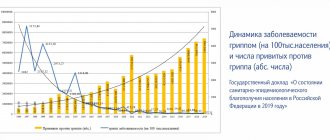
The annual flu vaccination campaign will start in September 2021. In this article, we will answer the main questions related to the seasonal epidemic of respiratory diseases and talk about the vaccines that are available to children and their parents this season.
Available: Ultrix quadri, Grippol Plus, Sovigripp and Flu-M.
Influenza vaccine (inactivated)
Used in children over 6 months, adolescents and adults. Manufacturer – Russia.
Grippol® plus is an anti-influenza trivalent inactivated polymer-subunit vaccine. It is a protective antigen (hemagglutinin and neuraminidase) isolated from purified influenza viruses type A and B grown on chicken embryos, associated with a water-soluble high-molecular immunoadjuvant N-oxidized derivative of poly-1,4-ethylenepiperazine (azoximer bromide). The antigenic composition of the vaccine changes every year in accordance with the epidemic situation and WHO recommendations. The vaccine causes the formation of a high level of specific immunity against influenza. The protective effect after vaccination, as a rule, occurs after 8-12 days and lasts up to 12 months, incl. in elderly people. Protective titers of antibodies to influenza viruses after vaccination of people of different ages are determined in 75-95% of vaccinated people.
Should my child be vaccinated against the flu?
“The flu vaccine can be given to children as young as 6 months. This is necessary and safe,” GMS Clinic pediatrician Daria Zakharova told readers of the Internet portal “Healthy Children” about common sense and myths around vaccinations.
Influenza is the most dangerous disease among all acute respiratory viral infections. The likelihood of complications of the disease with influenza is much higher than with other acute respiratory viral infections, and the complications themselves develop faster. The most common complications are pneumonia and purulent otitis media.
The only effective way to prevent influenza is vaccination.
How does the flu shot work?
The principle of operation of all vaccines is approximately the same. After the vaccine is administered, the body produces protective antibodies in response to the introduction of antigens - harmless particles of the virus. These antibodies protect us from becoming infected with influenza in the future. The body produces a sufficient amount of antibodies to avoid getting sick approximately 14 days after vaccination. The vaccine only protects against influenza; it does not work against other types of acute respiratory viral infections. But this is not required, because all other respiratory viral infections, except influenza, as a rule, are quite mild and in most cases do not have any complications.
Will getting a flu shot help prevent you from getting sick?
The effectiveness of the flu shot is about 90%. 9 out of 10 people who are vaccinated will not get sick at all after exposure to the influenza virus. Even if a person gets sick, the disease itself will be very mild and the likelihood of complications will be minimal. Vaccines have proven to be highly effective in studies. They are created annually in accordance with the recommendations of experts from the World Health Organization (WHO). The composition of the vaccine changes from year to year because the influenza virus tends to mutate. To create a vaccine, three strains of the influenza virus are selected, which, according to WHO, are most likely to spread this year.
How often should you get flu shots?
Vaccination must be done annually, once a year. Children who have not previously been vaccinated are given two vaccinations at intervals of a month.
When should you get a flu shot?
The optimal time for vaccination is September and October. It is necessary to vaccinate at least a month before the expected increase in incidence, which usually occurs at the end of October - beginning of November. There are times when this happens earlier, sometimes later.
Why are many mothers against vaccinations?
Firstly, people underestimate the possible consequences of the flu and do not understand what it is. Secondly, people are afraid of side effects because they think they heard something somewhere, someone told them or they read on the Internet that the vaccine is poorly tolerated. This is an incompetent opinion.
Now there are more and more people who prefer to refuse vaccination, because information appears on the Internet that vaccination is not necessary. It is important to get vaccinated! This is the only effective way to prevent influenza that has proven its effectiveness.
At what age can children start getting flu shots?
From six months.
What side effects may occur in children?
During the first two to three days, the child may feel slightly unwell; a small child may become slightly moody and have a fever. Side effects are quite rare - out of 20 vaccinated children, about 1 may have a mild temperature reaction. As a rule, vaccination is very easy and without any consequences. The risks are minimal. And these risks are completely justified, since the risk of complications with influenza is much worse than a possible reaction to the vaccine in the form of a mild fever.
What should you do if your child has a fever after vaccination?
If the temperature rises above 38.5 °C, it must be brought down with antipyretic drugs for children. But such a temperature reaction is extremely rare. If a child has a fever after a flu vaccination and the high temperature lasts for more than two days, then the vaccination most likely has nothing to do with it. This is a reason to consult a doctor, since a possible cause in this case is an infection. That is, the vaccination was done during the incubation period, and the disease manifested itself immediately after it.
If a child had a reaction after the first vaccination, will it happen again after the second?
It’s completely optional, there is no such pattern.
Do children need to be tested before getting a flu shot?
An examination by a pediatrician or therapist is required. The doctor will decide if tests are needed. As a rule, they are not required.
Which flu vaccine is best for a child?
There are several types of vaccines, they differ in the production method. All of them are approved and approved for use, including in children. There is no difference in the effectiveness of these vaccinations. The difference is in tolerability - it depends on how the child’s body will react to this vaccination. There is no significant difference in which flu vaccine you get, the most important thing is to get vaccinated. In our clinic we use Influvac and Vaxigrip vaccinations - these are highly purified vaccines that are excellently tolerated. Also a low-reactogenic, highly purified vaccine is Grippol Plus.
Where can I get my child a flu shot?
In city children's clinics, in private clinics, in schools.
How to get vaccinated at the clinic?
You need to make an appointment with your pediatrician and tell them you want to get vaccinated. The pediatrician will examine the child and decide whether he can be vaccinated or not.
The child is offered a flu shot at school. This is not dangerous?
Not dangerous. But parents need to clarify whether the school will examine the child by a specialist before vaccination, this is important! And clarify which vaccine the doctor is going to use.
Source: healthy-kids.ru
pharmachologic effect
Grippol® plus is an anti-influenza trivalent inactivated polymer-subunit vaccine. The antigenic composition of the vaccine changes every year in accordance with the epidemic situation and WHO recommendations. The vaccine causes the formation of a high level of specific immunity against influenza. The protective effect after vaccination, as a rule, occurs after 8-12 days and lasts up to 12 months, incl. in elderly people. Protective titers of antibodies to influenza viruses after vaccination of people of different ages are determined in 75-95% of vaccinated people. The inclusion of the immunomodulator azoximer bromide in the vaccine preparation ensures an increase in the immunogenicity and stability of antigens, increases immunological memory, significantly reduces the vaccination dose of antigens, and increases the body's resistance to other infections by correcting the immune status.
What is the difference between Sovigrippa and Grippol plus
Sovigripp is a domestic pharmaceutical product to combat viral infection. Applicable since 2013. The drug contains influenza strains of medium activity. Every year, the vaccine undergoes variability as a result of the antigenic mutation of the pathogen, which makes it possible to increase its effectiveness in eliminating pathogenic flora.
The active and auxiliary components are:
- Hemagglutinin of different types of virus.
- Thiomersal in combination with the mercury emblem.
- Sovidon.
- A buffer mixture containing sodium and potassium hydrogen phosphates, potassium dihydrogen phosphate and clean water.
The pharmacological agent is intended for parenteral administration into the muscle. This is the buttock, thigh or shoulder area.
Grippol Plus is a Russian liquid vaccine in the form of an injection solution. Refers to third generation vaccination drugs. Therefore, the active component of the product is the virus antigens, neutralized by chemical means. They rarely cause allergy symptoms.
The vaccine contains glycoproteins from several strains of influenza A and B types. Excipients are azoximer bromide and a phosphate-salt mixture. The vaccine is used for subcutaneous and intramuscular administration.
As for preservatives, they are used when dispensing large vials of the drug, which helps eliminate microbial contamination. Thus, Sovigrippa uses thiomersal with ethyl mercury, and the Grippol plus vaccine contains no chemical additives at all.
Indications
Specific prevention of influenza in children from 6 months of age, adolescents and adults without age restrictions . The vaccine is especially indicated for people at high risk of complications from influenza:
- over 60 years old, preschool children, schoolchildren;
- adults and children who often suffer from acute respiratory infections, suffering from chronic somatic diseases, incl. diseases and malformations of the central nervous system, cardiovascular system and bronchopulmonary system, bronchial asthma, chronic kidney disease, diabetes mellitus, metabolic diseases, autoimmune diseases, allergic diseases (except allergy to chicken protein), chronic anemia, congenital or acquired immunodeficiency , HIV-infected;
The vaccine is also indicated for persons whose profession has a high risk of contracting influenza or infecting others with it, including:
- health workers, employees of educational institutions, social services, transport, trade, police, and military personnel.
Safety and side effects
Sovigripp and Grippol plus are the most effective and safest drugs on the Russian market. This property of vaccines is explained by the reduction in the pathogenic effects of influenza viruses due to chemical agents.
But despite this, vaccines can cause the following side effects:
- Signs of an influenza infection include fever, cough, runny nose and malaise.
- Headache.
- Allergic manifestations in the form of itching, rash and hyperemia.
- Formation of a limited infiltrate in the injection area.
- Gastrointestinal disorders.
Severe side effects occur less often. These are erythema nodosum, neuralgia and paresthesia.
Immunization is highly not recommended in case of individual intolerance to chicken protein, severe disease conditions and the appearance of undesirable symptoms after the first vaccination.
Dosage regimen
Vaccination is carried out annually in the autumn-winter period.
- For children over 3 years of age, adolescents and adults, the vaccine is administered intramuscularly or deeply subcutaneously into the upper third of the outer surface of the shoulder (into the deltoid muscle), and for younger children - intramuscularly into the anterolateral surface of the thigh.
- Children aged 6 to 35 months inclusive are administered 0.25 ml twice with an interval of 4 weeks.
- For children over 36 months and adults, the vaccine is administered once in a dose of 0.5 ml.
- Children who have not previously had the flu and have not been vaccinated may receive the vaccine twice with an interval of 3-4 weeks.
Vaccine options
The first influenza vaccines were made from killed or neutralized viruses, they are called whole virion vaccines, as well as from attenuated strains, the so-called live vaccines.
Almost all modern vaccinations for the prevention of influenza are inactivated (killed) vaccines with a replaceable strain composition. Influenza viruses for all vaccinations without exception are grown on chicken embryos, which is reflected in the list of contraindications for vaccination. Most inactivated whole-virion influenza shots consist of purified and concentrated viruses cultured in chicken embryos that have been inactivated by formaldehyde or UV irradiation. Inactivated vaccines, in turn, are divided into whole-virion vaccines, which are based on undestructed whole influenza viruses; pre-killed and purified, split, or split vaccines, which include particles of destroyed virions, that is, the full antigenic composition (external and internal proteins). Subunit influenza vaccines are also used, which consist of a mixture of two viral proteins: hemagglutinin and neuraminidase. Therefore, these vaccines have a minimal number of adverse reactions.
Virosomal vaccines are a new technology in the production of vaccination material. These vaccinations contain an inactivated virosomal complex with surface antigens of the influenza virus. Virosomes enhance the immune response to vaccination. The virosomal vaccine does not contain preservatives (thiomersal) and is well tolerated.
In Russia, the following inactivated trivalent influenza vaccinations are mainly used: “Grippovac”, “Vaxigrip”, “Begrivac”, “Agrippal S1”, “Grippol”, “Grippol plus”, “Influvac”, “Fluarix”, “Inflexal V” ( virsomal vaccine). A total of 18 vaccinations have been registered in Russia.
Classification of trivalent influenza vaccines
| Generation and type | Compound | Main characteristics | Examples |
Live vaccines | |||
| Whole virion vaccines | Live attenuated unpurified virus |
|
|
Inactivated vaccines | |||
| I – whole virion vaccines | Whole virus that has undergone inactivation and minor purification |
|
|
| II – split (split) vaccines | Particles of destroyed virus, surface and internal proteins and lipids |
|
|
| III – subunit vaccines | Highly purified influenza virus surface antigens (hemagglutinin and neuraminidase) |
|
|
| IV – subunit adjuvanted vaccines | Highly purified surface antigens of the influenza virus and an effective safe immunoadjuvant Polyoxidonium |
|
|
| Highly purified influenza virus surface antigens embedded in liposomes |
|
| |
| Highly purified surface antigens of influenza virus and adjuvant Sovidon |
|
| |
Classification of quadrivalent influenza vaccines
| Generation and type | Compound | Main characteristics | Examples |
| II – split (split) vaccines | Particles of destroyed virus, surface and internal proteins and lipids |
|
|
Reactogenicity is the ability of a vaccine to cause any side effects when introduced into the body (fever, local swelling, etc.)
Drug interactions
Grippol® plus can be used simultaneously with inactivated and live vaccines of the National Preventive Vaccination Calendar (except for BCG and BCG-M) and inactivated vaccines of the preventive vaccination calendar for epidemic indications (except for rabies). The vaccine can be administered against the background of basic therapy for the underlying disease.
Come get vaccinated at MAMARADA. A full range of vaccines for children and adults, family vaccinations - at a special price!
Principles and purposes of vaccination
Vaccination is especially important for people at higher risk of developing serious flu complications and for people who live with or care for people at high risk. WHO recommends annual influenza vaccination for the following population groups: pregnant women at any stage of pregnancy; children from 6 months to 5 years; seniors 65 years and older; people with chronic diseases; healthcare workers.
Since 2006, influenza vaccination has been included in the National Calendar of Preventive Vaccinations of the Russian Federation. The following are subject to annual vaccination: children from 6 months of age, children attending preschool institutions, students in grades 1-11, students of higher vocational and secondary vocational educational institutions, adults working in certain professions and positions (workers of medical and educational institutions, transport, public utilities and etc.), adults over 60 years of age.
It is important to note that the composition of vaccines changes every year. This is done to provide maximum protection against the “wild” influenza virus. This process is carried out under the control of the World Health Organization. It is she who predicts the strains of the flu virus that will circulate in the expected season and sends these strains to vaccine manufacturers. In most countries, influenza vaccination is carried out annually.
Post-vaccination reactions
Whole-virion influenza vaccinations are relatively highly reactogenic. Therefore, when using them, general reactions may develop in the form of increased body temperature, headache, weakness, as well as local reactions in the form of swelling, redness and pain at the injection site. Usually these reactions are mild and go away on their own.
Subunit, split, and virosomal vaccines are the least reactogenic of all flu vaccines. Only in 3% of cases are vaccinated people allowed to develop adverse reactions.
Vaccine effectiveness
The use of influenza vaccination reduces the incidence rate by 1.4-1.7 times, helps reduce the severity of the disease, and prevents the development of severe complications and deaths. The vaccine is effective in all age groups in approximately 70-90% of cases.
Immunization reduces hospitalizations for pneumonia by 40% in healthy adults and by 45 to 85% in older adults. In addition, the frequency of otitis media is reduced by 36-69%, exacerbations of chronic bronchitis by 20%, and the number of exacerbations of bronchial asthma is reduced by 60-70%. In organized groups of elderly people (nursing homes, boarding schools), mortality from influenza is reduced by 80%.
Immunity after administration of the vaccine is formed within 14 days and lasts throughout the season. Unfortunately, the immunity developed after vaccination is short-lived. This is largely due to the high variability of the circulating influenza virus, the emergence of a new or even the return of an old subtype of the virus. In this regard, the anti-influenza immunity developed in the previous year does not protect against the disease in the current year. Therefore, annual immunization is necessary using only the vaccine of the current year of production. Vaccinations with last year's vaccines are only 20-40% effective.
Contraindications
For all influenza vaccines:
- hypersensitivity to chicken protein or any other component of the vaccine
- severe fever or allergic reactions after previous vaccination with influenza vaccines.
Influenza vaccination is postponed until the end of acute manifestations of the disease and exacerbation of chronic diseases. For mild ARVI, acute intestinal and other diseases, vaccination is carried out immediately after the patient has established a normal temperature.
The live vaccine is not used in children under 3 years of age, pregnant women and people with impaired immunity.