As for women, vaginal discharge is normal. They moisturize the vaginal walls and protect the genitals from infection. As for 10-12 year old girls, they should not have vaginal discharge, because... their hormonal levels are too low, and their glands are not yet functioning.
Before the onset of menstruation in girls (about a year in advance), leucorrhoea begins to leak from the vagina, which indicates hormonal changes in their body. The discharge should be creamy and homogeneous, without an unpleasant odor (or a slightly sour odor).
It is clear that discharge in women should not be painful, cause itching, swelling of the skin or other unpleasant sensations. This can only indicate pathology:
Trichomoniasis. Copious white, greenish or purulent, yellowish-brown discharge with an unpleasant odor, accompanied by itching and/or burning, painful urination.
Thrush (candidiasis). Itching and thick, profuse discharge, similar to lumps of yellowish cottage cheese. Exhausting intense itching of the genitals and irritation (redness, swelling) of the external genitalia.
Bacterial vaginosis. The amount of discharge increases significantly, the color of the discharge is grayish-white or yellowish, and an unpleasant fishy odor appears. Symptoms worsen after sexual intercourse.
Chlamydia. Characteristic is yellow discharge, often accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen and painful urination.
Goorean. Moderate foamy yellowish-white discharge, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, pain when urinating and, often, intermenstrual bleeding.
Colpitis. The discharge is varied: liquid, watery, sometimes thick, purulent, often foul-smelling, often mixed with blood.
Acute inflammation is accompanied by itching, burning or heat in the genital area.
Oncological diseases of the internal genital organs are often accompanied by thick, liquid-like discharge.
Causes of clear vaginal discharge
Physiological hormonal changes
Normally, the amount of vaginal secretion increases as you approach ovulation, due to the action of the hormone estrogen.
Leucorrhoea is odorless, its consistency is quite thick, mucous, and in appearance it resembles “sticky snot” or egg white. For several days after ovulation, you may experience watery, clear vaginal discharge. The secretion is small in volume; patients often notice stains on their underwear or a small amount of mucus on their panty liner. The symptom is not accompanied by itching, general health remains good. At puberty, the appearance of clear, odorless vaginal discharge is caused by sharp jumps in estrogen during the formation of the menstrual cycle, and the effect of other hormones and active substances on the secretion of the cervical glands. Teenage girls may complain of profuse, clear leucorrhoea (“like water”) occurring on different days of the cycle. If you have cloudy mucous discharge with a sour odor, itching in the external genital area, or discomfort in the lower abdomen, you should consult a specialist.
Stressful situations
A common cause of watery, odorless discharge is chronic stress, overwork at work, and sudden climate change. All these situations have an adverse effect on hormonal levels, which causes disruption of the secretory function of the glands of the vestibule of the vagina and cervix. The disorder is typical for young emotional girls. Often, clear vaginal discharge is combined with decreased libido, general weakness and deterioration in performance. If the symptom persists for a long time, you should visit the office of an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Allergic inflammation
With this type of inflammatory reaction, the vaginal discharge is very liquid and transparent. In the acute phase of the allergy, the discharge is profuse and accompanied by intense itching in the vagina and perineal area. Many women note that the symptom is associated with the use of intimate hygiene products and wearing synthetic underwear. These factors provoke allergic colpitis (vaginitis). If clear, odorless discharge is observed after sexual intercourse, this may be due to an allergy to latex or polyurethane in barrier contraceptives.
Viral sexually transmitted infections
Transparent watery discharge from the genital tract may be accompanied by viral infections transmitted through sexual contact. The most common infections are herpes simplex virus and human papillomavirus. In this case, in women the area of the perineum and vulva, urethra, rectum, vagina, cervical canal can be affected, and with advanced herpes - the bladder, uterus and fallopian tubes.
- Genital herpes.
In the initial period, vesicular rashes are filled with transparent exudate. Their appearance is accompanied by unbearable painful itching and a burning sensation in the affected area. When the vesicles are opened, the liquid flows out, which causes a feeling of constant humidity in the intimate area. Gradually, the serous contents of the vesicles change to cloudy, purulent or hemorrhagic, so the nature of the discharge also changes. Common symptoms include weakness, muscle pain, temperature rise, and enlarged lymph nodes in the groin. - Genital condylomas.
They are single nodules or multiple growths in the form of a “cockscomb” or “cauliflower” of pale pink or grayish color. Accompanied by itching and paresthesia, clear watery vaginal discharge, weeping of the skin and mucous membranes. Condylomas of the anogenital area are prone to injury during scratching and sexual intercourse, so some women report bloody discharge from the vagina.
Helminthiasis
Parasitic infestations are more common in little girls, which is facilitated by poor hygiene and an alkaline environment in the vagina, which facilitate the attachment and reproduction of helminths. With helminthiasis, a thick mucous discharge (like egg white), usually odorless, is noted. Girls complain of itching of the perineum and anal area, and white worm larvae are found on the fabric of their underwear. With prolonged vaginal helminthiasis, transparent mucous discharge with a rotten odor is possible; streaks of blood are sometimes visible in the mucus.
Rare causes
- Endocrine diseases
: hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency. - Vitamin deficiencies A and E
. - Decreased immunity
: with prolonged viral or bacterial infections, chronic diseases.
When secretion is normal
The secretion of a healthy woman is characterized by the following signs:
- its volume does not exceed five milliliters per day (one teaspoon);
- it should have a whitish, transparent or milky tint and a uniform texture;
- the structure of the secretion should be thick, viscous or mucous and have small compactions up to 4 mm;
- the discharge should not be accompanied by an odor;
- White discharge in women should not be accompanied by redness, itching or swelling.
If a woman's white, odorless discharge meets these criteria, then there is no need to worry. In addition, leucorrhoea may not be a pathological condition even in the case of natural causes that characterize the woman’s condition.
Diagnostics
If clear vaginal discharge is detected, a consultation with a gynecologist is required to rule out pathological causes of the condition. A diagnostic search involves a comprehensive study of the mucous membrane of the genital tract, assessment of hormonal levels, and identification of concomitant pathologies. Patients are prescribed instrumental and laboratory methods, the most informative of which are considered:
- Gynecological examination.
During a visual examination of the vagina and cervix in the speculum, attention is paid to the condition of the mucous membrane, the presence of areas of hyperemia or erosion. Adolescent girls undergo a rectal examination and palpation of the uterus through the anterior abdominal wall. Be sure to take a vaginal smear for microflora. - Instrumental inspection
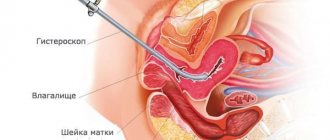
. For a detailed study of the cervical epithelium, extended colposcopy is used, which includes testing with acetic acid and Lugol's solution to exclude precancerous conditions. To clarify the cause of mucous discharge with a specific odor, hysteroscopy and hysterosalpingography are additionally used. - Laboratory diagnostics
. To identify pathogenic microbes and signs of dysbiosis, an analysis of the vaginal microflora is performed. Microscopy of a vaginal smear can detect helminth eggs. Transparent discharge without a noticeable odor, occurring at various periods of the menstrual cycle, is an indication for determining the levels of estrogen and progesterone. Viral pathogens are detected by PCR methods.
When vaginal discharge is combined with discomfort and pain in the lower abdomen, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs is recommended to exclude diseases of the uterus or appendages. To confirm the allergic origin of genital discharge during an exacerbation of the disease, an immunogram is performed, and after relief of symptoms, an allergy test is performed. If there are difficulties in diagnosis, they resort to consultations with other specialists.
Taking a gynecological smear for examination
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Clear vaginal discharge that occurs during or before ovulation does not require specific treatment. Women are advised to maintain hygiene standards and use panty liners. It is advisable to reduce the amount of cosmetic products used for intimate hygiene so as not to cause irritation of the reproductive organs or allergies. If the color or consistency of the discharge changes, or an unpleasant odor appears in the discharge, you should contact a gynecologist to find out the cause of the disorder.
Conservative therapy
If the patient has an inflammatory process in the genitals or extragenital pathology, the treatment regimen is selected individually. Systemic drug therapy is complemented by local effects: baths with antiseptics and medicinal herbal decoctions are indicated; vaginal suppositories with lactobacilli are used to restore the vaginal microflora. The most commonly used medications are:
- Anthelmintic drugs
. Selectively act on pathogens of helminthic infestations at different stages of the life cycle. Medicines are combined with vaginal antiseptics in the form of suppositories to quickly eliminate the cause of discharge. - Antiviral drugs
. Prescribed for confirmed viral etiology of clear discharge. Drugs with antiviral activity are used, both local (in the form of creams, ointments, vaginal suppositories) and systemic (tablets, injection solutions). The basic agents are acyclovir and interferon. For preventive purposes, before sexual debut, women are recommended to be vaccinated against herpes and against HPV. - Antihistamines
. Effectively relieve itching and discomfort in allergic vaginitis, reduce the amount of discharge. For severe systemic allergies, short-term use of corticosteroid tablets is indicated. - Vitamins
. Retinol (vitamin A) improves the condition of the epithelial layer of the genital tract, eliminates irritation and itching. Alpha tocopherol is prescribed to normalize hormonal levels and increase progesterone levels in the second phase of the cycle. - Destruction of condylomas
. Various methods are used to remove genital warts: cryosurgery, laser coagulation, chemical destruction, radio wave surgery, etc. Combination therapy, which involves a combination of a destructive method and antiviral therapy, significantly reduces the percentage of relapses of genital warts.
The key condition for complete recovery in diseases during which transparent leucorrhoea is released is taking the prescribed treatment under the supervision of a gynecologist until the symptoms completely disappear. Subsequently, a preventive examination by a specialist is recommended once every six months, sufficient rest, a diet rich in vegetables and fruits or taking vitamin complexes, avoiding contact with allergens, careful adherence to intimate hygiene, and the use of barrier contraception.
When should you see a doctor?
Contacting a specialist is necessary when leucorrhoea is of a recurring nature and is accompanied by itching, burning and other unpleasant symptoms.
Too much mucus during the day is also abnormal.
Systematic discharge may also be a sign of an allergic reaction or incorrectly prescribed hormonal therapy. Only a doctor can accurately determine the presence of pathology and diseases.
Useful articles on the topic: Green discharge in women Yellow discharge in women HIV symptoms in women
This article has been verified by Olga Zorina, a current qualified physician, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Rate how helpful this article was
4.6 46 people voted, average rating 4.6
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!