General information about male disease
Cystitis in men is an infectious disease. The prevalence of this disease in men is much less than in women. This is explained by the fact that it is more difficult for bacteria that cause the disease to enter the male body. The male urethra is longer, so the infection does not reach the internal organs of men as often as in women.
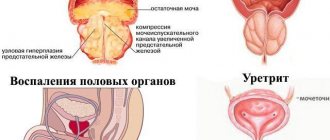
Cystitis is a disease that affects the genitourinary system, regardless of the person’s gender. The course and symptoms of the disease differ somewhat among representatives of different sexes, although there are common signs. Cystitis in men is a process of inflammation of the urinary system. With this disease, the mucous tissue of the bladder is affected, as a result of which the man experiences discomfort and cannot live a full life.
Manifestations of abnormal bladder activity: painful and frequent urination, the appearance of mucus and blood in the urine, repeated urges to visit the toilet at night. The patient may not immediately see a doctor; this is dangerous because of its consequences. Cystitis can become chronic and lead to other complications. In order not to progress the disease, try to contact experienced specialists at the Global Clinic Center in a timely manner.
Why choose treatment at the Urology Clinic named after. Fronshteina R.M.
- It is a leading institution in the field of urology.
- Service by medical staff is provided at the level of European quality.
- The clinic's staff includes world-renowned specialists.
- All services provided by the clinic are strictly confidential.
- When conducting examinations and treating patients, the latest laser and electronic technology is used.
- Treatment methods are focused on reducing trauma during endoscopic procedures.
- The use of an ultrasonic scalpel reduces the risk of blood loss during operations.
You can come to the clinic for a consultation from different regions and cities of Russia.
Bladder inflammation can be cured. It is imperative to take chemical medications, which must be prescribed by a doctor, and not self-medicate.
Classification of cystitis
There are several signs that form the basis for the classification of the disease.
By methods of manifestation
According to the methods of manifestation, there are two types of cystitis:
- Spicy
- Chronic
Acute cystitis in men can occur:
- first;
- no more than one case per year;
- with a frequency of 2 or more times every 365 days.
For the occurrence of acute cystitis, there are unfavorable factors in the form of uncontrolled use of certain medications and thermochemical effects on a man. An infection that enters the body of men can also cause certain symptoms characteristic of acute stage cystitis.
The chronic form of the disease can be divided into the following subtypes:
- Latent (symptoms of cystitis in men in this case are smoothed out). The frequency of occurrence of the disease is more than two cases per year, the disease is stable or with rare periods of exacerbations.
- Persistent. The process of inflammation and development of cystitis is diagnosed twice a year or more often.
- Interstitial. This is the most severe form of the disease. Cystitis progresses and can lead to serious complications.
According to the etiology of occurrence
Based on this characteristic, doctors distinguish such forms of cystitis in men as primary and secondary. Primary cystitis is in no way associated with other pathologies of men. This is an independent disease. The secondary form may be the result of problems in the genitourinary system and other organs of the patient. Men with prostate adenoma, diseases of the spinal column, abnormal development of the bladder, or ingestion of foreign fragments should be prepared for this kind of disease.
By localization of inflammation
Cervical, diffuse, trigonitis, focal form of cystitis - this diagnosis is made depending on the location of the source of the disease. Each type of disease is characterized by its own symptoms: with cervical cystitis, urine cannot be retained, the patient often “runs” to the toilet; the diffuse form is characterized by the extensive spread of inflammation; With trigonitis, clots of blood and pus appear in the urine.
Chronic cystitis: new in diagnosis and treatment
If the diagnosis of chronic bacterial cystitis in most cases does not cause difficulties, then treatment is not always effective, and the prognosis is not always favorable, since in some cases it is not possible to identify and then eliminate the cause of the disease. Treatment of chronic cystitis requires a doctor to have a broad outlook, knowledge of the problems of gynecology, neurology, and immunology. During the development of the disease, structural changes are ahead of clinical manifestations, and, conversely, during the recovery process, normalization of impaired functions occurs before the restoration of damaged structures, i.e., morphological manifestations are delayed compared to clinical ones [16]. Only mature epithelial cells are resistant to bacteria, while the barrier function of the epithelium in the presence of epithelial cells with a moderately differentiated ultrastructure is impaired. For the treatment and prevention of chronic recurrent lower urinary tract infections, etiotropic antibacterial therapy is used in 7–10-day courses. Research by Vozianova A.F., Romanenko A.M. et al. (1994) showed that complete restoration of mature surface epithelial cells of the bladder after their damage lasts at least 3 weeks [26]. Thus, in the absence of vigilance on the part of the attending physician and lack of due attention to the duration of pathogenetic treatment, another relapse may be layered on the reparative phase of the previous process. This in turn leads to increased collagen formation, discorrelation and sclerosis of subepithelial structures, which play a major role in the homeostasis of the bladder mucosa and its innervation [27]. Thus, a vicious circle arises: inadequate treatment - chronic inflammation - reactive changes and scarring of submucosal structures - tissue hypoxia - incomplete regeneration of the epithelium - another exacerbation of the process.
Treatment of chronic recurrent cystitis:
- Etiological: antibacterial therapy.
- Pathogenetic - correction of anatomical disorders, correction of immune disorders, improvement of microcirculation, treatment of STIs, correction of hormonal disorders, treatment of inflammatory and dysbiotic gynecological diseases, correction of hygienic and sexual factors, local treatment.
- Preventive - herbal diuretics, antibacterial therapy (including postcoital prophylaxis).
Etiological treatment is antibacterial therapy based on the following principles: duration (up to 7–10 days); choice of drug taking into account the isolated pathogen and antibiogram; prescribing antibiotics with bactericidal action. The drugs to which the largest percentage of sensitive strains of urinary infection pathogens have been isolated in Russia are: fosfomycin - 98.6%, mecillinam - 95.4%; nitrofurantoin - 94.8% and ciprofloxacin - 92.3% [28]. The most preferred are norfloxacin, ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin and levofloxacin due to the absence of unwanted adverse reactions.
The choice of antibacterial drug should be made on the basis of microbiological research data. If for acute uncomplicated cystitis, preference should be given to short courses of antibacterial therapy (3–5 days), then for chronic recurrent cystitis, the duration of antibacterial therapy should be at least 7–10 days for complete eradication of the pathogen, which in chronic cystitis can be localized in submucosal structures bladder walls [1, 5].
Antibacterial therapy. The drugs of choice are fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, norfloxacin, levofloxacin, lomefloxacin), which have very high activity against E. coli and other gram-negative pathogens of uroinfections. Non-fluorinated quinolones - nalidixic, pipemidic, oxolinic acids have lost their leading importance due to the high resistance of microflora to them, and cannot be the drugs of choice for recurrent urinary tract infections [18, 29].
The choice of fluoroquinolones is due to a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, and the creation of high concentrations in the blood, urine and tissues. The bioavailability of fluoroquinolones does not depend on food intake; they have a long half-life, which allows taking the drugs 1–2 times a day. They are distinguished by good tolerability and the possibility of use in renal failure. For norfloxacin, the half-life is 3–4 hours; for the treatment of exacerbation of cystitis, it is recommended to take 400 mg 2 times a day for 7–10 days. Ciprofloxacin is considered the most powerful antibiotic from the group of fluoroquinolones, since, providing a bactericidal effect in small concentrations, it has a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity and is quickly distributed and accumulates in tissues and biological fluids with high intracellular concentrations in phagocytes (take 500 mg 2 times a day). Currently, drugs have been created that provide ease of administration - once a day. An example would be Ificipro® OD, which is a new sustained-release formulation of ciprofloxacin.
When an STI is detected, a course of antibacterial therapy is required with the inclusion of macrolides, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, aimed at eradicating the pathogen, followed by monitoring of the microflora.
Pathogenetic treatment begins with recommendations for maintaining a work-rest regime and prescribing appropriate nutrition. Drink plenty of fluids. Increased diuresis helps flush out bacteria and other pathological impurities. Dysuric phenomena are reduced due to the action of concentrated urine on the mucous membrane of the bladder. Food should be complete in protein and vitamin content and promote intestinal motility. Currently, pathogenetically based algorithms for conservative treatment of inflammatory diseases of the lower urinary tract have been developed [18].
The availability of modern antibiotics and chemotherapy drugs makes it possible to quickly and effectively treat recurrent urinary tract infections and prevent their occurrence. The unreasonableness and irrationality of antibacterial therapy are factors leading to chronicity of the process and disturbances of immunoregulatory mechanisms with the development of immunodeficiency states. It is important that the immunodeficiency state may not have clinical manifestations [30]. The concept of “immunodeficiency” includes conditions in which there is an absence or decrease in the level of one or more immune factors. Studies conducted in our clinic have shown that patients with chronic cystitis have deviations in the immune status in the form of an increase or decrease in indicators from the average norm in 33.3%. An alternative to prescribing antibacterial drugs is to stimulate the patient’s immune mechanisms when prescribing immunotherapeutic drugs. One such preparation is a lyophilized protein extract obtained by fractionating an alkaline hydrolyzate of certain strains of E. coli. The drug is available in capsules and has the trade name Uro-Vaxom. Stimulation of nonspecific immune defense mechanisms by Uro-Vaxom is an acceptable alternative to low-dose long-term chemoprophylaxis of urinary tract infections [31].
The use of polyvalent bacteriophages in the treatment of chronic recurrent cystitis is noteworthy, which is especially important for patients with a polyvalent allergy to antibacterial drugs or the presence of multidrug-resistant pathogens. Despite the lack of placebo-controlled studies of the use of pyobacteriophages, the clinical effectiveness of these drugs is beyond doubt [18].
The most important element in the pathogenetic therapy of cystitis, which can prevent chronic inflammation, is immunomodulatory therapy. Regulators of immune reactions are cytokines, their main component being interferons (INFs). The functions of INF in the body are varied, but the most important function of INF is antiviral. In addition, INF are also involved in antimicrobial protection and have antiproliferative and immunomodulatory properties. INF are capable of modulating the activity of other cells, such as normal killer cells, increasing the lysis of target cells, the production of immunoglobulins, the phagocytic activity of macrophages and their cooperative interaction with T and B lymphocytes. Gamma-INF inhibits the growth of tumor cells and suppresses the intracellular proliferation of bacteria and protozoa [9, 30]. There are drugs containing exogenous INF. However, INF inducers have advantages over them because they are devoid of antigenic properties, their synthesis in the body is always strictly balanced and, thus, the body is protected from oversaturation with interferons [32]. For the first time, for the complex treatment of chronic recurrent cystitis, we used tilorone, the trade name of the drug “Lavomax®” (125 mg tablets). Taking the drug "Lavomax®" made it possible to achieve remission of the disease in 90%, eradication of microflora in the urine was achieved in 66.7%. The results of our studies showed the undoubted promise of using Lavomax® not only for the treatment, but also for the prevention of chronic cystitis.
The chronic process, taking into account the concomitant pathology of the patients, requires the mandatory use of drugs to combat tissue hypoxia - antihypoxants (Solcoseryl 200 mg, 1 tablet 2 times a day, course 14 days); venotonics (Eskuzan 20); antiplatelet agents that improve the “fluidity” of blood through the capillaries. A typical representative of the group of antiplatelet agents is Trental, which has a vasodilator, antiplatelet, angioprotective effect (100 mg 2-3 times a day, for a course of up to 30 days), the active substance is pentoxifylline. Pentoxifylline-Acri is easy to take, as it comes in a tablet form of 100 mg, improves microcirculation and oxygen supply to tissues, mainly in the limbs, central nervous system, and to a lesser extent in the kidneys. There are a lot of drugs that improve arterial and venous circulation. However, today there is a drug that can restore microcirculation and muscle tone of the bladder; its beneficial effect on immunity indicators has been proven. This is Prostatilen, which has proven itself in the treatment of prostate diseases - a complex of polypeptides isolated from the tissues of the prostate gland of cattle [33]. We were interested in the ability of peptides (cytomedines) to act as bioregulators in the body. Their action is presumably carried out through receptors located on the surface of cells. As a result of their introduction into the body, endogenous regulatory peptides are released and the effect of cytomedins is prolonged [34]. The drug “Vitaprost®” (50 mg rectal suppositories), traditionally used in the treatment of pathologies of the male genital area, was first used in the Nizhny Novgorod urology clinic for the treatment of chronic recurrent cystitis in women. By studying capillary blood flow in the bladder mucosa in patients with chronic recurrent cystitis using laser Doppler flowmetry (LDF) [35, 36], we obtained an objectively proven effect from the use of this drug (Fig. 3). In Fig. 3 and monitoring before treatment, microcirculation index (PM) - 4.7 perfusion units. In Fig. 3 b monitoring after treatment (PM - 18.25 perfusion units).
Before treatment, patients had a stagnant type of blood flow with reduced activity of microcirculatory components and tissue ischemia. The biostimulating drug “Vitaprost®”, used as pathogenetic therapy in the treatment of chronic cystitis, contributed to the rapid disappearance of the inflammatory process and stimulation of regenerative processes, which we monitored with CP OCT. The prescribed drug made it possible to achieve a rapid effect of analgesia and helped achieve social adaptation of the patients in a fairly short time.
Treatment of recurrent lower urinary tract infections occurring against the background of STIs, in the presence of dysplastic processes in the posterior urethra, bladder neck area, and bladder triangle should be aimed at eradicating atypical pathogens and restoring the mucin layer of the urothelium. The formation of a mucopolysaccharide layer, which normally covers the epithelium of the bladder, is considered a hormonal-dependent process: estrogens affect its synthesis, progesterone affects its secretion by epithelial cells. The use of female sex hormones intravaginally leads to proliferation of the vaginal epithelium, improved blood supply, restoration of extravasation and elasticity of the vaginal wall, increased glycogen synthesis, restoration of the population of lactobacilli in the vagina, and acidic pH. An example of estrogen for the treatment of urogenital disorders is the drug estriol - Ovestin, available in tablet form 2 mg and in the form of vaginal suppositories of 0.5 mg. When using any form, Ovestin is prescribed once a day.
In the presence of severe pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed that suppress the synthesis of prostaglandins and have a pronounced analgesic effect. Indomethacin, diclofenac and others are prescribed. The drugs are used in usual doses for 10–21 days, maintaining dosages for up to 2 months. The effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs usually lasts for 3–4 months after their discontinuation [1].
The prescription of antihistamines and antiserotonin drugs is necessary to eliminate etiological and pathogenetic factors. This could be the drug "Peritol" - an H1-histamine receptor blocker with a pronounced antiserotonin effect. It also stabilizes mast cells and prevents their degranulation with the release of biologically active substances. Its anticholinesterase activity affects the storage function of the bladder. The drug is taken with 2 mg - 1 time per day, gradually increasing the dose to 4 mg - 3 times a day for 3-4 weeks. Zaditen (ketotifen) is prescribed in a dose of 0.5–1 mg, 2 times a day for 2–3 months. Other antihistamines (Diazolin, Tavegil, Claritin) are also prescribed as usual for 1–3 months.
Causes of cystitis in men
Cystitis is most often provoked by various infections that penetrate the male body. The bladder, which contains intestinal, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, tuberculosis bacilli, staphylococci, gonococci, begins to malfunction, and inflammation of various etiologies and localization occurs. There are many unfavorable factors for the appearance of cystitis in men:
- weak immune system;
- powerful radiation exposure of men;
- allergy;
- prolonged and severe hypothermia;
- presence of infections;
- injuries in the bladder area.
Frequent stress, excessive passion for work, smoking, alcohol, and a disordered sex life have a detrimental effect on a man. Men who have undergone unprofessional surgical intervention in the area of the urethra and bladder should be warned about possible negative consequences. Trusting the professional doctors from the Global Clinic Center is the first step towards a successful solution to the problem.
Causes and risk factors for developing cystitis
Cystitis is divided into bacterial and non-infectious. In most cases, inflammation of the bladder is caused by bacteria entering the urethra, most often Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally live in the gastrointestinal tract, and when they enter the bladder, they begin to exhibit their pathogenic properties.
Non-infectious factors can also cause inflammation in the bladder.
- Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome). The cause of this chronic inflammation remains unclear.
- Cystitis caused by taking medications, in particular chemotherapy.
- Post-radiation cystitis that occurs after radiation therapy to the pelvic area.
- Cystitis that occurs against the background of concomitant pathologies such as diabetes mellitus, urolithiasis, prostatitis.
Symptoms of male cystitis
The most common symptoms of cystitis in men are:
- Frequent (often with difficulty and pain) urination.
- Change in urine odor.
- Presence of pus and bloody discharge in the urine.
- Burning and itching when urinating.
Specific symptoms may be accompanied by general negative signs: weakness, decreased ability to perform usual work, painful manifestations in the groin, scrotum, bladder, increased body temperature. A man with cystitis becomes nervous, irritable, vulnerable to other diseases - the presence of these symptoms varies from person to person. The intensity of the signs of the disease increases along with the neglect and progression of cystitis.
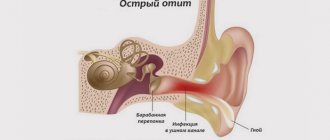
Symptoms and signs of male cystitis, characteristic of acute and chronic forms of the disease
Acute cystitis is characterized by a frequent urge to urinate, while the amount of urine is minimal, about 15 ml; sometimes the urge is accompanied by urinary incontinence.
The presence of pain, burning and cutting when urinating is considered the main symptom of cystitis. In this case, the pain can be either very strong, almost unbearable, or quite tolerable. Pain occurs at the beginning of urination and at the end. It can also be difficult to empty the bladder, despite the urge. Between visits to the toilet, a man is usually tormented by aching pain in the groin, penis, and pubic area.
Acute cystitis may be accompanied by intoxication of the body, fever, severe sweating, chills, loss of strength, and headaches. In severe cases of the disease, it is recommended to hospitalize the patient.
Severe acute cystitis often takes on a gangrenous and hemorrhagic form. In this case, the urine in men becomes cloudy, mixed with blood and mucus, has an unpleasant odor, and its amount is reduced to a minimum and does not exceed 400 ml per day.
Chronic cystitis has less pronounced symptoms. The pain is usually moderate, frequent urges are not observed, there are no bloody impurities in the urine, only mucous. Despite this, the disease is easy to recognize, because the course of the disease occurs in waves and has both remissions and exacerbations.
Diagnostics
The success of treatment largely depends on timely diagnosis. Modern methods of diagnosis are used by medical specialists from the Global Clinic Center. The doctor who conducts the appointment carefully listens to the patient’s complaints, taking an anamnesis of the disease. After this, the patient will be asked to do a urine test. The Nechiporenko method and bacterial culture are effective diagnostic methods.
The speed and smoothness of the process of urine passage through the urethra and other organs of the excretory system can be determined by the uroflowmetry method. The use of an endoscope in cytoscopy makes it possible to examine the bladder from the inside. This method gives an accurate picture of possible organ pathologies.
The male type of cystitis can be diagnosed using an ultrasound of the prostate to identify the amount of residual urine. The use of ultrasound to examine the bladder is difficult due to the overcrowding of this organ. A blood test for general analysis is also prescribed to patients to identify the causes of the disease.
Methods for diagnosing cystitis
Diagnosis of cystitis is carried out using laboratory and instrumental studies.
Laboratory diagnostics
Laboratory diagnosis of cystitis includes a general blood test and clinical urine test. In some cases, a urine test according to Nechiporenko may be required. In order to identify the causative agent of the disease, a cultural study (bacteriological culture of urine) can be carried out.
Ultrasound of the bladder
Ultrasound of the bladder is the simplest and most informative study. It allows you to assess the degree of damage to the bladder wall, the extent of the process, and detect stones and tumor processes that may accompany cystitis.
More information about the diagnostic method
Cystoscopy
In cases of frequently recurring cystitis, cystoscopy may be performed.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Treatment
Treatment comes down to a whole range of effective measures that must be followed.
Medicines
The main drugs that fight back cystitis are antibiotics. The patient may be admitted to a hospital or take these medications on an outpatient basis. It all depends on how far the disease has progressed. Specific antibiotic preparations are determined by the doctor after determining the cause and nature of the disease and studying laboratory tests. Qualified specialists of the Global Clinic Center will take all measures to ensure that the treatment is as effective as possible. Doctors will prescribe medications against infections if this is the cause of the disease. For severe pain, effective painkillers will be recommended.
Phytotherapy
Decoctions of herbs that have a diuretic and anti-inflammatory effect will complement drug treatment. For cystitis, brew bearberry, lingonberry leaf, and horsetail. They will help to quickly relieve inflammation, “expel” residual urine from the bladder, and normalize the process of urination. The use of phytotherapeutic drugs should be discussed with your doctor and used in combination with medications.
Physiotherapy
This technique is not suitable for patients with exacerbation of the disease. The disease in a chronic form or after its acute period has passed can be treated with additional physiotherapeutic methods:
- electrophoresis;
- use of medicinal mud;
- treatment with magnets;
- UHF, etc.
Treatment of cystitis
Prescribing antibacterial drugs is the first line of treatment. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of pathogen, the clinical picture of the disease and general health.
- First episode of cystitis. Improvement occurs in a short time. Despite this, you should undergo a course of treatment prescribed by your doctor.
- Recurrent cystitis may require a longer course of antibiotic therapy, cystoscopy and bladder biopsy.
For intense pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are indicated.
Treatment methods for acute cystitis
Treatment of acute cystitis in women necessarily includes general measures. This means adherence to bed rest, drinking plenty of water with a volume of water of 2.5-3 liters per day, refusal of sexual activity for the entire period of treatment. Nutrition for acute cystitis should be balanced, avoiding fried, fatty, spicy and sweet foods. Hot baths and bladder lavage are contraindicated in the acute stage.
The standard treatment for acute cystitis often includes herbal medicines in the form of pharmaceutical herbal preparations. Useful herbal preparations with diuretic, tanning, antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects.
The main drugs for the treatment of acute cystitis are antibiotics. They are prescribed on the basis of bacteriological tests that identify the type of bacteria that caused the inflammation. Until the results are obtained, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used, and then the doctor specifies the group of drugs that will be most effective against a specific type of bacteria. In addition to antibiotics, uroseptic, painkillers and antihistamines are used.
Predisposing factors
The main cause of cystitis in women is the close location of the urethra to the vagina and anus.
That is why the risk of the disease is higher in women than in men. [21] From a microbiological point of view, in 75-95% of cases, acute inflammation of the bladder mucosa is caused by Escherichia coli. It enters the bladder through the urethra and provokes inflammation. Other causative agents of the inflammatory process also include representatives of the Enterobacteriaceae family, such as Proteus mirabilis and Klebsiella pneumoniae, as well as Staphylococcus saprophyticus. [20, 21]