Tags:
gastrointestinal diseases, colitis
5/5 — (1 vote)
Colitis is one of the most common pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. It is an inflammatory disease of the large intestine (or rather, its mucous membrane) with pronounced symptoms , which we will talk about later. The disease can be complicated by inflammatory processes in the stomach and small intestine . It often accompanies some other acute and chronic diseases (influenza, pneumonia, typhoid, mumps, malaria, etc.).
It happens that this disease, due to similar symptoms, is confused with irritable bowel syndrome and for this reason is sometimes misdiagnosed. But since irritable bowel syndrome is not associated with the colon, then, accordingly, it cannot have anything in common with colitis.
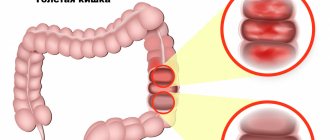
Colitis
Types of colitis
There are two types of colitis: acute and chronic. The disease usually begins with an acute form with characteristic pain, flatulence and nausea. But prolonged acute colitis can cause the development of a chronic form of the disease.
Chronic colitis is characterized by the presence of pathological changes in the structure of the intestinal mucosa. The cause of these changes is a prolonged inflammatory process, which leads to degeneration of the affected tissues and dysfunction of the large intestine. Often inflammation of the large intestine can cause damage to the small intestine.
Colitis is also divided into several types depending on the causes of the disease:
- infectious colitis is associated with infectious diseases;
- nutritional problems arise due to malnutrition;
- toxic exogenous colitis caused by poisoning with harmful substances;
- endogenous colitis is observed due to intoxication with catabolic products;
- drug colitis develops under the influence of drugs;
- allergic colitis becomes an allergic reaction of the body to pathogens;
- Mechanical colitis is the result of regular mechanical irritation of the intestinal mucosa.
In some cases, inflammation of the large intestine can be caused by several factors. Then doctors diagnose combined colitis.
“Hand in hand” with dysbiosis
There are two forms of colitis - acute and chronic . In both the first and second cases, the infectious component plays a special role in the occurrence and development of the disease - most often bacterial dysentery . It can be triggered by other representatives of pathogenic microflora (for example, coli bacteria, staphylococci, streptococci, bacteria of the Proteus group, etc.). In other words, colitis goes “hand in hand” with dysbacteriosis. Inflammation can also be caused by previous intestinal infections and poor diet, as well as inadequate therapy with various medications. As practice shows, the causes of inflammation are indeed multiple. Let's summarize the main factors :
- infection in the gastrointestinal tract;
- infection with salmonella, staphylococci and other pathogenic microflora due to consumption of poor-quality food;
- the presence of worms (but not in all cases);
- inadequate, monotonous diet (mainly carbohydrates);
- allergies to certain types of food;
- chronic constipation;
- alcohol abuse;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules (for example, touching food with dirty hands);
- long-term use of certain antibiotics that can provoke dysbacteriosis;
- intoxication (poisoning with lead, arsenic and its preparations, mushrooms);
- nervous and emotional tension, stress.
Colitis ulcerosa - all Stages
Symptoms of intestinal colitis
With chronic colitis, the patient feels pain in the abdomen, often on the left, but sometimes it is not possible to localize the source of the pain. The pain intensifies after eating and decreases after defecation. A feeling of heaviness in the abdomen, bloating and flatulence are possible. A characteristic symptom of colitis is stool disorder with mucus and blood in the stool. Constipation may be replaced by diarrhea; the patient often feels the “urge” to defecate without excreting feces.
Colitis may also be accompanied by more “general” symptoms that are not directly related to the gastrointestinal tract, such as fever, weakness and joint pain. The patient loses his appetite, which leads to weight loss. If colitis is accompanied by acute inflammatory processes, then all clinical symptoms appear more clearly.
IBD in children: growth and development of the body is at risk
Ulcerative colitis in children can appear even before the age of one year and very quickly lead to total damage to the colon. If left untreated, the disease can result in a serious disruption of the physiological process of development of the child’s body: growth retardation or retardation in physical development. If endocrine pathology is not detected, a good pediatrician will definitely prescribe a gastrointestinal tract diagnosis for the child. In addition, this pathology causes serious psychological problems in both children and schoolchildren.
Diagnosis of colitis
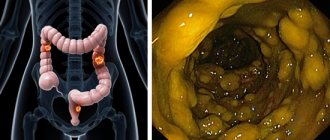
Colitis is diagnosed as a result of a whole range of tests. This includes: macro and microscopy of stool, general blood test, contrast irrigoscopy and colonoscopy. These tests make it possible to detect the presence of helminth eggs, inflammation, and also to study the anatomical and functional features of the large intestine and the condition of the colon mucosa. During a colonoscopy, samples are taken for further histological examination. A proctologist also examines the patient; he examines the anus to exclude the possibility of hemorrhoids, paraproctitis and other pathologies.
Intestinal dysfunction can be complicated by inflammation. In addition, colitis may not be the main disease, but accompany the development of a colon tumor. Therefore, doctors take a biopsy of suspicious areas of the intestinal wall to conduct additional tests and exclude the possibility of malignant neoplasms. If enteritis or other diseases are suspected, a number of diagnostic procedures may be prescribed, for example, an ultrasound of the abdominal organs and functional tests to identify markers of inflammation of the liver and pancreas.
Survey
Colonoscopy
- Cost: 25,000 rub.
More details
Diagnosis begins at a consultation with a gastroenterologist with examination and questioning. The nature of pain and discomfort and their duration play a big role. When diagnosing colitis, a whole range of instrumental studies is used:
- Colonoscopy. The most common endoscopic examination of the intestine.
- Sigmoidoscopy (examination of the rectum and anal area).
- Laboratory examination of stool (scatology, bacterial examination, inflammatory markers - calprotectin and others).
- X-ray examination using a contrast agent (irrigoscopy). Allows you to detect the exact localization of inflammation.
- Biopsy of the mucosa for histological examination. Allows you to clarify the diagnosis and exclude the possibility of a malignant neoplasm, which often manifests itself with the same symptoms as colitis.
Diagnostics is aimed at collecting the maximum amount of data about the disease. The doctor tries to find out the cause (it must be eliminated during treatment) and to clarify the localization of the inflammatory process. The more accurate the examination, the easier it is to choose effective treatment tactics.
Treatment of intestinal colitis
Treatment for colitis depends on its type. Chronic colitis during periods of exacerbation is best treated in a hospital proctology department. If the cause of colitis is an infection, then it will be treated in the infectious diseases department.
A proper diet plays an important role in the treatment of colitis; it is also prescribed by a doctor. The patient's diet should not contain foods that can mechanically or chemically irritate the intestines, for example, fermented milk products. The patient will have to take food in pureed form, in small portions and at least 4-5 times a day. You will also have to give up foods that contribute to gas formation, for example, cabbage and legumes.
Lightly dried unsweetened wheat bread, lean meat and fish are allowed. It is better to steam food. As the patient's condition improves, the list of permitted products is increased.
If the nature of the disease was infectious, then the treatment will be a course, medications for antibacterial therapy will be prescribed by the doctor. For any form of colitis, moderate physical activity and physical therapy are useful.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Sigmoidoscopy | 2 500 |
| Colonoscopy (video colonoscopy) | 7 000 |
| Irrigoscopy | 7 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Prevention of colitis
A good preventative measure to prevent the occurrence of colitis is a balanced diet. Proper nutrition will minimize the risk of various gastrointestinal diseases. It is recommended to exclude the consumption of alcohol, spices, canned food, and switch to fractional meals.
People with diagnosed chronic diseases of the large intestine should be under the supervision of specialists and undergo periodic medical examinations. It is better for them to avoid excessive physical activity and stress, not work at night and monitor their sleep patterns.
Even if you have not suffered from colitis before, no one is immune from this disease. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment of the disease are important, so undergo regular preventive examinations and consult a doctor at the first symptoms of colitis. Do not experiment with self-medication; drug abuse can only harm you.
Causes
The causes of colitis can be a violation of the character and diet:
- poor eating habits;
- irregular poor nutrition;
- alcohol abuse;
- eating poor quality food.
Colitis often occurs as complications of gastrointestinal diseases (pancreatitis, chronic gastritis, hepatitis), and they can also result from food poisoning or intestinal infections. Taking various medications often has a negative effect on the intestinal flora; the resulting dysbiosis provokes inflammation in the large intestine. The reasons for the development of colitis include congenital pathologies of human development and functional insufficiency.
Advantages of endoscopic examination in a paid clinic
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is carried out after appropriate preparation - following a special diet and complete cleansing of the intestines with the help of potent laxatives.
- In a European-style clinic, the patient will receive detailed recommendations on balancing the diet, which will help them calmly, without weakness or discomfort, undergo the stage of fasting and cleansing the intestines.
- Modern equipment allows a highly qualified specialist to conduct an examination with pinpoint precision without damaging the intestinal mucosa.
- The systematic process will take no more than 20 minutes, after which the patient will wake up in the room without experiencing any negative sensations.
- Patients who have already undergone intestinal endoscopy note that their expectations of something painful and terribly unpleasant were absolutely not justified.
Be attentive to your health! If sudden intestinal problems do not go away within 2-3 weeks, consult a specialist.
| +7 (495) 134-06-66 Write to WhatsApp | Moscow, st. Kantemirovskaya 53, k1 | Mon-Sat: from 9 to 21, Sun: from 9 to 20 |
| +7 (495) 134-06-66 Write to WhatsApp | Moscow, Kashirskoe highway, 51, k3 | Mon-Sat: from 9 to 21, Sun: from 9 to 20 |