Vitamins for pregnant women - how to choose the best? Comparing the most popular complexes
Everyone knows: a pregnant woman uses up her vitamins and minerals for two. However, today the range of vitamin and mineral complexes is so large that it is difficult not to get confused.
Which drug should I choose? To answer this question, it is worth carefully analyzing their composition.
What must be included in the complex for pregnant women? Are the dosages and forms of nutrients important?
For comparison, we have selected the most popular complexes intended for expectant mothers. Our rating includes 7 drugs: Alphabet Mom's Health, Complivit Mama, Pregnoton Mama, Vitrum Prenatal, Complivit Trimester, Elevit, Femibion.
A comparison of their compositions is given in the table.
| Complex | Vitamins | Minerals | Additionally |
| Alphabet Mom's health | Beta-carotene, B 1, B2, B5, B6, folic acid, B12, PP, C, D3, E, K, biotin | Electrolytic iron, copper, magnesium, manganese, selenium, zinc, molybdenum, calcium, chromium, phosphorus, iodine | L-taurine |
| Vitrum Prenatal | A, B1, B 2, B6, folic acid, B12, PP, C, D3, E | Iron (fumarate), calcium, zinc | |
| Complimentary Mom | A, B1, B 2, B6, folic acid, B12, PP, C, D2, E | Iron (fumarate), calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, copper, zinc, manganese | |
| Complivit Trimester (I, II and III) | A, B1, B 2, folic acid, B5, B 6, B12, PP, C, D3, E, P | Iron (fumarate), copper, selenium, manganese, calcium, magnesium, zinc, iodine | Lipoic acid, lutein |
| Pregnoton Mom | B1, B2, B3, B5, B 6, folic acid + calcium L-methylfolate, B12, C, D3, E, biotin | Iron in liposomal form, iodine, selenium, zinc | Omega-3 DHA |
| Femibion Natalcare (1 and 2) | B1, B 2, B5, B6, folic acid + L-methylfolate, B12, PP, C, E | Iodine | Omega-3 DKG (only in Natalcare 2) |
| Elevit Pronatal | A, B1, B 2, B6, folic acid, B12, PP, C, D3, E, biotin | Iron (fumarate), calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, zinc, calcium, copper, manganese |
The first thing to note is the wide variety of micronutrients. A number of complexes include, in addition to vitamins and minerals, other important substances - such as Omega-3, taurine, lutein. A more detailed study reveals that each complex includes folic acid, but iodine, which regulates the functioning of the thyroid gland, is not present everywhere. The same can be said about calcium and iron. This means that simply by comparing formulations, we will not be able to choose the best drug. Therefore, we will have to investigate the issue deeper.
Most experts believe that the most important micronutrients during pregnancy are folic acid, iodine, and iron. Omega-3 PUFAs are often added to them. Let's study what effect this four has and whether it is present in popular drugs.
Folic acid: what is important?
Folic acid, or vitamin B9, is the most important vitamin for pregnant women. Our mothers and grandmothers also took it during the period of bearing a child. It is not surprising that vitamin B9 is included in all vitamin complexes for expectant mothers.
Folic acid deficiency can cause serious developmental problems in the fetus:
1. In the first trimester, a lack of vitamin B9 is especially dangerous, because it can cause a defect in the closure of the neural tube, spina bifida, and underdevelopment of the brain.
2. In the second trimester, folic deficiency leads to disturbances in the development of the heart, blood vessels, and organs of the urinary system.
3. In the third trimester, a deficiency of this vitamin affects the child’s growth and brain health.
Unfortunately, a lack of vitamin B9 is genetically determined in half of the population of our planet. About 50% of people do not produce enough of the enzyme needed to convert folic acid into its active form, methylfolate. There are also those who do not synthesize the enzyme at all - their number (according to various estimates) is from 5 to 25%. These people should only take methylfolate. It is absorbed regardless of genetic characteristics, that is, deficiency will not occur.
The active form of vitamin B9 - methylfolate - is contained in only two drugs: Femibion and Pregnoton Mama.
Complivit Mama for pregnant and lactating women
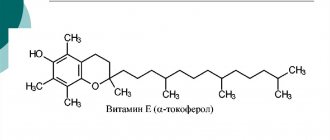
Trade name: Complivit “Mama” for pregnant and nursing women International name: Multivitamins+Multimineral Pharmacological group: multivitamin + minerals Pharmacological group according to ATC: A11AA04. Multivitamins and microelements Pharmacological action: multivitamin, hematopoietic, metabolic Pharmacodynamics: Combined multivitamin preparation with micro- and macroelements, the effect of which is determined by the effects of its constituent components. Tocopherol (vitamin E) has antioxidant properties, maintains the stability of red blood cells, prevents hemolysis, and has a positive effect on the functions of the gonads, nervous and muscle tissue. Vitamin E deficiency in early pregnancy can cause miscarriage. Retinol (vitamin A) plays an important role in redox processes and is involved in the synthesis of mucopolysaccharides, proteins, and lipids. Promotes normal spermato- and oogenesis, development of the placenta, growth, normal development and differentiation of embryonic tissues, incl. epithelial structures and bone tissue. Participates in the formation of visual pigments necessary for normal twilight and color vision, ensures the integrity of epithelial tissues, and regulates bone growth. Thiamine hydrochloride (vitamin B1) as a coenzyme is involved in carbohydrate metabolism and the functioning of the nervous system. Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is an essential catalyst for cellular respiration and visual perception. Pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6) as a coenzyme takes part in protein metabolism and the synthesis of neurotransmitters. During pregnancy, it is necessary for women who have previously taken oral contraceptives, which deplete pyridoxine reserves in the body. Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) is involved in the synthesis of nucleotides, is an important factor in normal growth, hematopoiesis and development of epithelial cells, and is necessary for the metabolism of folic acid and myelin synthesis. Nicotinamide (vitamin PP) is involved in the processes of tissue respiration, fat and carbohydrate metabolism. Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) ensures collagen synthesis, participates in the formation and maintenance of the structure and function of cartilage tissue, bones and teeth, affects the formation of hemoglobin, and the maturation of red blood cells. Vitamin C increases the body's resistance to infections and reduces inflammatory reactions. Calcium pantothenate, as a component of coenzyme A, plays an important role in the processes of acetylation and oxidation, promotes the construction and regeneration of epithelium and endothelium. Folic acid takes part in the synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, nucleic acids, and is necessary for normal erythropoiesis. In the early stages of pregnancy, it reduces the risk of developing neural tube defects in the fetus. Iron is involved in erythropoiesis, as part of hemoglobin it ensures the transport of oxygen to tissues, prevents the development of anemia in pregnant women, especially in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Copper prevents anemia and oxygen starvation of organs and tissues, helps prevent ospeoporosis, and strengthens the walls of blood vessels. Manganese has anti-inflammatory properties and prevents the development of osteoarthritis. Zinc is necessary for the normal formation of the fetal skeleton and tissue regeneration, participates in the formation of certain hormones, including insulin, and reduces the likelihood of developing a number of intrauterine anomalies. Magnesium normalizes blood pressure, has a sedative effect, reduces the likelihood of developing preeclampsia, spontaneous abortion, and premature birth. Calcium is involved in the formation of bone tissue, promotes normal blood clotting, participates in the transmission of nerve impulses, contractions of skeletal and smooth muscles, and in the regulation of cardiac activity. Phosphorus strengthens bone tissue and teeth, enhances mineralization, and is part of ATP, the source of cell energy. Pharmacokinetics: The effect of the drug is the combined effect of its components, therefore, kinetic observations are not possible; all components together cannot be traced using markers or biostudies. Indications for use: Prevention and treatment of hypovitaminosis and mineral deficiency: - during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding), - with unbalanced and poor nutrition. To increase the body's resistance as part of complex therapy for infectious and other chronic diseases. The period of convalescence after illness. Contraindications: - hypervitaminosis A, - increased levels of calcium and iron in the body, - urolithiasis, - pernicious B12-deficiency anemia, - children, - hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Dosage regimen: The drug is recommended to be taken 1 tablet. 1 time/day The duration of the course is determined individually. The drug should be taken after breakfast with water. Side effects: Allergic reactions are possible.
Overdose The patient should be informed that in case of accidental overdose, consult a doctor. Treatment: temporary discontinuation of the drug, gastric lavage, intake of activated charcoal, and, if necessary, symptomatic therapy. Interaction: The drug contains iron and calcium, therefore, when tetracycline antibiotics and fluoroquinolones are used together, the absorption of the latter from the gastrointestinal tract is slowed down. Ascorbic acid enhances the pharmacological effect and side effects of antimicrobial agents from the sulfonamide group (including an increased risk of developing crystalluria). With the simultaneous use of antacid drugs, which include aluminum, calcium, magnesium, and cholestyramine, iron absorption decreases. When used together with thiazide diuretics, the risk of hypercalcemia increases. Special instructions: It is not recommended to take this drug simultaneously with other multivitamin preparations to avoid overdose. When prescribing the drug, it should be taken into account that the daily dose of retinol acetate during pregnancy should not exceed 5000 IU. It is possible that urine may turn an intense yellow color, which is not dangerous, because due to the presence of riboflavin in the composition of the drug.
Pregnancy and lactation The drug is used during pregnancy and lactation according to indications in recommended doses.
Manufacturer: Pharmstandard-UfaVITA OJSC, Russia Registration certificate holder: Pharmstandard-UfaVITA OAO, Russia Release form: film-coated tablets, polymer jar Registration data: P N002958/01 dated 10.13.2008 Registration certificate status: valid Pharmaceutical article number: P N002958 /01-120110
Manufacturer: Pharmstandard-Ufa Vitamin Plant OJSC, Russia Registration certificate holder: Pharmstandard-Ufa Vitamin Plant OJSC, Russia Forms of release: film-coated tablets, contour cell packaging, film-coated tablets, polymer jars Ingredients: alpha-tocopherol acetate 20 mg [ in the composition of the semi-finished product: alpha-tocopherol acetate, gelatin, sucrose, corn starch, sodium aluminosilicate], ascorbic acid 100 mg, iron fumarate 10 mg [in terms of iron], calcium pantothenate 10 mg, calcium phosphate dihydrate 19 mg [in terms of iron phosphorus], calcium phosphate dihydrate 25 mg [in terms of calcium], magnesium oxide 25 mg [in terms of magnesium], manganese sulfate monohydrate 2.5 mg [in terms of manganese], copper sulfate pentahydrate 2 mg [in terms of copper], nicotinamide 20 mg, pyridoxine hydrochloride 5 mg, retinol acetate 567.5 mcg = 1650 IU [in the semi-finished product: retinol acetate, butylhydroxytoluene, gelatin, corn starch, sucrose], riboflavin 2 mg, thiamine hydrochloride 2 mg, folic acid 400 mcg, cyanocobalamin 5 mcg, zinc sulfate heptahydrate 10 mg [in terms of zinc], ergocalciferol 6.25 mcg = 250 IU [in the semi-finished product 0.5%: ergocalciferol, soybean oil] Shelf life: 2 years Registration data: P N002958/01 dated 10/13/2008 Status of the registration certificate: valid Pharmaceutical article number: P N002958/01-120110, FSP 42-0610-4084-05
"Iron" necessity
Iron levels are one of the “sick” topics in the relationship between the expectant mother and her attending physician. Pregnant women have to constantly take tests for hemoglobin. If they show decreased levels, the doctor will immediately prescribe iron supplements. The need for this measure is easy to explain.
The blood volume in a pregnant woman's body becomes larger, and hemoglobin is needed for the formation of red blood cells (iron is one of its components). If there is not enough iron, the fetus may develop oxygen starvation, and the mother may develop iron deficiency anemia. This condition can lead to serious consequences: lack of weight in the baby, underdevelopment, premature birth.
What seems complicated here? If the doctor prescribed iron, then you need to take it. However, there is a problem: iron in the form of salts (namely, in this form it is contained in supplements) is poorly absorbed (about 10%) and causes side effects: constipation, vomiting, severe abdominal pain. It is for this reason that many pregnant women stop taking iron supplements even with low hemoglobin levels.
However, today a solution to this problem has emerged - iron in liposomal form. This iron is in a shell of lipids, due to which it is absorbed 4.7 times better than standard forms, and does not cause discomfort from the gastrointestinal tract.
If you experience nausea, pain or other discomfort while taking iron supplements, switch to liposomal iron. It is well absorbed and has no side effects.
| Alphabet Mom's health | Vitrum Prenatal | Complimentary Mom | Complivit Trimester | Pregnoton Mom | Femibion | Elevit Pronatal |
| Electrolytic iron | Iron (fumarate) | Iron (fumarate) | Iron (fumarate) | Liposomal iron | — | Iron (fumarate) |
To be or not to be, to drink or not to drink... Do pregnant women need vitamin supplements?
Doctors recommend that almost every woman take various vitamin preparations during pregnancy. But do pregnant women need to take vitamins? Isn't a balanced diet enough? We asked these and other questions to Ekaterina Aleksandrovna Minchenkova, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Expert Clinic Smolensk.
— Ekaterina Aleksandrovna, what is the role of vitamins in the body in general and in the body of a pregnant woman in particular?
— Vitamins are special substances that everyone (not just women) need in small quantities for the normal functioning of the body. They participate in metabolism, are biological accelerators of chemical reactions occurring in the cells of the body, etc. A pregnant woman has a higher need for vitamins and microelements, because the fetus also needs them.
— What vitamins can you get from food?
— Most vitamins are not formed in our body, but come from food. If a pregnant woman eats a full, rational, varied diet, then she does not need additional vitamins and minerals (with some exceptions). They will be easily obtained from food in sufficient quantities. No vitamin supplement can match the positive effects of proper nutrition.
— Speaking about nutrition, you said “with some exceptions.” That is, despite the correct diet, pregnant women should still take some vitamins? And if so, which ones?
- Yes. During pregnancy, doctors prescribe certain vitamins and microelements, even if the woman eats normally. I will dwell in detail on those that I consider the most important. The #1 prenatal vitamin is vitamin B9, or folic acid. Probably, it would be possible to do without additional intake of other vitamins, but it’s impossible without folic acid. This is explained by the fact that the most convincing evidence about the need for additional vitamin intake in preparation for pregnancy and in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy was obtained only for folic acid. A lack of this vitamin may increase the likelihood of neural tube defects in the fetus, as well as some other defects (cleft lip, palate, congenital heart defects, malformations of the urinary tract and limbs, congenital hydrocephalus).
The recommended dose of folic acid is 400–500 mcg (micrograms) per day, but in rare cases it may be higher. To cover the daily dose of this vitamin, you need to eat 500 g of liver (chicken, goose, pork, beef, cod, etc.) or 1 kg of salad. It is difficult to provide the required daily amount of folic acid from food, so the doctor prescribes it in the form of a drug.
Next is vitamin D. It is formed in the body under the influence of ultraviolet rays (the main way it is obtained), and comes in some quantity from certain foods. All pregnant women may be recommended to take an additional dose of 600–1200 IU/day. But it is better to visit a doctor to decide whether it is necessary or not.
Supplemental vitamin B12 may be indicated for vegans and vegetarians.
I would also like to talk about microelements - they are also important for a pregnant woman’s body. All women in the CIS countries are recommended to take additional iodine in the form of potassium iodide. Before pregnancy, the iodine dose is 100–150 mcg per day. With the onset of pregnancy, throughout its entire duration and during breastfeeding, the dose increases to 250 mcg per day. But usually, covering the need for iodine is distributed as follows: we get 50 mcg from food, and 200 mcg we take in the form of a drug. For diseases of the thyroid gland, consultation with an endocrinologist is mandatory.
Calcium at a dose of 1000 mg per day should be obtained daily from food or mineral supplements if the woman does not consume calcium-containing foods.
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). WHO still does not recommend additional intake of this component during pregnancy and insists on a healthy diet. A sufficient supply of omega-3 is necessary for the proper formation of the vision organs and brain of the unborn child. In 2021, a study was conducted that included several thousand pregnant women. A diet high in omega-3s has been shown to reduce the risk of preterm birth from 7% to 2%, as well as the risk of low birth weight babies.
Excellent sources of omega-3 PUFAs include salmon, tuna and seafood. If you use them 2 times a week, then you do not need additives and dietary supplements with this component. Everyone else should think about changing their diet or taking them additionally (of course, after consulting a doctor).
— You talked about the possible consequences of a lack of folic acid. What can a deficiency of microelements lead to in a pregnant woman and unborn child?
— Children born to mothers with mild to moderate iodine deficiency are more likely to have behavioral disorders in the form of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Severe iodine deficiency in pregnant women is fraught with an increase in the incidence of stillbirths and infant mortality, miscarriages, the birth of low birth weight children, and children with mental retardation.
A lack of calcium also leads to negative consequences: bone density decreases, which leads to the development of osteoporosis in women during menopause and an increased risk of fractures in old age. Possible heart rhythm disturbances, muscle spasms, and convulsions. In pregnant women, especially those at risk, the likelihood of developing gestational hypertension (high blood pressure) and preeclampsia (a pathology in which blood pressure rises during pregnancy, edema forms, and protein appears in the urine) increases.
Calcium is best absorbed from dairy products, 2-3 servings of which will provide the daily intake. 1 serving is equal to 200 ml of milk, kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk, or 200 g of yogurt, or 100 g of cottage cheese or 40 g of cheese.
Iron deficiency in the mother’s body before pregnancy and in its early stages can “cross out” all subsequent efforts of parents and teachers in educating their children. The developing brain of an unborn baby is especially sensitive to a lack of iron in the body, including when there is a hidden deficiency, when hemoglobin is normal and iron reserves are low.
Many people know that iron is needed for the formation of hemoglobin, which can bind oxygen. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells, which deliver oxygen to the cells. And if there is little oxygen, then the cells suffer. Imagine feeling short of breath. So it is here: the brain cells of a still small person (3–12 weeks of pregnancy), not receiving enough oxygen, divide more slowly, which simplifies neural connections, the gray matter suffers, and your baby will no longer become a genius, even if you responsibly began taking Iron supplements after 12 weeks of pregnancy.
— Is it possible to take prenatal vitamins without a doctor’s prescription?
- No. I recommend taking vitamins only after consulting a doctor if a deficiency has been established. People who may be at increased risk of developing vitamin deficiencies include:
- obese people;
- vegans;
- having some intestinal diseases;
- people with low socioeconomic status;
- experiencing real hunger
and some others. For these women, additional vitamin intake will be justified.
— Can vitamin supplements taken during pregnancy be harmful or useless?
— At the moment, there is no evidence that multivitamins prevent the development of any diseases, that they are necessary and useful. That is, they turned out to be ineffective. Vitamins usually contain more than 5 components. And even a very qualified clinical pharmacologist will not calculate all the options for the interaction of active components in a living organism. According to many studies, most multivitamin complexes are not absorbed by the body. They contain components (vitamins and microelements) that are incompatible with each other: calcium and iron, fat- and water-soluble groups of vitamins, zinc and folate. B1, B6 and B12, although from the same group, are “at odds” with each other or enhance each other’s negative effects. Therefore, if you take vitamins, it is better to take them separately, and only those that are really necessary.
Often the dosages of the components do not correspond to the recommended ones (for example, folic acid is recommended at a dose of 400 mcg per day, and in multivitamins it is often contained in an amount of 200 mcg, etc.).
Any supplements or vitamin complexes containing vitamin A should be avoided due to its possible teratogenic effect (that is, the ability to cause malformations in the child during pregnancy).
There are no natural vitamins on the modern pharmaceutical market. Without exception, all preparations contain vitamins or their analogues, which are obtained synthetically. Natural ones are found only in food products.
— Do prenatal vitamins have side effects?
- Certainly. Firstly, like any other drugs, there can be an allergic reaction to them. Side effects from the gastrointestinal tract are also common: nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, etc. The load on the liver is high. Excessive intake of some vitamins can lead to cancer.
— Is it possible for a pregnant woman to take vitamins if she has uterine fibroids? And if so, which ones?
— There are no restrictions or features in terms of taking vitamins.
— Are there any contraindications to taking vitamins for pregnant women?
— Contraindications are the same as for all other drugs. Increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drug or their intolerance, hypervitaminosis, severe renal failure and some others. Therefore, only a specialist can prescribe them.
I would like to finish with the words of one professor: even after eating a fruit with nitrates, a person will receive more useful vitamins and microelements than by taking one synthetic tablet. Not verbatim, but conveyed the meaning.
Interviewed by Marina Volovik
You can make an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist here. ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
The editors recommend:
Rules for healthy eating. What should you eat to stay healthy? Life without meat: fashion, philosophy or benefit to the body? How to determine that the body does not have enough iodine? Myths and truth about thyroid diseases
For reference:
Minchenkova Ekaterina Aleksandrovna
In 2014 she graduated from the Faculty of Medicine of Vitebsk State Medical University. In 2015 – internship in obstetrics and gynecology. Currently, he is an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Expert Clinic, Smolensk. Reception is conducted at the address: st. March 8, 20.
Do I need iodine?
Pregnancy and childbirth can proceed normally only if the woman and child receive sufficient amounts of iodine. The fact is that iodine is part of hormones that directly regulate the intrauterine development of the fetus. Why is iodine deficiency dangerous?
- The child has a high probability of developmental delay, congenital hearing and speech defects (deafness, deaf-muteness), as well as mental retardation and underweight.
- A woman has a goiter of the thyroid gland (overgrowth).
However, iodine deficiency is a common situation for 70% of the Russian population. Research data from the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences show that no more than 37% of the required amount of iodine enters the body of a pregnant woman with food.
As with iron, large doses of iodine scare women. However, these doubts and fears are in vain: taking iodine-containing complexes is not recommended only for women with Graves' disease. This is a rare disease, occurring in only 2% of the world's population.
| Alphabet Mom's health | Vitrum Prenatal | Complimentary Mom | Complivit Trimester | Pregnoton Mom | Femibion Natalcare I and II | Elevit Pronatal |
| Iodine 150 mcg | — | — | Trimester 1 Iodine 200 mcg Trimester 2 Iodine 150 mcg Trimester 3 Iodine 100 mcg | Iodine 150 mcg | Iodine 150 mcg | — |
Complivit Trimesterum 2 tab N30(OTISI)
A combined multivitamin preparation with micro- and macroelements, the compatibility of the components in 1 tablet is ensured by a special technology for the production of vitamin-mineral complexes. This vitamin-mineral complex was created specifically taking into account the changing needs of a woman’s body for vitamins and microelements at different stages of pregnancy. The effect of the drug COMPLIVIT Trimester 2 trimester is due to the effects of its constituent components: Vitamin A (retinol) - necessary for bone growth, normal reproductive function, for the regulation of division and differentiation of the epithelium, as well as for the normal function of the retina of the eye. Retinol is involved in the formation of the organ of vision and skeleton during intrauterine development of the fetus. Vitamin E (a-tocopherol) - has an antioxidant effect: it inhibits the reactions of free oxidation of radicals and unsaturated fatty acids, prevents the formation of peroxides that damage cell membranes. Promotes normal growth and development of the fetus, reduces the risk of arterial hypertension during pregnancy. Vitamin B1 (thiamine) - plays an important role in protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolism, as well as in the processes of nerve excitation in synapses. Participates in carbohydrate metabolism, as well as in the synthesis of nucleic acids, proteins and lipids. During pregnancy, thiamine reduces the risk of congenital malformations in the fetus. Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) - regulates redox processes, participates in tissue respiration, carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism, as well as in the synthesis of hemoglobin and erythropoietin. Necessary for normal growth and development of the fetus. Lack of riboflavin during pregnancy leads to fetal pathology: limb deformities, cleft palate, hydronephrosis, hydrocephalus, congenital heart defects. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) - participates in metabolism; necessary for the normal functioning of the central and peripheral nervous system. Prevents the development of nausea and vomiting during toxicosis of pregnant women by normalizing the function of the nervous system. Helps increase the absorption of magnesium in the intestines. With a lack of pyridoxine, the risk of developing preeclampsia, anemia, and oligohydramnios increases. Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) - is involved in the regulation of redox processes, carbohydrate metabolism, blood clotting, and tissue regeneration; increases the body's resistance to infections. A lack of vitamin C increases the risk of premature miscarriage. The need for vitamin C increases in the 2nd and 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Nicotinamide (vitamin PP) - is involved in the metabolism of fats, proteins, purines, and tissue respiration. Reduces the risk of fetal malformations. Folic acid - participates in the synthesis of amino acids, DNA and RNA, stimulates erythropoiesis. Folic acid reduces the risk of complications during pregnancy that develop against the background of a deficiency in folic acid consumption: spontaneous miscarriage, premature birth, premature placental abruption. Calcium pantothenate is a preparation of pantothenic acid, which plays an important role in metabolism: it is involved in carbohydrate and fat metabolism, synthesis of acetylcholine and steroid hormones; accelerates regeneration processes. Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) - is involved in many metabolic processes and is necessary for DNA synthesis. Cyanocobalamin is involved in the formation of myelin, a component of the sheath of nerve fibers; If there is a deficiency of cyanocobalamin during pregnancy, the process of formation of the myelin sheath of the nerves may slow down in the fetus. Increases the resistance of red blood cells to hemolysis. Increases the ability of tissues to regenerate. Vitamin D3 (colecalciferol) - is involved in the regulation of calcium-phosphorus metabolism, increases the absorption of calcium in the intestines and the reabsorption of phosphates in the kidneys. Promotes bone mineralization, the formation of the bone skeleton and teeth in the fetus, and is necessary for the normal functioning of the parathyroid glands. Deficiency of colecalciferol can lead to the development of rickets in the fetus, osteomalacia and osteoporosis in the pregnant woman. Rutoside (rutin) - has an angioprotective effect: it reduces the rate of water filtration in the capillaries and their permeability to proteins. In the presence of venous insufficiency and lymphostasis, it reduces swelling of the lower extremities. Thioctic acid (lipoic acid) - plays an important role in the energy balance of the body, is involved in the regulation of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, has a lipotropic and antioxidant effect, improves liver function, and also improves the nutrition of the nervous system. cells. Lutein is a carotenoid necessary for the normal functioning of the retina. Protects the eyes from damage resulting from exposure to ultraviolet light, is a component of the antioxidant system of the retina, and also provides protection to the retinal photoreceptors from oxygen radicals formed during the adverse effects of radiation of various origins on the eye. Iron - takes part in erythropoiesis; is an important component of hemoglobin, which ensures the transport of oxygen to tissues. Prevents the development of iron deficiency anemia during pregnancy and its consequences in children of the first year of life - disruption of the adaptation system and increased morbidity. Manganese - plays an important role in cell metabolism, is part of the active center of many enzymes, and is involved in protecting the body from the harmful effects of peroxide radicals. An imbalance of manganese in the fetoplacental system in pregnant women leads to disruption of the ossification processes in the fetus, which leads to intrauterine growth retardation and a lag in the physical development of children during the first year of life. Copper is necessary for the normal absorption of iron, the formation of connective tissue, cells blood. Copper deficiency provokes the development of breathing disorders in newborns. Zinc is involved in metabolism and stabilization of cell membranes. It is part of the main enzymes and participates in various biochemical reactions. Zinc stimulates skin regeneration processes and hair growth, and also has an immunomodulatory effect. Zinc is involved in cell division and differentiation; its deficiency leads to the birth of an immature and/or low-weight fetus, as well as the formation of malformations of various organs and systems. Magnesium - reduces the excitability of nerve cells and is involved in many enzymatic reactions. Magnesium takes part in the formation of muscle and bone tissue, as well as in protein synthesis. Replenishes magnesium deficiency that occurs during pregnancy and reduces the risk of increased uterine tone, spontaneous abortion, intrauterine growth retardation, as well as the development of late gestosis. Calcium - is involved in the formation of bone tissue, the blood clotting process, in the regulation of nerve conduction and muscle contractions , including in maintaining stable cardiac activity. Calcium reduces the risk of complications caused by calcium deficiency, including those occurring during pregnancy (decreased bone density and strength, bone and muscle pain, leg cramps, dental caries, arterial hypertension, palpitations). Calcium is necessary for the formation of bones and teeth, the nervous system, heart and muscles of the fetus; its use helps prevent rickets in children in the first year of life. Selenium is a trace element that is part of all cells of the body. Provides antioxidant protection to cell membranes, potentiates the effect of vitamin E. Selenium is necessary for the functioning of the immune system, as well as for the maturation of the surfactant system of the thyroid gland; participates in lipid and protein metabolism. Reduces the risk of complications during pregnancy that develop against the background of iodine deficiency: gestosis, spontaneous abortion. Prevents the occurrence of congenital intrauterine malformations of the brain, disorders of the thyroid gland, musculoskeletal system, and retardation in physical and mental development.
What about calcium?
Calcium is not always included in vitamin and mineral complexes for pregnant women. The reason lies in the ambiguity of this mineral. It is undoubtedly extremely important for the normal development of the fetus and the well-being of the mother: without it, cramps often appear, bones become fragile, and teeth suffer. But, on the other hand, if there is too much calcium, problems may arise. If there is an excess of calcium, the placenta becomes calcified, which interferes with the supply of necessary substances to the fetus. The woman’s pelvic bones become too hard and diverge worse, and the baby’s skull becomes rigid, which can cause complications during childbirth.
However, these are not all the problems associated with calcium. It interferes with the absorption of iron when both elements enter the body at the same time. But iron is needed by the body of mother and child. Therefore, doctors tend to prescribe calcium supplements only when there is clearly a deficiency. In this case, calcium is most often prescribed as a separate drug, since quite a lot of calcium is needed to combat deficiency, and it simply “will not fit” in a tablet or capsule with other useful substances.
To solve these problems, manufacturers had to work hard. Thus, the Alphabet Mom’s Health complex includes both components, but they are in separate tablets. This solution made it possible to leave a large dosage of calcium, but to exclude its contact with iron. Manufacturers Femibion and Pregnoton Mama excluded calcium in favor of iron. There is very little calcium in other preparations; it will not help cope with the deficiency.
| Alphabet Mom's health | Vitrum Prenatal | Complimentary Mom | Complivit Trimester | Pregnoton Mom | Femibion Natalcare I and II | Elevit Pronatal |
| Calcium (in a separate tablet) 250 mg (25%) | Calcium 200 mg (20%) | Calcium 25 mg (2.5%) | Trimester 1 30 mg (3%) Trimester 2 40 mg (4%) Trimester 3 50 mg (5%) | — | — | Calcium125 mg (12.5%) |
Complivit tablets p/o No. 60
Name
Complivit tab p/o in jars No. 60 in unitary enterprise No. 1
Description
Tablets are biconvex round, white coated, with a characteristic odor. The cross section shows two layers.
Main active ingredient
Multivitamin+multimineral
Release form
pills
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
A combined preparation containing a complex of vitamins and minerals, which are important factors in metabolic processes. The compatibility of the components in 1 tablet is ensured by a production technology special for vitamin preparations. Retinol (vitamin A) is involved in the formation of visual pigments and is necessary for twilight and color vision; ensures the integrity of epithelial tissues, regulates bone growth. Thiamine (vitamin B1) as a coenzyme is involved in carbohydrate metabolism and the functioning of the nervous system. Riboflavin (vitamin B2) is the most important catalyst for the processes of cellular respiration and visual perception. Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) as a coenzyme takes part in protein metabolism and the synthesis of neurotransmitters. Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) is involved in the synthesis of nucleotides and is an important factor in normal growth, hematopoiesis and development of epithelial cells; necessary for folic acid metabolism and myelin synthesis. Nicotinamide is involved in the processes of tissue respiration, fat and carbohydrate metabolism. Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) ensures collagen synthesis; participates in the formation and maintenance of the structure and function of cartilage, bones, teeth; affects the formation of hemoglobin and the maturation of red blood cells. Rutoside (rutin) is involved in redox processes, has antioxidant properties, prevents oxidation and promotes the deposition of ascorbic acid in tissues. Calcium pantothenate, as a component of coenzyme A, plays an important role in the processes of acetylation and oxidation; promotes the construction and regeneration of epithelium and endothelium. Folic acid takes part in the synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, nucleic acids; necessary for normal erythropoiesis. Lipoic acid is involved in the regulation of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, has a lipotropic effect, affects cholesterol metabolism, and improves liver function. α-tocopherol acetate (vitamin E) has antioxidant properties, maintains the stability of erythrocytes, and prevents hemolysis; has a positive effect on the functions of the gonads, nervous and muscle tissue. Iron is involved in erythropoiesis and, as part of hemoglobin, ensures the transport of oxygen to tissues. Copper prevents the development of iron deficiency anemia and oxygen starvation of organs and tissues, and helps prevent osteoporosis. Increases the strength and elasticity of blood vessels, affecting connective tissue proteins. Calcium is necessary for the formation of bone matter, blood clotting, the process of transmission of nerve impulses, contraction of skeletal and smooth muscles, and normal myocardial activity. Cobalt regulates metabolic processes and increases the body's defenses. Manganese plays an important role in metabolism, is part of many enzymes, and strengthens; bone and cartilage tissue. Zinc has immunomodulatory properties, promotes the absorption of vitamin A, regeneration and hair growth. Magnesium helps normalize blood pressure, stimulates, together with calcium, the production of calcitonin and parathyroid hormone, and prevents the deposition of calcium salts in the kidneys. Phosphorus strengthens bone tissue and teeth, enhances mineralization, and is part of ATP, the source of cell energy.
Pharmacokinetics
Water-soluble vitamins (B vitamins, vitamin C, thioctic acid) and minerals are well absorbed in quantities that meet the body's daily needs. Amounts exceeding tissue saturation levels are excreted in urine and sometimes in feces. A regular supply of vitamins and minerals is important to maintain adequate tissue concentrations, since they accumulate in the body in limited quantities. After oral administration, fat-soluble vitamins A and E are well absorbed in the small intestine in the presence of fat. The removal of fat-soluble vitamins from the body is carried out slowly; when high doses enter the body, cumulation is possible.
Indications for use
Replenishing the deficiency of vitamins and minerals when the need for them cannot be satisfied by the composition of the diet.
Directions for use and doses
Take orally after meals. To prevent vitamin and mineral deficiency - 1 tablet 1 time per day. For conditions accompanied by an increased need for vitamins and minerals - 1 tablet 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 4 weeks. Repeated courses - on the recommendation of a doctor.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
The use of the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Precautionary measures
Urine may turn an intense yellow color, which is due to the presence of riboflavin in the drug and does not pose a danger. Concomitant use with other medications containing vitamins and minerals is not recommended. Patients with diabetes should take into account that the sugar content in Complivit® is 184.78 mg (in 1 tablet). Taking vitamins does not replace a balanced diet. Do not exceed the indicated dosage. High doses of some components may be hazardous to health. This drug should be used with caution in patients who have had hypersensitivity reactions to azo dyes, acetylsalicylic acid and other prostaglandin inhibitors, as well as to other multivitamin preparations. Prescribed with caution for liver damage, a history of peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, cholelithiasis, chronic pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, and the presence of neoplasms. Vitamin C may interfere with test results for urine glucose, uric acid, and serum creatinine. Taking higher doses of folic acid, vitamin B12, and iron may mask some forms of anemia.
Interaction with other drugs
While taking the drug, you should refrain from drinking alcohol, since alcohol reduces the absorption of certain vitamins. Vitamins A and E mutually enhance the effect and are synergists. Retinol reduces the anti-inflammatory effect of glucocorticoids. Nitrites and cholestyramine interfere with the absorption of retinol, so their simultaneous use with the drug is not recommended. To avoid the possibility of developing hypervitaminosis A, it is not recommended to use the drug together with other drugs containing vitamin A. Vitamin A is not prescribed simultaneously with retinoids; their combination is toxic. Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron, increases the toxicity of sulfonamides (the possibility of crystalluria), penicillins, and reduces the effectiveness of heparin and indirect coagulants. The absorption of vitamin C decreases when used simultaneously with oral contraceptives. Concomitant use of ascorbic acid with antacids containing aluminum may increase urinary excretion of aluminum. Therefore, the combined use of antacids and COMPLIVITA is not recommended, especially in patients with renal failure. Concomitant use of salicylates with ascorbic acid may increase the urinary excretion of ascorbic acid. Vitamin B2 is incompatible with streptomycin and reduces the effectiveness of antibacterial drugs (oxytetracycline, doxycycline, erythromycin, tetracycline and lincomycin). Therefore, it should be taken at least 3 hours before taking the antibiotic. Tricyclic antidepressants, imipramine and amitriptidine, inhibit the metabolism of riboflavin, especially in cardiac tissue. Vitamin B6 affects the metabolism of certain medications. High doses of vitamin B6 reduce the antiparkinsonian effect of levodopa. Pyridoxine increases the peripheral conversion of levodopa and thus reduces its effectiveness in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Vitamin B6 is an antagonist of isoniazid and thiosemicarbazones, correcting sideroblastic anemia caused by these anti-tuberculosis drugs. The amount of vitamin B6 is reduced when taken simultaneously with oral contraceptives. Vitamin B6 affects polarization processes in the area of neuromuscular synapses, and therefore can weaken the curare-like effect. Large doses of pyridoxine may lead to decreased serum concentrations of phenytoin and phenobarbital in some patients. Colchicine, cimetidine, calcium supplements, ethyl alcohol, neomycin, para-aminosalicylic acid, biguanides, cholestyramine, potassium chloride and methyldopa reduce the absorption of vitamin B12. Chloramphenicol and vitamin C affect the absorption of vitamin B12. Serum concentrations of cyanocobalamin may be decreased when oral contraceptives are taken concomitantly. Folic acid may reduce plasma concentrations of anticonvulsants, in particular phenytoin, phenobarbital and primidone, resulting in a possible mutual reduction in clinical effectiveness. Therefore, patients receiving antiepileptic therapy may require dosage adjustments and careful medical supervision if taking folic acid. Medicines containing folic acid or its derivatives may reduce the effectiveness of methotrexate. Antibodies that cross-react with other folic acid analogues, including methotrexate, folinic acid (leucovorin) and aminopterin, have been found in patients with hypersensitivity to folic acid.
Contraindications
Individual intolerance to the components of the drug, children under 15 years of age.
Compound
Excipients (core): talc (E 553) - 5.07 mg, potato starch - 14.05 kg, citric acid (in the form of citric acid monohydrate) (E 330) - 14.14 mg, povidone (low molecular weight polyvinylpyrrolidone, povidone K-17) (E 1201) - 1.60 mg, collicoate® Protect (macrogol and polyvinyl alcohol copolymer 55-65%, polyvinyl alcohol 35-45%, silicon dioxide 0.1-0.3%) - 0.32 mg, calcium octadecanoate (calcium stearate) (E 470) - 5.04 mg, sucrose (granulated sugar) - 27.10 mg. Excipients (shell): wheat flour - 71.40 mg, magnesium hydroxycarbonate (basic aqueous magnesium carbonate) - 93.33 mg, gelatin - 0.54 mg, titanium dioxide (E,171) - 4.59 mg, talc ( E 553) - 0.33 mg, beeswax (E 901) - 0.33 mg, water-soluble methylcellulose (E 461) - 1.80 mg, sucrose (granulated sugar) - 157.68 mg.
Overdose
With long-term use, significantly exceeding the recommended course of 4 weeks, and exceeding the recommended daily dose, the following conditions may occur: impaired glucose tolerance, drowsiness, paresthesia, blurred vision, arrhythmias, change in urine color, hypercalciuria, hemolytic anemia (in some patients with deficiency glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase), hyperthermia, irritability, hyperhidrosis, temporary increase in aspartate aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, lactate dehydrogenase. In case of overdose, you should consult a doctor. Treatment: temporary cessation of taking the drug, activated carbon orally, gastric lavage, symptomatic treatment.
Side effect
Recommended doses are usually well tolerated. Some people may experience adverse reactions: From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions to the components of the drug are possible, including anaphylactic shock, bronchospasm. From the nervous system: headache, dizziness. From the digestive tract: gastrointestinal disorders, dyspepsia, constipation, diarrhea, increased secretion of gastric juice. From the skin and subcutaneous tissue: rash, urticaria, itching, redness.
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Store in original packaging to protect from moisture and light. Keep out of the reach of children.