the whole list
Peptic ulcer disease is a chronic disease that occurs with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission, the main symptom of which is the formation of a defect (ulcer) in the wall of the stomach and/or duodenum.
An ulcer is a defect in the mucous membrane that has a clear boundary. A superficial ulcer is called erosion. Peptic ulcer disease is detected in 5–10% of the adult population.
Depending on the location, ulcers are divided into gastric and duodenal (duodenum - duodenum).
The ratio of gastric and duodenal ulcers is approximately 1: 4. Young people have a lower incidence of gastric ulcers compared to duodenal ulcers (1: 13). Conversely, in middle-aged and elderly patients the frequency of gastric ulcers increases.
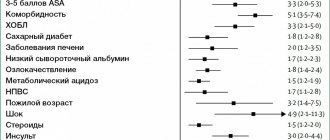
Along with peptic ulcer disease as an independent disease, it is now customary to distinguish secondary symptomatic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum that occur under the influence of stress, circulatory disorders, taking antipyretics, painkillers (acetylsalicylic acid, indomethacin, diclofenac, ibuprofen) and others.
Depending on the cause, there are:
- stress ulcers (for example, with myocardial infarction, widespread burns, after neurosurgery, etc.);
- drug-induced ulcers (taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hormones and other medications);
- endocrine ulcers (with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, hyperparathyroidism);
- ulcers in certain diseases of internal organs (Crohn's disease, atherosclerosis of the branches of the abdominal aorta, etc.).
Stomach ulcer, its types and stages
Gastric ulcer (hereinafter referred to as PUD) is a disease in which a mucosal defect occurs and the submucosal layer may be affected. This is a chronic disease that occurs in waves, with periods of exacerbation and remission.
An ulcer can be localized in different parts of the stomach:
- subcardial and cardiac - in the upper part;
- antrum - in the lower section;
- in the body - in the middle part;
- in the pyloric canal - at the transition to the duodenum.
The size of the ulcer is:
- small - up to 5 mm in diameter;
- medium - in diameter 6-19 mm;
- large - 20-30 mm in diameter;
- gigantic - more than 30 mm in diameter.
There are also ulcers associated with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (hereinafter referred to as HP) and those not associated with it.
The disease occurs in several stages:
- exacerbations - the occurrence of a defect in the mucous membrane;
- scarring - the formation of connective tissue at the site of the ulcer;
- remission - healing of the defect.
The stage of cicatricial and ulcerative deformation of the organ is distinguished separately.
Diagnostics
- General clinical analysis of blood and urine
- Analysis of stool for coprogram
- Fecal occult blood test
- Biochemical blood test (liver tests, cholesterol, alkaline phosphatase)
- ECG
- X-ray of the chest organs in 2 projections and X-ray of the abdominal organs (to exclude perforation of ulcers)
- X-ray of the esophagus, stomach with barium mixture
- Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary system
- 24-hour pH monitoring in the lower esophagus and stomach
- EGDS
- Non-invasive tests for the determination of Helicobacter pylori (respiratory)
Main causes
The cause of a defect in the gastric mucosa is considered to be an imbalance between the aggressive secretions of the stomach and the protective qualities of the mucous membrane. To digest food, the stomach secretes pepsin and hydrochloric acid. To prevent them from destroying the stomach, mucus forms on its surface, protecting the organ. If more acid is produced and less mucus is produced, an ulcer may form. The background for such a pathology may be a decrease in gastric motility, a violation of the regenerative - restorative properties of the mucous membrane against the background of certain diseases.
The main etiological cause of ulcer formation is damage to the mucous membrane of the HP. This bacterium successfully survives in an acidic environment and produces an enzyme that causes an inflammatory reaction with subsequent formation of a defect. Helicobacter pylori is detected in 82% of patients suffering from gastric ulcers.
Another reason may be uncontrolled use of anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs, such as aspirin.
Provoking factors may be:
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- constant consumption of spicy food;
- stressful situations;
- hereditary predisposition;
- dry food;
- eating disorder.
Gastric ulcers often develop against the background of certain diseases, such as atrophic gastritis and hormonal pathologies.
Prevention and recommendations
It is necessary to exclude those factors that lead to the development of peptic ulcers and monitor your health in the presence of a hereditary predisposition, even if nothing bothers you.
Risk factors for developing peptic ulcers:
- Helicobacter pylori infection
- hereditary predisposition
- blood type I (0)
- bad habits (tobacco smoking, drinking alcohol and its surrogates)
- increased stomach acidity
- violation of working and rest conditions, frequent stress
- taking ulcerogenic medications (hormones, ibuprofen, Nise, Nurofen, diclofenac and others)
- non-compliance with food intake
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (cholecystitis, pancreatitis, gastritis, gastroduodenitis)
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, systemic diseases, chronic renal failure.
Symptoms of the disease
Peptic ulcer usually manifests itself more often in spring and autumn, during the period of exacerbation of the disease. The first sign of the disease is pain that occurs immediately after eating. This is due to the fact that pepsin and hydrochloric acid released during meals aggressively affect the defect unprotected by mucus. Moreover, the manifestations of pain symptoms increase within an hour after eating. The pain is localized in the epigastric region, in the region of the heart, and can radiate - radiate under the scapula, as in a heart attack. At the height of the pain syndrome, nausea often occurs, which can result in vomiting, which brings relief.
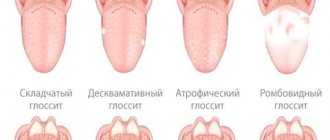
Other dyspeptic manifestations and signs of illness: heartburn, loss of appetite, constipation. A coated tongue may indicate stomach problems. Against this background, the patient quickly loses weight.
Treatment of the disease
Gastric ulcers are well treated with conservative methods, which include pharmacotherapy and physiotherapeutic procedures. In emergency and some other cases, surgical intervention is indicated.
Drug treatment
The treatment of gastric ulcers uses complex pharmacotherapy, including medications aimed at the root cause of the pathology, relieving irritation of the mucous membrane and creating a protective barrier for gastric juice and relieving pain. The main group of drugs includes:
- Proton pump inhibitors are long-acting drugs that reduce gastric secretory activity.
- Antacids - envelop the mucous membrane, protecting it from the aggressive effects of gastric juice, and reduce its acidity.
- Antibacterial drugs are aimed at eradication (destruction) of Helicobacter pylori. The best effect is achieved when antibiotics are combined. For peptic ulcers, macrolides, antiprotozoal drugs, penicillin and tetracycline antibiotics are prescribed.
- Bismuth preparations relieve inflammation and form an insoluble colloid that creates a protective film when combined with protein.
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenate) - normalizes the production of hydrochloric acid, stimulates the regeneration of the mucous membrane.
- Methylmethionine sulfonium chloride, also called vitamin U, acts as a cytoprotector that helps reduce gastric secretion and heal gastric ulcers.
Treatment can be supplemented with other drugs aimed at eliminating the causes of ulcerative pathology.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy helps ulcer healing and can be used in complex therapy. The mechanisms of self-regulation and adaptation are beneficially affected by:
- laser puncture - exposure of bioactive points with a laser beam;
- EHF therapy - the influence of electromagnetic waves in the millimeter range;
- magnetotherapy - exposure to low-frequency magnetic fields.
Ultrasound therapy is used to improve gastric motility in case of gastric atony. This procedure also improves blood supply to the organ, reduces the number of bacteria and relieves inflammation.
Surgery
Emergency surgery is performed in case of massive bleeding and perforated gastric ulcer. Surgical intervention is also indicated for complicated forms of ulcers in the case of a non-healing ulcer, as well as for malignancy, when the pathology becomes malignant. In some cases, gentle methods are used: laparoscopy or endoscopy.
specialist
Our doctors will answer any questions you may have
Tumasova Anna Valerievna Gastroenterologist
Ask a Question
Diet and bad habits for stomach ulcers
Diet for gastrointestinal ulcers is an essential part of treatment. During the acute period, nutrition should be as gentle as possible, gentle on the mucous membrane and not stimulating the secretory activity of the stomach. In the first two days, preference is given to slimy soups with rice water without vegetables and meat, jelly or warm tea with sugar and crackers. In the next 6 days, table No. 1 is used in therapeutic nutrition.
Authorized Products
General nutrition rules:
- include easily digestible foods in the diet;
- food should be warm
- Do not eat cold or hot foods;
- you need to eat slowly, in small portions
- products need to be crushed and ground;
- Baking, boiling, stewing is allowed;
- fried foods and spices are excluded;
- the break in eating should not be more than 3 hours;
- food must be chewed thoroughly.
The following foods and dishes are allowed for stomach ulcers:
- Slimy soups: with the addition of rice, semolina, oatmeal, you can add cream or butter;
- Slimy porridges: with water or milk from the same cereal, you can add cream;
- Fish and meat: lean beef, veal, turkey, rabbit, chicken. To prepare the meat, you need to boil it, pass it through a meat grinder, add butter, bake it into a soufflé puree, you can cook steamed cutlets, meatballs, meatballs;
- Eggs: soft-boiled, or steam omelet;
- Berries and fruits: baked unsweetened fruits, dried fruit compotes;
- Dairy products: milk, steamed pureed cottage cheese soufflé, cream.
- Drinks: weak tea with added cream or milk, rosehip decoction, milk or fruit jelly.
You can add refined vegetable oil or unsalted butter to dishes.
Prohibited Products
During an exacerbation, foods that irritate the gastric mucosa and increase the production of gastric juice are excluded: fatty meat, baked goods, preserves, canned and smoked foods, confectionery with cream, dishes with vinegar and spices, garlic.
Do not include vegetables with coarse fiber in the diet, as well as radishes, radishes, daikon, cabbage, tomatoes, turnips, and mushrooms.
It is necessary to avoid foods that cause fermentation processes: legumes, sweet fruits and juices, carbonated drinks.
During the treatment period, you are strictly prohibited from smoking and drinking alcohol.
Prevention of peptic ulcers
Stomach ulcers can be avoided if you follow some rules. First of all, give up bad habits, since ethyl alcohol and tobacco reduce the protective properties of the mucous membrane and irritate it.
Diet is no less important in prevention: you need to eat at a certain time, the interval between meals should not exceed 4 hours. You cannot eat dry food, as dry rough food injures the walls of the stomach.
For those who work at night, it is recommended to change jobs to work only during the daytime. It is necessary to avoid stress, treat inflammation of the stomach, hormonal diseases, and visit a gastroenterologist at least once every six months.
FAQ
Can peptic ulcer disease be inherited?
The ulcer itself cannot, but the risk factors for its development certainly do.
Is it possible to get a peptic ulcer?
In case of Helicobacter infection, the risk of developing peptic ulcers mainly of the duodenum and antrum is significantly higher.
Can an ulcer develop into cancer?
In the case of a long-term inflammatory process, metaplasia may develop - a change in the typical structure of the cells of the mucous membrane of the stomach and, less often, the duodenum, which significantly increases the risk of malignancy.
Can an ulcer be cured?
An uncomplicated ulcer heals itself, and the disease “peptic ulcer” and the process of ulcer formation are cured when the cause is identified (Helicobacter, bile reflux, drug-induced effects, endocrine diseases, etc.) and eliminated.
Is it possible to treat peptic ulcer without antibiotics?
If the peptic ulcer is not caused by the HP bacterium - of course, in the case of HP-associated disease - a course of antibacterial therapy is mandatory.