Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
This drug has a significant effect on alpha-adrenergic receptors, exhibiting a noticeable vasoconstrictor and pressor effect compared to adrenaline . At the same time, there is less stimulation of heart contractions, a weak bronchodilator effect and an effect on metabolism, and a pronounced hyperglycemic effect does not appear.
Norepinephrine is characterized by a cardiotropic effect, stimulating cardiac beta-adrenergic receptors, which can be masked by reflex bradycardia , high tone of the vagus nerve, provoked by high blood pressure .
When norepinephrine is administered, cardiac output increases and perfusion pressure in the coronary arteries increases, along with peripheral vascular resistance and central venous pressure.
This drug is widely used when it is necessary to increase blood pressure and increase heart contractions. But this is done primarily to increase peripheral vascular resistance and heart rate. In addition, blood flow in the vessels of the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract decreases. Ventricular arrhythmias . For this reason, norepinephrine is not used in complex cases of cardiogenic shock.
This can cause a vasoconstrictor reaction in peripheral vessels, which means their resistance can lead to an undesirable effect. The myocardial oxygen demand also increases significantly , which negatively affects the condition of the whole organism.
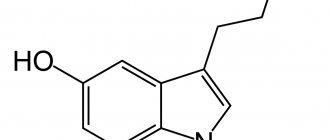
Serotonin
We are used to hearing about it as the “hormone of happiness”, while serotonin is not a hormone at all, and with “happiness” everything is not so simple.
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that not only brings positive emotions, but reduces sensitivity to negative ones. It provides support to “neighboring” neurotransmitters - norepinephrine and dopamine; serotonin is involved in motor activity, reduces general pain, and helps the body in the fight against inflammation. Serotonin also increases the accuracy of the transmission of active signals in the brain and helps to concentrate. An excess of serotonin (for example, from LSD use) increases the “volume” of secondary signals in the brain, and hallucinations occur. Lack of serotonin and an imbalance between positive and negative emotions are the main cause of depression.
The 5-HTTLPR gene encodes the serotonin transporter protein. The gene sequence contains a region of repeats, the number of which may vary. The longer the chain, the easier it is for a person to maintain a positive attitude and switch from negative emotions. The shorter it is, the higher the likelihood that a negative experience will be traumatic. The number of repetitions is also associated with sudden infant death syndrome, aggressive behavior in the development of Alzheimer's disease, and a tendency to depression.
Interaction
The simultaneous use of norepinephrine and inhalational anesthetics can lead to complicated ventricular arrhythmia.
Combination with adrenergic and serotonergic antidepressants, imipramine or amitriptyline leads to the development of paroxysmal hypertension , cardiac arrhythmia caused by an adrenergic blocking effect on the functioning of the nervous system.
The use of selective and non-selective MAO inhibitors, Linezolid , etc., together with Norepinephrine can enhance its pressor effect, so constant medical monitoring is required.
Destruction of neurotransmitters
The action of neurotransmitters is like a holiday, as if everyone had gone out into the street in a joyful crowd to watch the fireworks.
But the holiday cannot (and should not) last forever, and neon roses in the night sky must give way to the usual constellations and morning dawn. For this, the body has a function of transmitter reuptake - when the substance returns from the synaptic cleft back to the presynaptic membrane of the axon and the action of the neurotransmitter stops. But sometimes reuptake is not enough, and more effective measures are needed - the destruction of the neurotransmitter molecule. These functions are also performed by proteins. The COMT gene encodes the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase, which destroys norepinephrine and dopamine. How well you cope with stressful situations depends on how well the protein works. Those with an active form of the COMT gene—warriors by nature—receive reduced levels of dopamine in the frontal lobe of the brain, which is responsible for processing information and pleasurable sensations. Such people adapt better to stressful situations, they are open to communication, and they have better memory. But due to low dopamine levels, they experience less pleasure in life, are more prone to depression, and have less developed motor functions. A low-active variant of the COMT gene reverses the situation. Those with an inactive mutation have good fine motor skills, are more creative, but have poor pain tolerance, and when they get into a stressful situation, they become irritable, impulsive, and anxious. COMT gene mutations are also associated with Parskinsonism and hypertension.
The gene for the enzyme monoamine oxidase A MAOA is responsible for the deactivation of monoamines - neurotransmitters with one amino group, which include adrenaline, norepinephrine, serotonin, melatonin, histamine, dopamine. The better the MAOA gene works, the faster the “fog of mind” caused by a stressful situation is neutralized and the faster a person is able to make informed decisions.
Sometimes even the MAOA gene is called the “criminal gene”: certain gene mutations contribute to the emergence of pathological aggression. Due to the fact that the gene is located on the X chromosome, and girls have two copies of this gene, and boys only one, there are statistically more “born criminals” among men.
Let’s not blame everything on genetics - even with regard to the “furious” MAOA gene, everything is not simple: a study by New Zealand scientists showed that the connection between the gene and aggressive behavior only appears in the presence of traumatic experience.
Understanding how neurotransmitters work allows us to take a fresh look at habitual emotions, mood swings, and even reconsider our ideas about what actually shapes our personality. You can continue the fascinating process of self-discovery with the Atlas genetic test - an excellent opportunity to find out your variant of the COMT and MAOA gene.
PS Second and third parts.
Analogs
Level 4 ATX code matches:
Mezaton
Dobutamine
Dopamine
Dopamine
Adrenalin
Main analogues: Arterenol, Levarterenol, Levofed, Norarthrinal, Norepinephrine and Norexadrin .
Differences between Noranrenaline and Adrenaline
Adrenaline is produced by the adrenal medulla. This component is involved in various processes in the body: stimulating the breakdown of glycogen in liver hepatocytes, which leads to an increase in glucose in the blood , activates the lipase enzyme and the breakdown of triglycerides in adipose tissue, as well as glycogenolysis in muscle cells.
The contraction of the heart muscles also increases and blood pressure increases, the muscle and heart vessels dilate, but the vessels of the abdominal organs, skin and mucous membranes narrow. A significant influence of adrenaline on the body's response to stressful situations has been noted.
Norepinephrine has a pronounced vasoconstrictor effect, has less effect on heart contractions, has a weak bronchodilator effect and influence on metabolic processes.
The normal content of adrenaline in the blood is 88 mcg/l, and norepinephrine is in the range of 104-548 mcg/l.
The need to determine the concentration of these components arises when it is necessary to identify pheochromocytomas and carry out a differential diagnosis of hypertension.
How do neurotransmitters work?
Nerve cells communicate with each other using processes - axons and dendrites.
The gap between them is the so-called synaptic cleft. This is where the interaction of neurons occurs. Mediators are synthesized in the cell and delivered to the axon terminal - to the presynaptic membrane. There, under the influence of electrical impulses, they enter the synaptic cleft and activate the receptors of the next neuron. After activation of the receptors, the neurotransmitter returns back into the cell (so-called reuptake occurs) or is destroyed.
Neurotransmitters themselves are not proteins, so there is no “dopamine gene” or “adrenaline gene.” Proteins perform all the auxiliary work: enzyme proteins synthesize the neurotransmitter substance, transporter proteins are responsible for delivery, receptor proteins activate the nerve cell. Several proteins—and therefore several different genes—may be responsible for the proper functioning of one neurotransmitter.
Reviews about Norepinephrine
It should be noted that this drug is often used in critical cases when there is a fight for a person’s life. Therefore, it is impossible to find reviews about Norepinephrine left by patients. In such situations, people are unlikely to be able to assess the effect of a particular drug, and most likely do not even know that they received such treatment.
As a rule, medical specialists discuss this drug online. This is usually related to the question of how to increase Norepinephrine when critical situations arise. The fact is that this needs to be done quickly, but the speed of introduction of the solution is an important aspect of its use. Therefore, you have to use all your experience and knowledge, which helps a person not to die and conduct full-fledged intensive therapy.
The features of this drug are described in detail by Wikipedia, where it is reported that there is no need to administer it independently. As for medical professionals, it is important that they have sufficient experience and professionalism to use Norepinephrine in practice.
Dopamine
By activating neurons in different areas of the brain, dopamine plays multiple roles.
Firstly, it is responsible for motor activity and gives the joy of movement. Secondly, it gives a feeling of almost childish delight from learning new things - and the desire to search for novelty. Third, dopamine has an important function of reward and reinforcement of motivation: as soon as we do something useful for the life of the human species, neurons give us a reward - a feeling of satisfaction (sometimes called pleasure). At a basic level, we receive rewards for simple human joys - food and sex, but in general, the options for achieving satisfaction depend on everyone’s tastes - someone will get a “carrot” for completing the code, someone – for this article. The reward system is associated with learning: a person receives pleasure, and new cause-and-effect associations are formed in his brain. And then, when the pleasure passes and the question arises of how to get it again, a simple solution will arise - write another article.
Dopamine looks like an excellent stimulant for work and study, as well as an ideal drug - most drugs (amphetamine, cocaine) are associated with the action of dopamine, but there are serious side effects. An “overdose” of dopamine leads to schizophrenia (the brain works so actively that it begins to manifest itself in auditory and visual hallucinations), and a deficiency leads to depressive disorder or the development of Parkinson’s disease.
Dopamine has five receptors, numbered D1 to D5. The fourth receptor is responsible for the search for novelty. It is encoded by the DRD4 gene, the length of which determines the intensity of dopamine perception. The lower the number of repetitions, the easier it is for a person to reach the peak of pleasure. For such people, a delicious dinner and a good movie will most likely be enough.
The greater the number of repetitions - and there can be up to ten - the more difficult it is to get pleasure. Such people have to try hard to get a reward: go on a trip around the world, conquer the top of a mountain, do a somersault on a motorcycle, or bet their entire fortune on red in Las Vegas. This genotype is associated with the range of migration of ancient people from Africa across Eurasia. There is also sad statistics: among those convicted in prisons for serious crimes, the “unsatisfactory” variant of DRD4 is more common.
Norepinephrine price, where to buy
The price of Noradrenaline for a package of 10 ampoules is from 1,550 rubles.
You can buy Noradrenaline in Kyiv at a cost of 1300 UAH.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
ZdravCity
- Norepinephrine conc.
d/prig. solution for intravenous injection. 2 mg/ml 4 ml 10 pcs FKP Armavir biofactory 1324 rub. order - Norepinephrine conc. d/prig. solution for intravenous injection. 2mg/ml 8ml 10pcs FKP Armavir biofactory
RUB 1,538 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Norepinephrine Tartrate Agetan 2mg/ml 8ml N10 concentrate for solution for infusion
2403 UAH.order - Norepinephrine Tartrate Agetan 2 mg/ml 4ml No. 10 concentrate for solution for infusion
1602 UAH. order
References
- Rumyantsev, P.O., Yazykova, D.R., Slashchuk, K.Yu. and others. Personalized diagnosis of chromaffin tumors (pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma) in oncoendocrinology. Endocrine surgery, 2021. - No. 1.
- Repina, V.P. The influence of different concentrations of catecholamines on the functioning of immunocompetent cells. Human Ecology, 2008. - No. 2.
- Melnichenko, G.A., Troshina, E.A., Beltsevich, D.G. and others. Clinical recommendations of the Russian Association of Endocrinologists for the diagnosis and treatment of pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma, 2015. - T. 9. - No. 3.
- Beltsevich, D.G., Troshina, E.A., Yukina, M.Yu. Pheochromocytoma. Problem endokr., 2010. - No. 1.
How to increase norepinephrine in the body
The precursor to norepinephrine is dopamine, synthesized from the amino acid tyrosine, which comes with protein foods or is produced in the body as a derivative of phenylalanine.
Natural sources of tyrosine:
There is another source of increased norepinephrine in the body - medications, mainly antidepressants.
All antidepressants are designed to increase the level of one or another neurotransmitter. But these are medicines, not food additives. All these drugs can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor!
Catecholamines
Before informing the reader about the disruption of the biogenic amine system in schizophrenia, a few words should be said about the pathways of biosynthesis and metabolism of monoamines, as well as those brain structures that are associated with neurons sensitive to catecholamines.
This is also necessary due to the fact that such information will be useful when reading the chapter on pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia.
Hydroxylation of the phenylalanine molecule occurs with the participation of the enzyme phenylalanine-4-monooxygenase. The resulting tyrosine is successively converted into 3,4-dioxyphenylalanine-DOPA, dopamine, norepinephrine and adrenaline.
The stages of catecholamine biosynthesis are catalyzed by a “chain” of enzymes: tyrosine-3-monooxygenase-aromatic L amino acid decarboxylase-dopamine-beta-monoxidase-phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase. In this case, the enzyme tyrosine-3-monooxygenase has pronounced substrate specificity.
Catecholamines formed from tyrosine are capable of inhibiting the activity of this enzyme by feedback principle. The activity of tyrosine-3-monooxygenase changes under the influence of corticosteroids.
| | In order to prescribe the correct treatment for schizophrenia, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis. |
Thyroid hormones accelerate the conversion of DOPA to dopamine. Progesterone slows down the synthesis of dopamine and norepinephrine by reducing the activity of tyrosine-3-monooxygenase. Perhaps this circumstance explains the more favorable course of schizophrenia in women than in men.
The formation of norepinephrine from dopamine is considered a key link in determining the rate of catecholamine biosynthesis.
Norepinephrine is considered one of the main mediators of the adrenergic systems of the brain, and adrenaline most often plays the role of a modulator.
Among the methods for determining the prevalence of monoamines in the central nervous system, the immunochemical method for identifying the localization of protein components in catecholamine vesicles turned out to be the most accurate and informative. This method allows you to differentiate the localization of dopamine, norepinephrine and adrenaline.
Biogenic amines (norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, histamine) are found in the most important conductors of the sensory and motor systems, as well as in the pathways that provide higher functions of the cerebral cortex.
At the same time, out of the billions of neurons in the brain, only a few thousand cells contain biogenic amines. Many neurons containing biogenic amines are concentrated in specific regions of the brainstem. Neuronal axons emanating from these clusters or cell nuclei extend to almost all parts of the brain.
An important function of neurons containing biogenic amines should be considered the simultaneous modulation of synaptic activity in various parts of the central nervous system (Nicholas D. et al., 2003).
The conversion of norepinephrine to adrenaline mainly occurs at the level of neurons in the medulla oblongata. The main source of noradrenergic axons is considered to be clusters of neurons in the medulla oblongata and the pons. It is from here that the two ascending axon bundles originate. The anterior one enters the hypothalamus, and the posterior one goes to the hippocampus and cerebral cortex (Fuxe K., 1964).
The activity of dopamine beta monooxygenase, which catalyzes the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine, is suppressed by serotonin, tryptamine, histamine, and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO).
The conversion of norepinephrine to adrenaline by phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase is inhibited by phenamine derivatives, but is stimulated by ACTH and glucocorticoids.
Estrogens and thyroid hormones increase the rate of adrenaline formation, thyroid hormones inhibit monoamine oxidase, thereby promoting the accumulation of catecholamines.
In the central nervous system, norepinephrine usually acts as an inhibitory mediator of the cerebral cortex, less often in subcortical structures, in particular, in the hypothalamus, it acts as an excitation mediator.
Dopamine and serotonergic neurons are located in the periventricular, arcuate, suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus and in the preoptic area.
Most researchers believe that schizophrenia is based on impaired functioning of the catecholamine mediator system (dopamine, norepinephrine, adrenaline), accompanied by changes in their concentration in various brain structures, as well as activation of minor pathways of mediator metabolism, which leads to the formation and accumulation in brain tissue of substances that have psychotropic effect.
Result:
- Norepinephrine is a kind of neurotransmitter and hormone. The feeling of increased production of norepinephrine is common to many predators. Substance of hunters/extreme sports/gamblers.
- Norepinephrine is produced to a greater extent from Dopamine and to a lesser extent from the Kidneys.
- A large amount of norepinephrine can increase blood pressure too much and constrict blood vessels, the consequences are deterioration of hearing, vision, and intelligence. Little norepinephrine – what is called “routine/boring life”.
- A “normal” amount of norepinephrine will only make you happy. As has already been said in many articles, any extremes are evil. It is also sad to fall into depression despite having good intelligence. It is important to sometimes unwind and feel like a predator who controls his life, and it is better without serious stimulants.
Good luck!