The drug Glucose is a very necessary remedy for many patients. First of all, the medicine is necessary as a source of energy necessary to nourish tissues and cells. Cell activity depends on how well the body is able to metabolize the compounds.
First of all, glucose enters the body through consumed food. Once in the gastrointestinal tract, the substance breaks down into simple molecules, which enter the bloodstream and are distributed throughout the body.
There is no need to worry about what dose of a substance is needed, because the excretory system removes excess from the body.
Where does glucose come from?
Blood glucose reserves appear not only from food consumed.
If glucose levels begin to fall, the body will launch mechanisms to break down strategic reserves. Certain enzymes remove glucose molecules from the glycogen chain (stored in the liver) and send them into the bloodstream. Thanks to this process, normal glucose levels are maintained in the body.
It is important to know that after hypoglycemia, sharp jumps in plasma glucose levels often occur, which are very difficult to deal with.
The body also extracts glucose from fat reserves, but this process is lengthy. This method is used during heavy exercise or prolonged fasting.
Glucose Compound Formula: C6H12O6
The substance tastes sweet, odorless. It is highly soluble in water, in solutions of chloride, zinc and sulfuric acid. In industry it is synthesized due to the hydrolysis of cellulose, and in nature as a result of plant photosynthesis.
By the way, sucrose is twice as sweet as glucose. The substance has found application in medicine, industry and cooking.
Daily intake, the importance of its use.
Each part of the body needs its own “dose” of glucose. Brain cells and red blood cells absorb different amounts of this substance, but it is equally important. In order to calculate how much you need to consume, you should multiply your body weight by 2.6. The value that is obtained as a result of a simple mathematical operation will be the daily dose of glucose for the body.
When calculating an individual norm, a person must take into account the scope of his activity. Knowledge workers and people involved in computational and analytical work must consume more of this monosaccharide because their activities require more energy. A person who moves little, does not engage in mental work, gains excess weight, needs less of this “fuel”. For such a person, energy is taken from fat reserves.
When consumed in the right doses, glucose is a medicine, but when consumed in excess, it can become poisonous to the body.
Composition of the drug
One tablet of the drug contains 1 g of glucose monohydrate. The auxiliary ingredients are:
- Calcium stearate
- Potato starch
- Talc
- Stearic acid
Glucose tablets are produced in a round shape, their surface is flat.
If the drug is produced in a “set” with ascorbic acid, a chamfer and a dash are applied to the tablets.
The drug is placed in 10 pieces in blister packs. The cardboard package may contain 1 or 2 blisters and instructions for use.
Hypoglycemia
When there is little monosaccharide in the blood, the body also suffers. After all, what is glucose? This is a necessary substance for the body, like air for the lungs. When there is not enough of it, the body weakens, brain nutrition deteriorates, and a person faints more and more often. Other symptoms also include fatigue, muscle weakness, and poor coordination. The cells of the body do not receive proper nutrition, their division slows down, as does the regeneration process, which can lead to their complete death. There are several main causes of hypoglycemia. These include a lack of sweets in the diet, cancer, alcohol poisoning, and thyroid dysfunction.
In order to get rid of this disease or carry out prevention, you should review your diet. It is necessary to add products that contain glucose in their natural form. Benefits To have a complete understanding of what glucose is, it is necessary to consider its main functions - nutrition and energy saturation of the body. It is this monosaccharide that supports the functioning of the respiratory system, muscle contraction, heartbeat, and the functioning of the nervous system.
It helps activate metabolic processes and is itself easily digestible. Ensures performance. Improves memory, learning abilities, nourishes brain cells. Stimulates cardiac activity. Helps quickly saturate the body with food. Affects the normal functioning of the nervous system. Allows faster recovery of muscle tissue. Accelerates the neutralization of toxic substances in the liver. In addition, glucose is used as a component in anti-shock drugs and blood substitutes.
pharmachologic effect
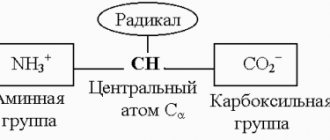
Glucose (dextrose) belongs to the category of monosaccharides. The substance is found in the juice of various berries (in particular grapes), which is why it is sometimes called grape sugar.
Oligosaccharides and disaccharides consist of glucose units.
Once in the digestive system, complex saccharides break down into fructose and glucose.
Glucose, as a monosaccharide, is found in:
- Lymph
- Blood
- Myocardium
- Skeletal muscles
Glucose is a participant in carbohydrate metabolism and affects metabolism.
Dextrose is necessary for carbohydrate nutrition of muscles and brain; the substance is well and quickly absorbed and helps improve human performance.
The harm of consuming glucose
However, for older people, glucose can be very harmful. This is especially true for people who have metabolic disorders. For example, the following complications may occur: sudden weight gain; thrombophlebitis; disruption of the pancreas; increased cholesterol levels; allergic reactions; inflammatory and heart diseases; arterial hypertension. The production of energy from glucose must be fully compensated by the energy costs of processes in the body.
The rate of its consumption for each is determined individually. Where can I find the required amount of natural monosaccharide? A lot of this substance is found in animal muscle tissue, berries, starch and fruits. The richest natural source of glucose is honey, which contains 80% of this monosaccharide. In addition, it contains fructose, which is no less beneficial for humans. Doctors and nutritionists agree that you should eat foods that will stimulate the body to produce natural sugars, and not revel in refined sugar and confectionery products. It is quite obvious which glucose will be more beneficial for the body.
Why is Glucose useful?
Glucose is widely used for the treatment of various pathologies, as it has a good effect on metabolic processes.
Pregnant women are prescribed glucose:
- If you suspect that the intrauterine fetus is smaller than the required size
- To reduce the chance of miscarriage
- To prevent premature birth
After consuming glucose, you feel better and fatigue goes away.
During pregnancy and lactation, it is necessary to constantly monitor plasma sugar levels.
Hyperglycemia
This disease develops if, after or before a meal, the amount of monosaccharide in the body does not meet the desired value. On an empty stomach, a healthy person should have 3.3-3.5 mm/l of glucose, and after eating - about 7.8 mm/l. If the indicator is higher, then the disease hyperglycemia may begin (the clinical symptom is an increase in the glucose level in the blood serum compared to the norm of 3.3-5.5 mmol/l).
Changing the amount of grape sugar in the body always affects health. It doesn’t matter in which direction the fluctuations occur, because they can lead to irreparable disorders.
When a person has hyperglycemia, blood sugar levels rise and insulin production increases. As a result of this, the pancreas works intensively, literally to the point of wear and tear. Over time, the organ becomes depleted and overall immunity weakens.
There is a risk of developing diabetes. When the blood glucose level crosses 10 mm/l, a person’s liver fails and the functioning of the circulatory system is disrupted. Excess sugar does not disappear from the body; it turns into fat. As a result, a number of diseases can develop: hypertension, atherosclerosis, heart attack, coronary disease. There may even be a cerebral hemorrhage.
Indications for use
The appearance of the pharmaceutical product depends on the manufacturing company and the presence of other components.
Doctors prescribe regular glucose in tablets, as well as its combination with ascorbic acid, for:
- During pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Avitaminosis and hypovitaminosis
- Increased need for vitamin C and glucose
In addition, the medication is necessary for children during periods of intensive growth.
Glucose is excellent for recovery after severe pathology and physical activity.
Contraindications to the use of Glucose
Glucose solution is contraindicated in patients who suffer from:
- hyperglycemia
- decompensated diabetes mellitus
- hyperosmolar coma
- impaired glucose utilization in the postoperative period
- hyperlactic acidemia
Intravenous administration of Glucose is carried out with caution when:
- chronic renal or heart failure
- hyponatremia
- Glucose tablets are contraindicated for:
- diabetes mellitus
- overhydration
- cerebral edema
- pulmonary edema
- circulatory diseases in which there is a high risk of pulmonary or cerebral edema
- acute left ventricular failure
Foods that lower blood sugar
The main reason for the development of this disease lies in the disruption of the pancreas. In order to protect yourself from illness, you should eat foods that lower sugar levels:
- oatmeal,
- seafood,
- blueberry juice,
- black currant,
- tomatoes,
- soy cheese,
- green tea,
- meat,
- fish,
- lemons,
- grapefruits,
- almond,
- peanut,
- watermelons,
- garlic and onion.
Glucose in ampoules, can I drink it?
Glucose can be taken orally, as its regular solution does not contain substances that can be harmful. The medicinal liquid tastes quite pleasant, reminiscent of ordinary sweet water.
You can drink glucose in ampoules if there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure or if a diabetic has exceeded the dosage of insulin. However, for these problems, it is wiser to drink strong, sweet tea.
In case of poisoning, glucose is often prescribed, but its oral use during intoxication can provoke additional vomiting.
In what cases and in what dosage is “medical” glucose prescribed?
Indications for use:
- hypoglycemia (low blood sugar concentration);
- lack of carbohydrate nutrition (with mental and physical overload);
- rehabilitation period after protracted illnesses, including infectious ones (as additional nutrition);
- decompensation of cardiac activity, intestinal infectious pathologies, liver diseases, hemorrhagic diathesis (in complex therapy);
- collapse (sudden drop in blood pressure);
- shock;
- dehydration caused by vomiting, diarrhea, or surgery;
- intoxication or poisoning (including drugs, arsenic, acids, carbon monoxide, phosgene);
- to increase the size of the fetus during pregnancy (in case of suspected low weight).
In addition, “liquid” glucose is used to dilute drugs administered parenterally.
Isotonic glucose solution (5%) is administered in the following ways:
- subcutaneously (single serving - 300 - 500 milliliters);
- intravenous drip (maximum rate of administration - 400 milliliters per hour, daily dose for adults - 500 - 3000 milliliters, daily dose for children - 100 - 170 milliliters of solution per kilogram of child weight, for newborns this figure is reduced to 60);
- in the form of enemas (a single portion of the substance varies from 300 to 2000 milliliters, depending on the age and condition of the patient).
Hypertonic glucose concentrates (10%, 25% and 40%) are used for intravenous injections only. Moreover, no more than 20–50 milliliters of solution are administered at one time. However, in case of large blood losses or hypoglycemia, hypertonic fluid is used for infusion (100 - 300 milliliters per day).
Remember, the pharmacological properties of glucose are enhanced by ascorbic acid (1%), insulin, methylene blue (1%).
Glucose tablets are taken orally, 1 to 2 tablets per day (if necessary, the daily portion is increased to 10 tablets).
Contraindications to taking glucose:
- diabetes;
- pathologies accompanied by an increase in blood sugar concentration;
- individual glucose intolerance.
Side effects:
- overhydration (due to the introduction of volumetric portions of an isotonic solution);
- decreased appetite;
- necrosis of subcutaneous tissue (when a hypertonic solution gets under the skin);
- acute heart failure;
- inflammation of the veins, thrombosis (due to rapid administration of the solution);
- dysfunction of the insular apparatus.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Remember, too rapid administration of glucose is fraught with hyperglycemia, osmotic diuresis, hypervolemia, and hyperglucosuria.
Mode of application
Children over three years of age and adults can take the classic form of the drug, 0.5-1 tablets three times a day. If the doctor considers it necessary to prescribe a combined form of the drug (with ascorbic acid), the dosage must be recalculated, taking into account the content of vitamin C in the tablet. Typically, the dose for treatment varies from 50 to 100 mg per day 3-5 times a day.
For preventive purposes, adult patients are allowed to take up to 100 mg of the drug per day. Children 6-14 years old should not take more than 50 mg of the drug per day.
It is important to understand that the dosage and duration of therapy must be adjusted by the attending physician.