For many of us, childhood memories remain the most vivid impressions in life. One of these memories I have is hiking in the forest during my summer holidays. Finding mushrooms and berries was a real adventure for me and my friends. Taught by our elders, we put on rubber boots, trousers, jackets, scarves and hoods, carefully covering everything except our faces and hands. It cannot be said that we liked this kind of preparation, but this issue was not subject to discussion. And as we got a little older, we ourselves began to understand that preventing tick bites is a really important thing.
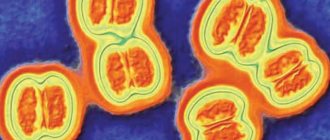
Tick bites themselves are not dangerous to humans. The danger arises if the tick is infected. They are carriers of tick-borne encephalitis, Lyme disease, typhus and others.
Tick-borne encephalitis is caused by a virus. This disease affects the central nervous system. Usually the disease occurs with pronounced symptoms, but a chronic course is also possible. Often tick-borne encephalitis leads to death or disability of the patient.
Why get vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis?
There are no drugs that directly affect the tick-borne encephalitis virus. The main way to prevent serious consequences is to prevent infection. Everyone knows that in the forest you need to dress appropriately and use repellent. However, every year ticks bite an average of 30 thousand people in each endemic area.
A more modern method of prevention is vaccination. Vaccination done in advance protects by 95-97% from the risk of contracting a terrible disease. The vaccination is carried out against tick-borne encephalitis. There is no vaccine against borreliosis.
If you come into contact with a tick, the Anti-Tick insurance policy will help you out. It allows you to submit a tick for research free of charge during the insurance period. The cost of one tick test for encephalitis and borreliosis is approximately twice the cost of the policy. The insurance includes consultations with specialists and aseptic tick removal. If the test results for encephalitis and borreliosis are positive, the insurance will cover the costs of treatment and rehabilitation worth up to 1 million rubles.
Types of vaccines
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is given using a number of drugs produced in Russia, Austria and Germany. All products are required to undergo numerous inspections and certification. For injections, formulations are used that contain a live, but many times weakened virus. It cannot provoke the development of the disease, but allows the body to develop a strong immunity to it.
The following types of drugs are popular:
- EnceVir.
This product is produced in Russia and is well tolerated by adults. It is not recommended for children, as the drug causes a number of side effects. - EnceVir Neo.
This product is also produced in Russia and is safer for children. It is administered even to children under 3 years of age. There were no significant side effects recorded - Encepur.
Produced in Germany. Children can be vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis as early as one year of age. The vaccine is well tolerated and very rarely causes negative consequences. - Mite-E-Vac.
This drug is manufactured in Russia. It can be administered to babies as early as one year of age. The composition is well tolerated and does not cause significant side effects. - FSME-Immun.
This drug is produced in Austria in two forms: for children from 12 months and for adults. It is recommended (in exceptional cases, with a high risk of infection) even for infants under one year old. Important! The doctor and parents should closely monitor the condition of the baby after administration of the drug.
All formulations are as effective as possible. Even if infected, the disease will be mild and will not cause complications.
Important! Foreign drugs are more expensive, but also more effective and safe.
How can vaccination help with a tick bite?
After a tick bite, the virus enters the human body. In response to this, antibodies are formed - protective proteins. They are the ones who fight the virus. But their production takes time. While they are being produced, the infection manages to damage many structures before it is rebuffed.
The body of a vaccinated person is pre-armed with antibodies. The virus receives a response from the first minute it enters the bloodstream. As a result, the disease does not develop because the virus is destroyed by antibodies.
Figuratively speaking, while the unvaccinated one is building a factory for the production of guns, the grafted one is already releasing all the ammunition at the enemy, destroying him even as he approaches the borders.
Features of the event
The encephalitis vaccine is given subcutaneously under the shoulder blade or in the deltoid muscle.
Important! The site of administration of the drug is determined by the manufacturer and depends on the composition. Recently, preference has been given to intramuscular formulations.
Before vaccination, you should definitely consult your doctor. He will examine the patient and determine whether he is healthy and whether he should be injected with the drug now or whether it is better to postpone the procedure. ARVI and other pathological conditions must be excluded. If necessary, the patient undergoes examination. As a rule, a general blood test is given. It allows you to exclude the presence of inflammatory and other negative processes in the body.
Myths about vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis
Myth No. 1.
Vaccination can make you sick.
This is wrong. The vaccine does not contain a live virus and cannot cause infection.
Myth No. 2.
After vaccination, you can ignore tick bites.
This is also incorrect. In addition to tick-borne encephalitis, ticks are carriers of several other diseases, so if you are bitten by a tick, you should still consult a doctor.
Myth No. 3.
Vaccine prophylaxis is carried out only for children and only in public medical institutions.
Not certainly in that way. You can get vaccinated either under the compulsory medical insurance policy or for a fee in any clinic that has the appropriate license. This type of prevention is available to both children and adults.
Myth No. 4.
If you do not go into the forest, the tick will not bite.
Those who go into the forested area once a year are not immune from tick bites. Even a single contact with a tick can be fatal.
Reaction and possible complications
All modern drugs (subject to proper storage and high quality) are well tolerated.
Possible reactions to vaccines are divided
on the:
- Local: slight redness of the skin and local increase in temperature
- General: slight increase in body temperature, weakness, slight malaise, headache, aching joints
All reactions resemble the onset of a cold. They are harmless and do not require medical advice.
As a rule, such reactions are caused by an individual “response” of the body or by the administration of a drug that has expired or violated storage conditions.
Who can be vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis?
First of all, people whose work involves being in the forest need to be vaccinated: mushroom pickers, hunters, students of geological, geographical and biological faculties.
People living in endemic areas also need to be vaccinated. Endemic zones are regions where the risk of infection is higher. The list of subjects is presented on the Rospotrebnadzor website, the list is updated annually.
When talking about risk groups, we single out only those categories in which the risk is maximum.
Contraindications:
- Allergy to the vaccine or its components;
- taking other medications (combined use may cause side effects);
- serious chronic diseases: heart attack, stroke, diabetes, oncology, epilepsy, tuberculosis, rheumatism, etc.;
- acute diseases (you can get vaccinated a month after complete recovery);
- pregnancy and breastfeeding.
At the medical center, you can not only get the actual vaccination, but also undergo all the necessary tests, receive qualified advice and recommendations from doctors. We use the Encevir vaccine. You can get vaccinated daily from 8.00 to 20.00. A doctor's examination before vaccination is included in the price.
When should you vaccinate against tick-borne encephalitis?
Planned prevention can be carried out at any time. However, it is best to carry it out in such a way that the third, final vaccination is completed by the beginning of spring.
If you plan to complete vaccination by the beginning of spring, then the vaccination schedule with the domestic vaccine will be as follows:
- 1st vaccination in July
- The 2nd vaccination should be given from August to February
- 3rd vaccination - after 9-12 months
If immunization is carried out with imported vaccines, the vaccination schedule will look like this:
- 1st vaccination in November
- The 2nd should be delivered from December to February next year
- 3rd vaccination - after 9-12 months
It is important to remember that after the second and third administration of the vaccine, extreme caution should be exercised for two weeks when visiting tick habitats. After two weeks after the 2nd injection, immunity is formed. In the future, it will be consolidated and extended by a third introduction.
With emergency vaccination, the second vaccination is performed two weeks after the first, and the formation of immunity occurs after another 1-2 weeks. Revaccination is carried out 9-12 months after the second injection of the vaccine.
Emergency vaccination is relevant in cases where it is necessary to quickly develop immunity, and there is not enough time to carry out vaccination according to the standard scheme.
If vaccination is carried out during periods of maximum tick activity, the risk of infection increases. Additional precautions must be taken. When infected and administered a vaccine at the same time, the risk of the disease developing in a more severe form increases.
Advantages of vaccination at MEDSI
- Use of high-quality and effective drugs.
All formulations are certified, properly stored and supplied only by trusted manufacturers - Vaccination safety.
Vaccination against encephalitis is given only after examination by a therapist or pediatrician. If necessary, the patient can be consulted by allergists-immunologists who see both adults and children. For patients with concomitant pathology, additional examinations, laboratory and functional diagnostics are possible - Experience of specialists.
Our professionals know how to administer medications correctly - Opportunities for appointments at any
time convenient for the patient - Vaccination of adults and children from one year onwards.
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis can be given according to indications or at the personal request of the patient - Mandatory health monitoring
before administering the drug. This reduces all risks of hazardous health consequences.
If you want to protect yourself from a dangerous disease, call us at +7 (495) 7-800-500. The specialist will tell you the cost of the service and make an appointment for you.
How to protect the injection site from water if you need to wash yourself
To take a shower and not worry about whether water will get on the injection or not, thereby provoking unpleasant consequences, you should take some precautions:
- If you need to bathe your child before bed, it is best to support him and make sure that he does not put his hand in the water. An adult can simply take a shower, holding the watering can with the hand in which the injection was injected.
- If there is any doubt about the precaution, showering instead of taking a bath with body immersion is also recommended.
- While bathing, you can cover the injection with a bandage and wrap your arm with plastic wrap. This will help prevent water from getting on the wound.
In any case, water procedures after vaccination are allowed, the main thing is to take care of the place where the vaccine was administered.
Office photo
Useful articles
Interesting facts about medicine History of vaccination Vaccination is one of the greatest achievements of medicine, allowing to save 2 to 3 million lives annually. Preview picture in attachment Healthy lifestyle Medical examination: typical misconceptions About the importance of the correct approach to interpreting the results of a medical examination Healthy lifestyle Sleep - strong and healthy Simple rules that will help make your sleep complete.
Show more articles
Subscribe to new promotions and latest news
Make an appointment
- More about the center
- Licenses and documents
- Our vacancies
- Contacts
- Ask a Question
- Leave feedback
- Territorial program
© 2002-2021 Medilux-TM LLC - Network of medical centers | Site map All information, including prices, is provided for informational purposes and is not a public offer (Article 435 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Article 437 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation)
INN: 7725100534 OGRN: 1037700249872
Medilux-TM LLC uses cookies (files with data about past visits to the site) to personalize services and provide user convenience. You can prevent the storage of cookies in your browser settings. MedSwiss takes the protection of personal data seriously - read the terms and conditions for processing it.
Accept user agreement
Risk of occurrence
Tick-borne encephalitis occurs not only among those who like to pick mushrooms in the forest and spend time at their summer cottage.
Many parasites hide in city parks, lawns and park areas. A child can catch a tick even while walking in the yard. The risk of infection transmission depends on the duration of the bloodsucker's suction. Males feed on blood for 20-30 minutes, and females remain at the site of the bite for 5-7 days, after which they leave the host’s body and lay eggs. It is important to consider that in many regions every second tick is infectious. Other methods of infection:
- Crushing the parasite on the skin. Even with a small abrasion, the virus can enter the bloodstream and trigger the development of encephalitis.
- Improper removal of ticks from the skin surface. In this case, the parasite is more likely to infect humans.
- Consumption of products obtained from the milk of an infected animal. Only careful heat treatment can destroy the virus in milk.
Children, elderly people and patients suffering from impaired immunity are more susceptible to infection. Ticks are most active from April to the end of September.