Pancreatitis in children occurs with the development of an inflammatory reaction in the tissues of the pancreas. In childhood, this pathology is often disguised as other diseases of the digestive tract (gastroduodenitis, gastritis, dysbacteriosis) and can occur for a long time with minor symptoms.
If signs of pancreatitis appear in children, you should contact a pediatrician or pediatric gastroenterologist. Without treatment, the disease becomes chronic and can cause complications, including pancreatic necrosis (a complication of acute pancreatitis with destruction of pancreatic tissue)1.
Reasons for the development of pancreatitis in a child
Pancreatitis in children develops under the influence of various external and internal unfavorable factors2:
- poor nutrition, overeating, excess fatty, spicy and overly spicy foods in the diet;
- severe allergic reactions to medications, food, environmental factors;
- congenital or acquired anomalies of the digestive organs;
- damage to the abdominal wall;
- progression of other gastrointestinal diseases*;
- benign and malignant neoplasms in the pancreas;
- helminthiases;
- endocrinological diseases;
- past viral diseases;
- hormonal disorders;
- uncontrolled use of medications.
Regardless of the reasons for the development of pancreatitis in children, the child needs qualified medical care and a comprehensive examination.
Based on diagnostic data, specialists identify factors that provoke an inflammatory reaction in the pancreas, select an effective treatment regimen, and carry out prophylaxis to prevent further relapses.
Acute pancreatitis: treatment and first aid
When initial symptoms of the disease appear, you must call an ambulance. Treatment of acute pancreatitis takes place exclusively in a hospital setting under the constant supervision of specialists.
While waiting for doctors, to alleviate the patient’s condition, you can put cold on his stomach. As for medications, you can take any antispasmodics - papaverine, no-shpu, smazmalgon, etc. From the moment the first symptoms appear, you should stop any food intake (including juices) and go to bed. Doctors say that no medicine treats pancreatitis better than cold, hunger and rest.
Treatment in a hospital is carried out taking into account the clinic. Antispasmodics, prokinetics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antisecretory, antibacterial drugs are used (for the prevention or treatment of bacterial complications). Treatment is carried out by infusion (through a dropper). Diet therapy (when the patient is allowed to resume eating) is of great importance. Enzyme preparations are used during meals.
Acute pancreatitis in children
The acute form of pancreatitis can develop as a result of an infectious lesion of the body against the background of damage to the pancreas. The disease often occurs after overeating and eating excessively fatty foods, as well as against the background of viral infections and helminth infections.
Acute inflammation of the gland is accompanied by a pronounced destructive-inflammatory process. The child must be hospitalized to avoid the development of complications and serious disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system2.
Timely consultation with a doctor will help to avoid negative consequences, for example, the development of purulent peritonitis (infectious inflammation of the peritoneum).
Pancreatitis: symptoms and treatment
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory disease of the pancreas. The pancreas is involved in the digestion process and also produces insulin, the lack of which threatens the patient with diabetes. Pancreatitis can be acute or chronic.
Development of pancreatitis
Pancreatitis develops due to dysfunction of the pancreas when digestive enzymes are activated prematurely and damage the tissues of the organ. Doctors identify the following causes of pancreatitis:
- diseases of the gallbladder and duodenum;
- alcohol abuse;
- metabolic disorders;
- taking certain medications;
- genetic predisposition;
- changes in hormonal levels;
- unhealthy diet, overeating;
- some infections (hepatitis, chicken pox, etc.);
- previous operations on the biliary tract or stomach.
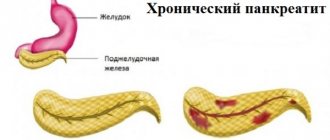
Chronic pancreatitis in children
Signs of chronic inflammation of the pancreas in children are determined primarily by the form of the disease and the condition of other organs of the digestive tract. Typically, children are bothered by aching pain under the chest, which intensifies after eating fatty and spicy foods, physical and psycho-emotional fatigue.
Chronic pancreatitis in childhood most often develops against the background of unfavorable heredity. If parents and close relatives develop a similar disease, the risk of its development in the child increases significantly.
The chronic course of the inflammatory process can lead to irreversible changes in pancreatic tissue and dysfunction of the organ. If characteristic signs of exacerbation appear, such as abdominal pain, bitterness in the mouth, vomiting, frequent and loose stools, you should contact a specialist. Self-medication may increase the inflammatory response.
Pancreatitis
Multislice computed tomography (MSCT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdominal organs, sometimes with contrast, which allows for a more detailed assessment than ultrasound of the size and structure of the pancreas, the condition of its ducts, the presence of complications, and to exclude pathology of other abdominal organs cavities. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) of the abdominal organs is a highly informative method, even with minimal changes in the pancreas, used to determine indications for surgical treatment.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), which involves a combination of radiological and endoscopic instruments to assess the condition of the pancreatic duct and its branches. The study allows you to obtain pancreatic secretions, as well as carry out a number of therapeutic manipulations - dilate the ducts, remove a stone, etc.
Endoscopic elastography of the pancreas makes it possible to determine the stiffness and rigidity of the tissue, assess the degree of fibrosis (irreversible changes) and the exocrine function of the pancreas.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is performed to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
Which doctors should I contact?
The diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic pancreatitis is carried out either by general practitioners or by doctors.
It is important to understand that the cause of abdominal pain can be not only diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but also cardiological, urological, gynecological diseases, as well as lesions of the musculoskeletal system.
Any abdominal pain necessarily requires a medical examination to determine treatment tactics. Treatment of pancreatitis
A prerequisite for the treatment of acute and chronic pancreatitis is the cessation of drinking alcohol and smoking.
During the period of exacerbation of the disease, fasting is recommended. During the subsidence of the exacerbation and during the period of remission, patients are advised to eat nutritious meals 5-6 times a day in small portions.
Preference should be given to foods high in proteins and complex carbohydrates, dietary fiber, and vitamins. The decision to limit fat is made individually.
Drug therapy includes several groups of drugs.
Painkillers can be taken only after examination by a doctor - if pain occurs (as needed) or as a course.
If the pancreas does not produce enough enzymes, the doctor prescribes enzyme replacement therapy.
Drugs that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and lead to a decrease in the production of pancreatic juice are indicated to relieve exacerbation of pancreatitis.
In addition, the doctor may recommend taking vitamins and antidepressants (to reduce the symptoms of depression and the severity of pain). With the development of diabetes mellitus, carbohydrate metabolism disorders are corrected.
In some cases, surgical treatment may be required.
Complications
The most common complications of pancreatitis are considered to be cholestasis (impaired outflow of bile), infectious diseases (phlegmon and abscess of the pancreas, septic conditions), rupture of the pseudocyst (fluid-filled cavity) and pancreatic duct, intra-abdominal bleeding, erosions (superficial defects of the mucous membrane) and ulcers in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, diabetes mellitus, carbohydrate metabolism disorders, malabsorption of nutrients.
A variety of cardiovascular, pulmonary, hematologic, and metabolic complications are possible.
Prevention of pancreatitis
To prevent exacerbation of pancreatitis, it is recommended to eat at least 4-5 times a day in equal portions and not to overeat. The diet should be varied and include a sufficient amount of dietary fiber, which is found in grains, vegetables and fruits. Animal fats (fatty meats, rich soups, high-fat dairy products) should be limited.
An important component of preventing pancreatitis is limiting alcohol consumption and quitting smoking.
Sources:
- V.T. Ivashkin, I.V. Maev, A.V. Okhlobystin et al. Recommendations of the Russian Gastroenterological Association for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic pancreatitis. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology No. 4, 2014, p. 70-97.
- Clinical recommendations. Chronic pancreatitis in adults. Russian Gastroenterological Association, 2021.
- THOSE. Polunina. Chronic pancreatitis: exocrine insufficiency and its correction. Attending physician No. 6, magazine, 2021, p. 71-77.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Reactive pancreatitis in children
Reactive pancreatitis develops in children against the background of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, toxic damage (for example, due to drug poisoning), or an allergic reaction. In the overwhelming majority, the cause of the inflammatory process lies in the exacerbation of cholelithiasis and liver diseases.
Reactive pancreatitis develops several hours after adverse effects of internal and external factors. The following symptoms are noted3:
- pain that increases after eating;
- signs of gas formation;
- heartburn;
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- traces of bile and mucus in the vomit.
Diagnosis of pancreatitis in children
The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, the results of the survey, examination of the child and the data of the examination. When palpating the abdomen, the gastroenterologist detects local pain in the epigastric region (in the upper and middle parts of the abdomen, between the costal arches). In order to identify concomitant pathologies of the digestive organs, specialists can also prescribe2:
- general radiography of the gastrointestinal tract*;
- computed tomography;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI**.
Treatment of pancreatitis in children
The choice of treatment methods for pancreatitis in children requires a careful study of the medical history, examination data and examination of the child. The acute form of the disease often requires hospitalization of the child. The inflamed pancreas needs rest, which can only be ensured by strict adherence to the following conditions2:
- bed rest;
- diet;
- possible short-term therapeutic fasting;
- drug treatment, including the administration of glucose, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, as well as drugs intended to normalize digestion, for example, the drug Creon®.
In case of severe destruction (impaired functioning) of the pancreas, urgent surgical treatment is required.
Due to the high risk of complications, pancreatitis in childhood requires specialist supervision. Even if the symptoms of the inflammatory process are mild, it is necessary to consult a specialist to prevent undesirable consequences.
Gastroenterologists pay special attention to the development of measures to prevent exacerbations of pancreatitis in children. Prevention includes maintaining a balanced diet appropriate for the child’s age, preventing toxic damage to the body as a result of infectious processes and the course of diseases of internal organs.
Symptoms of pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a disease that in 90% of cases is accompanied by a violation of the secretion of digestive enzymes by the gland. The result of such a lesion is a deterioration in the functioning of the child’s gastrointestinal tract with the appearance of characteristic symptoms. The most common signs of pancreatitis in children are:
- pain in the abdomen - the discomfort is girdling in nature and radiates to the back;
- flatulence;
- violation of bowel movements such as diarrhea;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea, vomiting;
- increase in body temperature to 37-38°C.
In infants and newborns, the symptoms of pancreatitis are less severe than in children of the older age group.
Sometimes parents may not even notice any special changes in the baby’s behavior. In adolescents, the symptoms of the disease differ in brightness and intensity. This is due to the influence of a significant number of provoking factors. The clinical picture of the disease depends on the form and duration of the pathological process, as well as the degree of damage to the pancreas. With chronic inflammation, the pain can be of a protracted, aching nature. At the same time, the child loses body weight, the condition of the skin, nails, and hair worsens.
If any of these signs are detected, parents should seek help from a doctor. Early diagnosis of pancreatitis with the prescription of adequate treatment helps to quickly stabilize the baby’s digestive function and minimize the risk of complications.
Diet for pancreatitis in children
With pancreatitis, the child must follow a diet.
The following foods and drinks are excluded2:
- fresh bread and pastries;
- sparkling water;
- fatty dairy products;
- smoked meats, seasonings and spices;
- store-bought juices;
- fat meat;
- cabbage;
- lemons;
- credit;
- legumes;
- coffee.
Slimy porridges prepared with vegetable decoctions are useful. You can use meat broths made from poultry (skinless chicken), veal, rabbit, which are previously steamed or boiled. During an exacerbation, food should be pureed and free of lumps and rough pieces that can injure the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.