Sodium bicarbonate, sodium bicarbonate, sodium bicarbonate, baking soda are the names of the same chemical compound, known to every person as “baking soda.” It is a good leavening agent for dough. Soda solution can relieve toothache. But this is not the entire range of applications of this “miracle” substance. In fact, it is difficult to do without sodium bicarbonate in everyday life, in cooking, in medicine, and in many other areas of activity.
History of creation
Baking soda has been used in baking since ancient times. It was found by archaeologists during excavations of caves of the 1st-2nd centuries BC. Then it was extracted from the ash of seaweed or found in the form of a mineral. This chemical compound was actively used in ancient Egypt.
For the first time, the chemical formula of the compound - NaHCO3 - was established by the French scientist Henri de Monceau. Thanks to this discovery, baking soda began to be produced synthetically, which significantly reduced its cost and expanded its range of uses. Since the discovery of the formula, methods for its synthesis have constantly changed, improved, and become more economically profitable.
Methods of obtaining
Content:
- History of creation
- Chemical properties
- Beneficial features
- Possible harm
- Medical use
- Use in cooking
- Application on the farm
- Use in cosmetology
- Other uses
- Industrial use
- How to select and store
The first method of industrially producing sodium carbonate was to dissolve rock salt in water, mix the solution with limestone and charcoal, and then heat it in a furnace. However, as it turned out, the output was not baking soda, but soda ash. In addition, this activity left a lot of toxic waste (calcium sulfide and hydrogen chloride), so it was quickly abandoned.
Today, baking soda is produced in two ways - “dry” and “wet”, each of which is based on the carbonization reaction (enrichment of the solution with carbon dioxide).
Types of soda
From a chemical point of view and area of application, there are several types of soda: baking soda (drinking soda), ash soda (linen soda) and caustic soda (sodium hydroxide).
How is soda made?
Today, baking soda is produced using a method that was invented back in 1861 by the Belgian chemist Ernest Solvay.
The Solvay method turned out to be more environmentally friendly and effective than all previous methods of making soda. It was Solvay who built the first soda plant in Russia in 1883 on Berezovoy Island in the Perm province, which is still in operation today! True, they produce soda ash and lime milk there, which, despite their names, are not at all suitable for food, but are necessary for the chemical industry. To obtain sodium bicarbonate (also known as sodium bicarbonate, sodium bicarbonate and baking soda), you need limestone, deposits of which are located near production in the city of Sterlitamak. Limestone is burned in kilns, lime is obtained and a saline solution is added to it, and the resulting mixture is evaporated with ammonia. This produces technical sodium bicarbonate, but it is not baking soda yet - it needs to be purified. To do this, soda is dissolved in water and lye, then bicarbonate decomposes in a decarbonizer under the influence of steam: purified sodium bicarbonate precipitates, and harmful substances are removed. Next, the product is filtered, dried, crushed and packaged in packs.
Soda never remains indifferent in the company of vinegar
Chemical properties
Sodium bicarbonate is a weak acid salt of carbonic acid. They are small colorless crystals, which, when the temperature rises to 50-60°C, begin to “give up” a molecule of carbon dioxide, gradually decomposing to sodium carbonate (soda ash).
Reacts with acids to form salts (chloride, acetate, sodium sulfate) and carbonic acid, which instantly breaks down to water and carbon dioxide. The powder is poorly soluble in water and is easily separated by filtration.
Task 33
Task 33.1
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Demo version of the KIM Unified State Exam in Chemistry 2019
Solution
1) Under the specified conditions (H2SO4, 180 ᴼC), intramolecular dehydration of 1-propanol occurs with the formation of propylene (substance X1):
2) The interaction of propylene with HCl leads to the formation of 2-chloropropane (substance X2) (hydrohalogenation reaction):
3) When 2-chloropropane reacts with an aqueous solution of NaOH, –Cl is replaced by a hydroxyl group, isopropanol is formed (substance X3):
4) Isopropanol under the influence of H2SO4 upon heating (180 ᴼC) undergoes intramolecular dehydration to form propylene (substance X1):
5) When exposed to an aqueous solution of KMnO4, propylene enters into a hydroxylation reaction to form propylene glycol (substance X4):
Task 33.2
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Open Unified State Exam task bank
Solution
1) Alkaline hydrolysis of 1,1-dibromopropane will lead to the formation of aldehyde - propanal:
2) When interacting with an acidified solution of potassium dichromate, propanal is oxidized into propanoic acid:
3) As a result of the reaction of propanoic acid with chlorine in the presence of red phosphorus, 2-chloropropanoic acid is formed:
4) 2-Chloropropanoic acid reacts with sodium bicarbonate to form the corresponding sodium salt:
5) The interaction of the sodium salt of 2-chloropropanoic acid with iodoethane leads to the formation of the corresponding ester - 2-chloropropanoic acid ethyl ester:
Task 33.3
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Open Unified State Exam task bank
Solution
1) Methylcyclohexane in the presence of platinum when heated will undergo a dehydrogenation reaction to form toluene:
2) As a result of the reaction with an aqueous solution of potassium permanganate, toluene is oxidized to potassium benzoate:
3) Fusion of potassium benzoate with potassium hydroxide will lead to the formation of benzene:
4) Nitrobenzene is obtained by nitration of benzene with a mixture of concentrated nitric and sulfuric acids:
5) Nitrobenzene is reduced by hydrogen released during the interaction of Fe and HCl to aniline. The latter can then react with HCl to form the corresponding salt - phenylammonium chloride:
Overall reaction equation:
Task 33.4
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Open Unified State Exam task bank
Solution
1) n-Butane in the presence of an AlCl3 catalyst isomerizes to isobutane:
2) The interaction of isobutane with bromine in the light will lead to the formation of 2-bromo-2-methylpropane:
3) 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane under the influence of an alcohol solution of potassium hydroxide is dehydrohalogenated to form isobutene (isobutylene):
4) The reaction of isobutene with a solution of potassium permanganate acidified with sulfuric acid will lead to the oxidation of the hydrocarbon with the formation of acetone and carbon dioxide:
5) Hydrogenation of acetone on nickel will lead to the formation of isopropyl alcohol (isopropanol):
Task 33.5
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Open Unified State Exam task bank
Solution
1) As a result of the interaction of benzene with chloromethane in the presence of an AlCl3 catalyst, an alkylation reaction occurs with the formation of toluene:
2) Bromination of toluene in the presence of the FeBr3 catalyst leads to the formation of 4-bromotoluene (p-bromotoluene) and 2-bromotoluene (o-bromotoluene):
3) The reaction of 4-bromotoluene (p-bromotoluene) with bromomethane and sodium metal leads to the formation of p-xylene (Wurtz-Fittig reaction):
4) Oxidation of p-xylene by the action of a solution of potassium permanganate acidified with sulfuric acid will lead to the formation of terephthalic acid:
5) Terephthalic acid with ethyl alcohol in the presence of a catalyst H2SO4 will enter into an esterification reaction to form an ester - terephthalic acid diethyl ester (diethyl terephthalate):
Task 33.6
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Open Unified State Exam task bank
Solution
1) Thermal decomposition of methane (temperature about 1000 ° C) leads to the formation of acetylene:
2) Acetylene adds water in the presence of divalent mercury cations to form acetaldehyde (Kucherov reaction):
3) The resulting ethanal (acetaldehyde) reacts with an ammonia solution of silver (I) oxide (silver mirror reaction), as a result of the oxidation of the aldehyde, ammonium acetate is formed:
4) Subsequent interaction with calcium hydroxide converts ammonium acetate to calcium acetate:
5) The decomposition of calcium acetate when heated will lead to the formation of acetone:
Task 33.7
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Open Unified State Exam task bank
Solution
1) Catalytic hydrogenation of divinyl (1,3 butadiene) leads to the formation of butene-2:
2) The reaction of butene-2 with a solution of potassium permanganate acidified with sulfuric acid will lead to the oxidation of the hydrocarbon with the formation of acetic acid:
3) Chlorination of acetic acid in the presence of red phosphorus will lead to the formation of chloroacetic acid:
4) Chloroacetic acid reacts with excess ammonia to form aminoacetic acid (glycine):
Cl-CH2-C(O)OH + 2NH3 → H2N-CH2-C(O)OH + NH4Cl
5) Subsequent interaction of aminoacetic acid with magnesium hydroxide converts the amino acid into the corresponding magnesium salt:
2H2N-CH2-C(O)OH + Mg(OH)2 → [H2N-CH2-C(O)O]2Mg + 2H2O
Task 33.8
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Open Unified State Exam task bank
Solution
1) Trimerization of ethylene (acetylene) when heated in the presence of activated carbon leads to the formation of benzene:
2) As a result of the alkylation of benzene with chloromethane in the presence of aluminum (III) chloride, toluene is formed:
3) Chlorination of toluene in the light will lead to the formation of benzyl chloride:
4) Benzyl chloride reacts with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide to form benzyl alcohol:
5) A solution of potassium dichromate acidified with sulfuric acid oxidizes benzyl alcohol into benzoic acid:
Task 33.9
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Open Unified State Exam task bank
Solution
1) As a result of the reaction with an aqueous solution of potassium permanganate, toluene is oxidized to potassium benzoate:
2) Fusion of potassium benzoate with potassium hydroxide will lead to the formation of benzene:
3) As a result of the alkylation of benzene with propylene in the presence of aluminum (III) chloride and hydrogen chloride, isopropylbenzene (cumene) is formed:
4) Isopropylbenzene is chlorinated in the light to produce 2-chloro-2-phenylpropane:
5) 2-Chloro-2-phenylpropane reacts with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide to form 2-phenylpropanol-2:
Task 33.10
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Open Unified State Exam task bank
Solution
1) Benzene is hydrogenated with excess hydrogen in the presence of platinum to cyclohexane:
2) Cyclohexane is brominated in the light to form bromocyclohexane:
3) Bromocyclohexane is dehydrobrominated under the action of an alcohol solution of potassium hydroxide to form cyclohexene:
4) Cyclohexene adds water to form cyclohexanol:
5) Cyclohexanol is oxidized under the action of a solution of potassium dichromate acidified with sulfuric acid into cyclohexanone:
Task 33.11
Write the reaction equations that can be used to carry out the following transformations:
When writing reaction equations, use the structural formulas of organic substances.
Source - Open Unified State Exam task bank
Solution
1) Methyl propionate undergoes a hydrolysis reaction to form propionic acid and methanol:
2) Methanol reacts with hydrogen chloride to form chloromethane:
3) Chloromethane alkylates benzene to form toluene:
4) As a result of nitration of toluene with a mixture of concentrated nitric and sulfuric acids, 4-nitrotoluene (p-nitrotoluene) is obtained:
5) 4-Nitrotoluene is reduced by hydrogen released during the interaction of Fe and HCl to 4-methylaniline (p-toluidine). The latter further reacts with HCl to form the corresponding salt:
Overall reaction equation:
Beneficial features
The benefits of sodium bicarbonate come from its alkaline pH. It is the ability to react with acids and alkalize the environment that underlies the following beneficial properties of baking soda:
- acid neutralizing;
- antiseptic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- antipruritic;
- drying;
- antifungal;
- sputum thinner;
- softening and whitening skin.
Such a variety of useful properties allows this compound to be used in folk and traditional medicine to treat many diseases and normalize human well-being in various pathological and physiological conditions.
Possible harm
Baking soda should be consumed internally in limited quantities and according to strict indications. Bicarbonate crystals in large quantities are toxic to the mucous membrane of the digestive system and can cause severe irritation and allergic reactions.
It is not recommended to use solutions based on sodium bicarbonate for people suffering from erosive and ulcerative processes of the stomach and intestines, low stomach acidity and anacid gastritis.
If you regularly inhale carbon dioxide vapor or bicarbonate crystals, for example, in the production of soda, irritation of the respiratory mucosa may occur.
Frequent use of soda solution threatens persistent organic disorders of the digestive system. Alkalinization of gastric juice occurs, as well as a shift to the highly alkaline side of the intestinal contents.
Sodium bicarbonate solution for infusion 40 mg/ml 200 ml, 28 bottles
Registration Certificate Holder
DALHIMFARM (Russia)
Dosage form
Medicine - Sodium hydrocarbonate
Description
Solution for infusion
transparent, colorless.
1 ml
sodium bicarbonate 40 ml
Excipients
: water for up to 100 ml.
100 ml - bottles for blood and blood substitutes (1) - cardboard packs. 100 ml - bottles for blood and blood substitutes (35) - cardboard boxes. 200 ml - bottles for blood and blood substitutes (1) - cardboard packs. 200 ml - bottles for blood and blood substitutes (28) - cardboard boxes. 400 ml - bottles for blood and blood substitutes (1) - cardboard packs. 400 ml - bottles for blood and blood substitutes (15) - cardboard boxes.
Indications
Metabolic acidosis (including with diabetes mellitus, infections, intoxication, kidney disease, anesthesia, in the postoperative period); as a symptomatic remedy for relieving heartburn, discomfort in the epigastrium associated with increased acidity of gastric juice; symptomatic treatment of cough with viscous and difficult to separate sputum in various diseases of the respiratory tract; sea and air sickness.
For local use: inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, eyes, upper respiratory tract, for loosening earwax.
Contraindications for use
Conditions accompanied by the development of metabolic alkalosis.
pharmachologic effect
An antacid that regulates the blood circulation hormone. It has alkaline properties, increases the alkaline reserve of the blood. When taken orally, it quickly neutralizes the hydrochloric acid of gastric juice and has a quick but short-term antacid effect. Irritates the receptors of the gastric mucosa, increases the release of gastrin with secondary activation of secretion, can cause discomfort in the stomach (due to its distension) and belching.
It has an expectorant effect by reducing the viscosity of sputum due to a shift to the alkaline side of the reaction of bronchial mucus.
When absorbed, it leads to the development of alkalosis. Alkalinization of urine prevents the deposition of uric acid in the urinary tract.
Relieves symptoms of sea and air sickness.
Drug interactions
With simultaneous use, the excretion of amphetamine in the urine decreases due to an increase in urine pH under the influence of sodium bicarbonate.
When ingesting sodium bicarbonate while using lithium carbonate in established maintenance doses, a decrease in the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma is possible, which is due to the influence of sodium ions.
When used simultaneously with methotrexate, the excretion of methotrexate in the urine increases and its toxic effect on the kidneys decreases due to an increase in urine pH under the influence of sodium bicarbonate.
With simultaneous oral administration, the absorption of tetracyclines is reduced.
Due to the increase in urine pH under the influence of sodium bicarbonate, there is a delay in the excretion of ephedrine from the body and an increased risk of side effects (tremor, anxiety, sleep disturbances, tachycardia).
With intravenous drip administration of sodium bicarbonate, the antihypertensive effect of reserpine may be enhanced.
Dosage regimen
Apply orally, parenterally, locally externally. The dosage regimen depends on the indications and route of administration.
Side effect
With long-term use
possible development of alkalosis (sometimes uncompensated), accompanied by loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, pain in the epigastric region, anxiety, headaches, and in some severe cases tetanic convulsions; increased blood pressure, flatulence (when taken orally).
special instructions
It is not recommended to use systematically due to the fact that when hydrochloric acid of the stomach is neutralized with sodium bicarbonate, carbon dioxide is released, which has a stimulating effect on the receptors of the gastric mucosa, increases the release of gastrin and can cause a secondary increase in secretion. In addition, with long-term regular use, urine may become alkaline and increase the risk of phosphate stones.
Intensive removal of CO2 can provoke perforation of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
In patients with underlying heart or kidney disease, excess sodium intake causes edema and heart failure.
Use for renal impairment
Restrictions for impaired renal function - With caution.
In patients with underlying kidney disease, excess sodium intake causes edema and heart failure.
Medical use
Sodium bicarbonate is widely used in medicine. At the same time, soda is used in various fields: dermatology, gastroenterology, cardiology, pulmonology, dentistry, toxicology, and ENT pathologies. Sodium bicarbonate helps against heartburn, nausea, motion sickness.
This substance is used internally in the form of a soda drink and externally in dry form, in the form of a paste or aqueous solution for rubdowns, lotions, and baths.
In dentistry
Rinsing the mouth with a solution of sodium bicarbonate relieves local inflammation, relieves toothache, strengthens gums, and eliminates unpleasant odor. Baking soda can be used as a toothpaste substitute to whiten teeth.
In gastroenterology
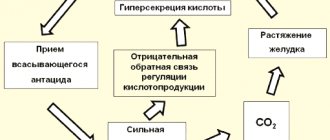
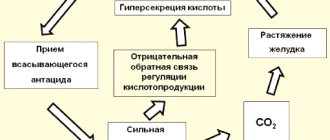
For nausea, make a strong soda solution (1 tablespoon per glass of water) and drink it slowly. For severe heartburn, it is recommended to dissolve a teaspoon of soda in a glass of water and drink. Thus, the patient’s condition improves for some time. However, it should be noted that if you experience frequent heartburn, you should consult a doctor and not treat yourself with soda at home. The habitual intake of an alkaline solution causes a neutralization reaction between hydrochloric acid and soda, resulting in the release of a lot of carbon dioxide, which causes bloating. The resulting carbon dioxide irritates the chemoreceptors of the stomach, thereby stimulating a reflex increase in the formation of gastric juice.
In cardiology
Hydrocarbonate baths help normalize blood pressure and heart rate, which is useful in case of interruptions in the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. Soda increases urination, which reduces the total volume of circulating blood. As a result, the pressure of the blood column on the walls of blood vessels decreases and blood pressure drops slightly.
Taking sodium bicarbonate solution orally with a sharp increase in blood pressure is a first aid remedy for a hypertensive crisis at home. If you drink a soda drink along with antihypertensive medications, the effect will increase.
In dermatology
Soap and soda baths and applications help get rid of fungal nail infections, as well as calluses and corns. A paste of baking soda and water should be used to treat areas of skin burns when exposed to acids, as well as areas of skin with sunburn. You need to moisten the areas of mosquito bites and other insects on the skin with water with baking soda dissolved in it. For severe itching, you can sprinkle the skin with dry powder.
If you have problems with the smell of sweat, treat your armpits with a soda solution. Bacteria and fungi that multiply in sweat and produce acids that cause an unpleasant odor will die. Sodium bicarbonate neutralizes these acids and exhibits a moderate antiseptic effect.
Hydrocarbonate-based foot baths are made for fungal diseases of the feet and nails. They also help soften rough heel skin before a pedicure. Hot baths of a strong solution of baking soda help with felon (purulent inflammation under the nail).
For ENT pathologies
Sodium bicarbonate, when released into viscous sputum, reacts with the acids contained in it. The resulting bubbles of carbon dioxide and water dilute the mucus, increase its quantity and make coughing easier.
To prepare an expectorant for tracheitis, laryngitis, bronchitis, as well as for severe cough, dilute a teaspoon of baking soda in 200 ml of warm milk. This elixir is drunk before bed. Instead of such a drink, you can do steam inhalations with soda. A tablespoon of powder is diluted in a liter of hot water and breathed over it. To enhance the effect, you can add a few drops of essential oils of eucalyptus, pine or rosemary to the solution. Gargling with a solution of salt and soda relieves inflammation of the tonsils with sore throat.
Intravenous administration of a sterile aqueous solution of sodium bicarbonate is often used in intensive care, infectious diseases departments and toxicology for poisoning and intoxication. metabolic acidosis.
Types of soda
There are several sodium salts that contain the word “soda” in their names:
Soda ash or sodium carbonate (Na2CO3).
Crystalline or washing soda (Na2CO3×10H2O).
Baking soda, bicarbonate of soda or sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3).
Caustic soda, sodium hydroxide, caustic soda, caustic soda, caustic alkali (NaOH).
Soda was first described in 1801 by the German pharmacist B. Rose. Nowadays, it is widely used for both industrial and domestic purposes.
Qualitative reaction to sodium cation ( Na + )
Alkali metal compounds give flames different characteristic colors. To confirm the qualitative composition of the starting substances, it is necessary to add a small amount of this substance to the flame of an alcohol lamp. Sodium salts give the flame of a spirit lamp a yellow color.
Qualitative reaction to carbonate ion (CO 3 2- ) and bicarbonate ion ( HCO 3 - )
Carbonate and bicarbonate ions give a qualitative reaction with H+. The visual effect of this reaction is the release of gas. To determine the presence of a carbonate ion in a solution, it is necessary to interact with a solution containing the Ca2+ cation. In this case, a white precipitate will form. The bicarbonate ion does not have this effect, since calcium bicarbonate (Ca(HCO3)2) is a water-soluble substance.
N a 2 CO 3 + CaC l 2 → CaC O 3 ↓ + 2 N aC l
2Na+ + CO32- + Ca2+ + 2Cl‾ → CaCO3↓ + 2Na+ + 2Cl‾
Ca2+ + CO32- → CaCO3↓
NaHCO 3 + HCl → NaCl + H 2 O + CO 2 ↑
Na+ + HCO3- + H+ + Cl- → Na+ + Cl- + H2O + CO2↑
HCO3- + H+ → H2O + CO2↑
Na 2 CO 3 + 2HCl → 2NaCl + H 2 O + CO 2 ↑
2Na+ + CO32- + 2H+ + 2Cl- → 2Na+ + 2Cl- + H2O + CO2↑
2H+ + CO32- → H2O + CO2↑
Evidence that carbon dioxide is actually being released is the cloudiness of limewater when CO2 is passed through it as a result of the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate.
CO 2 + Ca ( OH ) 2 → CaCO 3 ↓ + H 2 O
With further passage of carbon dioxide through the solution, dissolution of the precipitate is observed as a result of the reaction:
CaCO 3 + H 2 O + CO 2 → Ca(HCO 3 ) 2
Carbon dioxide is heavier than air and does not support combustion, so if you collect carbon dioxide in a glass with a burning candle in it, it will go out.
Formation of sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate from sodium hydroxide
When excess carbon dioxide is passed through a solution of sodium hydroxide, as well as when the NaOH solution is left in the open air for a long time, the following reaction occurs:
C O 2 + 2 N aOH → N a 2 C O 3 + H 2 O
CO2 + 2Na+ + 2OH- → 2Na+ + CO32- + H2O
CO2 + 2OH- → CO32- + H2O
N a 2 C O 3 + C O 2 + H 2 O → 2 Na HC O 3
2Na+ + CO32-+ CO2 + H2O→ 2Na+ + 2HCO3-
CO32-+ CO2 + H2O→ 2HCO3-
In this regard, the “old” solution of sodium hydroxide, when interacting with an acid, gives a qualitative reaction to the carbonate ion.
Determination of the medium (pH) of solutions of carbonate, bicarbonate and sodium hydroxide
We apply solutions of carbonate, bicarbonate and sodium hydroxide to the universal indicator. Using the pH scale values, we determine the solution environment. For sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) pH ≈ 8 is a weakly alkaline environment, sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) pH ≈ 12 and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) pH ≈ 14 is a highly alkaline environment.
Sodium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate are salts that are formed by a strong base and a weak acid, so they undergo hydrolysis in solution.
N a 2 C O 3 + H 2 O ↔ N aHCO 3 + NaOH
N aHC O 3 + H 2 O ↔ N aOH + H 2 O + C O 2 ↑
If you heat a solution of sodium bicarbonate to a boil and boil for a while, and then determine the medium of the solution, the universal indicator will show a pH of ≈ 12. This can be explained by the process of converting sodium bicarbonate into sodium carbonate when heated.
2 N aHC O 3 → N a 2 CO 3 + H 2 O + C O 2 ↑
Hydrolysis (mutual enhancement of hydrolysis)
When two salts interact, formed by a strong base and a weak acid, as well as a weak base and a strong acid, a mutual enhancement of hydrolysis occurs, and not an exchange reaction, as it might seem at first glance.
For example:
2А1С1 3 + 3 N а 2 С O 3 + 3Н 2 O → 2А1(ОН) 3 ↓ + 6 N аС1 + 3С O 2 ↑
2Al3+ + 6Cl- + 6Na+ + 3CO32- + 3H2O → 2А1(ОН)3↓ + 6Nа+ + 6С1- + 3СО2↑
2Al3+ + 3CO32- + 3H2O → 2A1(OH)3↓ + 3СO2↑
2 F eC1 3 + 3 N a 2 C O 3 + 3H 2 O → 2 F e (OH) 3 ↓ + 6 Na C1 + 3C O 2 ↑
2Fe3+ + 6Cl- + 6Na+ + 3CO32- + 3H2O → 2Fe(OH)3↓ + 6Nа+ + 6С1- + 3СO2↑
2Fe3+ + 3CO32- + 3H2O → 2Fe(OH)3↓ + 3СO2↑
2Cr C 1 3 + 3N a 2 C O 3 + 3 H 2 O → 2Cr( OH ) 3 ↓ + 6Na C 1 + 3 C O 2 ↑
2Cr3+ + 6Cl- + 6Na+ + 3CO32- + 3H2O → 2Cr(OH)3↓ + 6Nа+ + 6С1- + 3СО2↑
2Cr3+ + 3CO32- + 3H2O → 2Cr(OH)3↓ + 3СO2↑
Conclusion
Carrying out qualitative reactions helps to establish the exact composition of the starting substances.
The medium of the salt solution (pH) will depend on the strength of the acid and base from which the salt under study is formed.
- Alkali metal hydroxides easily react with carbon dioxide contained in the air.
The course of the reaction and the nature of the products formed depend on the composition of the interacting salts.
Studying the chemical properties of the substances around us contributes to their competent use in various life situations.
Literature:
- Encyclopedia for children. [Volume 17.] Chemistry [Text] / ed. board: M. Aksenova, I. Leenson, S. Martynova and others - 2nd ed., revised. - M.: World of Avanta+ encyclopedias, AST, 2013. - 656 p.
- Lidin R. A., Alikbekova L. Yu. Handbook for high school students and applicants to universities [Text] / R. A. Lidin, Alikbekova L. Yu. - M.: AST PRESS SCHOOL, 2006. - 512 p.
- Leenson I. A. Transformation of substances. Chemistry [Text] / I. A. Leenson. - M.: OLMA Media Group, 2013. - 303 p.
Use in cooking
Sodium bicarbonate is also widely used in cooking. The ability of soda to release carbon dioxide when quenched with vinegar allows it to be used as a leavening agent. Slaked soda adds fluffiness to omelette and dough. You can quench soda with vinegar or add powder to sour cream or kefir dough. In the second case, lactic acid will play the role of vinegar.
Adding it to legume dishes allows you to reduce their cooking time. Using baking soda in a meat marinade can soften tough muscle fibers. Berry and fruit mousses, when a pinch of soda is added to them, become sweeter, and coffee and tea become more transparent and aromatic.
In order to get rid of nitrates in vegetables, they need to be soaked in a soda solution. Darkened potatoes can be lightened using the same method.
Application on the farm
The substance is also irreplaceable in everyday life. It is an excellent cleaning agent. To restore their shine, chrome items and silverware are rubbed with dry soda, washed with soapy water, and then wiped dry with a soft cloth.
Sodium bicarbonate powder applied to a damp sponge will remove scratches and abrasions on vinyl flooring. Tile, kitchen stove, sink and plumbing fixtures can be cleaned of dirt by treating them with a thick mixture of baking soda and water. The same mixture helps get rid of the specific cat odor in places where there were “marks”.
To remove odors
The good hygroscopicity of sodium bicarbonate is the reason why it quickly absorbs odors, so it can be used to eliminate various odors. To get rid of unpleasant odors in the refrigerator, you need to pour dry powder into a glass and place it in the refrigerator door. By changing the contents of the glass as needed (once every 1-2 months), you can permanently get rid of the specific “refrigeration” smell.
If the smell of sour milk persists, the “smelling” containers should be cleaned with dry powder. Do the same with dishes that smell of fish.
If you pour a few tablespoons of powder into the drain hole, and after a few minutes turn on warm water, you can eliminate the unpleasant odor from the siphon under the sink.
Baking soda will also help deal with the unpleasant odor from the carpet. To do this, sprinkle the carpet with powder, leave it for 20-30 minutes, and then vacuum it thoroughly. However, this method is only suitable for non-fading carpets.
Using baking soda, you can also prevent the appearance of unpleasant odors, for example, from a washing machine or dishwasher when they are idle for a long time. When leaving home for a long time, you should rub the inside surface of the machines with dry bicarbonate and leave their doors ajar, and after returning, run them in the rinsing mode.
For clothing care
When machine washing, it is good to add baking soda to the washing powder. This will help get rid of the unpleasant odor in the washing machine, improve the quality of washing and the aroma of washed clothes. Clothes that smell bad can be washed in a machine by sprinkling them generously with baking soda.
A wet swimsuit will not become moldy and will not smell unpleasant if, after swimming in a pool or natural body of water, you put it in a bag with soda, and rinse it thoroughly and dry it at home.
Why else do you need soda?
Was this whole complex process of making baking soda invented just to make the loaves fluffier? This product can be very useful in everyday life, while it is absolutely safe, non-toxic, fire and explosion proof.
Soda is a universal detergent and cleaner: for dishes, tiles, sinks, bathrooms, but it does not harm the skin of your hands and is completely washed off with water. Using soda, you can descale the kettle (2 tbsp soda + 500 ml boiling water, 5 hours) and clean the drain pipes (5 tbsp soda + 100 ml vinegar, 1 hour).
Another feature of soda is that it not only cleans, but gets rid of unpleasant odors, so it can be applied to the carpet or upholstered furniture, left for 10-15 minutes, and then vacuumed.
Soda is a mild abrasive that cleans and disinfects children's clothes and toys, while being absolutely safe for babies' skin. To effectively remove stains and eliminate unpleasant odors during washing, you can add soda: unlike some washing powders, soda is hypoallergenic.
Baking soda is an excellent cleaning agent
Use in cosmetology
Baking soda is an excellent cosmetic product. A scrub made from crushed oatmeal and dry sodium bicarbonate has a good cleansing and whitening effect. After such a scrub, the skin becomes soft, and its regular use gets rid of acne. To add shine to your hair after washing your hair, you need to treat it with a solution of soda and lemon juice.
For weight loss
Sodium bicarbonate is also used for weight loss. To lose up to 2 kg in one procedure, you can fill a bath with warm water and dissolve 0.5 kg of sea salt and 0.3 kg of regular baking soda in it. Anyone losing weight needs to immerse themselves in such a bath for 20 minutes. In this case, the water temperature should be about 40°C. A soda-salt solution relaxes muscles, relieves fatigue and nervous tension, cleanses lymphatic vessels, and reduces tissue swelling. After a bath, you don’t need to dry yourself: just put on a warm robe. It is better to do such water procedures before bed.
Industrial use
Baking soda as a food additive E500 is used by the food industry in the production of bakery, flour, confectionery, sausage products, carbonated drinks, as well as for cleaning industrial equipment.
The chemical industry uses sodium bicarbonate in the production of dyes, reagents, household chemicals, and foams. Powder fire extinguishers are filled with bicarbonate.
In light industry, soda is used in tanning, for the production of artificial leather, silk and cotton fabrics.