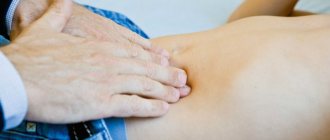
We asked Larisa Tretyakova, gastroenterologist, doctor of the highest category, head of the department of the PharmMed Clinic , to tell us what most often hurts in the epigastric area, how to understand your own sensations and what diagnostic procedures are necessary in this case.
Almost every resident of a big city has experienced pain in the upper abdomen - right in the triangle under the ribs. Most often, epigastric pain indicates diseases of the digestive system.
Let's first figure out exactly what organs are located here. This is the stomach that passes into the duodenum. To the left of the stomach is the pancreas, which is responsible not only for digestion, but also for hormonal control - in particular, it produces insulin, which cells need to absorb nutrients. The spleen is also located here, which is responsible for purifying the blood and functioning of the immune system. To the right of the stomach the gallbladder and liver are densely packed. All of these organs (with rare exceptions) can be a source of pain localized in the epigastric region.
The Deepest Essence of Digestion
Every high school student knows that digestion occurs in the stomach. Aggressive hydrochloric acid attacks the food entering the stomach, and it begins to break down into easily digestible components.
| Not often, but it happens | |
| Epigastric pain may be a signal of myocardial infarction. After all, in the area of the solar plexus there are not only the digestive organs - the lungs and heart are nearby. So you should not tolerate acute abdominal pain. If it doesn’t work, call an ambulance. In addition, epigastric pain may be of neurological origin. That is, in the thoracic spine, one or another nerve is sandwiched between the vertebrae - and the signal is transmitted along the nerve to the stomach. A neurologist will be able to “decipher” such pain after an X-ray or CT scan of the spine. | |
But not every school graduate knows that a person without a stomach can live relatively normally. Because only the first stage of digestion takes place here. Much more important processes occur in the next “compartment” - the duodenum. The pancreatic ducts and the common bile duct exit here.
The gall bladder accumulates bile produced by the liver, and as soon as food enters the duodenum, the bile is sent there to help with digestion. An equally important role in digestion is played by the so-called “pancreatic juice” - the secretion of the pancreas, which also enters the duodenum through the ducts.
After food is “processed” in the duodenum, it is sent for further digestion and absorption in the small intestine.
Causes of pain
The solar plexus is a massive concentration of nerve processes, fibers and nodes that radiate in different directions.
It is located where the chest meets the upper abdomen. Pain in the solar plexus can cause disturbances in the functioning of this particular area:
- Mechanical injury (impact, bruise). Strikes to where the solar plexus is located unsettle the opponent for a long time. Severe injury can lead to loss of consciousness, cardiac arrest, rupture of the diaphragm and other serious complications.
- Solar plexus neuritis. This inflammatory disease is called solaritis; it can be provoked by mechanical and infectious factors.
Most often, painful sensations have nothing to do with the work of this nerve center. May cause discomfort:
- gastritis;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach or duodenum;
- tumors of benign and malignant types, localized near the solar plexus (in the stomach, intestines, pancreas);
- disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas;
- duodenitis;
- severe helminthiasis;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- cholelithiasis.
A doctor can find out the exact cause of discomfort.
Gastritis, ordinary and not very
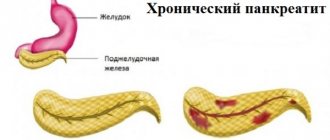
The most common disease that causes pain in the epigastric region is gastritis, that is, inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Depending on the nature of the disease, gastritis can be acute or chronic.
The danger of chronic gastritis is that most cases of stomach cancer develop against the background of a long course of this seemingly harmless disease.
The type of gastritis is divided into superficial gastritis, in which only the mucous membrane becomes inflamed, and atrophic - in this case, against the background of inflammation, the stomach glands that produce hydrochloric acid gradually die.
| How can you examine the stomach? | |
| Unfortunately, not every person can safely undergo gastroscopy. The test is not a pleasant one. Therefore, now one of the most common (albeit paid) services is gastroscopy in a dream. If you have no contraindications to general anesthesia, then you can sleep through the entire examination with a clear conscience and not get negative impressions. Another innovative research method involves the patient swallowing an endoscopic capsule. A small device goes on a journey through the digestive tract and “makes a movie” along the way. Due to the fact that such a study is the least traumatic and most informative (the esophagus, stomach and entire small intestine are examined), it costs much more than all alternatives. | |
Unfortunately, it is possible to identify the type of gastritis and, accordingly, decide on treatment only after an examination, colloquially called “gastroscopy” - during this procedure, an endoscope is inserted into the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
In fact, the study is called “esophagogastroduodenoscopy”, because during the procedure the doctor examines the patient’s esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. It is very important to carry out this study in as much detail and quality as possible, since gastritis very often “adjacent” to duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum) and pathology of the esophagus.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis and its prevention
Conservative treatment of osteochondrosis in the thoracic spine is intended to stop or at least slow down degenerative changes, restore normal back mobility and eliminate symptoms that cause discomfort to the patient.
Therapeutic treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis involves the simultaneous use of:
- medications
(chondroprotectors, neuroprotectors, muscle relaxants, anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics); - methods of physiotherapeutic complex
; - therapeutic exercises
; - orthopedic regime
.
Patients are also advised to change their diet and lifestyle.
In case of severe irreversible changes in the intervertebral joints , in which pain and nerve conduction disorders are not relieved by medications,
surgery is recommended for patients
. It helps stop the death of nerve tissue and prevent life-threatening or disabling consequences of thoracic osteochondrosis. Depending on the situation, complete or partial resection of the intervertebral disc or its replacement with an artificial one, narrowing of the spinal canal or other surgery may be indicated.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
Physiotherapy
The objectives of physiotherapy for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region are to reduce pain and inflammation, relieve spasms, strengthen the muscle corset, restore the function of the nerve roots and normal blood circulation.
To relieve the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, the following are successfully used:
- Magnetic therapy
is one of the most effective anti-inflammatory techniques. Improves metabolic processes in tissues and relieves swelling. - Laser therapy
. Promotes biological activation of regenerative processes. Helps eliminate the consequences of trophic disorders and relieve inflammation. - Drug electrophoresis
. Allows you to restore tissue nutrition and relieve inflammation - the effect of the procedure depends on the medications used. - Medicinal phonophoresis
. Ensures deep penetration of the active ingredients of medications into soft tissues. - Massotherapy
. Helps relax muscles, eliminate tension and improve the supply of nutrients to the tissues of the spine. In the early stages, it eliminates the main symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis - a feeling of pain in the sternum - in a few sessions. - Acupuncture
. Stimulation of muscles and nerve endings helps relieve pain, restore sensitivity and eliminate swelling. - Ultrahigh frequency therapy
. Increases the permeability of capillary walls, improves blood flow and ensures the flow of protective cells into the site of inflammation. - Shock wave therapy
. It starts the processes of restoration of bone and cartilage tissue, prevents the deposition of calcium salts on the vertebral surfaces. - Balneotherapy
. As a rule, mud and ozokerite applications are used, less often paraffin. Radon and hydromassage baths are also recommended for patients. They help improve metabolism and restore sensitivity in affected tissues. - Amplipulse therapy
. It has a neurostimulating, analgesic and trophic effect, activates metabolic processes, and facilitates breathing. - Kinesiotherapy
(physical therapy, massage, traction therapy, kinesiotaping). Allows you to strengthen ligaments and skeletal muscles, restore mobility in the back and eliminate even persistent spasticity. Prevents the formation of osteophytes and narrowing of the canals in which the spinal roots are located.
In addition to physical therapy sessions, for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, patients may be recommended an orthopedic corset, which allows them to relieve the load on the spine.
Exercise therapy and massage
Therapeutic exercises and massage help strengthen the back muscles and relieve stress on the spine. With daily sessions, they help achieve stable drug-free remission, increase range of motion, and eliminate neurological manifestations of the disease. These treatment methods also prevent complications of osteochondrosis.
. For example, congestion in the lungs (with thoracic osteochondrosis it is difficult to breathe deeply), due to which patients are susceptible to pneumonia, as well as coronary heart disease.
Dosed physical activity helps relieve compression of the nerve roots, improve blood circulation and nutrition of the intervertebral discs. The optimal frequency and duration of gymnastic classes is determined by the exercise therapy instructor. As a rule, 3-4 exercises of 10-15 minutes a day are enough.
.
The exercises recommended for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis include the following:
- Stand straight, feet together, hands at your sides. As you exhale, raise your arms up and bend back, then inhale deeply. Lower your arms and lean forward, slightly arching your back in a dome-shaped manner (to do this, lower your head and shoulders as you exhale).
- Sit on a chair and, while inhaling, place your hands behind your head. Bend back and rest your shoulder blades on the back of the chair, exhaling.
- Get on all fours and arch your back. After maintaining the position for 3 seconds, bend your back with a crampon.
- Lying on the floor on your stomach, place your palms on the floor and, raising yourself on your arms, try to move your head as far back as possible, lifting your chest off the floor.
- Lie on your stomach and extend your arms at your sides. Perform the “yoke” exercise, trying to simultaneously raise your head and legs.
- Sit on the floor and stretch your legs in front of you. Reach the fingers of your right hand to the toe of your left foot and vice versa.
- Do a plank exercise (about 30 seconds).
- Perform hangs on the horizontal bar (or, in the absence of a horizontal bar, secure your fingers on the door frame and try to stretch your back as much as possible).
Bends to the side while raising your arm will also be helpful. All exercises should be performed 8 to 10 times
.
To treat thoracic osteochondrosis, various massage techniques are used, incl. acupressure and vacuum massage. For self-massage at home, patients are recommended the following movements:
- stroking the cervical-collar, scapular and axillary areas
; - squeezing with the thumb and index finger
(grabbing the skin and soft tissues); - trituration
; - kneading
(it should be done extremely carefully, it is advisable to entrust this technique to a specialist).
Massage should not be performed during exacerbations of the disease or during severe inflammation.
Drug treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
To treat the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- help relieve pain, calm inflammation and disperse swelling. They can be used both systemically (in the form of tablets, capsules and injections) and locally (in the form of ointments, gels, creams, compresses and solutions for medicinal electrophoresis). - Hormonal drugs
- to eliminate acute and chronic neurological pain. Used in cases where NSAIDs demonstrate insufficient effectiveness. - Muscle relaxants
are prescribed to reduce muscle tone and eliminate spasms of skeletal muscles. This helps alleviate pain and has a positive effect on tissue trophism. - Blood circulation correctors
- strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation in small capillaries that nourish the periosteum and other structural elements of the vertebral joints. Reduce discomfort and reduce the risk of complications. - Neuroprotectors
- to preserve and restore sensitivity during compression of nerve roots and relieve neurological symptoms. This group also includes cholinesterase inhibitors, which improve nerve impulse transmission and help restore normal muscle tone.
For structural restoration of tissues affected by the degenerative process, the following are used in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- chondroprotectors (Artracam)
are essential bioactive substances that trigger the processes of regeneration of cartilage and bone tissue. Serves to prevent the growth of osteophytes and narrowing of the spinal canal. They help a weakened body grow stable and resilient cartilage cells. Taking Artracam significantly improves the shock-absorbing properties of intervertebral discs, making them more elastic and resistant to damage; - vitamin complexes
- help normalize metabolic processes and prevent excess oxidation in tissues.
To relieve excruciating pain that interferes with the patient’s daily activities, the doctor may recommend a medical blockade with anesthetics. Diuretics are used to eliminate swelling and relieve compressed nerves and blood vessels.
Prevention of thoracic osteochondrosis
To prevent symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, you should:
- Take care to maintain healthy posture. This is facilitated by walking, swimming and therapeutic exercises to strengthen the muscles of the back, chest, abs, and shoulder complex.
- When working sedentarily, properly arrange your workplace and perform physical warm-up whenever your back and neck begin to become stiff (ideally, bend to the sides, stretch, and rotate your shoulders every 2 hours).
- Avoid back injuries and promptly seek help from an orthopedic traumatologist, even in the case of a seemingly insignificant bruise. Other diseases of the musculoskeletal system should not be triggered, especially in the joints of the lower extremities.
- If possible, unload the spine during the day (to do this, just lie on the floor for 40 minutes).
- Protect yourself from hypothermia and stress.
- Take chondroprotectors to protect joints for at least 3 months a year. Regardless of the strength of the muscular corset, the human spine is anatomically not adapted to vertical loads, and therefore requires additional support.
- Adjust weight if it is overweight. In addition to maintaining a low-carb diet, you should eat a diet high in vitamins and minerals. In the spring-autumn period they can be taken in tablet form.
- Sports activities that involve jumping from heights or lifting heavy weights should be limited.
- It is advisable to sleep on a semi-rigid bed, and for prolonged sitting, choose hard furniture. This helps maintain muscle tone and relieve stress on the spine. If possible, you should purchase an orthopedic mattress and shoe insoles.
- Do not lift loads weighing more than 10 kg. The load should be distributed evenly, with muscle tension and without transferring to one side. If necessary, use a special sports corset. It is undesirable to hold loads in outstretched arms for a long time.
- Women should avoid wearing high-heeled shoes. The optimal heel height is 2-4 cm.
These recommendations will also be useful for those who are already sick - they will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the spine and will help to significantly slow down pathological changes.
And remember: the main thing in the prevention of thoracic osteochondrosis is consistent adherence to healthy habits.
Let chest pain never bother you!
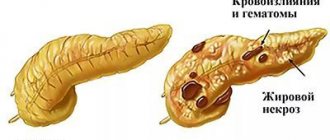
Pancreatitis is a threat to life
Acute pain in the epigastrium can be a symptom of pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas. This organ can sluggishly signal a problem with regular, mild pain. And this means it’s time for an examination.
But if the pain in the epigastrium has become almost unbearable, plus stool disturbances and vomiting develop, in some cases an increase in temperature, then this means acute pancreatitis. And this is an indication for urgent hospitalization.
Pancreatitis usually occurs when pancreatic secretions (pancreatic juice) stagnate. The duct that should carry secretions into the duodenum is blocked by a stone, cyst, swelling or pus. But the juice continues to be produced and enthusiastically digests the gland itself. Therefore, in acute pancreatitis, delay is literally death.
Oddly enough, pancreatitis often attacks young people who lead an active lifestyle, love to eat, sometimes drink, and, most importantly, are subject to constant stress.
| Interesting! | |
| Vegetarians are less likely to suffer from peptic ulcers than people who eat meat. If the "ulcer" increases the fiber content in the diet, this will reduce the frequency of exacerbations of the disease. Lately, doctors have been “prescribing” fiber even during exacerbations of ulcers. | |
Problems with the pancreas can be diagnosed in advance - before the development of acute pancreatitis - using a simple ultrasound and blood test. If an ultrasound shows any problems with the pancreas, the doctor may prescribe a computed tomography scan - a study that gives a layer-by-layer image of the gland and allows you to examine in detail the essence of the problem.
Pain due to damage to the solar plexus
True pain in the middle of the sternum can be the result of injury, intense physical activity, as well as neuritis and neuralgia.
Physical exercise
In this case, the pain takes on an acute, stabbing and burning form. The severity of the pain syndrome is so intense that it forces the person to stop and take a break. This kind of soreness is temporary and is associated with sports or hard work. Rest enough, don’t overwork yourself in the future, create a work schedule, and the problem won’t bother you anymore.
Abdominal pain during physical activity is not dangerous and pathological, but if it becomes permanent, then this may be a signal of the development of a serious pathology
Injuries
An intense blow can lead to rupture of the diaphragm and the appearance of a hernia, which can only be eliminated through surgery. In mild cases, the blow causes the diaphragm muscle to contract. As a result, it is difficult for a person to breathe, and he may even lose consciousness.
Along with acute burning pain, patients complain of the following symptoms:
- burning inside the abdomen;
- nausea;
- urge to defecate;
- breathing problems, in particular, it is difficult for the patient to take a breath;
- dull pain at the site of the projection of the heart;
- the patient takes a characteristic position: lies on his side, bends his legs at the knee and presses them to his stomach.
As for first aid, the victim should be laid down, ensure normal breathing, straightening the torso. You can also massage the affected area. In severe cases, it may even be necessary to use ammonia.
If the victim experiences vomiting, convulsions, or severe abdominal pain, immediately call an ambulance. If breathing stops, chest compressions will be required. If pain persists after the blow, then the development of an inflammatory reaction can be suspected.
Neuralgia
Bacterial and viral infections can cause neuritis. The inflammatory process can also be caused by external factors: nerve compression, injury, intoxication. I often associate neuritis with hypothermia.
With neuritis, the nerves that make up the solar plexus become inflamed, which causes specific pain in the upper abdominal cavity. People who lead a sedentary lifestyle or engage in excessive physical activity are susceptible to neuritis.
With neuritis, characteristic symptoms appear, namely:
- attack of acute pain. It acquires a stabbing and boring character;
- a painful attack can spread throughout the abdominal cavity and even radiate to the back;
- feeling of fullness and heat in the middle of the abdomen;
- Stress and physical activity only increase the severity of pain.
With neuralgia, the solar plexus nerves are irritated; the clinical manifestations of neuritis and neuralgia are very similar; a neurologist will help with differential diagnosis
When using solarium, the solar plexus tissues become inflamed and irritated. Patients complain of burning, boring pain in the solar plexus area. Along with this, dull pain in the heart and chest, heaviness in the abdomen, bloating, belching, heartburn, and constipation appear. Solarite causes a feeling of heat inside the abdomen, while the body temperature remains normal.
Treatment of solarium is carried out using physiotherapeutic methods, massage, breathing exercises, as well as anti-inflammatory and antispasmodic agents.
For neurological disorders, treatment includes taking B vitamins, stimulants of biological origin, as well as drugs to increase the conductivity of nerve fibers and improve blood flow.
Treatment methods
Despite the fact that pain and other manifestations are not always considered a sign of any disease, experts recommend visiting a doctor in a timely manner to undergo a full diagnostic examination.
If the cause is tight clothing or some minor injury, no special treatment is required. Usually, eliminating the predisposing factor and physical rest helps get rid of the symptom.
If the discomfort is associated with diseases, a full examination is necessary, followed by the prescription of medications to normalize the condition. Depending on the cause, the treatment regimen may differ.
Medications
Pain in the solar plexus and difficulty breathing are common reactions in some diseases of the internal organs. To date, there is no standard universal regimen for all patients. The treatment plan is determined depending on the cause of the symptom, as well as the severity of associated abnormalities.
However, there are medications that are most often included in treatment courses due to their high effectiveness:
- Ibuprofen indicated in cases where symptoms are provoked by an inflammatory disease of internal organs. The drug helps eliminate pain, discomfort, reduces body temperature, which somewhat alleviates the condition of patients. Take 2-3 tablets per day at equal time intervals. Treatment usually lasts no more than 5-7 days.
- Ketarol has pronounced analgesic properties and is used to improve the condition of pain and discomfort due to injuries, osteochondrosis or neuralgia. The drug relieves pain and somewhat slows down the progression of the inflammatory process. In combination with other agents, it increases the effectiveness of therapy. Tablets are taken for 5-7 days, 1 tablet 2-3 times a day, depending on the severity of the manifestations.
- No-spa has antispasmodic properties and helps eliminate spasms of the diaphragm and chest muscles. If discomfort is caused by excessive tension or compression, the drug helps to significantly improve the condition. Take 2 tablets 2 times a day for 10-14 days. In each case, the duration of therapy may vary depending on the patient's condition.
- Almagel eliminates heartburn, nausea and some other symptoms of the digestive tract if discomfort in the solar plexus is caused by pathologies of the digestive system. The product is taken 5 ml 2-3 times a day. Treatment can last from 1 to 3 weeks depending on the severity of symptoms. In most cases, taking the drug is combined with the use of other medications.
- Teraflex is indicated for osteochondrosis, which is accompanied by pain in the solar plexus. The product contains components with chondroprotective properties, which helps not only stop the progression of osteochondrosis, but also significantly improves the condition. Patients are usually prescribed to take 2 tablets of the drug per day for 2-3 months. In each case, therapy can be extended according to individual indications.
- Amoxicillin is indicated in cases where pain and difficulty breathing occurs against the background of pathologies of the respiratory system of inflammatory origin. The drug has antibacterial properties and helps destroy the most common bacteria that cause inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system. The medicine is taken orally in 2-4 tablets, depending on the severity of inflammation. Treatment lasts up to 2 weeks. The drug is considered quite effective, especially when prescribed in a timely manner.
- Gastrocepin is used for pathologies of the digestive tract, namely damage to the stomach. For gastritis and gastroduodenitis, the drug stimulates tissue restoration and prevents the progression of the pathological condition. The greatest effect is achieved when the drug is administered intramuscularly in the form of a solution of 2 ml per day. Treatment lasts 10 days. The product is effective, the first results can be obtained quite quickly.
- Omez is indicated for patients who suffer from gastritis, gastroduodenitis or peptic ulcer. The drug suppresses the activity of the digestive system, slightly reduces the concentration of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, which weakens the negative effect on the mucous membranes. The drug is taken for 2-4 weeks, depending on the severity of the symptoms of the underlying disease. The dosage is 1 tablet, taken 3 times a day.
- Cerucal helps eliminate nausea and also prevent vomiting that occurs against the background of pathologies of the digestive system. The drug is administered intramuscularly, 2 ml 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days. The medicine is not used as the only method of therapy, as it only eliminates specific symptoms. It is effective and helps eliminate pain and discomfort in the solar plexus area if symptoms are caused by disorders of the digestive system.
Cerucal - Gordox is indicated for diagnosing pancreatitis. The drug helps stop the progression of the disease and prevents the destruction of organ cells. The drug is administered intravenously using a dropper, but after first adding 10 ml of solution in 200 ml of sodium chloride. Treatment lasts up to 2 weeks. The drug is prescribed quite often and is considered effective.
- Lesfal is indicated for patients who suffer from pathologies of the liver and gallbladder, and against this background, patients experience pain in the solar plexus area. The solution is administered intravenously at 5-10 ml per day, treatment lasts up to 2 weeks, helps prevent the progression of pathologies.
- Lazolvan is prescribed for pain and difficulty breathing due to inflammatory pathologies of the respiratory system. In this case, patients have a cough, and the product has mucolytic properties and stimulates the removal of sputum. It is allowed to take 2-6 tablets per day, depending on the severity of the condition. Treatment lasts up to 14 days, but in each case it can be extended or shortened according to individual indications.
- Ceftriaxone is prescribed for advanced pathologies of inflammatory origin. Most often, the remedy is indicated for bronchitis and severe pneumonia. The drug is administered intravenously or intramuscularly at 2-4 g per day, which depends on the severity of the condition. Before administration, the product is dissolved in 10-20 ml of sodium chloride. The therapeutic course lasts 10-14 days. The drug is considered effective and helps prevent complications as the disease progresses.
You cannot independently draw up a treatment regimen or extend the course, or exceed the dosage. This can cause complications. Such doses are considered standard, but can be adjusted individually if necessary.
Folk remedies
Pain in the solar plexus and difficulty breathing are signs that are not always a symptom of the disease. There are no folk remedies that completely eliminate the disorder, but some natural compounds alleviate the condition and can prevent the progression of the disease.
Mint infusion has antispasmodic and sedative properties, eliminates nausea and heartburn in patients with pathologies of the digestive tract. It must be taken for 10 days, 200 ml before bedtime. You can prepare the product from 3 g of dry mint and 200 ml of boiling water, the infusion time is 20 minutes. It is allowed to add sugar or honey to the drink.
An alcoholic tincture of motherwort helps ease the work of the heart and improve the condition of hypertension. If pain in the solar plexus and difficulty breathing are associated specifically with heart pathologies, the remedy significantly improves well-being.
For 100 ml of alcohol or vodka, you need to take 20 g of dry and pre-crushed raw materials, leave for 2 weeks. Take the filtered product 20-30 drops 2 times a day for 2 weeks.
Chamomile infusion is considered a universal remedy for eliminating symptoms that occur against the background of pathologies of the digestive tract. The product eliminates pain and heartburn.
Spasms the muscle layer and also helps improve digestion. As a result, the progression of diseases slows down. You can prepare an infusion from 2 g of dry plant and 250 ml of boiling water. After infusion for 20 minutes, the infusion should be filtered and taken 250 ml 2 times a day. Therapy lasts from 10 to 14 days.
The use of any traditional medicine recipes is allowed only after consulting a doctor. Despite the relative safety of the drugs, they have contraindications and can provoke various complications.
Other methods
If pain and difficulty breathing occurs as a result of a purulent focus in the lungs or fluid accumulation, pleural puncture can be identified among additional methods of therapy. The procedure involves inserting a thick needle into the affected area to remove fluid or pus.
It is carried out in a medical institution and involves preliminary local anesthesia of the affected area. The manipulation takes from 1 to 4 hours depending on the purpose of its implementation. Usually it does not cause severe discomfort and is well tolerated by patients. During diagnosis, the specialist also collects biological material to be sent to the laboratory for research.
Depending on the results obtained, subsequent treatment tactics are developed.
Solarite is a common cause of pain in the epigastric region
Solaritis is a disease in which an acute inflammatory process develops in the solar plexus. Pain radiating to the lower back, lower abdomen and back is a characteristic symptom of solaritis. The nature of the unpleasant sensations is always painful. The pain is sharp, boring, burning. Most patients are forced to resort to strong anesthetic drugs - but this approach to therapy does not affect the cause of the disease, and the pain returns.
Solarite can provoke the following conditions:
- hypothermia;
- low immunity (including human immunodeficiency syndrome);
- chronic stress;
- excessive physical activity;
- recent severe infectious disease;
- surgery, general anesthesia, implantation.
If solaritis is not treated, the pain will intensify and eventually severe pathologies of the nervous system may develop. Treatment requires a course of physiotherapy, nootropics, exercise therapy, giving up bad habits and changing lifestyle.
Excessive exercise
Physical education and sports have health benefits. But if you exercise too hard during weightlifting, pain may develop. Powerlifting and working with serious weights is a rather traumatic activity. Beginners often perform barbell exercises without proper technique and without the supervision of an experienced trainer, which leads to many health problems.
Pain in the solar plexus after physical activity is also not uncommon. For example, if you carry heavy building materials from place to place for several hours or unload large goods, you should not be surprised at the appearance of pain in the solar plexus. What is it and how to deal with it in this case?
The first rule for treating pain in the epigastric region after physical work and heavy lifting is complete rest. Bed rest for two to three days is necessary for the body to recover from overwork. If you do not follow this rule and continue to overwork, complications are possible (the development of a hernia, in women - prolapse of the uterus, inflammation of the solar plexus nerves).