Release form
Powder for preparing a solution for infusion therapy. In bags of 50 g.
Powder for the preparation of a solution for topical use and oral administration. In bags of 10, 25 and 50 g.
Solution for infusion 4%. Available in 2 and 5 ml in disposable containers made of polymer materials; 100, 200 and 400 ml bottles; 100 and 250 ml in polymer containers.
Tablets 0.3 and 0.5 g.
Suppositories for rectal use 0.3, 0.5 and 0.7 g, 10 suppositories per package.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Helps restore the disturbed balance of water and electrolytes, as well as acid-base balance.
During the dissociation (in chemistry and biochemistry - the reversible decomposition of complex substances into individual elements and/or constituent components) of sodium bicarbonate, the bicarbonate anion is released. It binds hydrogen ions, resulting in the formation of a carboxylic acid, which subsequently breaks down into water and carbon dioxide (released during respiration).
This causes an alkaline shift and an increase in the buffer capacity of the blood.
Sodium bicarbonate increases osmotic diuresis and excretion of Na and Cl ions from the body, reduces the acidity of urine, and prevents the sedimentation of uric acid in the urinary system.
Bicarbonate anion does not penetrate into the intracellular space.
The pharmacokinetic profile of the drug has not been studied.
Benefits and harms
Despite the fact that alkalinity is not standardized in most types of water (except bottled), alkalinity has a physiological effect: when drinking water with high alkalinity, negative consequences for the body are inevitable. Free alkalinity is the most dangerous. It is better to control total and carbonate alkalinity (in the absence of free alkalinity) by the content of hydrocarbonates. Their content should not exceed 400 mg/l.
With increased alkalinity, the following is observed:
- violation of acid-base balance;
- decreased alkaline reserve of blood;
- decreased acidity of gastric juices;
- acceleration of urea filtration;
- increased risk of developing hypoacid gastritis.
Indications for use: what does baking soda treat?
Use in medicine is indicated for diseases that are accompanied by an increase in the acidity of digestive juice in the stomach, peptic ulcer , metabolic acidosis (including acidosis that develops in the postoperative period or against the background of diabetes mellitus , infectious disease , intoxication ).
Treatment with the drug is used for inflammatory ophthalmological diseases , as well as for inflammatory diseases of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and oral cavity .
The medicinal properties of baking soda are used in cases where there is a need to loosen earwax and dilute the secretions of the bronchial glands , to alkalize urine and reduce discomfort in mild infections of the urinary system , and in tubular (tubular) renal acidosis .
Sodium bicarbonate is also used in therapy aimed at removing cystine and urate kidney stones .
Contraindications
Contraindications for treatment with baking soda:
- hypersensitivity;
- conditions that are accompanied by the development of alkalosis .
In addition, hypochloremia and hypocalcemia . In the first case, taking sodium bicarbonate can provoke a long-term decrease in absorption in the digestive canal and vomiting, which in turn leads to a significant loss of chlorine ions by the body, including severe alkalosis .
Taking soda during hypocalcemia may be accompanied by tetanic convulsions and an increased risk of alkalosis .
Side effects
Long-term use of sodium bicarbonate leads to alkalosis (increased blood pH), the clinical manifestations of which are:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- deterioration of appetite (to the point of complete loss);
- stomach ache;
- tetanic convulsions (in especially severe cases);
- increase in blood pressure.
When using suppositories, a laxative effect may develop, the urge to defecate, rumbling, diarrhea and flatulence .
Sodium bicarbonate: instructions for use
Instructions for use of sodium bicarbonate powder
Sodium bicarbonate powder is used to prepare aqueous solutions for washing, rinsing and inhalation use.
For stomatitis , rhinitis , laryngitis and a number of other diseases of the mouth, nose and throat, prepare a solution with a concentration of 0.5-2%.
To wash the skin and mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract when they are damaged by acids, poisonous (phosphorus and organochlorine) and irritating substances, a two percent solution should be used.
Instructions for solution for intravenous administration
The solution for infusion should be used under control of the alkaline state of the blood. For adults it is administered by drip, into a vein or rectally, for children - intravenously.
The product can be used pure or diluted. For dilution, use a five percent glucose solution (in a 1:1 ratio).
The rate of administration is 60 drops/min, the daily dose is up to 200 ml. The frequency of infusions depends on the acid-base balance readings.
Newborn children are administered into a vein at a dose of 4-5 ml/kg, children of other age groups - at a dose of 5-7 ml/kg.
The need for repeated administration is determined by indicators of acid-base balance (acid-base balance).
How to take sodium bicarbonate tablets?
The tablets are taken orally several times during the day. A single dose for an adult varies from 0.5 to 1 g, for a child - from 0.1 to 0.75 g (depending on age and indications).
Treatment according to Neumyvakin: how to treat with soda so as not to harm?
Following the recommendations of Professor Neumyvakin, sodium bicarbonate (sodium bicarbonate is the same as soda) should be taken on an empty stomach about 20-30 minutes before breakfast and dinner. If possible, you can introduce another dose during the daytime.
The main principle of treatment is that taking soda cannot be combined with the digestion process. This is due to the fact that when food enters the stomach, an acidic environment is formed in it. The environment of an empty stomach is neutral.
Begin treatment with half a coffee spoon of the product per day. For dilution, use 200 ml of hot milk or a similar volume of hot water. You should not boil water/milk, as this will result in a completely different formula. You can also take soda without stirring it in liquid, but simply drink it with it.
Treatment is carried out in three-day courses, between which intervals of the same duration are maintained. If the body reacts normally to taking soda, the single dose can be increased to 7-10 grams (corresponding to the volume of 1 teaspoon).
After three days of regular use of the drug, you should again take a three-day break.
Gradually, monitoring the person’s health status and not forgetting the need to take breaks in treatment, the dose is increased to 7-30 grams.
The beneficial properties of sodium bicarbonate are due to the ability of this product to neutralize acid, maintain an optimal balance of acids and alkalis in the body, and also increase the body’s alkaline reserve.
Using soda, acid deposits in the digestive canal, kidneys and liver are removed, and blood vessels are cleaned. A soda enema given after taking Piperazine increases the effectiveness of the latter when infected with pinworms and roundworms .
In addition to oral administration, rinsing the mouth and throat with a solution of baking soda and hot baths with the addition of sea salt and soda are also very beneficial for human health. The water should be heated to a temperature of 39-42˚C, salt and soda are taken, respectively, at the rate of 100 and 200-250 g per 100 liters of water.
This procedure allows you to improve your skin and musculoskeletal system. Biochemical and energy processes begin to restore in cells, hemodynamics increase, and oxygen absorption by tissues improves. As a result, well-being is normalized, mental performance and physical endurance increase.
Sodium bicarbonate is taken to treat diabetes , cancer , drug addiction, alcoholism and substance abuse.
In addition, soda dissolves deposits harmful to the spine and joints, alleviates the patient’s condition with gout , osteochondrosis , rheumatism , polyarthritis , cholelithiasis and urolithiasis .
Treating Cancer with Baking Soda: Sodium Bacarbonate Against Cancer
Tullio Simoncini (a doctor from Italy) believes that cancer is nothing more than a greatly overgrown colony of fungi of the genus Candida, and the traditional interpretation of the nature of the disease is fundamentally incorrect.
What in official medicine is considered to be uncontrolled cell division, in his opinion, is a process that the body launches on its own to fight thrush .
Following this theory, it can be assumed that the fungus, which is usually well controlled by the immune system of a healthy person, begins to actively multiply in a weakened body, forming a large colony.
When an organ is infected with thrush , the immune system reacts to it by building a protective barrier from the body's cells. Metastasis can be explained by further growth of the colony and migration of the fungus in the body.
Only cells of a normally functioning immune system can destroy the fungus. Thus, the key to recovery is a strong immune system.
The reason for decreased immunity and, consequently, the occurrence of many serious diseases is a decrease in pH. If we talk about cancer , then the optimal environment for their development is an acidic environment, that is, an environment in which the pH value does not exceed 5.41.
In a newborn child, for comparison, it is 7.41, and in a healthy adult it should range from 7.3 to 7.4.
The recommendations in the Physician's Handbook, dated 1973, indicate that patients with a pH of 7.25 or lower should be prescribed alkalizing therapy, or, in other words, they are recommended to take from 5 to 40 grams of soda per day.
Soda restores intracellular metabolism , prevents the loss of potassium and enhances the absorption of oxygen.
Sodium bicarbonate for the treatment of cancer is taken on an empty stomach, half an hour before meals, starting with a volume equal to a fifth of a teaspoon, and gradually increasing the dose by 2-3 times.
A single dose is diluted in 200 ml of hot milk (very warm water) or washed down with the same amount of water/milk. You need to take the “medicine” 2 or 3 times a day.
Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda)
Sodium bicarbonate
(English
sodium bicarbonate
; synonyms:
sodium bicarbonate, sodium bicarbonate, baking soda, baking soda
) is an antacid that normalizes acid-base balance.
Sodium bicarbonate is a chemical substance
Sodium bicarbonate is an acidic sodium salt of carbonic acid. Chemical formula of sodium bicarbonate: NaHCO3. Sodium bicarbonate is a white, odorless, crystalline powder with a salty-alkaline taste. Sodium bicarbonate is stable in dry air, but decomposes slowly in humid air. Easily soluble in water to form alkaline solutions. The acidity of a five percent sodium bicarbonate solution = 8.1 pH. Sodium bicarbonate is practically insoluble in ethanol. Molecular weight 84.01. Sodium bicarbonate reacts with acids to form a salt and carbonic acid, which immediately breaks down into carbon dioxide and water.
Sodium bicarbonate - medicine
Sodium bicarbonate (this is its name in pharmaceuticals) is the international nonproprietary name (INN) of the drug. According to the pharmacological index, sodium bicarbonate belongs to the groups “Regulators of water-electrolyte balance and acid-base balance” and “Antacids”, according to ATC - to the group: “B05 Plasma-substituting and perfusion solutions” and has codes B05CB04 and B05XA02. In addition, in the group “A02 Drugs for the treatment of diseases associated with acidity disorders” there is a five-digit code “A02AH Antacids in combination with sodium bicarbonate”.
Sodium bicarbonate therapy for pregnant and nursing mothers
Due to the unwanted side effects of sodium (edema and weight gain), some experts advocate the use of alternative antacids that do not contain sodium bicarbonate in pregnant women. FDA Fetal Risk Category for sodium bicarbonate therapy is "C" (animal studies have shown adverse effects on the fetus and there have been no adequate studies in pregnant women, but the potential benefit associated with the drug in pregnant women may justify its use , despite the existing risk). Due to the lack of data on the excretion of sodium bicarbonate into breast milk, there are no restrictions for the treatment of breastfeeding mothers.
Baking soda is a traditional but dangerous remedy for relieving heartburn.
| All moods and voices Chewed down to one. Enough soda for heartburn! So this is your result, skill? B.L. Parsnip. "All moods and voices." 1936. |
Sodium bicarbonate is a traditional remedy for relieving heartburn, an absorbable antacid. Absorbed antacids are those that either themselves or the products of their reaction with gastric acid dissolve in the blood.
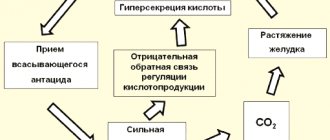
A positive quality of absorbed antacids is the rapid decrease in acidity after taking the medicine. Negative - short duration of action, acid rebound (increased secretion of hydrochloric acid after the end of the drug's effect), the formation of carbon dioxide during their reaction with hydrochloric acid, stretching the stomach and stimulating gastroesophageal reflux (see the figure on the right from the article by D.S. Bordin)
. Absorption of bicarbonates into the blood can lead to the development of systemic alkalosis, and their long-term use in combination with a dairy diet can lead to the development of Burnett's syndrome (milk-alkali syndrome).
After taking 3 g of sodium bicarbonate, the pH of the gastric contents remains above 3 pH units for only 75 minutes. The carbon dioxide formed during neutralization causes belching and bloating. As a rare complication after taking sodium bicarbonate, gastric rupture due to the sudden release of a large amount of gas has been described (A.V. Okhlobystin).
In the 19th century, “soda” was one of the most popular remedies for heartburn; for example, P.I. constantly took it. Chaikovsky.
Sodium bicarbonate in acid-suppressing drugs
Despite the negative attitude towards sodium bicarbonate as a means of relieving heartburn, it is sometimes included in medications intended to reduce acidity in the upper gastrointestinal tract, in sufficient quantities to be considered as another active ingredient (although the instructions for this sodium bicarbonate may be listed among the excipients rather than the active substances).
Proton pump inhibitors
.
There are two versions of the proton pump inhibitor Zegerid
.
Zegerid itself is prescription and over-the-counter Zegerid OTC
.
Zegerid is not registered in Russia, but Omez Insta
. Both medicines contain omeprazole and sodium bicarbonate. In the US, Zegerid is marketed as the only "immediate response" proton pump inhibitor that does not have the "overnight acid breakthrough" phenomenon. It is intended for relief of symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease, short-term (4-8 weeks) therapy of erosive esophagitis, confirmed by endoscopy, gastric and duodenal ulcers. The content of omeprazole and sodium bicarbonate in various dosage forms of these drugs is given in the table:
| Main Ingredients | Zegerid , capsule | Zegerid , capsule | Zegerid , sachet* | Zegerid , sachet* | Zegerid OTC , capsule | Omez Insta , sachet* |
| Omeprazole , mg | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 | 20 | 20 |
| Sodium bicarbonate , mg | 1100 | 1100 | 1680 | 1680 | 1100 | 1680 |
Note.
*) The sachet contains powder for the preparation of a suspension for oral administration. Alginates.
The only medicine for the treatment of acid-related diseases from this group approved in Russia, as well as in the USA, is
Gaviscon
and its variants Gaviscon Forte and Gaviscon Double Action. In addition to the “main” active ingredient - sodium alginate, Gaviscon contains sodium bicarbonate and calcium carbonate. When sodium alginate enters the stomach, it quickly reacts with its acidic contents, resulting in the formation of an alginate gel that has an almost neutral acidity value (gel pH is about 7). The gel forms a protective barrier on the surface of the stomach contents, preventing the occurrence of gastroesophageal reflux. In case of regurgitation or reflux, the gel enters the esophagus, where it has a neutralizing effect on hydrochloric acid and pepsin that enter during reflux and additionally protects the mucous membrane of the esophagus. The content of sodium alginate and sodium bicarbonate in various dosage forms of Gaviscon is given in the table:
| Main Ingredients | Gaviscon , 10 ml suspension | Gaviscon , chewable tablet | Gaviscon forte , 10 ml suspension | Gaviscon Double Action , chewable tablet | Gaviscon Double Action , 10 ml suspension |
| Sodium alginate , mg | 500 | 250 | 1000 | 250 | 500 |
| Sodium bicarbonate , mg | 267 | 133,5 | — | 267 | 213 |
Sodium bicarbonate in other medicines
In addition to the medications described above for the treatment of acid-dependent diseases, sodium bicarbonate is included as an active ingredient, in particular, in the following medications:
- osmotic laxative Endofalk
, one sachet of which includes: macrogol 3350 52.5 g, sodium chloride 1.4 g, sodium bicarbonate 715 mg, potassium chloride 185 mg - osmotic laxative Lavacol
, one sachet of which includes: macrogol 4000 12.0 g, sodium sulfate anhydrous 1.0 g, sodium bicarbonate 0.6 g, sodium chloride 0.2 g, potassium chloride 0.2 g - antitussive drug Codelac
, one tablet of which contains: codeine 8 mg, sodium bicarbonate 200 mg, licorice root powder 200 mg, thermopsis lanceolate herb powder 20 mg - a drug for the treatment of cough that has a mucolytic and expectorant effect, Codelac Broncho
, one tablet of which contains: ambroxol hydrochloride 20 mg, sodium glycyrrhizinate 30 mg, thermopsis dry extract 10 mg, sodium bicarbonate 200 mg - solution for infusion with detoxification effect Gemodez-N
, 100 ml of which contains: medical povidone with a molecular weight of 8000 6 g, sodium chloride 550 mg, potassium chloride 42 mg, calcium chloride 50 mg, magnesium chloride anhydrous 500 mcg, sodium bicarbonate 23 mg
The use of sodium bicarbonate in the study of the stomach (Noller test)
The Knoller test (alkaline test) is performed to obtain information about the amount of hydrochloric acid in the patient’s stomach, the intensity of acid formation, and also, indirectly, the amount of gastric juice. The test is carried out simultaneously with the intragastric pH-metry
, 20 minutes after stabilization of acidity under basal conditions or 45 minutes after the administration of stimulants. At a pH equal to or higher than 4.0, the alkaline test is not performed.
The patient drinks 0.5 g of sodium bicarbonate dissolved in 30 ml of distilled water. Typically, the pH in the body of the stomach is recorded below 2.5. As a result of the introduction of alkali into the stomach, the pH values change to alkaline and remain at the same level for a certain time, and then, after some time, called “alkaline time,” they return to the original ones. The alkaline time determines the state of acid production in the patient’s stomach (S.I. Rapoport et al.):
| Assessment of hydrochloric acid production in the stomach | Alkaline time , min | |
| on an empty stomach | upon stimulation | |
| Sharply increased acid production | <10 | <5 |
| Increased acid production | 10–20 | 5–10 |
| Normal acid production | 20–25 | 10–15 |
| Reduced acid production | >25 | >15 |
The figure shows an example of a pH gram in
three sections of the stomach
(in the antrum - lower graph, in the body of the stomach - middle and in the cardiac section of the stomach closest to the esophagus - lower graph) of a patient with chronic superficial gastritis and high acidity in the antrum. Basal acidity is shown (the first 30 minutes, basal - that is, before any stimulation) and acidity after the alkaline test (AL) and histamine stimulation (HT).
Bicarbonates as a natural means of protecting the gastrointestinal tract from acid
In the stomach and duodenum, bicarbonate ions HCO3– are secreted by surface epithelial cells. Bicarbonates play a vital role in the digestive process, neutralizing hydrochloric acid and protecting the tissues of the digestive organs from its effects.
In an acidic environment, bicarbonate ions react irreversibly with hydrogen ions to form water and carbon dioxide:
H+ + HCO3– = H2CO3 = H2O + CO2
Bicarbonates, together with mucus, constitute the so-called pre-epithelial level of protection of the gastric mucosa. Mucus cannot protect the epithelium from H+ ions without bicarbonates constantly entering it, also secreted by the surface epithelium. With the help of bicarbonates, a pH gradient is maintained in the mucus: on the surface facing the lumen of the stomach, the environment is acidic, and on the epithelial cells it is neutral or slightly alkaline. Immediate mixing of bicarbonates with the acidic secretion in the lumen and neutralization does not occur: the mucus layer forms a barrier, due to which the pH gradient exists (T.L. Lapina).
Bicarbonates are also secreted by the ductal cells of the pancreas and, together with pancreatic juice, enter the duodenum, where they participate in the neutralization of hydrochloric acid (O.A. Sablin et al.).
Bicarbonate in mineral waters
Hydrocarbonate ions HCO3– are present in almost all natural mineral waters.
To determine them in water, GOST 23268.3-78 “Healing mineral drinking waters, medicinal table waters and natural table waters” is used. Methods for determining bicarbonate ions". According to GOST R 54316-2011. “Natural drinking mineral waters. General technical conditions" the content of bicarbonates is indicated on consumer packaging (on the labels of bottles of mineral water). Content of hydrocarbonates in some natural mineral waters (g/l):
- healing mineral waters:
- Nagutskaya-17 — 5.0–7.2
- Essentuki No. 17 — 4.9–6.5
- Nagutskaya-56 — 4.2–5.6
- Essentuki No. 4 - 3.4–4.8
- Narzan - 1.0–1.5
- Kashinskaya - less than 0.05
- Gelendzhikskaya 117 — 0.35–0.7
- Essentuki Novaya-55 - 0.2–0.35
Bicarbonate anions give mineral water an alkaline character and most often combine with sodium cations to form sodium bicarbonate. Sodium bicarbonate waters increase the alkaline reserve of the blood, have an antacid effect (by reducing the concentration of H+ ions), reduce pyloric spasm and accelerate the evacuation of gastric contents, which helps reduce pain and dyspeptic symptoms. Alkaline waters thin and help remove excess mucus, which is formed during inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, urinary and respiratory tracts. In addition, they improve nucleic acid metabolism, reduce the formation of uric acid and promote the removal of excess from the body, alkalize bile and increase the secretion of bilirubin, cholesterol and mucus. In diabetes mellitus, these waters reduce hyperglycemia and increase tolerance to carbohydrates. And finally, in combination with bicarbonate, macro- and microelements, in particular iron, are better absorbed from the intestine (Baranovsky A.Yu. et al.).
Professional medical articles addressing the role of bicarbonates and sodium bicarbonate in gastroenterology
- Mikheev A.G., Nevsky D.I., Rakitin A.B., Rakitin B.V. Study of pH dynamics in alkaline dough // Izvestiya VUZov. North Caucasus region. Natural Sciences. – 2006. Special issue. – pp. 44–46.
- Sablin O.A., Grinevich V.B., Uspensky Yu.P., Ratnikov V.A. Stomach. Methods for studying alkaline secretion. Functional diagnostics in gastroenterology. St. Petersburg 2002
- Lapina T.L. Possibilities of medicinal effects on the cytoprotective properties of the gastroduodenal mucosa // Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. – 2006. – No. 5. – volume XVI. – c. 2–7.
- Ushkalova E.A. Clinical pharmacology of modern antacids // Farmateka. – 2006. – No. 11. – p.1–6.
- Gelfand B.R. , Filimonov M.I., Mamontova O.A. and others. Prevention and treatment of stress damage to the gastrointestinal tract in patients in critical conditions // Methodological recommendations. - Moscow. - 2010. - 34 p.
On the website in the literature catalog there is a section “Antacids”, containing articles devoted to the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract with antacids. Back to section
Overdose
hyperalkalosis and tetanic convulsions may develop . hyperalkalosis develops, the drug should be discontinued. If there is a risk of developing tetany of calcium salt of gluconic acid ( calcium gluconate injected into a vein .
Interaction
Under the influence of sodium bicarbonate, urine pH increases, which leads to:
- decreased amphetamine ;
- reducing toxicity and increasing excretion of methotrexate ;
- delaying the elimination of ephedrine and increasing the risk of developing side effects associated with its use - sleep disturbances, increased anxiety, tremor , tachycardia .
When using a maintenance dose of lithium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate helps to reduce the plasma concentration of lithium, which is due to the influence of Na ions.
The drug helps reduce the absorption of tetracyclines when taken orally.
A solution for infusion when administered drip into a vein can enhance the antihypertensive effect of reserpine .
The solution reacts with acids ( ascorbic, nicotinic, etc.), alkaloids (caffeine, atropine , theobromine , apomorphine , papaverine ), salts of calcium, heavy metals (copper, zinc, iron), magnesium, cardiac glycosides , which is accompanied by precipitation or hydrolysis (decomposition) of organic compounds. Therefore, these substances should not be dissolved in sodium bicarbonate solution.
Also, do not mix sodium bicarbonate with solutions that contain phosphorus.
Sodium bicarbonate powder for solution for external use 10g
Name
Sodium bicarbonate pores 10g pack.
Description
White crystalline powder, odorless, slowly decomposes in moist air. Aqueous solutions have an alkaline reaction.
Main active ingredient
Sodium bicarbonate
Release form
Powder
pharmachologic effect
Sodium bicarbonate is a white crystalline powder that dissolves in water to form alkaline solutions. A solution of drinking sodium bicarbonate is used as a weak antiseptic for rinsing, and also as an acid neutralizing agent.
Indications for use
in complex therapy of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity; as a neutralizer for burns of the skin and mucous membranes with acids.
Directions for use and doses
Sodium bicarbonate is used to prepare aqueous solutions for rinsing and washing. For stomatitis, 0.5%-2% solutions are used for rinsing (1 teaspoon of sodium bicarbonate per 1 liter of water - 1 teaspoon of sodium bicarbonate per 1 glass of water). To wash the skin and mucous membranes when acids, irritants and toxic substances (organophosphorus and organochlorine) come into contact with them - 2% sodium bicarbonate solution (1 teaspoon of sodium bicarbonate per 1 glass of water).
Precautionary measures
It is not recommended to take sodium bicarbonate orally. When used orally, urine may become alkaline and increase the risk of phosphate stones. A shift in the acid-base state to the alkaline side with short-term use is not accompanied by clinical symptoms, however, with chronic renal failure, a significant deterioration of the condition is possible. Vomiting, which often accompanies peptic ulcer disease, can increase the severity of alkalosis. The drug is not recommended for use internally to treat heartburn and stomach pain. This is due to the fact that when hydrochloric acid of the stomach is neutralized with sodium bicarbonate, carbon dioxide is released, which has an exciting effect on the receptors of the gastric mucosa, enhances the release of gastrin and can cause a secondary increase in gastric secretion - “acid rebound”. Intense release of CO2 can provoke perforation of the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. In patients with underlying heart or kidney disease, excessive Na+ intake causes edema and heart failure. Use during pregnancy and lactation. If indicated, the use of the drug is possible only after assessing the balance of benefits and risks for the mother and fetus/child. Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and other potentially dangerous mechanisms. Does not affect.
Interaction with other drugs
When used together, urinary excretion of amphetamine is reduced due to an increase in urine pH under the influence of sodium bicarbonate. When ingesting sodium bicarbonate while using lithium carbonate, a decrease in the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma is possible, which is due to the effect of sodium ions. When used together with methotrexate, the urinary excretion of methotrexate is increased and its toxic effect on the kidneys is reduced due to the increase in urine pH under the influence of sodium bicarbonate. When taken orally with sodium bicarbonate, the absorption of tetracyclines is reduced. Due to the increase in urine pH under the influence of sodium bicarbonate, there is a slowdown in the excretion of ephedrine from the body and the possibility of developing adverse reactions (tremor, sleep disturbances, anxiety, tachycardia) increases.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, hypocalcemia, conditions that are accompanied by the development of alkalosis; hypochloremia.
Compound
Sodium bicarbonate - 10 g.
Overdose
An overdose of sodium bicarbonate increases the side effects. Supportive and symptomatic treatment is necessary.
Side effect
With prolonged use - alkalosis and its clinical manifestations: nausea, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, anxiety, tetanic convulsions; increased blood pressure; when using suppositories - urge to defecate, laxative effect, flatulence, diarrhea, rumbling. If the above adverse reactions or adverse reactions not listed in these instructions for medical use of the drug occur, you should consult a doctor.
Storage conditions
Keep out of the reach of children. Store in a place protected from moisture at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
special instructions
What is sodium bicarbonate? All about baking soda
Everyone knows what soda is. It is a fine white crystalline powder with a specific salty-alkaline taste. According to Wikipedia, the substance is completely non-toxic to the human body, and is also explosion and fireproof.
The Pharmacopoeia states that the powder is stable in dry air, practically insoluble in 95% alcohol and highly soluble in water. Decomposes slowly when exposed to moisture.
If sodium bicarbonate is calcined, it loses weight. When the powder is calcined at a temperature of 280-300°C, its mass decreases by at least 36.6%.
The substance is known as sodium bicarbonate, baking (or drinking) soda, sodium bicarbonate (or bicarbonate). Baking soda is a pure substance and is an acid salt of sodium and carbonic acid (H2CO3).
Neutralizes acids (quite often there are instructions like “hydrochloric or nitric acid neutralized with soda”).
The chemical formula of baking soda (or, in other words, the formula of sodium bicarbonate) is NaHCO3. The rational formula of sodium bicarbonate is CHO3Na.
The name of the substance in Latin is Sodium bicarbonate (Sodium hydrogen carbonate).
Sodium bicarbonate is produced in accordance with GOST 2156 76. The standard is valid and applies to the product that is produced for the needs of the chemical, light, food, pharmaceutical and medical industries, retail trade and non-ferrous metallurgy.
Are soda ash and baking soda the same thing? Soda ash - what is it?
Sodium bicarbonate and soda ash are two different products that should not be confused. What is soda ash? This is a substance with the chemical formula Na2CO3. Its main difference from sodium bicarbonate is the degree of alkaline activity.
If sodium bicarbonate is a weak alkali with a pH value of 8.1, then soda ash exhibits strong basic properties (its pH value is 11).
In the All-Russian Classifier of Products, baking soda and soda ash are assigned different OKPD codes.
Soda ash is used for household needs: softening water, cleaning dishes, tiles, washing floors, clearing pipe blockages, preventing scale formation, etc.
Healing properties, benefits and harms of baking soda
The areas of application of sodium bicarbonate are quite diverse. It is used to prevent strokes, treat cancer and a number of other serious diseases, alcoholism, tobacco and any other types of addiction (including toxic and narcotic substances), to remove harmful substances and toxins from the body, and for hair care.
Many Russian doctors recommend using the healing capabilities of baking soda as a worthy alternative to traditional methods of treatment.
Soda destroys acidosis and provokes an alkaline shift, which is accompanied by alkalization of digestive juices, dissociation of water contained in the body into OH- and H+ ions due to amino acids, enzymes, amine alkalis, D- and RNA nucleotides and general improvement of the body.
In a healthy person, the bile and juices of the pancreas and Bruttner glands , and the duodenal should be alkaline: digestion can only proceed normally in an alkaline environment. In addition, an alkaline environment is destructive for parasites - roundworms , worms from the genus Opisthorchis , pinworms , tapeworms , etc.
of thiamine , choline , vitamin PP , pyridoxine , and cobamide increases significantly .
With increased acidity, saliva also becomes acidic, which is why a person’s tooth enamel gradually begins to deteriorate. Therefore, for the treatment of caries and alkalization of saliva, the use of fluoride-containing pastes is supplemented with the administration of soda.
A.T. Ogulov, for example, strongly recommends using this product in the treatment of dental and oral diseases for gum massage, rinsing and oral administration.
A teaspoon of baking soda diluted in a glass of water is a well-known remedy for heartburn. Sodium bicarbonate is also used for the face: adding a pinch of soda every day to the foam or gel for washing, you can thoroughly cleanse the skin of blackheads and a layer of keratinized surface cells, relieve inflammation and get rid of acne.
A mask made from oatmeal (1 cup) and baking soda (1 teaspoon) ground into powder helps very well with rashes. Mix the ingredients well and pour into a glass jar. To prepare the mask, pour a tablespoon of the mixture with water to make a paste. The mass is applied to the face for 15-25 minutes.
The big advantage of the product is that it has no contraindications and is suitable for all skin types.
Soda is used for insect bites, sunburn, cystitis , bad breath and feet, diaper rash, migraines and colds.
Large doses of soda are not absorbed with water and cause diarrhea, which makes it possible to use sodium bicarbonate as a mild laxative.
Knowing everything about what baking soda is and how healthy it is, you should determine whether you can always drink it. So, when can sodium bicarbonate, instead of being beneficial, harm the body?
The drug is dangerous in case of any concomitant diseases of the kidneys and heart, individual intolerance, as well as if it comes into contact with the mucous membrane of the eyes.
When taken systematically, carbon dioxide begins to be released in the stomach, which has a stimulating effect on the receptors of the gastric mucosa, stimulates the release of gastrin and can cause a secondary increase in secretion. Regular use also increases the risk of phosphate stone formation.
The removal of carbon dioxide can cause perforation of the walls of the digestive canal.
What are the benefits of drinking soda in everyday life?
In everyday life, sodium bicarbonate is used in baking bakery and confectionery products, to retain unpleasant odors in the cat's litter box, to clean the trash can from dirt and odors, to wash tiles, wallpaper and bathroom fixtures, to wash hands after working with strong-smelling products (onions, garlic, etc.). d.), speeding up the cooking of legumes, as a remedy for ants.
How to clean your heels with baking soda? What are soda foot baths made from?
Baking soda is often used to soften heels and eliminate unpleasant foot odor. To prepare a bath, add a tablespoon of sodium bicarbonate and a couple of drops of any essential oil to a liter of warm water. Keep your feet in water for 15 minutes (it’s better to take a bath at night).
After the skin has softened, it should be carefully treated with pumice. Then the feet are rinsed with water and lubricated with a rich cream, and socks are put on top.
You can use warm milk instead of water.
To prepare a foot scrub, you can mix 1 teaspoon of vegetable oil (for example, olive) with a tablespoon of soda, or you can simply dilute the soda with water to a paste. The mixture is applied to the skin and massaged well to remove rough skin.
Helena Roerich about baking soda
Roerich E.I. (Russian religious philosopher, public figure and writer) considered the healing properties of baking soda to be so strong that regular use of this simple and affordable remedy twice a day can prevent many diseases, including cancer.
When under severe stress, Elena Ivanovna herself took up to 8 coffee spoons of baking soda per day, pouring them onto her tongue and washing it down with water. She advised children to dilute soda in hot milk. This recipe in folk medicine is often used to treat colds that are accompanied by a severe cough.
Hot milk and soda, brought almost to a boil, relieves not only pain and inflammation in the throat, but also body aches.
Drinking baking soda is the easiest and most natural method to solve the problem of constipation. In addition, the substance neutralizes toxic substances well.
In the works of E.I. Roerich also mentions the treatment of cancer with sodium bicarbonate. The author points out that soda is an important component of human blood. It is present in plasma and lymphoplasm , which contains lymphocytes . Presumably, soda is necessary for the energy supply of lymphocytes - cells that are responsible for the body's immune response.
Precautionary measures
of alkalosis appear, you should take a break from treatment. If the drug is used to correct acidosis , blood glucose levels should be kept under control.
Alkalinity
Description: multi-level integral parameter reflecting the concentration of anions of weak organic and inorganic acids in water, mainly coal. Characterizes the direction of hydro- and geochemical processes, the corrosive aggressiveness of water towards concrete, steel, heating boilers, and steam generators.
Determination methods: titrimetry using indicators, potentiometric determination.
Types of alkalinity
| Type | Conditioning |
| Free alkalinity | Presence of carbonate ions CO2−3 and hydroxyl ions OH− in water in waters with pH > 8.3 |
| Carbonate alkalinity | The presence in water of carbonic acid dissociation products - carbonates CO2−3 and bicarbonates HCO−3, which are in equilibrium |
| Total alkalinity | The presence in water of anions of weak inorganic and organic acids, titrated with a strong acid |
Methods used at the MSU Test Center for determining the concentration of hydrocarbonates in natural environments
| Regulatory document for the methodology | Determination method | Equipment |
| Water | ||
| GOST 31957-2012 | titrimetry | auxiliary equipment |
| RD 52.24.493-2006 | titrimetry | auxiliary equipment |
| The soil | ||
| GOST 26424-85 | titrimetry | scales |
Occurrence: Hydrocarbonates HCO−3, carbonates CO2−3, hydroxide ion OH− and weak organic and inorganic acid ions appear naturally in natural water through the dissolution of carbon dioxide, minerals and host rocks in water when water comes into contact with soil. Therefore, almost all types of water are characterized by an alkalinity different from zero. Alkalinity is closely related to pH, so different alkalinities may not be present in water at the same time.
Analogs
Synonyms are the drugs Soda Buffer and Sodium bicarbonate . The 4th level ATC code is the same as Glucyl , Potassium chloride , Calcium , Xylate , Lactoxyl , Magnesium sulfate , Sodium chloride , Plerigo , Reamberin .
Lose weight with baking soda. The benefits and harms of baking soda
Baking soda for weight loss is used to change acidity in the body, normalize digestion and facilitate a number of other physiological processes, as well as reduce appetite.
The recipe for baking soda for weight loss is as follows: freshly squeezed juice of 3 lemons and 1 tbsp. spoon of sodium bicarbonate per liter of water.
The danger of using baking soda for weight loss is that systematically taking sodium bicarbonate solution can provoke the occurrence of a number of diseases of the digestive system (or aggravate existing diseases).
A safer recipe for losing weight is soda baths. Sodium bicarbonate in hot water (36-37°C) stimulates the opening of pores and the removal of toxins, due to which the body is freed from excess weight and reduces its volume.
To prepare a 150-200 liter bath, dilute 200 g of soda in a small volume of very hot water.
Even if such a procedure does not radically solve the problem of excess weight, its benefits for the body will be enormous, since it will cleanse the lymphatic system , reduce the appearance of cellulite (especially if you add essential oils to the water), improve the condition of the skin and strengthen the nervous system.
Rationing
Things are complicated with standardization of alkalinity. This group of parameters in water itself is not standardized. However, bicarbonates are standardized (only in bottled water), which partially determine the value of alkalinity. The carbonate content is not directly standardized, but given that the pH in drinking water is strictly standardized, free alkalinity in drinking water should be zero.
Maximum permissible concentration (MPC) of hydrocarbonates in various types of water
| Rationing | MPC, mg/l |
| Bottled water of the first category SanPiN 2.1.4.1116-02 | 0–400 |
| Bottled water of the highest category SanPiN 2.1.4.1116-02 | 30–400 |
| Water from centralized water supply systems SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01 | — |
| Water bodies of fishery importance Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation No. 552 | — |
| Recreational water use objects SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00 | — |
| Swimming pool water SanPiN 2.1.2.1188-03 | — |
| Wastewater in domestic wastewater systems Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 644 | — |
| Wastewater in storm drainage systems Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 644 | — |
Reviews
Baking soda is a time-tested remedy “for beauty, cleanliness and health.” These are the reviews about Sodium bicarbonate that can be found on the Internet. It is used for facial cleansing, teeth whitening and caries treatment, for weight loss and hair care, and also for pregnancy detection.
By the way, reviews of baking soda for weight loss are very optimistic, but only in cases where it was considered not as a panacea, but as an adjuvant. Some girls note that after a soda bath they immediately lost up to 2 kg of weight, but without physical activity and nutritional adjustments, the procedures would not have given a visible result.
Alternative medicine uses Sodium Bicarbonate to treat cancer. It is quite difficult to find reviews about soda treatment for oncology describing the results of treatment by the person himself. What is known is that patients of the doctor who promotes this method of treatment also die.
There are no statistics on people cured of cancer using soda. Self-medication when it comes to cancer is fraught with loss of time and the chance of cure.
Price of Sodium bicarbonate
You can buy sodium bicarbonate in the form of a 4% solution at a pharmacy for 15-28 UAH. In Russian pharmacies its price ranges from 103 to 160 rubles (depending on the volume of the bottle and the manufacturer).
How much does baking soda cost?
The price of baking soda per kg is on average 2.5 UAH (17-25 Russian rubles), for a pack of 500 g - 3.8 UAH (11-16 Russian rubles).
You can buy sodium bicarbonate in bulk for about 3.2-3.5 thousand UAH/t (about 10 thousand rubles/t).
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
ZdravCity
- Sodium bicarbonate solution for inf.
40mg/ml vial. 200ml No. 28 JSC Dalkhimfarm 1880 rub. order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Sodium bicarbonate (vial 40 mg/ml 200 ml) Dalkhimpharm
RUB 1,685 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Sodium bicarbonate 4% 100 ml solution TOV "Yuriya-Pharm", Ukraine
27 UAH.order - Sodium bicarbonate 4% 200 ml solution TOV "Yuriya-Pharm", Ukraine
35 UAH order
Carbonates and bicarbonates
HYDROSPHERE
The main source of hydrocarbonate and carbonate ions in surface waters are the processes of chemical weathering and dissolution of carbonate rocks such as limestones, marls, dolomites, for example:
CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O <–> Ca2+ + 2HCO3-;
MgCO3 + CO2 + H2O <–> Mg2+ + 2HCO3-.
Some of the hydrocarbonate ions come with precipitation and groundwater. Hydrocarbonate and carbonate ions are carried into reservoirs with wastewater from chemical, silicate, soda industries, etc.
As hydrocarbonate and especially carbonate ions accumulate, the latter may precipitate:
Ca(HCO3)2–> CaCO3 + H2O + CO2;
Ca2+ + CO32-–> CaCO3.
In river waters, the content of hydrocarbonate and carbonate ions ranges from 30 to 400 mg HCO3-/dm3, in lakes - from 1 to 500 mg HCO3-/dm3, in sea water - from 100 to 200 mg/dm3, in precipitation - from 30 up to 100 mg/dm3, in groundwater – from 150 to 300 mg/dm3, in groundwater – from 150 to 900 mg/dm3.
Carbonates and bicarbonates are the components that determine the natural alkalinity of water. Their content in water is determined by the processes of dissolution of atmospheric CO2, the interaction of water with limestone located in adjacent soils and, of course, the life processes of respiration of all aquatic organisms.
The determination of carbonate and bicarbonate anions is titrimetric and is based on their reaction with hydrogen ions in the presence of phenolphthalein (for the determination of carbonate anions) or methyl orange (for the determination of bicarbonate anions) as indicators. Using these two indicators, it is possible to observe two equivalence points: at the first point (pH 8.0-8.2) in the presence of phenolphthalein, the titration of carbonate anions is completely completed, and at the second (pH 4.1-4.5) - bicarbonate -anions. Based on the titration results, it is possible to determine the concentrations in the analyzed solution of the main ionic forms that determine the consumption of acids (hydroxy, carbonate and bicarbonate anions ),
as well as the values of free and total alkalinity of water, because they are stoichiometrically dependent on the content of hydroxol, carbonate and bicarbonate anions. For titration, titrated solutions of hydrochloric acid with a precisely known concentration value of 0.05 g-eq/l or 0.1 g-eq/l are usually used.
The determination of bicarbonate anions is based on the reaction:
CO3 2- + H+ = HCO3.
The presence of carbonate anion in concentrations determined analytically is possible only in waters whose pH is more than 8.0-8.2. If hydroxo anions are present in the analyzed water, a neutralization reaction also occurs when determining carbonates:
OH-+H+=H2O.
The determination of bicarbonate anions is based on the reaction:
HCO3-+H+=CO2+H2O.
Thus, when titrating with phenolphthalein, the anions OH- and CO32- are involved in the reaction with acid, and when titrating with methyl orange - OH-, CO32- and HCO3-.
The value of carbonate hardness is calculated taking into account the equivalent masses of carbonate and bicarbonate anions participating in the reactions.
When analyzing carbonate natural waters, the accuracy of the results obtained depends on the amount of acid consumed for titration with phenolphthalein and methyl orange. If titration in the presence of phenolphthalein usually does not cause difficulties, because there is a color change from pink to colorless, then in the presence of methyl orange, when the color changes from yellow to orange, it is sometimes quite difficult to determine the end of the titration. This can lead to a significant error in determining the volume of acid used for titration. In these cases, to more clearly identify the moment of completion of titration, it is useful to carry out the determination in the presence of a control sample, for which purpose the same portion of the analyzed water is placed next to the titrated sample (in a second bottle), adding the same amount of indicator.
As a result of the titration of carbonate and bicarbonate, which can be performed either in parallel in different samples or sequentially in the same sample, to calculate the concentration values it is necessary to determine the total amount of acid (V0) in milliliters consumed for the titration of carbonate (VK) and bicarbonate (VGK). It should be borne in mind that when determining the acid consumption for titration using methyl orange (Vmo), sequential titration of both carbonates and bicarbonates occurs. For this reason, the resulting volume of acid Vmo contains a corresponding proportion due to the presence in the initial sample of carbonates that have been converted into bicarbonates after reaction with the hydrogen cation, and does not fully characterize the concentration of bicarbonates in the initial sample. Consequently, when calculating the concentrations of the main ionic forms that determine the consumption of acid, it is necessary to take into account the relative consumption of acid during titration with phenolphthalein (Vph) and methyl orange (Vmo). Let's consider several possible options, comparing the values of Vf and Vmo.
1. Vf = 0. Carbonates, as well as hydroxo-anions, are absent in the sample, and acid consumption during titration with methyl orange can only be due to the presence of hydrocarbonates.
2. Vph ¹ 0, and 2Vph < Vmo. In the initial sample there are no hydroxo anions, but both hydrocarbonates and carbonates are present, and the proportion of the latter is equivalently estimated as VK = 2VФ, and of hydrocarbonates - as VGK = VMO – 2VФ.
3. 2 VФ = Vmo. There are no bicarbonates in the initial sample, and the consumption of acid is due to the content of almost only carbonates, which are quantitatively converted into bicarbonates. This explains the double consumption of Vmo acid compared to UV.
4. 2 VФ> Vmo. In this case, there are no hydrocarbonates in the initial sample, but not only carbonates are present, but also other acid-consuming anions, namely hydroxo-anions. In this case, the content of the latter is equivalent to Von = 2Vph – Vmo. The carbonate content can be calculated by composing and solving a system of equations:
5. VФ = Vmo. Both carbonates and bicarbonates are absent in the initial sample, and the consumption of acid is due to the presence of strong alkalis containing hydroxo anions.
The presence of free hydroxo anions in noticeable quantities (cases 4 and 5) is possible only in wastewater.
Mass concentrations of anions (not salts!) are calculated based on the equations for the reactions of acid consumption by carbonates (Ск) and bicarbonates (Сгк) in mg/l according to the formulas:
| WITH k= 2 • V.A. WITH gk = ( V.A. | Where V k and N – exact concentration of titrated hydrochloric acid solution (normality), g-eq/l; V A – volume of water sample taken for analysis, ml; 60 and 61 – equivalent mass of carbonate and bicarbonate anions, respectively, in the corresponding reactions; 1000 – conversion factor for units of measurement. |
The results of titration with phenolphthalein and methyl orange make it possible to calculate the alkalinity of water, which is numerically equal to the number of acid equivalents used to titrate a 1-liter sample. At the same time, acid consumption during titration with phenolphthalein characterizes free alkalinity, and with methyl orange - total alkalinity, which is measured in mEq/l. The alkalinity indicator is used in Russia, as a rule, when studying wastewater. In some other countries (USA, Canada, Sweden, etc.), alkalinity is determined when assessing the quality of natural waters and is expressed by mass concentration in CaCO3 equivalent.
It should be borne in mind that when analyzing waste and contaminated natural waters, the results obtained do not always correctly reflect the values of free and total alkalinity, because in water, in addition to carbonates and bicarbonates, compounds of some other groups may be present.