Acne and its common consequence, post-acne, are a fairly acute and common dermatological problem. The term “acne” refers to acne or inflammation of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, which is accompanied by the formation of numerous pimples of different sizes and types. Most often, this disease occurs in adolescents, lasts for years and is difficult to treat. Although it can also develop in adulthood, including after 30-35 years.
According to the latest data, more or less 85% of people suffer from acne, and in 15-30% of cases the disease is severe and requires complex, long-term complex treatment. Acne affects those areas of the skin where sebaceous glands are most concentrated. Therefore, very often it affects the face, which causes serious psychological complexes. But acne can also occur on other parts of the body, in particular the back. At the same time, one of the common complications of the disease is post-acne, i.e. persistent changes in the skin in the form of spots, and more often scars of different sizes, which are extremely difficult to deal with, but still possible.
Peculiarities of skin structure and acne development
Human skin is a heterogeneous tissue. It has 3 layers:
- The epidermis is the top layer of skin in contact with the environment. It, in turn, consists of several more layers, the top of which is called the horny or outer layer. It is formed by cells that have lost their nucleus and other organelles and have a strong cell membrane called corneocytes, which are dead keratinocytes.
- The dermis is the middle and most important layer of the skin, which is responsible for all its functioning. After all, it is in it that blood vessels and numerous nerve endings are concentrated. Moreover, it is in the dermis that fibroblast cells are responsible for the tone and youth of the skin, synthesizing collagen and elastin fibers. It also contains sebaceous, sweat glands and hair follicles.
- Hypodermis or subcutaneous fat is the lowest layer of skin, represented by loose connective tissue and fat cells called adipocytes. Its thickness directly depends on the area of the body, gender and nature of nutrition. Therefore, on the face, subcutaneous fat is poorly expressed, but on the hips, especially in women, it is well expressed.
From the point of view of considering the issue of the development of acne, dermatologists and dermatocosmetologists are most interested in the dermis, or rather the activity of the sebaceous glands and other appendages of the skin, i.e., sweat glands and hair. The sebaceous glands are responsible for the synthesis of sebum, also called sebum. It is necessary to retain moisture in the skin, protect it from ultraviolet rays and the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, and also to bring antioxidants to the surface of the skin and prevent oxidative damage. The functioning of the sebaceous glands is regulated by hormones of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and adrenal cortex, the work of which is in direct relationship with the activity of other endocrine glands. Therefore, any changes in hormonal levels lead to the functioning of the sebaceous glands being disrupted in one direction or another.
It is to the sebaceous glands that we owe such an unwanted shine to the skin of the face in the so-called T-zone: on the forehead, nose and chin.
Often, hormonal fluctuations provoke more active production of sebum, which is called seborrhea. It is classified as a separate disease, the presence of which can be indicated by:
- enlarged skin pores, including the formation of comedones (popularly called blackheads);
- oily or dry flaking skin;
- rapid contamination of hair, which leads to the need to wash your hair much more often, including daily or even more often.
Hormonal disorders that provoke the development of seborrhea also lead to changes in the composition of sebum. As a result, the content of androgens (male sex hormones) increases and the amount of estrogens (female sex hormones), as well as linolenic acid, decreases. Sebaceous gland receptors are sensitive to androgens. Therefore, an increase in their number provokes more active production of sebum or sebum.
Both men and women produce both androgens and estrogens in their bodies, but in different quantities. Moreover, androgens are precursors of estrogens, i.e., the starting compounds for the synthesis of female sex hormones.
Linolenic acid is responsible for maintaining a slightly acidic environment on the skin, which is an effective prevention of the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into it. Therefore, when the content of this unsaturated organic acid in sebum decreases, it becomes alkalized. This leads to a decrease in the barrier properties of the skin and the creation of favorable conditions for the development and reproduction of various microorganisms on its surface and penetration from the inside of the skin.
Causes of acne development
Activation of sebum synthesis, changes in its composition, in particular a decrease in the concentration of linoleic acid, is the main reason for the development of inflammatory processes in the skin, i.e., the occurrence of acne.
In the course of research, it was found that acne is most often provoked by:
- anaerobic lipophilic corynebacteria, in particular Propionibacterium acnes;
- aerobic bacteria, including Staphylococcum epidermidis;
- lipophilic fungi Pityrosporum ovale et orbiculare.
The most dangerous from the point of view of acne development are Propionibacterium acnes. These microorganisms are capable of synthesizing a variety of enzymes, including lipase, which destroys the walls of hair follicles.
The main problem is that all these microorganisms are a component of the normal microflora of the skin of the face, i.e. they are constantly present on it and in the normal state of immunity, the activity of the endocrine glands, and metabolism, their number is strictly regulated and cannot cause harm or provoke the development of diseases. Therefore, acne can be a consequence of various disorders in the body, i.e., the influence of endogenous causes, including decreased immunity and hyperandrogenism, i.e., increased synthesis of androgens (testosterone and dihydrotestosterone). Therefore, the disease often occurs when:
- puberty;
- endocrine diseases, in particular diseases of the ovaries and testicles, adrenal glands, pituitary gland and hypothalamus;
- obesity;
- premenopause and menopause;
- hyperkeratosis;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- suffering from severe infectious diseases;
- long-term stress, chronic fatigue syndrome.
Often the tendency to develop acne is inherited.
But the reasons for the development of acne can also lie in the action of external causes, which include the negative influence of sunlight. This is due to the fact that with active exposure to ultraviolet radiation, the skin's immunity sharply decreases, i.e. its ability to suppress the growth and reproduction of microorganisms living on it. As a result, the bacteria and fungi listed above are able to multiply uncontrollably and form colonies around the sebaceous glands, as they feed on the secretion they produce - sebum.
Acne also often occurs in bodybuilders of both sexes. This is due to the fact that in order to achieve their goals, they are forced to eat high-calorie foods and often take anabolic steroids. Such drugs contain substances that are derivatives of testosterone. Therefore, their use for a long period of time leads to changes in hormonal levels and the development of seborrhea, and then acne. Such cases have even been identified as a separate form of acne - bodybuilding acne.
If women take anabolic steroids, in addition to acne, they may experience a decrease in voice tone, male-pattern hair growth, menstrual irregularities, even amenorrhea. But in both cases, bodybuilders risk decreased fertility.
Pathogenesis
In its development, the disease sequentially goes through a number of stages:
- excessive secretion of sebum;
- the occurrence of follicular hyperkeratosis, which consists of an increase in the thickness of the stratum corneum of the epithelium in the area of the mouths of the hair follicles, which leads to the formation of comedones;
- proliferation of microorganisms in clogged hair follicles, as they feed on the sebum produced;
- an inflammatory process that becomes the body’s reaction to the accumulation of metabolic products of microorganisms (can be observed on the surface of the skin or in its deep layers) and manifests itself in the formation of red papules, pustules, and nodules.
Often, as the duration of the disease increases, the number of inflammatory elements increases. In this, a direct role is played not only by blockage and damage by microorganisms to other sebaceous glands, but also by the rupture of their walls as a result of the accumulation of sebum and its distribution in the thickness of the skin.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The main sex hormones that regulate the activity of the sebaceous glands are androgens . They affect the development and increase in the size of the sebaceous glands in androgen-dependent areas of the skin, the hyperproduction of sebum and the proliferation of keratinocytes in the ducts of the sebaceous glands, the hair canal and the mouths of the pilosebaceous follicles.
According to the inflammatory concept of acne, the chain of pathogenetic events begins with androgen-induced inflammation of the sebaceous gland . This causes proliferation and active desquamation of keratinocytes in the upper part of the pilosebaceous follicles. Progressive hyperkeratosis and the associated difficulty in the outflow of sebum lead to the formation of comedones , which subsequently transform into papules and pustules or spontaneously regress.
Overproduction of sebum contributes to changes in its qualitative composition. In sebum, the concentration of linoleic acid decreases, which suppresses the expression of transglutaminase and is involved in the synthesis of the main components of the intercellular matrix. This leads to an increase in the pH of sebum and a change in the permeability of the walls of the follicles and the stratum corneum of the epidermis.
Sebum stagnation creates anaerobic conditions that are optimal for the proliferation of propionibacterium acnes in the pilosebaceous follicles. They secrete substances that damage the walls of ducts and glands, as well as factors that attract neutrophils.
The release of lysosomal enzymes by neutrophils further reduces the strength of the follicle wall, which ultimately leads to their rupture. The contents enter the dermis, where local inflammation develops according to the “foreign body reaction” type.
Exogenous factors contributing to the development of acne:
- taking sex hormones, anabolic steroids ( Fig. 1 );
- high glycemic index diet;
- smoking;
- whole milk;
- fast food;
- chocolate;
- various occupational hazards;
- hot and humid climate.
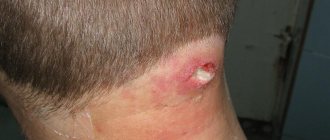
Rice. 1. Acne on the shoulder and back of an athlete due to the use of anabolic steroids (Danish national service on dermato-venereology)
https://www.danderm-pdv.is.kkh.dk/atlas/4-120-9.html
Forms and symptoms
Acne can visually manifest itself in quite different ways and occur in mild, moderate and severe forms. Therefore, many patients may not even realize that they have this dermatological disease. Symptoms of acne may include:
- open and closed comedones;
- milia - white dense acne, resembling grains, usually painless (most often located under the eyes and on the upper eyelids, less often on the forehead, cheeks, cheekbones);
- oily hair;
- papulopustular elements and nodes, which are often very painful;
- peeling of the skin or, conversely, the presence of an oily sheen.
Modern classification involves dividing all cases of acne into juvenile acne, adult acne, childhood acne, including newborns.
Depending on how acne manifests itself, there are 3 main forms:
- comedonal;
- papulopustular;
- conglobate.
At the same time, starting with the appearance of open and closed comedones, acne can eventually transform into a papulopustular rash, etc. Therefore, these forms are considered as stages of the disease. In mild forms of the disease, single comedones, papules and/or pustules are observed. In the moderate form, in addition to these single elements, single nodes are attached, while in the severe form, multiple papules and pustules, as well as conglobate nodes, are observed.
Comedonal form
This form is characterized by the formation of blackheads or comedones, which is considered as the first stage in the development of acne. Its signs can appear as early as 8-year-old children and initially consist of increased oiliness of the skin and hair. Over time, small comedones begin to form at the mouths of the sebaceous glands, which tend to transform into closed comedones. These are the same painless and non-inflamed blackheads that can appear as small bumps of normal skin color and with a white protruding tip of sebum.
Comedones often cannot resolve on their own, since the thickened walls of the mouths of the sebaceous glands prevent the arbitrary removal of accumulated secretions out. Since the sebaceous gland, despite the blockage of its duct, continues to function and produce new portions of sebum, its walls gradually stretch, and the pressure on them increases in direct proportion to the amount of accumulated sebum. This causes the formation of papules and pustules, i.e. the development of the papulopustular form of the disease.
Papulopustular form
This form is already characterized by the formation of papules and pustules against the background of the presence of open and closed comedones, as well as traces of resolved elements on the skin (post-acne), and their number directly depends on the severity of the disease. Papules are dense or soft formations that rise above the surface of the skin. At the same time, pustules mean formations rising above the surface of the skin with clearly visible white contents.
Often, with papulopustular acne, rashes are observed not only on the face, but also in the décolleté area, as well as on the back.
Acne conglobata
The conglobate form of acne is considered the most severe. It is characterized by the formation of large elements that rise greatly above the level of the skin and can reach large sizes and merge with each other. Conglobate acne is dense to the touch and very painful on palpation. They can form both on the face and on other parts of the body. But they are more often found on the back.
Conglobate acne can exist for months without opening. But if this does happen, long-term non-healing ulcers form in their place, leaving deep scars.
Post-acne – a common consequence of acne
According to the latest data, acne resolves with the formation of post-acne in 40% of cases. This term refers to the occurrence of skin changes in places where the inflammatory process persists for a long time and the formation of the largest papules, pustules and nodules. Thus, post-acne may manifest itself:
- pigment spots - the result of squeezing out comedones, pustules and papules, as well as the action of sunlight, which led to a violation of pigment formation (most typical for patients with dark skin and late acne;
- stagnant or erythema spots - occur due to impaired microcirculation in the area of inflammation;
- enlarged pores – a consequence of prolonged stretching of the walls of the sebaceous glands by excess sebum;
- pathological scars (atrophic (chipped, round, square), normotrophic, hypertrophic, keloid) - the result of severe facial acne, leading to damage to the perifollicular part of the dermis;
- atheromas - large subcutaneous cysts of the sebaceous glands, completely filled with sebum;
- milia or millet - small round white pimples that arise against the background of disturbances in the keratinization process.
Therefore, post-acne can reduce the quality of life no less than acne directly affecting the face. At the same time, the likelihood of developing post-acne increases with:
- severe papulopustular and conglobate forms of acne;
- persistence of the inflammatory process for more than a year, which is usually observed in the absence of treatment or its improper implementation;
- presence of post-acne in close relatives;
- squeezing out comedones, pustules, papules or exposure to other traumatic factors on the facial skin.
In this case, post-acne becomes not only a pronounced cosmetic defect, but can also lead to the development of a number of complications, including dangerous ones:
- exacerbation of herpes infection;
- depigmentation;
- formation of new scars;
- allergic dermatitis;
- persistent erythema (redness of the skin);
- secondary infection, which can result in erysipelas.
The risk of developing post-acne complications increases with trauma to the facial skin and especially with squeezing out acne.
Is it possible to sunbathe with acne?
The first effect of sun tanning or visiting a solarium seems to be positive: ultraviolet light has a slight bactericidal, drying effect, due to pigmentation, some camouflage of the rashes occurs and they become less noticeable. However, the long-term effects of ultraviolet radiation are not so good - there is an increase in sebum secretion and a thickening of the stratum corneum of the skin, which further complicates the outflow of excess sebum. That is, patients with acne should not sunbathe.
Diagnostics
If signs of acne occur, you should consult a dermatologist or dermatocosmetologist. The doctor will not only evaluate the number of elements, their nature, location and the presence of signs of post-acne, but will also clarify the patient’s dietary habits, whether close relatives have suffered from similar acne on the face, and a number of other points. In general, acne can be diagnosed and its severity determined at the first consultation, since the disease has a specific clinical picture.
But in order to choose the optimal treatment tactics, you need to accurately determine the cause of acne development and assess the general condition of the body. For these purposes, patients are prescribed:
- UAC;
- OAM;
- blood chemistry.
Identifying the cause of acne is extremely important, as it is a chronic disease. Therefore, in the absence of control, it can recur at any time when favorable conditions are created.
When diagnosing post-acne, the nature of facial skin changes, the presence of scars, their shape, depth, localization, and ability to smooth out when the skin is stretched are also assessed.
Forecast
Acne treatment always takes time, so the patient must be patient. During the treatment process there can be both improvements and deteriorations; periods of remission and intensification of the disease alternate. But over time, acne will respond to treatment.
In the absence of timely treatment, acne can progress to a severe stage, in which painful cysts form in large quantities, leaving behind deep scars. In addition, acne can significantly reduce the patient's self-esteem and lead to problems with social communication.
Acne treatment
Patients should be prepared for the fact that treatment for acne on the face, like other parts of the body, will be quite lengthy. It is always comprehensive and selected for each patient individually. First of all, all patients are recommended to limit their time in the sun and use sunscreens with a high SPF factor, which will need to be thoroughly treated with the face a quarter of an hour before going outside on sunny days, including during the cold season. A diet must also be prescribed, which consists of excluding frankly harmful foods, fried and fatty foods. Otherwise, acne treatment tactics are largely determined depending on its degree.
So, in mild cases, only external therapy is usually prescribed. It consists in:
- regular mechanical facial cleansing performed by a qualified dermatocosmetologist in a medical facility, but in no case in a beauty salon or at home;
- a course of chemical peels, which can be salicylic or pyruvic, depending on the characteristics of the skin;
- the use of keratolytics, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory agents for external use, retinoids.
It is strictly forbidden to squeeze out comedones and inflammatory elements on your own, as this not only increases the risk of developing post-acne, but can also be complicated by the addition of a secondary infection and even the development of sepsis.
For moderate facial acne, in addition to the remedies described above, systemic therapy is prescribed, which consists of taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs, including oral contraceptives (for women). The choice of drugs directly depends on the diagnostic results and the detected diseases that caused the development of acne.
Sometimes treatment is supplemented with superficial cryotherapy, laser therapy, and darsonvalization.
In severe cases of the disease, drugs based on isotretinoin are prescribed. But since it can provoke a number of undesirable consequences, treatment with it is carried out under the constant supervision of a dermatologist. Also, while using this drug, women of childbearing age must be prescribed reliable contraception.
Often, patients additionally require the help of a psychologist, since acne and post-acne provoke the emergence of serious complexes and leave a serious imprint on the patient’s mental state, undermining his self-confidence, leading to depression and other undesirable consequences.
Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Principles of treatment
Acne (pimples, acne vulgaris, acne, comedones, acne vulgaris) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that manifests itself as open or closed comedones and inflammatory lesions (papules, pustules, nodules).
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for acne treatment:
- M22 (Lumenis)
- Thermage (Solta Medical)
Today, acne, without exaggeration, can be called the most common skin disease among young people - according to statistics, up to 95% of boys and up to 83% of girls suffer from it. Approximately 60% of them have a mild form with a small number of rashes (so-called physiological acne). If acne occurs in adolescence, in 64% of adults, acne persists at the age of 20–30 years, in 43% at 30–40 years, in 15% at 40–50 years (more often in women).
Post-acne treatment
Treatment of the consequences of acne or post-acne is a more complex task than directly eliminating the inflammatory process. Nevertheless, it is no less important, since various scars, age spots and other traces of inflammatory elements represent a serious cosmetic problem and sharply reduce the quality of life of patients.
Today there are several methods for correcting post-acne. The choice of specific ones is made based on the severity of the situation. These include:
- chemical peels;
- hardware procedures;
- injection therapy;
- surgery.
But for treatment to be effective, especially for moderate and severe post-acne, it must be comprehensive and combine different methods of influencing the skin of the face. At the same time, it is important not to rush, but to systematically work on eliminating post-acne, since after each procedure the skin needs restoration.
For deep scars, before starting correction, subcision may be required, i.e., destruction of the adhesions that connect it to the surrounding tissues.
Chemical peels
To eliminate post-acne in the form of stagnant spots and shallow square scars, chemical peels of varying depths of exposure using various acids are used. In other cases, they can only act as a component of complex therapy. This:
- superficial chemical peels (salicylic, glycolic, pyruvate, milk);
- medium (Jessner peel, trichloroacetic peel);
- deep (phenolic).
Today, deep chemical peels are performed extremely rarely for post-acne conditions, since they often provoke a large number of complications.
Each chemical peel has its own indications and contraindications, not to mention the specifics of its implementation. Therefore, the choice of a specific one is carried out strictly on an individual basis.
Hardware procedures
Hardware methods are considered one of the most effective in the treatment of facial post-acne. These include:
- Classic dermabrasion is a procedure that involves using special tips with an abrasive surface to remove the top layer of skin. But its implementation is associated with severe painful sensations, which often forces it to be performed under general anesthesia. Therefore, today this method is used extremely rarely.
- Microdermabrasion is an analogue of classical dermabrasion, but involves a smaller depth of impact. Therefore, it is effective only against stagnant spots, square scars with a depth of no more than 0.5 mm.
- Laser resurfacing is one of the most effective methods for treating post-acne, including round and square scars of varying depths.
Injection therapy
Modern injection procedures used to improve the appearance of the face during post-acne include:
- Needling is a cosmetic procedure, the essence of which is to carry out numerous micro-perforations of the skin with a special roller. It is equipped with many needles, the length of which does not exceed 2 mm. Needling is most effective for removing congestive spots and atrophic superficial scars.
- Plasmolifting is a medical procedure that involves introducing platelet mass separated from the patient’s own blood into the deep layers of the dermis.
- Mesotherapy is a well-known cosmetic procedure, the essence of which consists of numerous intradermal injections of individually selected mesopreparations, which include vitamins, enzymes, amino acids, nucleotides, organic acids and other biologically active compounds.
Surgery
Today, scar removal can be done through traditional surgery or laser destruction. Surgical methods are used extremely rarely and only in the most complex cases, in particular with large hypertrophic and keloid scars. But in the latter case, there is a risk of re-formation of the scar, since keloids tend to grow due to mechanical trauma. To reduce this risk, long-acting suspension corticosteroids are injected into the scar area. In other cases, injections of enzyme preparations, in particular longidase and collagenase, are indicated.
Thus, acne treatment, although it can be quite complex and lengthy, is still much simpler than the fight against post-acne. Therefore, it is important to contact a dermatologist as soon as possible if acne of any nature appears on the face. This will allow you to notice the onset of the development of the disease at the earliest stages and eliminate it even before unsightly scars, age spots, etc. form on the face. But even if time is lost, do not despair. The modern level of development of medicine makes it possible to effectively combat acne of any severity, as well as post-acne, improving the appearance of the face and returning the patient to an active social life.
5 1 vote
Article rating
Preparations for topical use
Cleansers for certain skin conditions are considered an essential part of the therapeutic plan. In recent years, as a result of chemical synthesis, surfactants called detergents or “syndets” have been obtained, i.e. "synthetic detergents". The fundamental difference between syndets and soaps is that the pH value can be chosen more or less freely. For severe seborrhea, special acne soap is often used, but excessive facial hygiene with frequent washing should be avoided, since overhydration of the follicle leads to the accumulation of sebaceous gland secretions and can cause increased inflammation. Various creams, gels, emulsions, and solutions are used as hygiene and care products for oily skin with a tendency to acne. Shampoos can be divided into cosmetic and medical. Cosmetic shampoos can be liquid, creamy, aerosol, or oil-like. Medical shampoos are used to treat diseases of the scalp and contain antiseptics, active substances, and antifungal agents. For dandruff, the drug of choice is the frequent use of mild detergent shampoos, which are usually used 1-2 times a week. This procedure cleanses the scalp of scales, but in itself does not have a therapeutic effect. Shampoos containing the following components have a beneficial effect (for example: coal tar, ichthyol, piroctone olamine, zinc pyrithione, ciclopiroxalamine, plant extracts, selenium sulfide, AHA, BHA, ketoconazole - an antifungal component). At the multidisciplinary clinic CELT
We take a comprehensive approach to solving problems associated with impaired sebum secretion, using the most modern methods of treating this disease. Remember that self-medication is unsafe, as there is a risk of worsening the problem, therefore, at the first sign of acne, consult a dermatologist! If necessary, the dermatologist will refer you to another specialist (endocrinologist or gynecologist). Our clinic provides excellent laboratory diagnostics, where you can always take hormone tests with a referral from an endocrinologist to prescribe individual treatment. Be healthy, beautiful and cheerful! Make your face a source of pride!