often, inflammation completely covers the uterine appendages on both one and both sides, causing salpingoophoritis. This is inflammation of the ovary and fallopian tube at the same time. Previously, this process was called adnexitis.
This is a pathological condition with its consequences. This may also be a complication of an acute process in the form of the formation of a tubo-ovarian formation, its rupture with the development of peritonitis, the formation of adhesions, which can lead to infertility, as well as disruption of hormonal function.
Inflammation of the ovaries in women - symptoms and treatment
The specialist prescribes a course of therapy for the patient, focusing on the symptoms of the disease and data obtained during laboratory tests. The disease in the acute stage is subject to treatment in a hospital setting with a prescription for bed rest. In the first few days, painkillers, antibiotics, and also restoratives are used. After relief of the acute condition, the course is supplemented with various physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment of chronic ovarian inflammation comes down to properly selected antibacterial therapy. The specialist must determine how sensitive the pathogen is to certain medications. This will allow the doctor to prescribe the dosage of the drug and the duration of the course of taking it. Suppositories can be used to treat inflammation of the ovaries
(as an aid to relieve symptoms of the disease).
The best way to prevent the disease is to strengthen the body’s overall immunity. Women suffering from immune system disorders are advised to spend more time in the fresh air, lead an active lifestyle if possible, and take vitamins. A balanced diet should contain a significant amount of vegetables, fruits and dairy products.
Causes of oophoritis
The most common reasons for the development of oophoritis is the meeting of ovarian tissue with pathogenic microflora, bacteria that cause inflammation. An inflammatory response may occur in response to traumatic exposure.
Infectious agents. The most common cause of oophoritis. In response to the addition of a bacterial, fungal or viral infection, inflammatory processes begin to occur in the ovarian tissue. The more time passes without etiological treatment, the more advanced the process is formed, the more consequences and complications it will cause for the fair sex. The infection can involve both the ovaries, however, the fallopian tubes are often also included in the process.
The main infectious agents that cause inflammation in the uterine appendages:
- Gonococci. This is a bacterial infection that is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. It has an acute course and very pronounced long-term consequences in the form of the formation of a pronounced adhesive process. The latter leads to the formation of infertility.
- Chlamydia. These pathogenic microorganisms also cause a specific oophoritis, the peculiarity of which is that its course is very hidden. The consequences for the body are the same as for gonorrhea, however, the difficulty lies in identifying it. Since the woman may not have clinical symptoms, that is, complaints.
- Trichomonas is a common pathogen that can also be sexually transmitted through unprotected sex. Often, trichomoniasis also has an asymptomatic course; in some cases, foamy vaginal discharge may be disturbing. When a large part of the ovary is involved in the process, symptoms characteristic of oophoritis arise, and obstetricians-gynecologists will have to find out what its etiology is.
- Mycoplasma and ureaplasma. These are opportunistic microorganisms that can normally be contained in a certain amount in a woman’s vagina. If, under the influence of provoking factors, their number increases, then an inflammatory process caused by these microorganisms may occur. Such pathologies are called mycoplasmosis and ureaplasmosis.
- Tuberculous lesions of ovarian tissue should also not be excluded. When Mycobacterium tuberculosis enters a woman’s body, not only the lung tissue can be damaged, but also the reproductive organs, and the ovaries in particular.
Often, when oophoritis and salpingoophoritis form, the infection penetrates the uterine appendages in an ascending manner. This means that inflammation of the vulva and vagina first forms, which can penetrate the uterus, and then into the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
Acute and chronic 2-sided oophoritis: risk factors:
- Uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs;
- Using the vaginal douching technique;
- Violation of intimate hygiene rules;
- Stressful influences;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Immunological problems;
- Uncontrolled sexual intercourse;
- Lack of use of barrier contraception.
The anatomical and physiological features of the female reproductive system in the form of a closed cervical canal and thick cervical mucus perfectly separate the non-sterile environment of the vagina and the sterile uterine cavity. However, with immunological problems, disorders of the vagina and cervix, this natural barrier may be disrupted. And the infection can ascend through the upper floors of the reproductive system.
Factors contributing to the penetration of infection into the uterus and appendages:
- Performing abortion manipulation by curettage of the uterine cavity;
- Fractional diagnostic curettage of the uterine cavity;
- Use of intrauterine contraception (installation of a device);
- Spontaneous abortion;
- Childbirth.
- Surgical interventions on the abdominal and pelvic cavity organs.
All these factors have an important nuance - intrauterine intervention, which already increases the risk of bacterial complications such as endometritis (inflammation of the uterine mucosa), and salpingitis and oophoritis. Inflammation: oophoritis and viral damage. Also, one should not exclude the viral nature of the formation of oophoritis.
Inflammation of the ovaries - causes and consequences
The cause of the formation of pathology can be pathogens of gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, tuberculosis or mycoplasmosis. Also, the disease can be triggered by opportunistic microflora (staphylococci, streptococci, candida, E. coli). Factors that increase the risk of developing pathology include:
- surgical termination of pregnancy;
- hypothermia;
- unprofessional diagnostic and surgical procedures;
- use of intrauterine devices.
The most serious consequence of untimely treatment of the disease is infertility. In addition, oophoritis can result in serious complications, for example, a purulent abscess that provokes peritonitis.
Symptoms of oophoritis
Acute and chronic oophoritis has a characteristic clinical picture.
When diagnosed with oophoritis, symptoms may be as follows:
- Pain syndrome. Pain is one of the most characteristic and striking symptoms to which a woman can pay special attention. Oophoritis on the left is characterized by pain in the left iliac region, acute or chronic oophoritis on the right has a right-sided localization, respectively. The pain can have a different character: pulling, aching, sharp, cutting. It all depends on the progress of the process.
- Hyperthermic reaction. In simple terms, this is an increase in body temperature. This is due to a pronounced inflammatory process in the pelvis.
- Tachycardia is an increase in heart rate.
- Vomit.
- Pathological nature of discharge from the genital tract. Depending on the infectious agent that caused the infectious inflammation of the ovaries, the discharge may be yellow, green, foamy, purulent, bloody, thick, or increased in volume.
- Dyspareunia. This is painful sexual intercourse.
- If chronic oophoritis is present, the symptoms of such a process can be characterized by the absence of pregnancy for a year or more with unprotected sexual intercourse. That is, infertility.
Symptoms of oophoritis
Prevention
Qualitative prevention methods are based on:
- timely detection and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases;
- treatment of the partner if the disease has been detected;
- visiting a gynecologist once a year;
- excluding casual sexual relations;
- healthy lifestyle.
So, oophoritis is inflammation of the ovaries, often occurs as a concomitant disease and requires timely, individual and high-quality treatment. Due to severe pain, it is difficult to diagnose and can be differentiated from appendicitis and gynecological pathologies. Therapy is carried out comprehensively, it is aimed directly at the symptoms of the disease and the causes of ovarian inflammation. In some cases, surgical treatment is possible.
Treatment
If acute or chronic oophoritis is diagnosed, treatment should be prescribed immediately.
Acute oophoritis: treatment
- Antibacterial drugs. This is the main direction of treatment. Antibiotics are selected according to the pathogen that caused the process.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs.
- Detoxifying agents.
- Resorption therapy.
- Antihistamines.
In advanced cases with a diagnosis of acute oophoritis, surgical treatment may be necessary.
Treatment of oophoritis
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic measures are ultrasound, hysterosalpingoscopy (examination of the uterus, examination of the patency of the fallopian tubes), gynecological examination, bacterial culture of a vaginal smear. Laparoscopy is performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Since oophoritis has no specific symptoms, differential diagnosis with ovarian apoplexy, endometriosis, ovarian cyst, ectopic pregnancy, appendicitis, peritonitis, intestinal and renal colic, and intestinal tumors is of great importance.
Forms of the disease
Treatment of inflammation of the appendages in women should begin by determining the stage of the disease. There are three forms of development of adnexitis:
- chronic;
- acute;
- subacute
Any of the stages is accompanied by certain symptoms and is dangerous for the body. The lack of proper treatment will worsen the situation, and the consequences of the disease will be more severe.
Acute form of the disease
This stage of disease development occurs immediately after the end of the latent period of infection. The symptoms of this form clearly indicate the presence of problems in the gynecological area. The initial stage of inflammation of the appendages is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- increase in body temperature;
- the presence of purulent vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- chills;
- the presence of discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- increased sweating;
- decreased sexual desire;
- severe headaches;
- difficulty urinating;
- menstrual irregularities.
Most signs confirm the presence of a strong inflammatory process in the body. The development of adnexitis is indicated by problems with the regularity of the menstrual cycle and pain in the genital area.
Subacute form of the disease
At this stage, the signs of inflammation of the appendages are identical to the above symptoms. This is due to the fact that the subacute form is a periodic occurrence of exacerbations. The intensity of all symptoms is reduced. A complete absence of signs of the disease cannot be ruled out. In this case, diagnosing and monitoring the progress of treatment becomes very difficult. The presence of the disease at this stage is indicated by:
- irregular menstrual cycle, often accompanied by pain;
- slight decrease in sexual desire;
- pain that occurs in the lower abdomen, which is paroxysmal in nature.
The subacute stage gradually turns into the chronic stage. Correct therapy will alleviate the condition and prevent serious complications from developing.
Chronic form of the disease
Having passed to this stage, most diseases of the genital area lose their characteristic signs. Inflammation of the appendages is accompanied by symptoms that are characteristic of the subacute form, although they are less pronounced. The symptoms are as follows:
- the presence of unbearable pain during sexual intercourse;
- short period of menstruation, which does not exceed two days;
- lack of sexual desire;
- the presence of intestinal disorders;
- inability to get pregnant;
- presence of bloody vaginal discharge.
The chronic stage often transitions back to the subacute stage. This phenomenon occurs due to a strong decrease in the protective function of the immune system. This occurs when the body is significantly hypothermic or during prolonged exposure to a stressful situation. It is worth seeking gynecological help if there are several signs of inflammation of the appendages; self-treatment often leads to complications and infertility.
Diagnosis
Recognizing oophoritis is a complex process, because Its manifestations are similar to many diseases. To establish the transition of inflammation to the ovaries, the gynecologist:
- Interviews the patient - interested in past illnesses, birth history, presence of abortions, symptoms, duration of course.
- Conducts an examination - palpation, manipulation with a mirror.
- Refers for laboratory testing - analysis of vaginal secretions, blood, urine, urethral smear, bacterial culture.
- Uses instrumental methods - hysterosalpingography, ultrasound OMT, fallopian tubes (USGSS).
- He resorts to additional methods - tuberculin diagnostics, PCR analysis, ELISA, laparoscopy.
How to treat inflammation of the appendages: methods of folk and traditional medicine
Therapy is aimed at destroying the infection, restoring tissues affected by the disease and relieving pain. Inflammation of the appendages in women is treated not only with antibiotics, but also with drugs that support the immune system.
Drug therapy
Medicines are selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the presence of allergies. The following antibiotics are usually prescribed:
- Gentamicin;
- Claforan;
- Cephobid;
- Cefazolin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Doxycycline;
- Ofloxacin;
- Lincomycin.
For effective treatment, specialists use the complex use of the above remedies.
In addition to antibiotics, medications that have an anti-inflammatory effect are prescribed:
- Diflucan;
- Ibuprofen;
- Orphtofen.
To treat inflammation of the appendages in women, antihistamines are used, which reduce the risk of allergic reactions. Popular products in this category are Zodak, Zyrtec, Erius.
Surgery may be required at the initial stage of the disease. They resort to surgery in the following cases:
- adhesions in the pelvic organs;
- formation of a purulent cavity;
- loss of patency of the fallopian tube.
Therapy in the above cases is carried out in a hospital setting. It is impossible to cope with the disease at home.
Treatment of inflammation of the appendages in women with “grandmother’s recipes”
Traditional medicine helps stop the development of inflammation and the spread of infection. But they are not able to cure the patient, since only antibiotics can kill pathogenic microorganisms.
The following recipes are used in the treatment of adnexitis:
- For treatment, a decoction of a mixture of roots is used - Chernobyl, elecampane, peony, buckthorn and burnet. Two tablespoons filled with half a liter of hot water is enough. The broth is boiled over low heat for about half an hour, cooled and filtered for the same amount of time. Take half a glass 3-4 times a day. To improve the taste of the healing drink, honey is added. This bee product helps strengthen the immune system and gives the body strength to fight infection.
- They take a medicinal plant such as boron uterus and grind its dried leaves. A tablespoon of medicinal herb is poured with boiling water, one glass is enough. Leave to infuse, filter after two hours. The resulting decoction is taken in a third of a glass. It is recommended to consume 30 minutes before meals three times a day. The duration of the course is one month. After completing therapy with a decoction of boron uterus, it is recommended to drink an infusion of Yakut field grass for two months. To prepare the drink, add a tablespoon of dried herb to a glass of boiling water. Infuse and filter after four hours. A single serving is one teaspoon. The decoction is taken 3-4 times a day.
- Dried, pre-crushed flowers of coltsfoot, centaury and sweet clover are taken in equal proportions. Add a glass of boiling water to the resulting mixture and leave to infuse. After an hour, filter the broth using gauze. The cooled medicine is taken half a glass twice a day. Treatment with this method involves abstaining from sexual activity for the full course.
Gardnerellosis
The disease is not an STD. It is caused by gardnerella vaginalis, and, in fact, gardnerella is a manifestation of vaginal dysbiosis. That is, this is not inflammation in the vagina. That is why this disease is also called bacterial vaginosis.
Unlike other infections, with gardnerellosis the symptoms are pronounced and specific. Symptoms include heavy, thin vaginal discharge that is white or yellowish in color and has a very unpleasant odor, similar to rotten fish. This odor may become stronger during and after menstruation, as well as after sexual intercourse. This disease causes discomfort and burning in the external genital area.
During a gynecological examination, an experienced doctor will be able to immediately make a diagnosis, since the discharge has a slightly foamy characteristic appearance. In some cases, there may be no symptoms, so gardnerella can only be detected during an examination.
Gardnerella is located directly in the vagina. This infection most often does not penetrate further, therefore there are no symptoms such as, for example, pain in the lower abdomen.
Gardnerella and pregnancy
Gardnerella can cause a lot of trouble during pregnancy. It is possible, although very rare, that intrauterine infection may occur. Gardnerella can also cause inflammation of the uterus after childbirth or abortion. That is why bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy must be treated immediately when it is detected.
Gardnerella usually appears in a simple smear on the flora. The PCR diagnostic method is also used to identify them.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out in 2 stages. First, the infection is destroyed, and then the microflora in the vagina is restored.
At the 1st stage, drugs such as flagyl, fasigin, clindamycin, trichopolum are used.
The 2nd stage is longer, it can last 1 month or even more. Here you need to be patient, because... If the microflora is not restored, the disease will return again. Sexual activity during the treatment period is possible, but only if the partners use a condom.
In men, gardnerella “takes root” and does not develop, so treatment of sexual partners is not required.